Last Updated on November 18, 2025 by Ugurkan Demir
Osteoarthritis in the knee can really limit your daily activities. At Liv Hospital, we know how important it is to manage symptoms well. This helps improve your quality of life.
Effective management often involves a multi-faceted approach. This includes physical therapy, exercise, managing your weight, and using medications. New studies show that treatments like Embocept S in genicular artery embolization (GAE) are helping people with knee osteoarthritis.
We look at the best ways to manage osteoarthritis symptoms. This helps you make better choices for your care. Our aim is to give you a full view of your treatment options.
It’s important to know about knee osteoarthritis to manage its symptoms and improve life quality. This condition affects the cartilage and bone, causing pain, stiffness, and less mobility.
Knee osteoarthritis happens when cartilage breaks down. This cartilage usually cushions the joints. As it wears away, bone-on-bone contact occurs, leading to pain and inflammation.
Many factors can cause this, like age, genetics, obesity, and injuries. While there’s no cure, treatments can help manage symptoms. Studies, like the one by Magle Group on Embocept S, show promising results in treating knee osteoarthritis.
Many wonder if osteoarthritis can be cured. Right now, there’s no cure, but treatments can improve symptoms and life quality. It’s key to understand what treatments can do and what they can’t.
We aim to manage symptoms, slow disease progress, and improve function. Exploring different treatments helps achieve the best results. For example, stem cell therapy is being studied for its healing and pain-reducing effects.
Our goals for treating knee osteoarthritis include pain relief, better knee function, and keeping mobility. Effective management involves lifestyle changes, physical therapy, and sometimes medical treatments.
Understanding these goals helps patients choose the right treatments. We’re dedicated to providing care that meets each patient’s unique needs.
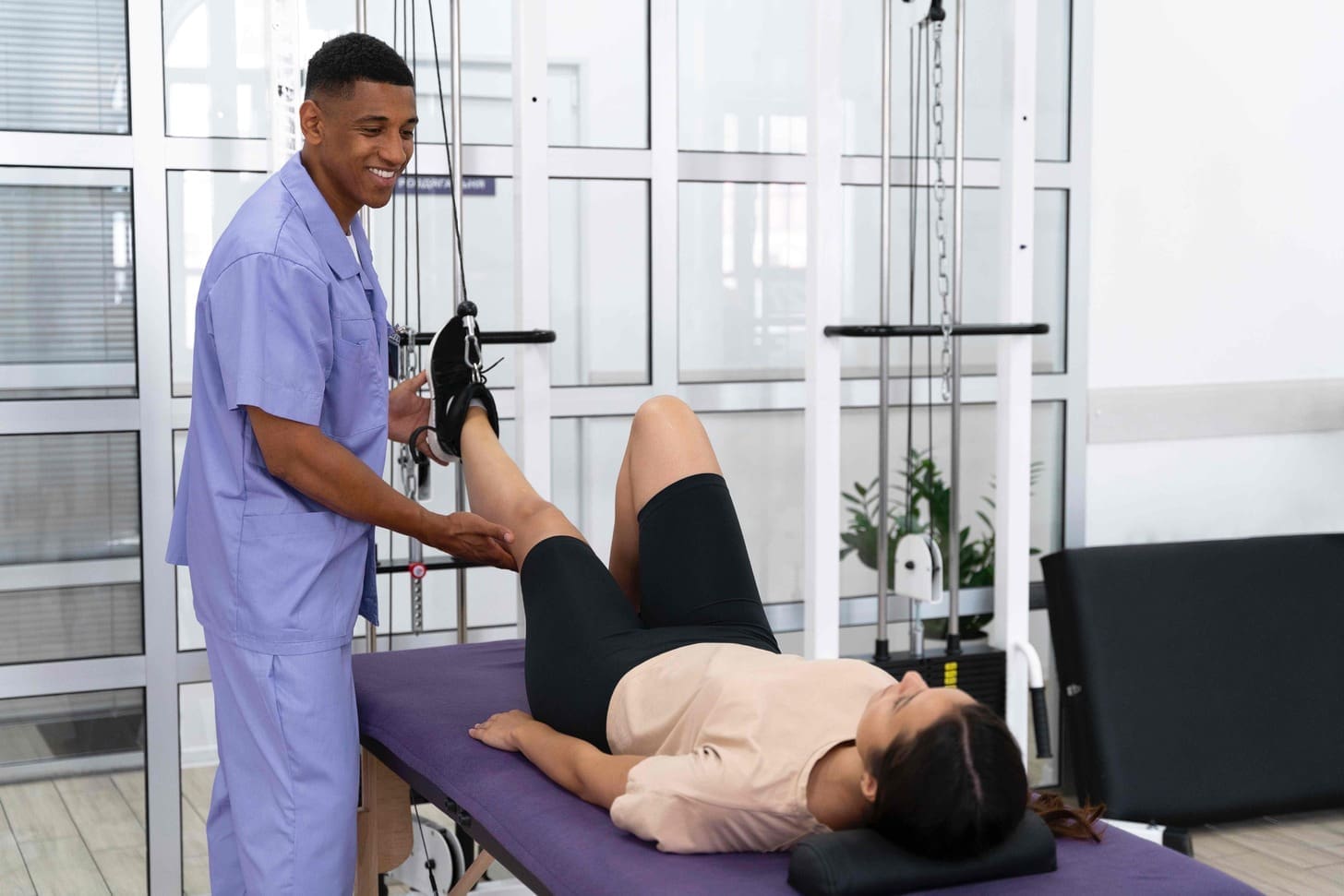
For those with knee osteoarthritis, physical therapy is key. It boosts mobility and cuts down on pain. It’s a vital part of managing the condition.
Physical therapy uses many methods to better knee function. Strengthening the muscles around the knee is a main goal. This helps support the joint and lessen strain.
Therapists also work on flexibility and joint mobility. This makes daily activities easier for patients.
“Physical therapy is a game-changer for many patients with knee osteoarthritis,” it’s said. It not only eases pain but also boosts functional ability. Personalized exercise programs lead to big improvements in knee function.
Physical therapists use various techniques for osteoarthritis. These include:
These methods together form a complete approach to managing osteoarthritis.
It’s important to find a physical therapist experienced in knee osteoarthritis. Look for therapists who know the latest treatments and can create a personalized plan. A personalized approach makes therapy more effective and addresses the patient’s unique needs.
Physical therapy is a key part of treating osteoarthritis in the knee. It improves knee function, reduces pain, and boosts mobility. This significantly enhances the quality of life for those with knee osteoarthritis.
Strengthening the muscles around the knee is a great way to manage osteoarthritis. Exercises that boost knee strength without strain can greatly improve joint function and reduce pain.
Low-impact exercises are great for those with knee osteoarthritis. Cycling and elliptical trainer workouts are good because they strengthen muscles without the stress of running or jumping.
Straight leg raises are another low-impact exercise. Lie on your back, bend one knee, and lift the other leg 6-8 inches off the ground. Hold for a few seconds before lowering it back down. This strengthens the quadriceps, which are key for knee stability.
Water therapy and swimming are highly recommended for osteoarthritis. Water reduces knee joint stress, allowing for more movement and muscle strengthening without weight-bearing exercise strain.
Swimming laps or doing water aerobics is very beneficial. These activities improve heart health and strengthen muscles around the knee. Water’s resistance also strengthens muscles without the impact of land-based exercises.
| Exercise | Benefits | Impact Level |
|---|---|---|
| Cycling | Strengthens quadriceps and hamstring muscles | Low |
| Straight Leg Raises | Strengthens quadriceps muscles | Low |
| Swimming | Improves cardiovascular health and strengthens muscles around the knee | Low |
Creating a sustainable exercise routine is key for managing osteoarthritis long-term. Start slowly and gradually increase exercise intensity and duration based on your progress.
Consistency is important. Set realistic goals and mix up exercises to keep things interesting. Working with a healthcare professional or physical therapist can help tailor a program that fits your needs.
By adding targeted exercises to their plan, people with osteoarthritis can see big improvements in knee strength and function. This can greatly improve their quality of life.
Managing weight is key to easing the pressure on the knee joint and reducing osteoarthritis symptoms. Excess weight can make knee osteoarthritis worse by putting more strain on the joint. So, it’s important to keep a healthy weight to manage osteoarthritis well.
Every pound of weight adds several pounds of pressure on the knee. For example, being 10 pounds overweight means your knees bear about 40 extra pounds. This extra pressure can speed up joint wear and tear, making osteoarthritis symptoms worse. Losing weight can lessen the strain on the knee, easing pain and improving function.
Eating a balanced diet is vital for managing weight and staying healthy. For those with osteoarthritis, some diets can be very helpful:
Diet alone isn’t enough; combining it with exercise is best for managing weight and osteoarthritis symptoms. Low-impact exercises like swimming, cycling, and brisk walking are great. They reduce joint stress while helping with weight loss and fitness.
We suggest the following:
By using a weight management strategy that includes a balanced diet and regular exercise, people with osteoarthritis can see big improvements in their symptoms and quality of life.
We look at the different medicines for osteoarthritis in the knee. These include NSAIDs or paracetamol. They help manage pain and swelling.
NSAIDs can help a lot with pain from osteoarthritis. But, they can cause stomach problems. Always talk to a doctor about the right NSAID and how much to take.
The good things about NSAIDs are:
But, there are also downsides:
Paracetamol is also used for osteoarthritis. It helps with pain, but it works differently for everyone. It’s safer than NSAIDs but can cause problems if taken too much or for too long.
Important things to remember about paracetamol are:
Topical treatments focus on the knee for pain. You can use creams, gels, or patches right on the knee. Examples include topical NSAIDs and capsaicin creams. They might have fewer side effects than pills.
The benefits of topical treatments are:
Injection therapies are a promising way to manage knee osteoarthritis symptoms. They involve putting medications directly into the knee joint. This can help relieve pain and slow down the disease.
We will look at the different types of injection therapies. We will also talk about their benefits and what patients can expect.
Corticosteroid injections are used to quickly reduce inflammation and pain. They are very effective during osteoarthritis flare-ups. Patients can feel relief in just a few days.
Hyaluronic acid injections aim to restore the knee joint’s natural lubrication. This treatment can improve joint mobility and reduce pain. It works best for patients with mild to moderate osteoarthritis.
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and stem cell injections are new treatments for knee osteoarthritis. PRP uses the patient’s own platelets to stimulate healing. Stem cell therapy aims to regenerate damaged joint tissue. These treatments show promise in potentially halting or reversing disease progression.
| Therapy Type | Primary Benefit | Typical Response Time |
|---|---|---|
| Corticosteroid Injections | Rapid pain relief | Within days |
| Hyaluronic Acid Injections | Improved joint lubrication | Several weeks |
| PRP Injections | Stimulates healing | Variable, often several months |
| Stem Cell Injections | Potential tissue regeneration | Variable, often several months |
In conclusion, injection therapies provide various options for managing knee osteoarthritis. From established treatments like corticosteroid injections to new therapies like PRP and stem cell injections, each has its benefits and drawbacks. The right therapy depends on the patient’s needs and the severity of their condition.
Braces, orthotics, and supportive devices are key in managing knee osteoarthritis. They offer extra support and stability. This helps reduce pain, improves function, and boosts the quality of life for those with knee OA.
Knee braces help support and stabilize the knee joint. They ease pain and enhance function. There are many types, each for different OA patterns and needs.
Custom orthotics are made for each person’s foot and knee alignment. They offer personalized support and correct biomechanical issues.
These orthotics reduce knee joint strain, improve foot mechanics, and ease OA pain.
Walking aids and assistive devices lessen knee joint load during daily tasks. They provide extra support and stability.
| Device | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Canes | Reduce weight-bearing stress on the knee |
| Walkers | Provide additional stability and support |
| Crutches | Help in redistributing weight and reducing knee stress |
Heat, cold, and electrical stimulation are key in managing osteoarthritis. They help reduce pain and stiffness. These methods are easy to find and can be used with other treatments to work better together.
Heat therapy is a simple yet effective way to manage osteoarthritis symptoms. Applying heat to the affected area can help ease pain and stiffness. Heat therapy increases blood flow, relaxes muscles, and reduces joint stiffness. There are several ways to apply heat therapy, including:
It’s important to follow best practices when using heat therapy to avoid burns or discomfort. Start with a comfortable temperature and adjust as needed. Also, limit the time spent on heat therapy to avoid overheating.
Cold therapy, or cryotherapy, is another effective treatment for osteoarthritis symptoms. Cold therapy reduces inflammation, numbs pain, and decreases swelling. It’s useful during flare-ups or when experiencing acute pain.
Methods for applying cold therapy include:
When using cold therapy, be careful not to apply ice directly to the skin to avoid ice burns. Wrapping the cold pack in a towel can help prevent this.
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) involves applying a small electrical device to the skin. TENS interrupts pain signals to the brain, providing relief from osteoarthritis pain. TENS units are portable and can be used as needed throughout the day.
| Therapy Type | Benefits | Precautions |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Therapy | Relieves pain and stiffness, improves joint mobility | Avoid burns by using appropriate temperatures |
| Cold Therapy | Reduces inflammation, numbs pain | Prevent ice burns by wrapping cold packs in towels |
| TENS | Interrupts pain signals to the brain | Use as directed, avoid using on sensitive areas |
By adding heat, cold, and electrical therapies to their treatment plan, patients with osteoarthritis can find significant relief. This can greatly improve their quality of life.
Many people with osteoarthritis are trying supplements and alternative treatments. These methods can help along with their usual care. They can offer more relief and better quality of life.
Some supplements are popular for osteoarthritis, with some evidence they help. Glucosamine and chondroitin are two well-known ones. But, how well they work can differ for each person.
| Supplement | Potential Benefits | Notable Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Glucosamine | May help maintain cartilage health | Effectiveness varies; some studies show minimal benefit |
| Chondroitin | Possibly reduces pain and slows joint damage | Often used in combination with glucosamine |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Anti-inflammatory properties | Can be found in fish oil supplements or consumed through diet |
Always talk to a healthcare provider before starting any supplements. They can affect other medicines you take.
Acupuncture and massage are being looked at for knee osteoarthritis pain relief. Acupuncture might help with pain and function, studies suggest.
Massage can ease muscle tension around the knee. This might help with movement and pain.
Yoga and tai chi can improve flexibility and balance. They are gentle and fit many fitness levels. This makes them good for many with osteoarthritis.
Adding these methods to a treatment plan can help with knee osteoarthritis. It can lead to more relief and a better life.
Creating a detailed plan to manage osteoarthritis symptoms is key to a better life. Knowing the different treatments helps patients work with their doctors. Together, they can make a plan that fits the patient’s needs and life.
Even though there’s no cure for knee arthritis, a good plan can help a lot. We suggest using a mix of treatments like physical therapy, exercise, weight control, and medicines. This way, you can get the best results.
When making a plan, think about your own situation. This includes how bad your osteoarthritis is, your health, and your lifestyle. A complete plan can help you manage your symptoms, improve your knee, and feel better overall.
Working with your healthcare team and trying different treatments is a big step. It helps you create a plan that’s just right for you. This leads to a better life quality.
There’s no single cure for osteoarthritis. But, many treatments can make symptoms better and improve life quality. We aim to reduce pain, enhance knee function, and keep mobility.
Osteoarthritis is a condition that wears down joint cartilage and bone. It can’t be fully cured. Yet, treatments can greatly improve symptoms and life quality.
The best approach is a mix of physical therapy, exercise, weight control, and medicines. Injection therapies, braces, and orthotics also help.
We mainly focus on knee osteoarthritis. But, treatments like topical creams, heat or cold, and acupuncture can ease hand pain.
To ease osteoarthritis pain, try physical therapy, exercise, weight control, and medicines. Injection therapies and alternative methods like acupuncture also work.
There’s no cure for osteoarthritis. But, a good management plan can greatly improve symptoms and life quality.
Yes, many treatments can manage osteoarthritis symptoms. These include physical therapy, exercise, weight control, medicines, and alternative methods.
A treatment plan that includes physical therapy, exercise, weight control, and medicines can help. Injection therapies, braces, and orthotics also aid.
Good treatments for osteoarthritis include physical therapy, exercise, weight control, and medicines. Alternative methods like acupuncture and massage can also help.
While a cure is not possible, treatments can improve symptoms and life quality. Our goals are to reduce pain, improve knee function, and maintain mobility.
Supplements like glucosamine and chondroitin are popular. But, evidence is mixed. Always talk to a healthcare provider before adding supplements.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!