Last Updated on October 28, 2025 by
At Liv Hospital, we know how important stem cell sources are in regenerative medicine. These cells can turn into different types, helping fix damaged tissues. We aim to give top-notch healthcare, supporting patients from around the world.
We lead in combining different medical fields to focus on the patient. Knowing where stem cells come from is key for safe treatments. Stem cell therapy has shown great promise in treating many health issues.
Stem cells are changing medicine in big ways. They can turn into many different cell types. This is helping us treat diseases and injuries in new ways.
Stem cells have special traits that make them very useful in medicine. They can grow and change into different cells. This is key for fixing damaged tissues.
They can also help control the immune system. This is good for treating autoimmune diseases and making organ transplants safer.
Stem cells can become many different cell types. This means they can fix or replace damaged tissues. It’s a big step towards treating many diseases, from heart problems to brain disorders.
Stem cells are important for fixing and growing new tissues. They can go to damaged areas and help heal. This is key for treating injuries and diseases where tissues are damaged.
As we learn more about stem cells, we’re entering a new era in medicine. There are many ways to treat diseases, and we’re excited to keep exploring and improving.
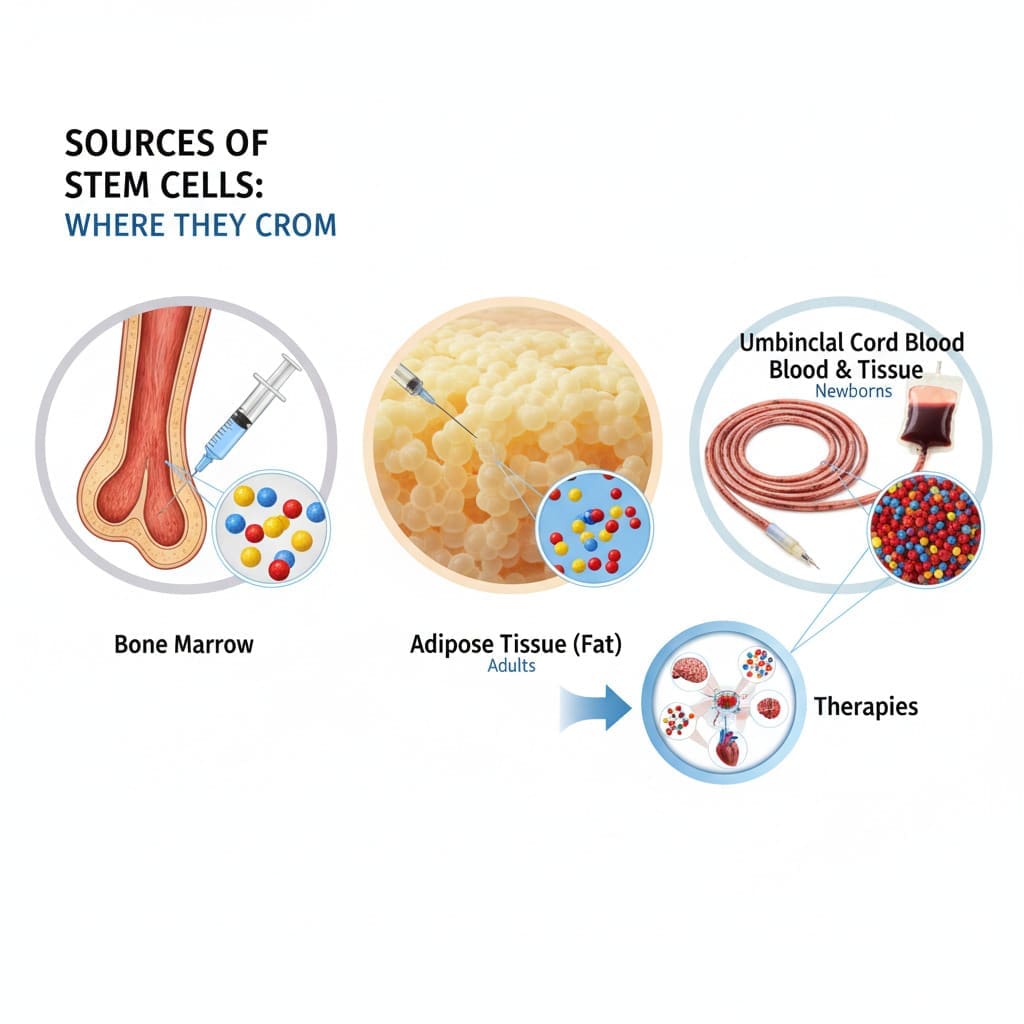
Stem cells are found in many parts of the body. This makes them both useful and challenging to collect. Knowing where they come from is key to improving medical treatments.
Stem cells can be found in several important places in our bodies. These include:
The ease of getting stem cells varies among sources. For example:
Each source has its own benefits and drawbacks. This affects the choice based on the intended use.
Many factors impact the quality and quantity of stem cells from different sources. These include:
Understanding these factors is key to improving stem cell collection and ensuring their therapeutic value.
Embryonic stem cells come from early-stage embryos. They can turn into any cell in the body. This makes them very useful for research and possible treatments.
These cells usually come from leftover blastocysts from in vitro fertilization (IVF). People who are trying IVF donate these blastocysts. They agree to this with their consent. The inner cell mass of the blastocyst is where the stem cells are found.
Using IVF blastocysts for stem cell research has helped us learn a lot. It has also helped in the field of regenerative medicine.
Embryonic stem cells are special because they can become any cell in the human body. This is key for:
Their ability to become any cell type is very valuable for medical research and treatments.
Using embryonic stem cells is regulated and raises ethical questions. These cells come from human embryos, which raises concerns about destroying life. Because of this, many countries have strict rules for their use in research.
Rules about using these cells vary a lot between countries. Researchers must follow these rules carefully to use these cells ethically and legally.
| Country | Regulatory Framework | Ethical Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Federal funding restrictions; state-level variations | Debate over embryo destruction |
| United Kingdom | Regulated by the Human Fertilisation and Embryology Authority | Strict guidelines for embryo research |
| Australia | National Health and Medical Research Council guidelines | Emphasis on ethical use and donor consent |
It’s important for researchers to know about these rules and ethical issues when working with embryonic stem cells.
Bone marrow is a key source of stem cells, used in many medical treatments. It’s known for its rich stem cell reservoir.
Bone marrow has two main types of stem cells. Hematopoietic stem cells make blood cells like red and white blood cells. Mesenchymal stem cells can turn into different cell types, like bone and cartilage cells.
Bone marrow aspiration is a way to get stem cells. A needle is inserted into the bone marrow, usually in the hip or sternum. This is done under local anesthesia to reduce pain.
This method needs careful handling to get high-quality stem cells safely.
Donors might feel sore or bruised after the procedure. They can usually go back to normal activities in a few days. But, it can take a couple of weeks to fully recover.
It’s important for donors to follow care instructions after the procedure. This helps ensure their safety and well-being.
Peripheral blood stem cell collection is key in stem cell therapy. It involves moving stem cells into the blood for collection. This is done through apheresis.
To get stem cells from the blood, we first mobilize them from the bone marrow. We use special protocols that include growth factors or medications. These help release more stem cells into the blood.
The right mobilization protocol is vital for success. We choose the best one for each patient based on their needs and health history.
After mobilizing stem cells, we use apheresis to collect them. Apheresis draws blood, separates stem cells, and returns the rest to the body.
This method collects a lot of stem cells while keeping other blood parts safe. Apheresis is usually done without keeping the patient overnight and is well-tolerated.
Peripheral blood stem cell collection has big advantages over bone marrow extraction. It’s less invasive, avoiding surgery.
Key advantages include:
These benefits make peripheral blood stem cell collection a good choice for donors and patients needing stem cell therapy.
Umbilical cord blood is gaining attention as a source of stem cells for medical use. Umbilical cord blood is a valuable resource that is often thrown away after birth. It has a high amount of stem cells that can help with many health issues.
Getting umbilical cord blood is easy and doesn’t hurt. It’s done by clamping the umbilical cord and putting the blood in a clean container. This method doesn’t affect the birth process and is safe for both mom and baby.
After getting the cord blood, it can be stored in public or private banks. Public banks offer the blood to anyone who needs it. Private banks keep it for the family’s future use.
Storing umbilical cord blood needs careful thought to keep it good. Freezing the cells at very low temperatures is the usual method.
Umbilical cord blood stem cells are promising for treating many diseases. They can help with some leukemias, lymphomas, and genetic disorders. Their use is growing in both kids and adults as research goes on.
| Condition | Pediatric Use | Adult Use |
|---|---|---|
| Leukemia | Yes | Yes |
| Lymphoma | Limited | Yes |
| Genetic Disorders | Yes | Limited |
As we learn more about umbilical cord blood, its importance in medicine will likely grow. It offers hope for patients all over the world.
Adipose tissue is now a key source for stem cells in medicine. It shows great promise for regenerative medicine.
Liposuction is a common way to get adipose tissue for stem cells. It’s safe and doesn’t hurt much, making it popular.
We use special liposuction to get good quality tissue. This method is gentle to protect the stem cells.
After getting the tissue, we process it to get the stem cells. We use enzymes and centrifuges to separate them.
Then, we grow the stem cells to have enough for treatments. We check their quality and strength carefully.
Fat-derived stem cells are plentiful and easy to get. They can turn into many cell types. This makes them great for medicine.
Research is looking into how these stem cells can help with diseases and injuries. We’re studying their use in treatments.
| Therapeutic Application | Current Status | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Tissue Repair | Ongoing Clinical Trials | Enhanced Healing, Reduced Scarring |
| Degenerative Diseases | Preclinical Studies | Potential Disease Modification, Improved Quality of Life |
| Cosmetic Procedures | Established Practice | Improved Aesthetic Outcomes, Minimally Invasive |
As research grows, adipose-derived stem cells will become more important in medicine. They offer hope for many patients.
Autologous and allogeneic stem cell donations are two ways to get stem cells for treatment. It’s important for patients and doctors to know the differences. This helps make the right choice for stem cell therapy.
Autologous stem cell donation uses a patient’s own stem cells. This method avoids graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) and reduces the need for drugs to suppress the immune system. We use autologous stem cells when a patient’s own cells are good for their treatment.
The benefits of autologous donation are:
Allogeneic stem cell donation uses stem cells from a donor. Finding a match between donor and recipient is key to avoid GVHD and ensure compatibility. We look at HLA typing to find the right donor.
The main points for allogeneic donation are:
Finding a match involves typing and screening donors and recipients. We use registries to list donors and their HLA types. This is vital for successful allogeneic stem cell transplants.
It’s important to compare the results of autologous and allogeneic stem cell donations. The choice depends on the patient’s condition, the disease being treated, and if a suitable donor is available.
| Donation Type | GVHD Risk | Immunosuppression Need | Donor Availability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Autologous | Low | Low | Always available (self) |
| Allogeneic | High | High | Dependent on donor match |
In conclusion, both autologous and allogeneic stem cell donations are important in medicine. We choose the best method based on the patient’s needs and treatment specifics.
Stem cell therapies are showing great promise in treating many diseases. We’ve looked at different sources of stem cells, like embryonic stem cells and fat tissue. Techniques for getting these cells, such as bone marrow aspiration, are key for their use in medicine.
Looking ahead, we expect better ways to get and use stem cells. This could lead to big steps in fixing damaged tissues and organs. The future of stem cell treatments is bright, thanks to ongoing research and new methods for harvesting and isolating these cells.
We get stem cells from places like bone marrow, blood, umbilical cord blood, and fat tissue. Each place has its own special uses in medicine.
Taking stem cells from blood is less painful than bone marrow. It also means patients can get back to normal faster. We use special methods to get the stem cells from the blood.
We take fat tissue through liposuction. Then, we process it to get the stem cells. This makes the stem cells ready for use in treatments.
Autologous donations use a patient’s own stem cells. Allogeneic donations use someone else’s. We make sure allogeneic donations are a good match for the best results.
Using embryonic stem cells is a big debate because of where they come from. They’re often from embryos from IVF. We follow strict rules to use them responsibly.
We get umbilical cord blood stem cells right after birth. The blood is then stored in banks. We handle and freeze it carefully to keep it good for later use.
These stem cells can help with many diseases in kids and adults. We’re always learning more about how they can help through research and trials.
After taking bone marrow, donors need to rest and manage pain. We make sure they know what to expect and how long it will take to get better.
We check the stem cells carefully. We look at how they were taken, processed, and stored. This makes sure they’re good for treatments.
News Medical: How Are Stem Cells Collected?
PubMed Central (NCBI): Stem Cell Mobilization and Apheresis for Autologous and Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!