At Liv Hospital, we know how important it is to understand the long-term effects of heart ablation. We also look at what happens if atrial fibrillation comes back. If you’re curious about the procedure’s lasting effects or what to do if your condition returns, we’re here to help. We offer trusted, up-to-date advice in personalized cardiac care.
Most patients stay in a normal rhythm after the procedure. But, how often it comes back can vary. We’ll talk about the general rates of recurrence and what affects them. This will prepare you for more detailed information in the next sections.
The cardiac ablation procedure is a complex method to treat atrial fibrillation. Atrial fibrillation (AFib) is a heart rhythm disorder with fast and irregular heartbeats. This procedure aims to fix the heart rhythm by destroying the bad electrical paths in the heart.
Cardiac ablation is a minimally invasive procedure that uses energy to destroy bad electrical paths in the heart. A cardiologist, called an electrophysiologist, performs this. The goal is to make scar tissue that stops the bad electrical signals causing AFib.
During the procedure, the patient is given sedation or anesthesia for comfort. An electrophysiologist puts catheters through a vein in the leg and guides them to the heart. The catheters use energy to make lesions on the heart tissue, destroying the bad electrical pathways.
The procedure’s complexity depends on the patient’s condition and the ablation technique used. Advanced mapping technologies help find and target the heart areas causing the arrhythmia.
There are several ablation techniques for treating atrial fibrillation, including:
Each technique has its benefits and is chosen based on the patient’s condition, the electrophysiologist’s expertise, and the arrhythmia’s specifics.
Understanding cardiac ablation is key for patients with atrial fibrillation. Knowing what to expect and the available techniques helps patients make informed decisions about their care.
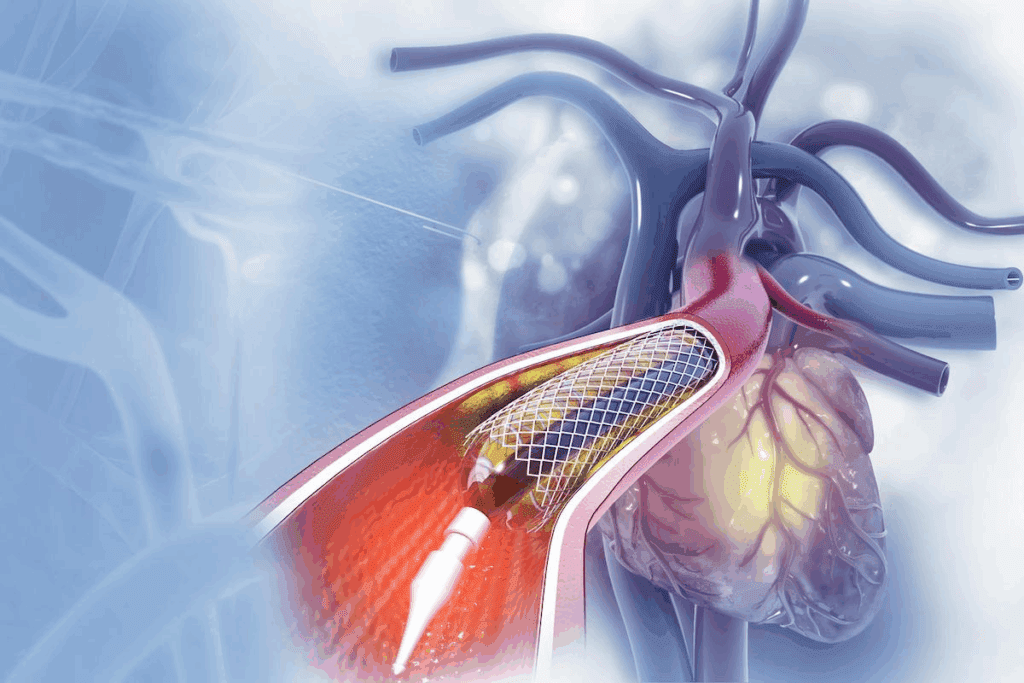
Six months after heart ablation, patients often wonder about their recovery and if atrial fibrillation will come back. Most have passed the initial recovery phase and want to know the long-term effects.
The first three months after heart ablation are called the “blanking period.” During this time, the heart adjusts to the procedure changes. Some patients might feel arrhythmias or other symptoms. It’s important to remember that early recurrences don’t always mean long-term failure.
“The blanking period is a critical time for the heart to heal and stabilize,” says Medical Expert, a leading electrophysiologist. “Patients should be monitored closely during this period.”
By six months post-ablation, most patients have made a big recovery step. The recovery time can vary, but patients usually see:
But, it’s important to remember that everyone’s experience is different. Things like the heart condition, other health issues, and lifestyle choices can affect recovery.
Patient experiences six months after heart ablation vary a lot. Some might not have any atrial fibrillation symptoms anymore. Others might have some episodes. A study found that about 70% of patients were free from atrial fibrillation at six months.
Many patients also say they feel better overall, with more energy and fewer symptoms. But, it’s key for patients to keep seeing their doctors to check on their health and adjust treatments as needed.
Following patients beyond six months shows that ongoing care is key for lasting success. We’ll dive deeper into this in later sections.
When we look at heart ablation success at six months, we check a few important things. At this time, both patients and doctors want to know if the treatment worked well.
Research shows that heart ablation success can vary. It can be between 20 to 40 percent. This change depends on many things, like the type of heart problem and how the ablation was done.
Success rates are better for some patients. For example, those with a certain type of heart rhythm problem can see success rates up to 70-80% at six months.
Many things can affect how well heart ablation works. These include:
Knowing these factors helps set realistic hopes and improve results for patients.
We check how well the procedure worked by looking at several things. This includes how the patient feels, what they say, and tests like ECG and Holter monitoring. These help see if the heart rhythm is back to normal.
Effective patient care goes beyond just the procedure. It also means following up and managing any symptoms that come back.
After cardiac ablation, atrial fibrillation can come back in different ways. It’s important to understand these patterns. This helps manage patient hopes and tailor care after the procedure. Atrial fibrillation can return based on when it happens.
Early return of atrial fibrillation, within the first three months, is common. This time is called a blanking period. The heart is healing, and some irregular rhythms are normal. Inflammation, temporary electrical issues, and the heart’s healing are factors.
Recurrence between 3 to 12 months after ablation is a key sign of success. By then, the inflammation has gone down, and the heart has healed. If it happens then, it might mean the ablation didn’t fully work or there are other issues.
Recurrence more than a year after ablation can have many causes. It might be due to worsening heart disease, new electrical pathways, or other heart problems. Dealing with late recurrence needs a detailed check-up to find the cause and the right treatment.
AFib can come back after ablation for many reasons. These include how our body works, our lifestyle, and the limits of the ablation procedure itself.
Several physiological factors can lead to AFib coming back after ablation. These include:
Lifestyle factors also play a big role in AFib coming back after ablation. These include:
Even though ablation is effective, there are limits to its success. These include:
Understanding these factors helps doctors better manage patient expectations. They can also work on strategies to lower the risk of AFib coming back after ablation.
AFib recurrence can be identified through various symptoms. Knowing these can greatly impact your treatment plan. After heart ablation, many wonder if atrial fibrillation symptoms will return. It’s important to understand what to look for for early detection and effective management.
The symptoms of AFib recurrence can differ from person to person. Yet, there are common signs to watch for. These include:
Some people may not experience any symptoms at all. Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are vital.
If you notice any of the symptoms mentioned, contact your healthcare provider. They can assess your condition and guide you on the next steps. You should also reach out if you experience:
To confirm AFib recurrence, your healthcare provider may recommend several diagnostic tests. These can include:
| Diagnostic Test | Description |
| Electrocardiogram (ECG) | A test that records the electrical activity of your heart. |
| Holter Monitor | A portable device that records your heart’s activity over 24 to 48 hours. |
| Event Monitor | A device worn for a longer period to capture intermittent symptoms. |
These tests help your healthcare provider understand your heart’s rhythm. They determine the best course of action.
Managing recurrent atrial fibrillation needs a mix of treatments. These include changing medications, cardioversion, and sometimes doing the procedure again. We’ll look at each option closely, focusing on their benefits and what to consider.
For many, the first step is tweaking their meds. This might mean changing the dose or type of anti-arrhythmic drugs. We look at the patient’s health, how bad their symptoms are, and how they’ve reacted to meds before.
The aim is to control the heart rhythm well without too many side effects. Common meds include:
| Medication Class | Examples | Primary Use |
| Class IC | Flecainide, Propafenone | Rhythm control |
| Class III | Amiodarone, Sotalol | Rhythm control |
| Beta-blockers | Metoprolol, Propranolol | Rate control |
Cardioversion is another option for recurrent AFib. It uses electrical shocks to get the heart back to normal. We might choose it if meds alone can’t control symptoms or if symptoms are severe.
Deciding on cardioversion depends on how long AFib has lasted, the patient’s health, and any other conditions that might affect the procedure’s success.
For some, doing the ablation procedure again might be needed if AFib comes back. We think about repeat ablation if other treatments haven’t worked well or if a more invasive approach is needed.
Choosing to do repeat ablation is a big decision. It involves weighing the benefits and risks and considering how likely it is to work for the patient.
Understanding the treatment options for recurrent AFib helps patients and doctors create a plan that fits the patient’s needs.
If you have atrial fibrillation again after an initial ablation, a second procedure might be needed. This can be worrying, but it’s good to know that repeat ablations are a valid option.
Research shows that a second ablation can work as well as the first. The Medical organization says that up to 80% of patients can see success with a second try.
Several things can affect how well a second ablation works. These include:
How many times you can have an ablation depends on your health, how bad your atrial fibrillation is, and how you’ve reacted to previous treatments. There’s no exact limit, but having to do it more than once might mean your condition is more complex.
“The decision to have another ablation depends on your symptoms, how much atrial fibrillation you have, and what you want.” – Medical Expert, Electrophysiologist
Later ablation procedures can be different from the first one. For example:
We’ll help figure out the best plan for you. We make sure any follow-up procedures fit your needs.
Heart ablation for atrial fibrillation has varying success rates over time. Several factors play a role in these outcomes. It’s important for both patients and doctors to understand these to make the best treatment choices.
About half of patients keep a normal heart rhythm five years after ablation. This shows the procedure’s long-term effectiveness.
Many things can affect how well heart ablation works long-term. These include:
Heart ablation can greatly improve a patient’s life. Benefits include:
Knowing the long-term effects of heart ablation helps patients and doctors achieve the best results together.
Getting lasting results after heart ablation is more than just the procedure. It needs ongoing care. We know that keeping the benefits of heart ablation going is key for better life quality for those with atrial fibrillation.
Handling comorbidities is a big part of care. Conditions like high blood pressure, diabetes, and heart failure can affect heart ablation success. We help patients manage these conditions well.
For example, controlling high blood pressure with meds and lifestyle changes can greatly help. Managing diabetes with diet, exercise, and meds can also lower complication risks.
| Comorbidity | Management Strategy | Benefits |
| Hypertension | Medication, Lifestyle Changes | Improved Heart Health |
| Diabetes | Diet, Exercise, Medication | Reduced Complications |
| Heart Failure | Medication, Monitoring | Enhanced Survival |
Changing your lifestyle is key to keeping heart ablation benefits. We suggest a heart-healthy lifestyle. This includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, and managing stress.
Dietary Changes: Eating more fruits, veggies, and whole grains is good for your heart. Cutting down on sodium and alcohol is also good.
Exercise Regularly: Exercise boosts heart health and lessens atrial fibrillation symptoms.
Regular checks are vital for catching issues early. We suggest regular check-ups and heart rhythm monitoring. This ensures the treatment works well.
With advanced monitoring tech, we can track heart rhythm changes. This lets us adjust treatments as needed. This proactive method keeps heart ablation benefits lasting.
By using a full care approach, managing comorbidities, making lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring, patients can get lasting results from heart ablation.
Atrial fibrillation is complex and needs a team effort. Doctors from different fields must work together. This includes cardiologists, electrophysiologists, primary care doctors, and more.
Electrophysiologists are key in treating atrial fibrillation. They use their knowledge of the heart’s electrical system. This lets them do precise procedures like catheter ablation.
They focus on the heart’s electrical issues. This helps find and fix the root causes of AFib. Their work leads to better treatment results for patients.
Primary care doctors are vital for managing AFib long-term. They keep an eye on the patient’s overall health. They also handle other health issues and make sure patients stick to their treatment plans.
Working together, electrophysiologists and primary care doctors give patients the best care. This teamwork makes treatments like ablation more effective.
Advanced care plans are key for managing complex AFib cases. These plans include custom treatments based on new research and technology. They also use new ways to reduce AFib coming back and improve life quality.
Using the latest in AFib care, doctors can give patients the best results. This team effort leads to better care and a better life for those with AFib.
Managing atrial fibrillation with heart ablation needs a full plan, not just the procedure. We’ve looked into the details of cardiac ablation. This includes its methods, recovery times, and success rates at key points.
It’s important to know when atrial fibrillation might come back and its signs. This way, we can act fast. Patients have choices like changing meds, cardioversion, or doing another ablation, based on their needs.
Working together, doctors and primary care teams give patients the best care. Managing other health issues, making lifestyle changes, and keeping up with check-ups help a lot. This way, people can live better and feel better too.
As we keep improving how we handle atrial fibrillation, heart ablation is a big help. With a focus on full care and teamwork, we can make a big difference. This improves the lives of those dealing with this condition.
Heart ablation’s lasting effect varies by person. Some see long-term relief from atrial fibrillation. Others may see symptoms return. Studies show many patients stay symptom-free at six months, but recurrence rates can rise over time.
Success rates at six months are high, with many patients staying free from atrial fibrillation. But, outcomes depend on many factors. These include the heart condition, the procedure, and the patient’s health.
Signs of AFib recurrence include palpitations, shortness of breath, fatigue, and chest discomfort. Patients should watch for these symptoms. If they notice any unusual or persistent changes, they should seek medical help.
Diagnosing AFib recurrence often involves electrocardiogram (ECG) testing. Other tests like Holter monitoring may also be used. These tests help doctors confirm atrial fibrillation and assess its severity.
Yes, repeat ablation procedures are possible. They may be necessary for those who experience AFib recurrence. The decision to have a second ablation depends on several factors, including the first procedure’s outcome and the patient’s health.
The number of ablations a patient can have varies. Some may have multiple procedures. Others may not be candidates for repeat ablations due to health or procedural factors.
Treatment for recurrent AFib includes adjusting medications, cardioversion, and repeat ablation. The choice depends on the patient’s symptoms, health, and previous procedures.
Managing comorbidities after heart ablation requires a holistic approach. This includes lifestyle changes, medication adherence, and regular monitoring. Patients should work closely with their healthcare providers to improve their health and reduce the risk of AFib recurrence.
Lifestyle changes that can help after heart ablation include a healthy diet and regular exercise. Managing stress and avoiding triggers are also important. Patients should discuss their specific needs with their healthcare providers.
A multidisciplinary approach is key in AFib management. It brings together various healthcare professionals. This ensures patients receive well-rounded care tailored to their needs, promoting better outcomes.
Electrophysiologists play a vital role in AFib management. They provide specialized care and perform procedures like cardiac ablation. They work with other healthcare professionals to create personalized treatment plans, ensuring effective care.
AFib return after ablation varies by individual. Some stay free from atrial fibrillation, while others experience recurrence. The likelihood of recurrence depends on the heart condition, procedure, and patient health.
If AFib recurs after ablation, patients should contact their healthcare provider. They will discuss the best next steps, which may include medication changes, cardioversion, or repeat ablation, based on individual circumstances.
National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2025). How Long Does Heart Ablation Last and What. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10460604
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!
WhatsApp us