Eardrum issues are a big problem worldwide, affecting millions. Research shows that about 5 out of 6 kids get an ear infection by age 3. Also, 1 in 8 Americans over 12 have hearing loss.
At Liv Hospital, we know how much ear conditions can hurt your life. We use a patient-first approach. We mix international medical standards with caring to help with eardrum problems. This way, we make sure our patients get the best support.
The 7 most common eardrum problems, including rupture (perforation), retraction, and inflammation (myringitis).
Key Takeaways
- Ear infections are common among children, with 5 out of 6 experiencing at least one by age 3.
- Hearing loss affects a significant portion of the American population over 12.
- Eardrum issues can lead to hearing loss, pain, and complications if untreated.
- Early diagnosis and treatment are key to keeping ears healthy.
- Liv Hospital offers a patient-centered approach to treating ear disorders.
Understanding the Eardrum and Its Function
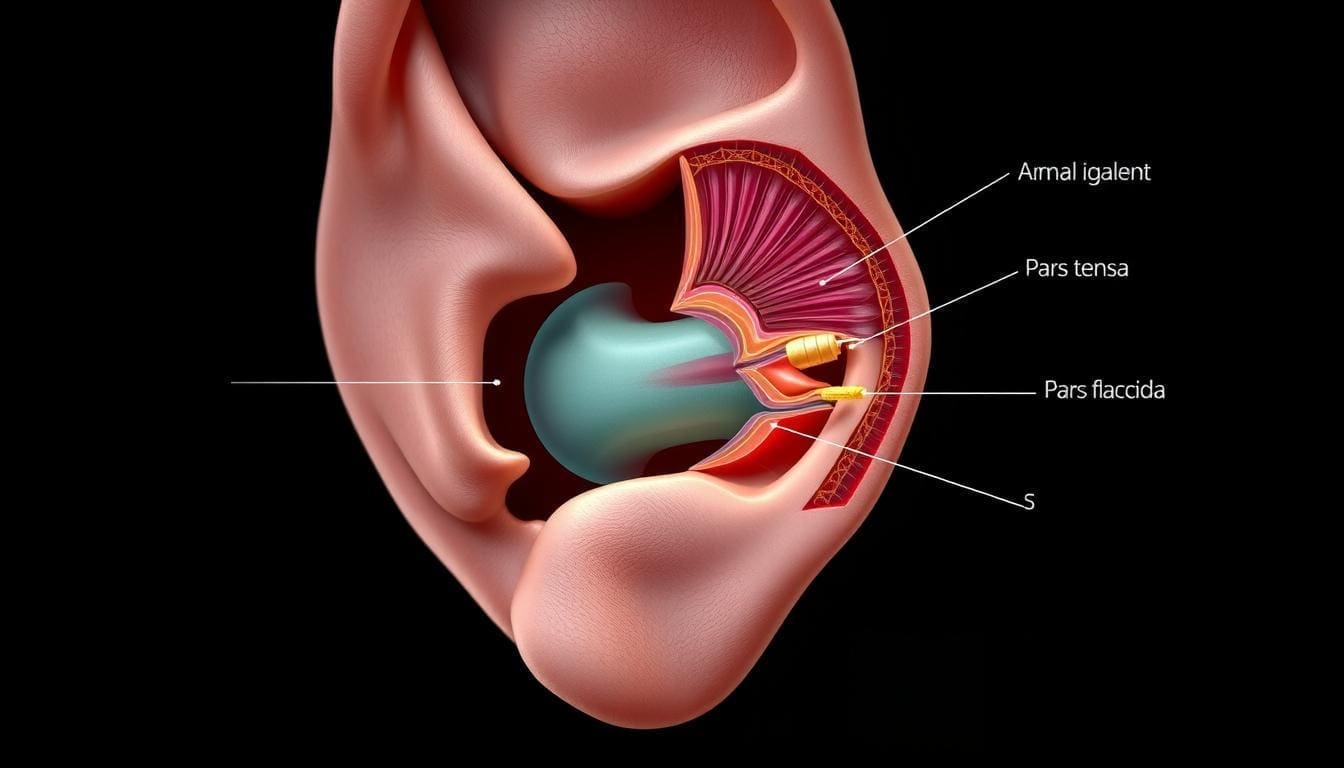
The eardrum, or tympanic membrane, is a key part of our ears. It separates the outer ear canal from the middle ear. It helps us hear by sending sound vibrations to the inner ear.
To understand the eardrum’s role, we need to know its anatomy and function.
Anatomy of the Eardrum
The eardrum is a thin, semi-transparent membrane at the end of the external auditory canal. It is approximately 1 cm in diameter. It is positioned obliquely, facing downward, forward, and laterally. The eardrum’s anatomy is complex, with several layers that work together to transmit sound.
How the Eardrum Works
The eardrum’s main job is to send sound waves to the ossicles in the middle ear. When sound hits the eardrum, it vibrates. These vibrations then go through the ossicles to the cochlea in the inner ear. There, they are turned into electrical signals that our brain interprets as sound.
The process involves several steps:
- Sound waves enter the ear canal and hit the eardrum.
- The eardrum vibrates in response to these sound waves.
- These vibrations are transmitted through the ossicles.
- The vibrations reach the cochlea, where they are converted into electrical signals.
- The electrical signals are interpreted by the brain as sound.
Importance of Eardrum Health
Keeping the eardrum healthy is key for good hearing and ear health. A healthy eardrum ensures sound is conducted properly. It also prevents hearing loss or infections.
Aspect of Eardrum Health | Importance | Potential Issues if Compromised |
Integrity of the Eardrum | Essential for sound transmission | Hearing loss, infections |
Eardrum Mobility | Critical for vibration transmission | Reduced hearing, discomfort |
Eardrum Hygiene | Prevents infections and damage | Infections, eardrum perforation |
Understanding the eardrum’s role in hearing and its importance in ear health helps us see why we must protect and maintain it.
Recognizing Eardrum Problems: Key Statistics
Eardrum problems affect people of all ages and genders. They are a big health issue worldwide. They can really impact someone’s life quality.
Prevalence Across Age Groups
Some age groups face more eardrum issues. Kids are often hit with middle ear infections. These can damage the eardrum. Otitis media affects up to 80% of children by the age of three (1).
Adults, on the other hand, might get eardrum problems from accidents or hearing loss as they get older.
A study showed that eardrum perforation is more common in younger kids. This is often because of ear infections or putting things in their ears.
Gender Differences in Eardrum Issues
There are gender differences in eardrum problems. For example, men are more likely to get traumatic eardrum rupture than women, with a ratio of 1.49:1 (2). This is due to different reasons like job risks and risky behaviors.
“The gender disparity in traumatic eardrum rupture highlights the need for targeted preventive measures, particularlly among men in high-risk occupations.”
Common Risk Factors
Several things can lead to eardrum problems. These include:
- Infections: Ear infections can weaken the eardrum, making it more likely to perforate.
- Trauma: Head injuries or sudden loud noises can cause eardrum rupture.
- Environmental factors: Loud noises, changes in air pressure, and poor ear hygiene can also cause issues.
Knowing these risk factors is key to preventing eardrum problems. Healthcare providers can target high-risk groups. This can help lower the number of eardrum disorders.
Tympanic Membrane Perforation
A perforated eardrum is a condition where the thin membrane in your ear gets damaged. This can cause various symptoms and complications. It’s important to know the causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Symptoms
A perforated eardrum can cause ear pain and hearing loss. You might also feel like your ear is full. Discharge or bleeding from the ear can indicate an infection.
Some people experience tinnitus, or ringing in the ears. The severity and type of symptoms depend on the size and location of the perforation.
Causes
Eardrum rupture can happen from several reasons. A direct hit to the ear or a severe ear infection can cause damage. Loud noises, like explosions, can also rupture the eardrum.
Activities like diving or air travel can cause pressure barotrauma. Inserting objects into the ear can accidentally cause a perforation.
Treatment
Treatment for a perforated eardrum depends on the severity. Sometimes, the eardrum heals on its own with care. This includes keeping the ear dry and avoiding certain activities.
For more severe cases, surgery like tympanoplasty might be needed. This surgery uses tissue to close the hole and restore function.
Recovery
The recovery time for a perforated eardrum varies. Smaller perforations heal faster than larger ones. Patients are advised to keep the ear dry and avoid strenuous activities.
With proper care and treatment, most people fully recover from a perforated eardrum. The recovery period can be a few weeks to several months, depending on the damage and treatment.
Otitis Media: Middle Ear Infection
Many people, including children, suffer from otitis media. It’s an infection or inflammation in the middle ear. This condition is a big health problem.
Types of Otitis Media
Otitis media comes in different types, each needing its own treatment. The main types are:
- Acute Otitis Media: This type starts suddenly. Symptoms include ear pain, fever, and hearing loss.
- Otitis Media with Effusion: Fluid builds up in the middle ear without an infection.
- Chronic Otitis Media: This is a long-lasting or recurring condition. It can cause serious damage if not treated.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The symptoms of otitis media vary. They include ear pain, hearing loss, fever, and irritability. Doctors use physical exams, medical history, and sometimes imaging to diagnose it.
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for otitis media depends on the type and how severe it is. Options include:
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics are used for bacterial infections to clear them up.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers help with ear pain and discomfort.
- Watchful Waiting: Sometimes, doctors will just watch and wait, like for otitis media with effusion.
Complications if Left Untreated
Untreated otitis media can cause serious problems. These include:
- Hearing Loss: Fluid in the middle ear can cause hearing loss that may not go away.
- Further Infections: Untreated otitis media can lead to more infections or spread to other parts of the ear.
- Eardrum Damage: Long-term infection can damage the eardrum or middle ear bones.
Seeing a doctor is key if symptoms don’t get better or get worse. This helps avoid these complications and manage otitis media effectively.
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
The Eustachian tube is key to ear health. Its dysfunction can lead to various issues. It connects the middle ear to the back of the nose and throat. It helps balance air pressure and drain mucus.
Impact on the Eardrum
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD) happens when the tube doesn’t open or close right. This causes air pressure imbalance in the ear. The eardrum might bulge or retract, causing discomfort and hearing loss.
Fluid buildup in the middle ear can also occur. This makes the condition worse.
Common Symptoms
ETD symptoms include ear fullness, hearing loss, and discomfort. Some people might hear ringing in their ears or feel ear pain. Severe symptoms like vertigo or hearing problems can also happen.
Causes and Risk Factors
ETD can be caused by many things, like colds or allergies. Flying or scuba diving can also cause it due to air pressure changes. Knowing these causes helps in prevention and management.
Treatment and Management
Treating ETD often means fixing the underlying cause. Nasal decongestants, ear exercises, and sometimes surgery are used. Simple actions like yawning or swallowing can help open the tube.
For serious cases, seeing a healthcare professional is best. They can find the right treatment for you.
Retracted Eardrum
A retracted eardrum happens when the eardrum moves back into the middle ear. This can cause discomfort and might affect your hearing.
Causes of Eardrum Retraction
Eustachian tube dysfunction is a common cause. It fails to keep air pressure balanced in the middle ear. This imbalance can pull the eardrum back.
Other reasons for eardrum retraction include:
- Recurrent ear infections
- Allergies
- Sinus infections
- Anatomical issues, such as a deviated septum
Recognizing the Symptoms
Symptoms of a retracted eardrum can be different. They often include:
- Hearing loss or feeling like your ear is full
- Ear pain or discomfort
- Tinnitus, or ringing in the ears
- Dizziness or vertigo
Spotting these symptoms early is key to avoiding worse problems.
Diagnostic Procedures
An ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist will examine you. They might use:
- Otoscopy to see the eardrum
- Tympanometry to check the eardrum’s movement
- Hearing tests to find out if you have any hearing loss
Treatment Options
Treatment for a retracted eardrum depends on the cause and how bad it is. You might need:
- Watchful waiting: Just watching to see if it gets better
- Eustachian tube exercises: To help the tube work better
- Surgical intervention: Like tympanoplasty to fix or replace the eardrum
We’ll choose the best treatment for you based on your situation.
Tympanosclerosis
Scarring of the eardrum, known as tympanosclerosis, can come from chronic infections or inflammation. It affects the tympanic membrane and can lead to hearing problems. We will look at the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment for tympanosclerosis.
Understanding Eardrum Scarring
Tympanosclerosis is when collagen and calcium salts build up in the eardrum, causing scarring. This can happen from repeated middle ear infections or Eustachian tube problems. The scarring makes the eardrum stiff, which can affect how it vibrates to sound waves.
Key factors contributing to tympanosclerosis include:
- Recurrent otitis media
- Chronic Eustachian tube dysfunction
- Previous eardrum perforation or surgery
Symptoms and Progression
The symptoms of tympanosclerosis vary. Some people might not notice anything, while others might hear less or feel their ear is full. It can cause hearing loss because the eardrum moves less.
The progression of tympanosclerosis can be slow, often developing over years. Regular check-ups with an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist are key to managing it well.
Diagnosis Methods
Diagnosing tympanosclerosis involves a detailed ear exam with an otoscope. The ENT specialist might also do tympanometry to check the eardrum’s mobility. Sometimes, a CT scan is needed to see how much scarring there is and its effect on the middle ear.
Diagnostic Method | Description |
Otoscopy | Visual examination of the eardrum using an otoscope |
Tympanometry | Assessment of eardrum mobility and middle ear function |
CT Scan | Detailed imaging of the middle ear structures |
Treatment Possibilities
The treatment for tympanosclerosis depends on how severe the scarring is and its effect on hearing. If the scarring is minor and doesn’t affect hearing much, waiting and watching might be the best option. But if the scarring is serious and affects hearing, surgery might be needed.
Surgery, like tympanoplasty, can repair the eardrum and improve its function. The decision to have surgery is made after careful evaluation and talking it over with the ENT specialist.
Cholesteatoma: Abnormal Skin Growth
Cholesteatoma is an abnormal skin growth in the ear. It can cause serious health problems if not treated. This condition happens when skin cells grow wrong in the middle ear, damaging nearby structures.
Formation and Development
Cholesteatoma can be either born with or develop later. The congenital form is present at birth. The acquired form comes later, often from ear infections or Eustachian tube issues. This growth can form a cyst or sac, damaging bone and tissue.
Warning Signs and Symptoms
Symptoms of cholesteatoma vary. Common signs include:
- Ear discharge or foul-smelling ear drainage
- Hearing loss or a feeling of fullness in the ear
- Ear pain or discomfort
- Dizziness or balance problems
Seek medical help if you notice these symptoms. Early treatment can prevent serious issues.
Diagnostic Approach
Diagnosing cholesteatoma involves several steps:
- Otoscopy: A visual check of the ear canal and eardrum
- Imaging tests: CT or MRI scans to see how far the condition has spread
- Hearing tests: To check how it affects hearing
A detailed diagnosis is key to finding the right treatment.
Surgical and Medical Interventions
Treatment for cholesteatoma usually means surgery. The goal is to remove the abnormal skin and fix any damage. Sometimes, a second surgery is needed to remove all affected tissue. Doctors may also use medicine to manage symptoms and prevent infections.
Dealing with cholesteatoma is tough, but with the right treatment, it can be managed. This helps avoid long-term problems.
Preventing and Managing Eardrum Problems
Protecting our ears is key to avoiding eardrum issues. Good ear care practices help keep our ears healthy. This way, we can prevent many common eardrum problems.
Proper Ear Cleaning Techniques
Proper ear cleaning is a big step in preventing eardrum problems. Avoid using cotton swabs or other objects that can push earwax deeper. This can damage the eardrum. Instead, clean the outer ear with a washcloth and don’t insert anything into the ear canal.
Safe ear cleaning practices include:
- Gently wiping the outer ear with a washcloth
- Avoiding the use of cotton swabs or other objects that can damage the eardrum
- Using ear drops to help loosen earwax if necessary
Protecting Ears During Air Travel and Diving
Air travel and diving can be risky for our eardrums because of pressure changes. To protect our ears, we can use several strategies.
Tips for protecting ears during air travel:
- Yawn and swallow during ascent and descent to help equalize ear pressure
- Use earplugs designed for air travel to help regulate pressure changes
- Avoid sleeping during takeoff and landing
For diving, it’s important to:
- Descend and ascend slowly to avoid rapid pressure changes
- Equalize ear pressure by pinching the nose shut and blowing gently
- Consider using specialized earplugs for diving
Noise Protection Strategies
Loud noises can harm our eardrums and cause hearing loss. It’s important to protect our ears from loud noises.
Noise Level (dB) | Risk Level | Protection Needed |
85 dB or less | Low | None or minimal |
86-100 dB | Moderate | Earplugs or earmuffs recommended |
101 dB or more | High | Earplugs or earmuffs required |
When to See a Doctor
Knowing when to see a doctor is key to managing eardrum problems. If we have persistent ear pain, hearing loss, or discharge, we should get medical help right away.
Signs that it’s time to see a doctor include:
- Persistent ear pain or discomfort
- Hearing loss or changes in hearing
- Discharge or bleeding from the ear
- Fever or other signs of infection
By following these guidelines and taking care of our ear health, we can avoid eardrum problems. This helps us keep our hearing good for life.
Conclusion
It’s important to understand and tackle eardrum issues to keep our ears healthy. This article covered different problems like perforated eardrums and infections. We also talked about issues like Eustachian tube problems and cholesteatomas.
Knowing the signs and causes of these problems helps us prevent and manage them. Safe ear cleaning and protecting ears during activities are key. These steps help keep our eardrums in good shape.
We stress the need for being aware and taking care of our eardrums. This way, we can avoid serious issues and stay healthy. Good ear care is vital for a happy and healthy life. We urge everyone to take care of their eardrums.
FAQ
What are the common symptoms of eardrum problems?
Symptoms include ear pain, hearing loss, and discharge. You might also feel like your ear is full or under pressure. If you notice these signs, see a doctor right away.
What causes a perforated eardrum?
A perforated eardrum can happen from trauma, infections, or loud noises. Knowing why it happened helps find the right treatment.
How is otitis media diagnosed?
Doctors use a physical exam and medical history to diagnose otitis media. They might also do tests like a tympanogram or CT scan. This helps confirm the diagnosis.
What is Eustachian tube dysfunction, and how does it affect the eardrum?
Eustachian tube dysfunction happens when the tube connecting the middle ear to the throat doesn’t work right. It can cause ear fullness, hearing loss, and discomfort. It’s often due to colds, allergies, or the shape of your ear.
Can a retracted eardrum be treated without surgery?
Sometimes, a retracted eardrum can be treated without surgery. But if it doesn’t get better or gets worse, surgery might be needed.
What is tympanosclerosis, and how is it treated?
Tympanosclerosis is scarring on the eardrum. Treatment depends on how bad it is. It might involve watching it or surgery to help hearing and symptoms.
How can I prevent eardrum problems?
To avoid eardrum issues, clean your ears right, protect them during air travel and diving, and use ear protection. Regular doctor visits can also catch problems early.
When should I seek medical attention for eardrum issues?
See a doctor for persistent ear pain, hearing loss, or discharge. Also, if you notice anything unusual or have ear health concerns, get advice from a healthcare professional.
Can ear problems be related to other health conditions?
Yes, ear issues can be linked to allergies, colds, or sinus infections. Knowing the cause can help manage your ear problems better.
How can I manage eardrum problems and maintain good ear health?
To handle eardrum issues and keep your ears healthy, follow your doctor’s advice, practice good ear care, and prevent further damage.
References
MedlinePlus. (n.d.). Sinusitis. Retrieved from https://medlineplus.gov/sinusitis.html









