Patients who have had their prostate removed face a scary reality: prostate cancer recurrence. At Liv Hospital, we get it. The fear of cancer coming back is real. When PSA levels go up, it’s a sign that cancer might be back, and more treatment is needed.
We know every patient is different. That’s why we tailor our care for recurrent prostate cancer. Our team works hard to find the best treatments. This includes radiation, hormone therapy, and new methods to help those facing prostate cancer relapse after surgery.
Key Takeaways
- Prostate cancer can recur after prostate removal, indicated by rising PSA levels.
- Personalized treatment plans are key for dealing with recurrent prostate cancer.
- Treatment options include radiation therapy, hormone therapy, and new treatments.
- Liv Hospital offers full care for patients with recurrent prostate cancer.
- Our team is dedicated to patient-centered care and innovation.
Understanding Prostate Cancer After Prostate Is Removed
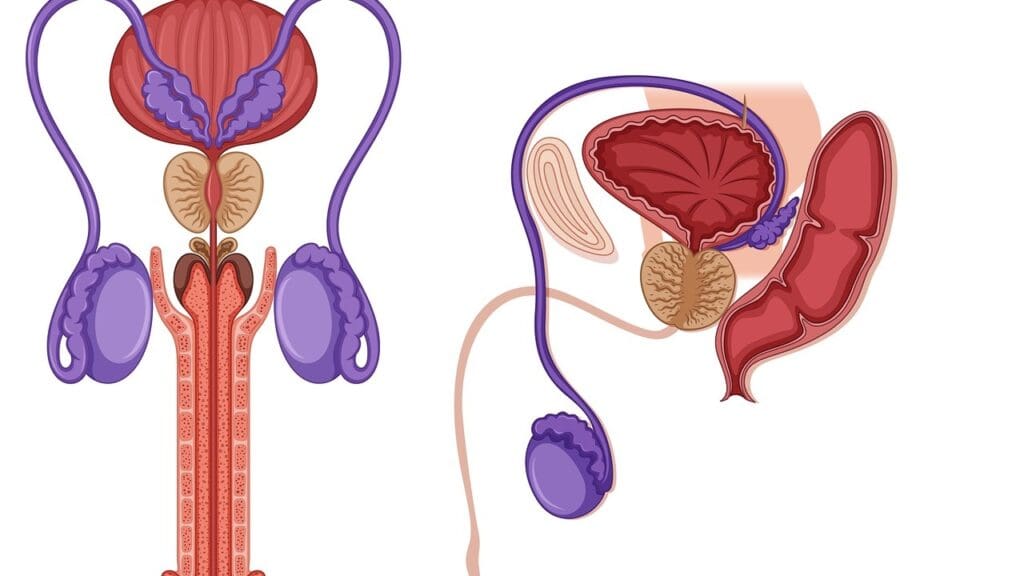
Removing the prostate gland doesn’t mean the risk of prostate cancer coming back is gone. After a prostatectomy, doctors watch patients closely for signs of prostate cancer recurrence. They look at the level of Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) in the blood.
What Is Biochemical Recurrence?
Biochemical recurrence, or PSA recurrence, happens when PSA levels go up after the prostate is removed. This means cancer might be coming back. Doctors use PSA tests to find even small increases in PSA levels. UCSF Urology says knowing about biochemical recurrence is key to figuring out what to do next.
How Common Is Prostate Cancer Recurrence?
How often prostate cancer comes back varies a lot. It depends on how aggressive the disease was and if there were cancer cells left behind during surgery. Studies show that 40–70% of patients with high-risk features might see their cancer come back. This shows why regular check-ups and follow-up care are so important.
Risk Factors for Recurrence
Some things make it more likely for prostate cancer to come back. These include the cancer’s stage, Gleason score, and how clean the surgical margins were. Patients with these risk factors need to be watched more closely and might need extra treatments to lower the chance of recurrence.
Detecting Recurrent Prostate Cancer
Spotting recurrent prostate cancer involves watching PSA levels and using advanced imaging tests. These steps help us find recurrence early, when it’s easier to treat.
Rising PSA Levels as Warning Signs
PSA levels rising after prostate removal might mean cancer is back. We keep a close eye on these levels. Even small increases can signal a problem.
PSA levels are checked through blood tests. We watch these levels over time to spot any changes. If PSA levels go up, we do more tests to find out why.
Imaging Tests for Recurrence Detection
Imaging tests are key in finding and pinpointing prostate cancer that comes back. We use CT scans, bone scans, and PET scans to see how far the cancer has spread.
| Imaging Test | Purpose | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| CT Scan | Assesses lymph nodes and surrounding tissues | Provides detailed cross-sectional images |
| Bone Scan | Detects cancer spread to bones | Helps identify bone metastases early |
| PET Scan | Evaluates cancer metabolism and spread | Offers insights into cancer activity and extent |
Distinguishing Local vs. Distant Recurrence
Telling local from distant recurrence is key for choosing the right treatment. Local recurrence means cancer is back in the same area. Distant recurrence means it has spread to other parts of the body.
We use imaging tests and other tools to figure out where the cancer is. Knowing if it’s local or distant helps us plan the best treatment for each person.
For local recurrence, treatments like radiation or surgery might be options. If it’s distant, treatments like hormone therapy or chemotherapy might be better.
External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT)
For those with prostate cancer that comes back after surgery, External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT) is a top choice. It’s a non-invasive method that sends precise radiation to the cancer site. This way, it hits the cancer cells hard but spares the healthy tissues around them.
Treatment Mechanism
EBRT sends high-energy beams from outside the body to the cancer spot. It’s customized for each patient to kill cancer cells and slow the disease’s growth. The treatment is given in several sessions, allowing healthy tissues to heal between each one.
Precision in treatment is key with EBRT. Thanks to modern tech, doctors can aim right at the tumor. This precision boosts treatment success and cuts down on side effects.
Effectiveness and Outcomes
EBRT is proven to be effective against recurring prostate cancer. Studies show it helps control the cancer and can even save lives. It improves patients’ quality of life by easing symptoms and possibly curing the cancer.
Success rates depend on several things, like the cancer’s stage and the patient’s PSA level. But EBRT is a mainstay in treating recurring prostate cancer. It offers hope to many patients.
Managing Side Effects
EBRT can lead to side effects like urinary troubles, bowel issues, and tiredness. How often and how bad these side effects are can differ for each person. Effective management strategies help lessen these effects, making life better during and after treatment.
Doctors and patients work together to keep an eye on side effects. They adjust the treatment as needed to make it work better without being too hard on the patient.
Proton Therapy for Recurrent Prostate Cancer
Proton therapy is a new way to treat prostate cancer that comes back. It uses special particles to kill cancer cells while protecting healthy tissues. This method is different from traditional X-rays because it targets cancer more precisely.
Precision and Reduced Side Effects
Proton therapy is known for its accuracy. It can focus a high dose of radiation on the tumor, sparing nearby healthy tissues. This means fewer side effects, like urinary problems and bowel damage, compared to old treatments.
The benefits of proton therapy for recurrent prostate cancer include:
- Reduced risk of side effects due to its precision
- Effective treatment of tumors with complex shapes
- Minimal damage to surrounding healthy tissues
Candidacy for Proton Therapy After Prostatectomy
Not everyone with prostate cancer that comes back can get proton therapy. To qualify, patients must go through tests and have their medical history checked. The size and location of the cancer, and the patient’s health, play big roles in deciding if they can get this treatment.
A recent newsletter from the Florida Proton Therapy Institute highlights the importance of understanding recurrent prostate cancer. This knowledge helps doctors choose the best treatment for each patient.
Treatment Outcomes and Quality of Life
Research shows proton therapy is effective for treating prostate cancer that comes back. Patients often see good results with little to no side effects. This makes proton therapy a promising option.
Proton therapy also helps keep patients’ quality of life high. It reduces damage to tissues around the tumor. This means patients can keep up with their daily routines without much trouble.
| Treatment Outcome | Proton Therapy | Traditional Radiation |
|---|---|---|
| Cancer Control Rate | 85-90% | 80-85% |
| Urinary Incontinence | Low Risk | Moderate Risk |
| Bowel Damage | Low Risk | Moderate Risk |
Hormone Therapy Options
Hormone therapy is key in fighting recurrent prostate cancer. It lowers male hormones, which help cancer grow. This makes it a vital treatment.
Androgen Deprivation Therapy (ADT)
Androgen Deprivation Therapy (ADT) is a main hormone therapy for prostate cancer. It can be done through surgery or medicine. The medicine lowers testosterone, slowing cancer growth.
Benefits of ADT: It lowers PSA levels and slows cancer.
Considerations: It can cause hot flashes, osteoporosis, and lower libido.
Second-Generation Hormone Therapies
For some, second-generation hormone therapies are suggested. These include abiraterone and enzalutamide. They target androgens more effectively than ADT. They’re used at different stages of cancer, often with other treatments.
- Abiraterone: Stops an enzyme needed for testosterone.
- Enzalutamide: Blocks androgen receptors, stopping testosterone from helping cancer grow.
Managing Side Effects of Hormone Treatment
It’s important to manage hormone therapy side effects. These include fatigue, weight gain, and low libido. Changes in diet and exercise, along with medicine, can help.
| Side Effect | Management Strategy |
|---|---|
| Hot Flashes | Lifestyle adjustments, medication |
| Osteoporosis | Calcium and vitamin D supplements, bisphosphonates |
| Fatigue | Exercise, energy conservation techniques |
Knowing about hormone therapy options and side effects helps patients make choices. Talking to a healthcare provider is key to finding the right treatment.
Combination Therapy Approaches
For patients with prostate cancer that comes back after surgery, new treatments are helping. We’ll look at how mixing different treatments can help these patients.
Radiation Plus Hormone Therapy
One good mix is using radiation therapy and hormone therapy together. Radiation targets cancer cells in one spot. Hormone therapy lowers testosterone, slowing cancer down. Research shows this combo can greatly improve how well cancer is controlled and survival chances.
The good things about this mix are:
- It helps control cancer better
- It can lead to longer life
- It might lower the chance of cancer coming back
Sequencing of Multiple Treatments
Choosing the right order for treatments is key in fighting prostate cancer that comes back. We plan carefully to make sure treatments work well together and don’t harm too much.
Important things to think about when planning treatment order are:
- Looking at the patient’s health and cancer
- Deciding the best first treatment
- Planning for next steps based on how the patient responds and side effects
Personalized Treatment Planning
Every patient with prostate cancer that comes back is different. We make plans that fit each person’s needs and situation.
Things we consider in making a treatment plan are:
- The type and stage of cancer
- The patient’s health and what they want
- The possible side effects and risks of treatments
Salvage Therapies for Post-Radiation Recurrence
Salvage therapies are key for patients with prostate cancer that comes back after radiation. It’s important to find new ways to manage the disease when it recurs.
Salvage Prostatectomy Considerations
Removing the prostate after radiation is an option for some. It’s best for those with cancer that’s come back but is in one place and who are healthy. A study on PubMed Central shows it can control cancer for a while.
Choosing to have the prostate removed is a big decision. There are risks like not being able to control urine or have an erection. But, many see the chance to fight cancer as worth it.
Key Considerations for Salvage Prostatectomy:
- Localized recurrence
- Good overall health
- Potential for long-term cancer control
- Risks of urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction
Focal Ablative Procedures
Focal ablative procedures are a less invasive way to treat cancer that comes back. They focus on the cancer spot, not the whole area. Methods include cryotherapy and high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU).
These procedures are good for those who don’t want big surgery or more treatments.
| Focal Ablative Procedure | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Cryotherapy | Freezing cancer cells | Minimally invasive, preserves surrounding tissue |
| HIFU | High-intensity focused ultrasound | Precise targeting, reduced risk of side effects |
Cryotherapy and HIFU Options
Cryotherapy and HIFU are two methods being used to treat cancer that comes back. Cryotherapy freezes cancer cells, and HIFU heats and kills them with sound waves.
“Focal therapies, such as cryotherapy and HIFU, represent a promising approach for managing recurrent prostate cancer, balancing cancer control and quality of life.”
Both are guided by images to target the cancer well. They can be done again if needed and might be used with other treatments.
In summary, there are many options for patients with cancer that comes back after radiation. Knowing the good and bad of each helps patients and doctors choose the best treatment.
Emerging Treatments and Clinical Trials
Research on prostate cancer is moving forward fast. New treatments are coming up to help those whose cancer comes back after surgery. These new methods could lead to better lives for patients facing recurrence.
Image-Guided Targeted Therapies
Image-guided targeted therapies are a big step forward in fighting prostate cancer that comes back. They use high-tech imaging to find and hit cancer cells right on. This way, they avoid harming healthy tissue nearby.
Methods like stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) and focal laser ablation are being tested in studies. They aim to see if they can effectively treat cancer that comes back.
These precise treatments might cut down on side effects and boost success rates. Scientists are working hard to make these methods better and find the right people for them.
Immunotherapy Approaches
Immunotherapy is another exciting area for treating prostate cancer that comes back. It uses the body’s immune system to fight cancer. Researchers are looking into checkpoint inhibitors and therapeutic vaccines to help the immune system fight prostate cancer cells better.
Studies are checking if these immunotherapy methods are safe and work well for prostate cancer that comes back. Even though results are just starting to come in, immunotherapy looks very promising for the future.
How to Find and Qualify for Clinical Trials
For those with prostate cancer that comes back, joining clinical trials can offer new treatments. To find trials, patients can look online at ClinicalTrials.gov or talk to their doctor.
Each trial has its own rules for who can join. They often look for people with certain levels of PSA or who have had certain treatments before. Patients should talk to their doctor to see if they might qualify for a trial.
Lifestyle Modifications to Support Treatment
When dealing with recurrent prostate cancer, the right lifestyle changes can make a big difference. A good approach to managing the disease includes medical treatment and changes in daily habits. These changes are key to improving treatment outcomes.
Dietary Considerations
Eating a balanced diet is important for prostate cancer treatment. We suggest eating foods rich in nutrients like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Adding foods high in antioxidants, such as berries and leafy greens, can help reduce side effects.
It’s also important to limit or avoid certain foods. Try to eat less processed meat and foods with a lot of saturated fats. Drinking plenty of water is also essential.
| Food Group | Recommended Foods | Foods to Limit |
|---|---|---|
| Fruits and Vegetables | Berries, leafy greens, tomatoes | Starchy vegetables like potatoes |
| Proteins | Lean meats, fish, beans, lentils | Processed meats, high-fat dairy |
| Grains | Whole grains like brown rice, quinoa | Refined grains like white bread |
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular exercise is vital for men with recurrent prostate cancer. Exercise helps manage side effects, improves health, and boosts quality of life. Aim for 150 minutes of moderate exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise weekly.
Walking, cycling, and swimming are great options. Strength training exercises help keep muscles and bones strong.
Stress Management and Mental Health
Managing stress and keeping mental health in check is key. We suggest trying stress-reduction techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing. Seeking help from mental health professionals can also be helpful in dealing with the emotional side of recurrent prostate cancer.
Doing things that bring joy and relaxation can help reduce stress. Building a support network of family, friends, and support groups can offer emotional support during tough times.
By making these lifestyle changes, men with recurrent prostate cancer can better support their treatment and improve their overall well-being.
Conclusion: Creating a Personalized Recurrence Treatment Plan
Creating a personalized treatment plan is key for patients with recurrent prostate cancer. Each patient’s needs and situation are different. A tailored plan can improve outcomes and quality of life.
A personalized plan considers the patient’s health, cancer details, and personal wishes. This way, we can create a treatment strategy that works well and is easy to follow.
There are many treatment options for recurrent prostate cancer. These include radiation, hormone therapy, and combining treatments. We help patients choose the best options for them.
By focusing on each patient’s needs, we can make treatments more effective. Our aim is to provide top-notch care and support. We want to ensure patients get the best care every step of the way.
What is biochemical recurrence, and how is it diagnosed?
Biochemical recurrence means PSA levels go up after removing the prostate. This could mean cancer is coming back. We check for this by watching PSA levels and doing imaging tests.
How common is prostate cancer recurrence after prostate removal?
How often cancer comes back after removing the prostate varies. It depends on the cancer’s stage and Gleason score. We watch PSA levels closely to see if cancer is coming back.
What are the risk factors for prostate cancer recurrence?
Factors that increase the chance of cancer coming back include a high Gleason score and positive surgical margins. We look at these to figure out the risk and plan treatment.
What is the role of imaging tests in detecting recurrent prostate cancer?
Imaging tests like PET scans and MRI help find cancer coming back. They show if cancer is in the prostate bed or nearby. These tests help us decide how to treat it.
What is the difference between local and distant recurrence?
Local recurrence means cancer is back in the prostate area. Distant recurrence means it has spread to other parts of the body. We treat each type differently.
How does External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT) work for recurrent prostate cancer?
EBRT sends precise radiation to the prostate area. It targets cancer cells. This helps control cancer and ease symptoms.
What are the advantages of proton therapy for recurrent prostate cancer?
Proton therapy is precise, which means less damage to healthy tissue. It also has fewer side effects. We consider it for localized recurrence or after previous radiation.
What is hormone therapy, and how does it work for recurrent prostate cancer?
Hormone therapy, or ADT, lowers testosterone levels. This slows cancer growth. We use it to treat cancer, often with other treatments.
What are the possible side effects of hormone therapy, and how are they managed?
Side effects of hormone therapy include hot flashes and osteoporosis. We manage these with medication and lifestyle changes. We also keep a close eye on how patients are doing.
How do we determine the best treatment sequence for recurrent prostate cancer?
We create a treatment plan based on the cancer’s stage and the patient’s health. We choose treatments carefully to get the best results and reduce side effects.
What are salvage therapy options for post-radiation recurrence?
Salvage therapies, like surgery or cryotherapy, aim to control cancer after radiation. We weigh the risks and benefits of each option to find the best treatment.
What emerging treatments are available for recurrent prostate cancer?
New treatments, like targeted therapies and immunotherapy, offer hope. We talk about clinical trials with patients to explore these options.
How can lifestyle modifications support treatment for recurrent prostate cancer?
Healthy habits, like a good diet and exercise, can help symptoms and overall health. We encourage patients to live a healthy lifestyle to support their treatment.
Can prostate cancer come back after radiation treatment?
Yes, cancer can come back after radiation. We watch PSA levels and use imaging tests to find recurrence. Then, we plan a new treatment.
Why can’t I have my prostate removed after radiation?
Surgery after radiation is tricky because of tissue changes and possible complications. We consider each case to see if surgery is an option.
Reference:
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/blog/after-prostate-cancer-treatment-a-new-standard-of-care-for-rising-psa-202312203001
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10741753/
- https://urology.ucsf.edu/patient-care/cancer/prostate-cancer/conditions/prostate-cancer-condition/recurrence
- https://www.floridaproton.org/newsletter/2022/april/when-prostate-cancer-returns
- https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2810262