Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
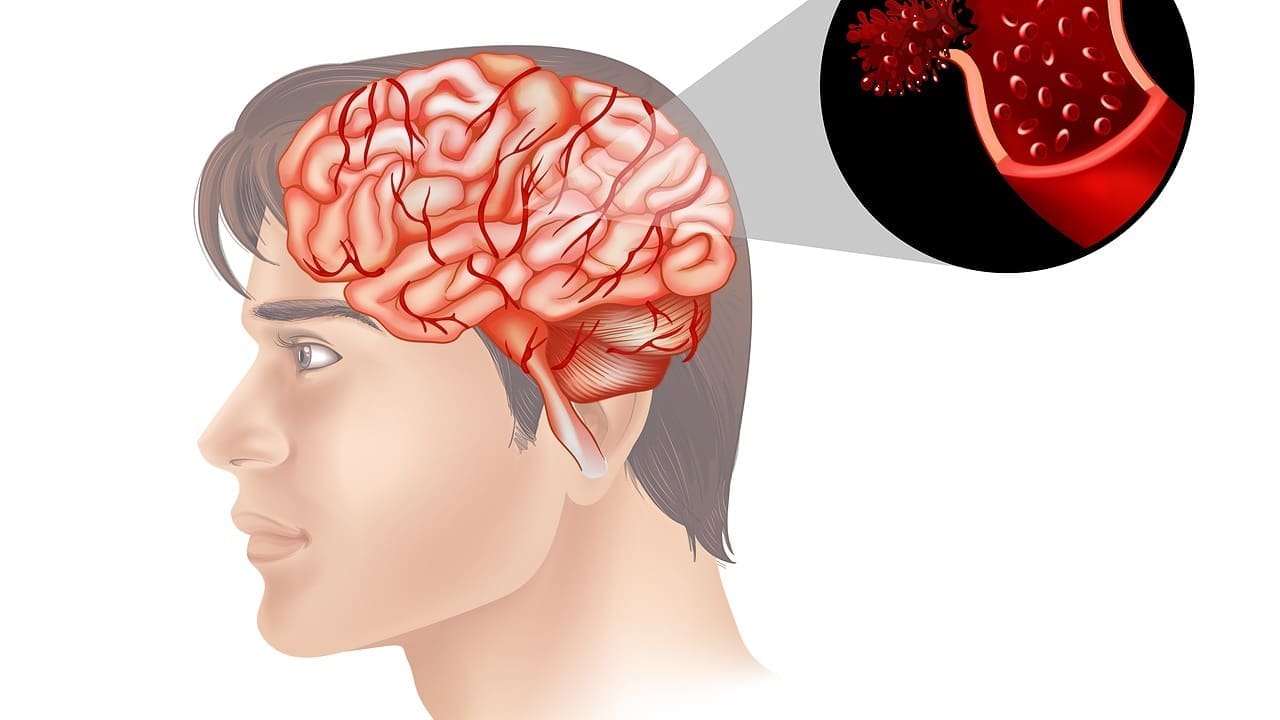
Hardening of arteries in the brain, also known as cerebral arteriosclerosis or cerebral atherosclerosis, is a serious condition. It can lead to strokes and neurological damage.
At Liv Hospital, we know the risks of this condition. We are committed to giving our patients the best care. Cerebral atherosclerosis happens when plaque builds up in blood vessels. This makes them thicken and narrow.
This condition often goes unnoticed, making it important to know the signs and risks. Our experts are here to help patients manage and understand this complex condition.
The hardening of arteries in the brain is called cerebral arteriosclerosis. It’s a condition that gets worse over time and affects brain health. Arteries that carry blood to the brain narrow and harden, reducing blood flow and causing symptoms.
Cerebral arteriosclerosis is when arteries in the brain harden. Atherosclerosis is when plaque builds up in arteries all over the body, including the brain. Atherosclerosis is a key factor in the development of cerebral arteriosclerosis. Knowing these terms helps us understand the condition and its health impacts.
We often use these terms together. But it’s key to know cerebral arteriosclerosis refers to the brain’s blood vessels. Plaque, made of fat, cholesterol, and more, builds up in these walls.
Plaque in the brain’s arteries builds up slowly, starting early in life. Atherosclerosis is when plaque builds up, making arteries hard and narrow. This can cut off blood flow to the brain, causing symptoms and raising the risk of stroke.
The damage starts with the inner layer of the artery. High blood pressure, smoking, and high cholesterol can cause this damage. Once damaged, plaque starts to build up, narrowing the artery and cutting off blood flow.
As plaque builds up, arteries narrow, cutting off blood flow to the brain. This can cause thinking problems, headaches, and even stroke. The narrowing of arteries is a key part of cerebral arteriosclerosis, affecting the brain’s function.
When blood flow is cut off, the brain doesn’t get the oxygen and nutrients it needs. This can damage brain tissue and lead to serious problems. Understanding how blood flow is cut off is key to seeing the risks of cerebral arteriosclerosis and why early medical help is important.
Understanding the causes and risk factors of cerebral atherosclerosis is key. We’ll look at factors like age, genetics, lifestyle, and medical conditions. These all play a part in developing cerebral atherosclerosis.
Age is a big risk factor for cerebral atherosclerosis. As we get older, our blood vessels wear out. This makes them more likely to get clogged and hard.
People over 65 face a higher risk. Knowing this helps us focus on prevention and early action.
Genetics and family history are also important. If your family has heart disease or stroke, you might be at higher risk. Certain genes can affect how your body handles cholesterol.
We use genetic information to tailor advice and monitoring. This helps those with a strong family history.
Lifestyle choices greatly affect your risk. Smoking, eating too much fat, not exercising, and being overweight all increase risk. These habits can lead to high cholesterol and diabetes, among other problems.
Changing your lifestyle can lower your risk. We stress the importance of eating right, exercising, and avoiding smoking.
Some medical conditions make arteries harden faster. High blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol are big risks. These conditions damage blood vessel linings, making them more prone to plaque.
Controlling these conditions is vital. We help patients manage them to prevent cerebral atherosclerosis.
It’s important to know the warning signs of hardening of brain arteries. This is because symptoms can vary a lot. They depend on which arteries are affected and how bad the blockage is. We’ll talk about the common symptoms of this condition.
Cognitive symptoms are often the first signs. They can include memory loss, trouble focusing, and problems solving or making decisions. As it gets worse, these changes can really affect your daily life and how well you feel.
Physical symptoms can show up in different ways. You might get frequent headaches, facial pain, or vision issues like blurred or double vision. These happen because of less blood flow to the brain and face.
Neurological symptoms are more serious. They can include weakness or numbness in your limbs, trouble with speech or understanding, and even seizures. These signs mean your brain function is badly affected and need quick medical help.
Knowing when to get emergency care is key. Look out for sudden severe headache, confusion, trouble speaking or walking, and sudden numbness or weakness. These are signs that need immediate medical attention. Quick action can greatly improve your chances and prevent lasting harm.
Understanding these warning signs and symptoms is key to managing hardening of brain arteries. Early detection and the right medical care can make a big difference in how well you do.
Healthcare experts use many methods to find out if arteries in the brain are blocked. They do a clinical check-up and use advanced imaging. This helps them see how bad the blockage is and what treatment is best.
The first step is a detailed clinical evaluation and looking at the patient’s medical history. This helps spot risk factors and symptoms that might show brain artery hardening.
Advanced imaging techniques are key in finding blocked brain blood vessels. These tools give clear pictures of the brain’s blood vessels. This lets doctors see how bad any blockages or narrowing are.
Besides clinical checks and imaging, blood tests help check heart health and find risk factors for brain artery hardening.
By using all these methods, doctors can accurately find and treat brain artery hardening. This helps lower the chance of stroke and brain function loss.
It’s important to know about ICAD because it’s a big risk for people with heart problems. ICAD is when arteries in the brain get narrow or blocked by plaque. This is because of atherosclerosis.
ICAD is a big health worry because it can cut down blood flow to the brain. This can cause many symptoms and even serious problems like stroke. It’s linked to high morbidity and mortality rates, so early diagnosis and treatment are key.
One of the worst things about ICAD is the chance of recurrent strokes. Strokes happen when blood flow to the brain is cut off. This stops brain tissue from getting oxygen and nutrients. ICAD makes it more likely for strokes to happen again because the plaque keeps building up.
Research shows that people with ICAD are more likely to have strokes again. This can cause a lot of disability and even death. So, it’s very important to manage ICAD well to stop these bad outcomes.
Some groups are more likely to get ICAD. These include people over 50, those with diabetes, and those with heart risk factors like hypertension and hyperlipidemia. Knowing these risk factors helps find problems early and prevent them.
Lifestyle and genetics also play a big part in getting ICAD. Knowing these can help make plans to lower the risk.
Managing cerebrovascular atherosclerosis disease requires a detailed plan. This plan includes lifestyle changes, medicines, and sometimes surgery or interventional procedures.
Medicines are key in treating cerebrovascular atherosclerosis disease. We use antiplatelet drugs to stop blood clots, anticoagulants to thin blood, and cholesterol-lowering drugs to reduce plaque.
These medicines help lower the risk of stroke and other disease complications.
Sometimes, surgery or interventional procedures are needed to improve blood flow to the brain. Angioplasty and stenting are common. A stent is a small mesh tube placed in the narrowed artery to keep it open.
A complete management plan is more than just medicine and surgery. It includes lifestyle changes like eating a heart-healthy diet, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and managing conditions like high blood pressure and diabetes.
| Treatment Approach | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Medication Strategies | Use of antiplatelet, anticoagulant, and cholesterol-lowering medicines. | Reduces risk of stroke and other complications. |
| Surgical and Interventional Procedures | Angioplasty and stenting to restore blood flow. | Improves blood flow to the brain, reducing stroke risk. |
| Lifestyle Modifications | Adopting a heart-healthy diet, regular exercise, quitting smoking. | Reduces overall cardiovascular risk, improves health. |
Hardening of the arteries in the brain can lead to severe complications if left untreated. These risks affect many areas of neurological health.
Untreated cerebral atherosclerosis can cause ischemic stroke. This happens when plaque blocks blood flow to the brain. It leads to tissue damage from lack of oxygen and nutrients.
Ischemic strokes can cause mild cognitive issues or severe disability. In some cases, they can even be fatal.
Ischemic stroke occurs when arteries narrow or block. This is often due to plaque buildup or blood clots. Quick medical help is key to reduce damage and improve outcomes.
Untreated hardening of brain arteries can also cause vascular cognitive impairment. This can lead to vascular dementia. Symptoms include memory loss, problem-solving difficulties, and mood changes.
Vascular dementia can greatly affect a person’s life and independence. It’s important to manage risk factors and treat cerebral atherosclerosis to prevent or slow cognitive decline.
The long-term effects of untreated cerebral arteriosclerosis are severe. It increases the risk of stroke and dementia. It can also cause chronic headaches, facial pain, and vision problems.
In severe cases, it can lead to significant disability or death.
| Complication | Description | Potential Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Ischemic Stroke | Restricted blood flow to the brain due to plaque buildup | Mild impairment to severe disability or death |
| Vascular Cognitive Impairment | Reduced blood flow damaging cognitive function | Memory loss, problem-solving difficulties |
| Long-term Neurological Effects | Chronic conditions resulting from prolonged reduced blood flow | Chronic headaches, facial pain, vision problems |
Understanding these complications shows why early intervention is vital. By managing cerebral atherosclerosis, individuals can lower their risk of these serious issues.
To prevent brain atherosclerosis, we need to focus on diet, exercise, and managing health conditions. These steps can greatly lower the risk of getting this condition.
A healthy diet is key in stopping brain atherosclerosis. Key dietary recommendations are:
Regular exercise is also important in preventing brain atherosclerosis. Exercise benefits include:
It’s recommended to do at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week.
It’s also important to manage any underlying medical conditions to prevent brain atherosclerosis. This includes:
By managing these conditions, people can lower their risk of brain atherosclerosis.
Finding cerebral arteriosclerosis early, even in people who don’t show symptoms, is key. Many don’t know they have it until a big event, like a stroke, happens. So, knowing how important early detection is is very important.
We suggest regular checks for those with a family history of heart disease, who are overweight, or have diabetes. Early screening can spot problems before symptoms show up. For those at high risk, tests like blood work, blood pressure checks, and imaging can give important health insights.
New medical tech has made finding cerebral arteriosclerosis early easier. Tools like high-resolution MRI and CT angiography show the brain’s blood vessels in detail. This lets doctors see plaque and artery narrowing.
These new tools are key in finding the condition in people who don’t show symptoms. This means doctors can act quickly.
One big challenge with cerebral arteriosclerosis is it can quietly get worse. It can go on without symptoms until a big event happens. Regular checks and knowing your risk factors are key to avoiding this.
We stress the need for patients to learn about symptoms and their own risk. This helps them stay safe.
At Liv Hospital, we use the latest care methods for patients with intracranial atherosclerotic disease. Our goal is to give each patient the best care possible. This ensures they get the best results.
Managing intracranial atherosclerotic disease needs a team effort. Our team includes neurologists, cardiologists, radiologists, and vascular surgeons. They work together to create a treatment plan that fits each patient’s needs.
The benefits of this team effort are clear:
| Specialty | Role in Treatment |
|---|---|
| Neurology | They handle the brain symptoms and problems. |
| Cardiology | They check and manage heart risks. |
| Radiology | They use imaging to see how the disease is growing. |
| Vascular Surgery | They do surgeries and procedures to fix blood flow. |
New treatments and technologies are always coming for intracranial atherosclerotic disease. We join clinical trials to give our patients the newest care options.
“The future of treating intracranial atherosclerotic disease is bright. New, better, and less invasive treatments are on the way. This will help patients live better lives.”
-Dr. Neurologist
Some new treatments include:
By always looking for new ways to help and working together, we offer our patients the best care. This care is both effective and complete.
Managing cerebral arteriosclerosis well needs a mix of lifestyle changes, medicine, and special care. We’ve covered the key parts of this condition, like its causes, signs, diagnosis, and treatment choices.
For those living with cerebral arteriosclerosis, being proactive is key. This means eating right, staying active, and handling any other health issues. These steps can greatly lower the chance of serious problems.
Handling cerebral arteriosclerosis also means acting fast and getting all-around care. It’s vital to work with doctors to make a plan that fits you. This team effort helps keep your brain healthy and lowers the risks of cerebral arteriosclerosis.
Understanding cerebral arteriosclerosis and tackling it in many ways can make life better for those dealing with it. Our aim is to offer top-notch healthcare and support to patients worldwide. We want to help them face the challenges of cerebral arteriosclerosis with hope and strength.
Cerebral arteriosclerosis is when the brain’s blood vessels harden. This happens because of plaque buildup. It limits blood flow to the brain.
Symptoms include memory loss and headaches. You might also feel weakness, numbness, and have trouble speaking.
It’s caused by age, genetics, lifestyle, and certain medical conditions. These factors can make arteries harden faster.
ICAD can cause blood vessels in the brain to narrow. This reduces blood flow, leading to strokes.
Treatments include medicines and surgeries. There are also plans to manage the condition and prevent problems.
Prevent it by eating right and exercising. Managing health conditions also helps reduce risk.
Untreated, it can cause strokes and dementia. It also has long-term effects on the brain. Early treatment is key.
Early detection catches cases before symptoms show. Screening high-risk people helps find it early.
ICAD stands for Intracranial Atherosclerotic Disease. It’s when brain blood vessels narrow and harden.
Doctors use clinical exams, imaging, and blood tests. These help diagnose and plan treatment.
Risk factors include age, genetics, lifestyle, and certain health conditions. These can increase the risk of developing it.
https://study.com/academy/lesson/what-is-cerebral-arteriosclerosis-symptoms-treatment.html
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!