Last Updated on November 26, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
When cancer metastasizes to the bones, it can lead to many problems. Knowing the signs of bone metastases is key to handling the condition well.
At Liv Hospital, we understand the challenges of metastatic bone cancer. Our team is committed to giving patients the care and support they need.
Spotting symptoms early can greatly help patients live better. We’ll talk about the common signs of cancer spreading to bones. We’ll also share ways to manage these symptoms.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the symptoms of bone metastases is vital for effective management.
- Early symptom recognition can greatly improve patients’ quality of life.
- Liv Hospital offers complete care and support for patients with metastatic bone cancer.
- Managing bone metastases needs a patient-focused approach.
- Our expert team is committed to providing top-notch healthcare services.
What Happens When Cancer Spreading to Bones Occurs
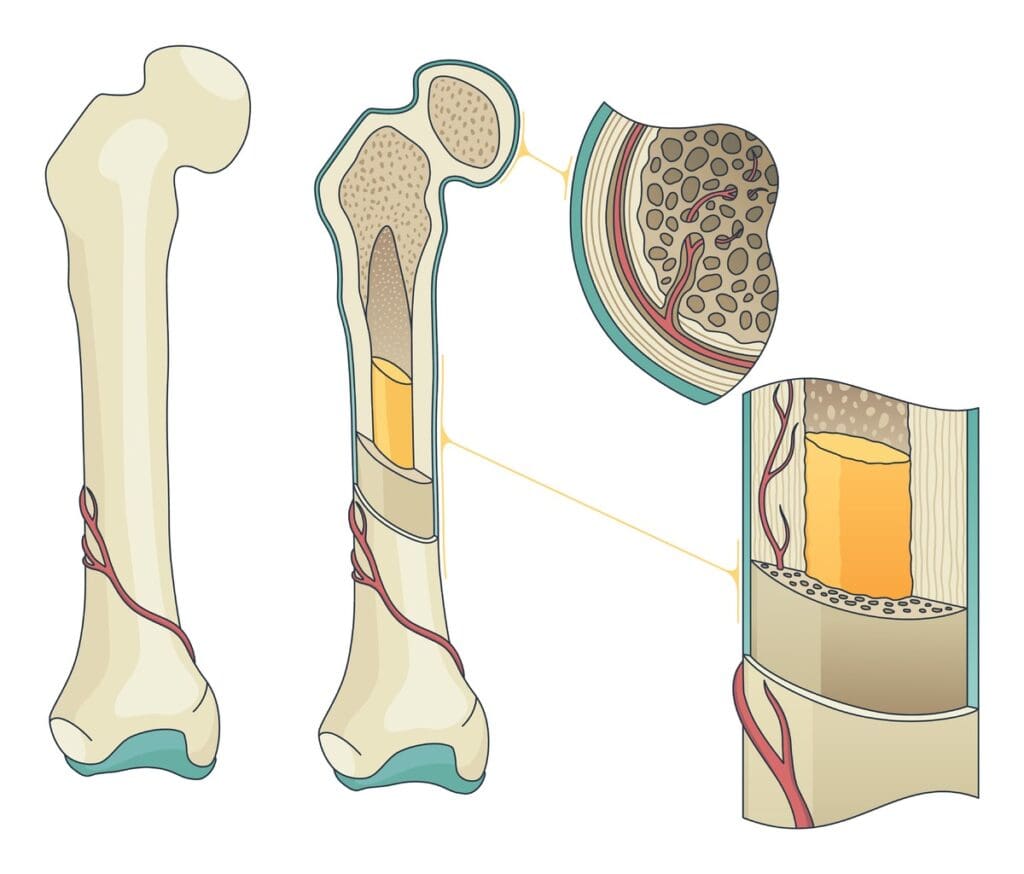
Bone metastasis happens when cancer cells move from their original site to the bones. This creates a new cancer growth area. It changes the patient’s health, causing many problems.
The Metastatic Process Explained
The steps to cancer spreading to bones are complex. First, cancer cells break away from their original tumor. Then, they move into the bloodstream or lymphatic system.
Once in the blood, they can travel to bones. There, they stick to the bone matrix and grow, forming a new tumor.
The process is detailed and involves many interactions. Cancer cells can mess with the bone’s normal repair process. This can cause bones to weaken or grow abnormally.
Common Primary Cancers That Metastasize to Bone
Some cancers are more likely to spread to bones. These include:
- Breast Cancer: Often spreads to bones.
- Prostate Cancer: Causes bones to grow abnormally.
- Lung Cancer: Spreads to bones, mostly in later stages.
- Kidney Cancer: Can cause bones to weaken.
- Thyroid Cancer: Some types, like follicular, can spread to bones.
Knowing which cancers spread to bones helps doctors. It helps them spot at-risk patients and care for them better.
Types of Bone Metastases and Their Effects
It’s important to know about the different types of bone metastases. This knowledge helps in managing and treating the disease. When cancer reaches the bones, it can cause various problems, depending on the type of metastasis.
Osteolytic Metastases
Osteolytic metastases destroy bone tissue. This type of metastasis breaks down bone material, making bones weak and prone to fractures. Osteolytic lesions are common in lung, breast, and kidney cancers.
The destruction of bone is caused by cancer cells and the bone environment. Cancer cells release factors that activate osteoclasts. These cells break down bone, leading to its destruction.
Osteoblastic Metastases
Osteoblastic metastases, on the other hand, form new bone tissue. This type of metastasis causes abnormal bone growth, increasing bone density. Osteoblastic lesions are often linked to prostate cancer.
Osteoblastic metastases are caused by cancer cells stimulating osteoblasts. These cells build bone. But, the new bone is often abnormal and can cause pain and increase the risk of fractures.
Mixed Lesions
Some bone metastases have both osteolytic and osteoblastic features, known as mixed lesions. In these cases, there is both bone destruction and formation happening at the same time.
Mixed lesions require a detailed treatment plan. It’s important to understand the specific characteristics of the metastases to manage the disease effectively.
In conclusion, the type of bone metastasis greatly affects how the disease is managed and treated. Knowing the differences between osteolytic, osteoblastic, and mixed lesions is key to providing the right care and improving patient outcomes.
How Bone Metastases Are Diagnosed
Diagnosing bone metastases involves several steps and tools. It’s key to know how far cancer has spread. This helps us choose the right treatment.
Imaging Tests for Detecting Bone Metastases
Imaging tests are essential for spotting bone metastases. They let us see inside the bones for any issues. Here are some common tests:
- X-rays: Good for finding big bone problems.
- CT scans: Show detailed pictures of bones.
- MRI scans: Great for seeing soft tissue and bone marrow.
- Bone scans: Spot areas where bone activity is high.
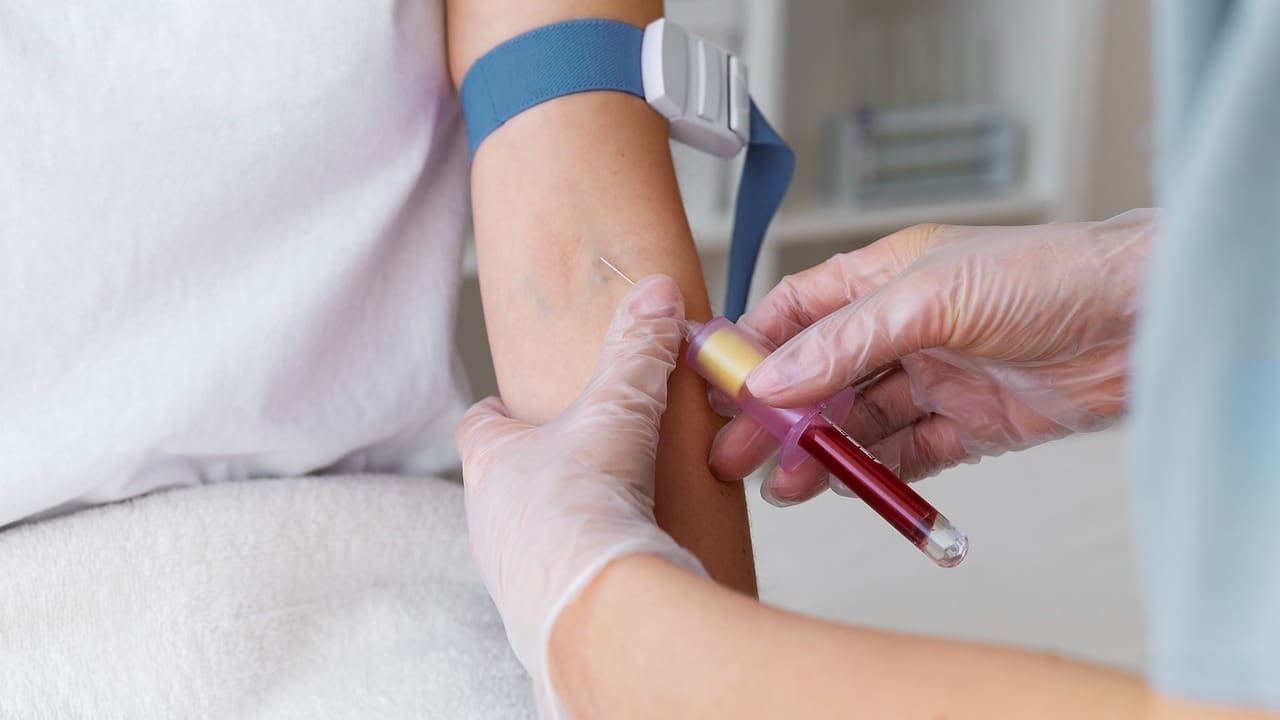
Blood Tests and Biomarkers
Blood tests are also vital for diagnosing bone metastases. They check for signs of bone changes and cancer. Some tests include:
- Alkaline phosphatase (ALP): High levels suggest bone involvement.
- Calcium levels: Odd calcium levels might mean bone metastases.
- Tumor markers: Specific to the cancer type.
Bone Biopsy Procedures
At times, a bone biopsy is needed to confirm bone metastases. It takes a bone sample for study. We do this when other tests aren’t clear or to find cancer cells in the bone.
Biopsy results help us understand the bone issue better. This lets us make a treatment plan that fits the person’s needs.
Symptom 1: Persistent Bone Pain
Bone pain that doesn’t go away is a common symptom of bone metastases. It can really affect a person’s life. This pain happens when cancer spreads to the bones, causing damage and pain signals.
Characteristics of Metastatic Bone Pain
Metastatic bone pain is different from other pains. It stays the same or gets worse over time if not treated. The pain can feel dull or sharp, depending on where and how much the bones are affected.
People often say the pain is worse at night or when they move. It can also make it hard to move or even cause bones to break. Knowing these details helps us find better ways to manage the pain.
Pain Management Strategies
We use many ways to help manage metastatic bone pain. Our goal is to make the patient’s life better. Here are some treatments we use:
- Medications: We use drugs like opioids and non-opioids to help with pain.
- Radiation therapy: This treatment can shrink tumors that press on bones or nerves, easing pain.
- Bisphosphonates: These drugs make bones stronger and can reduce pain from bone metastases.
- Other interventions: We also do nerve blocks or surgery to stabilize broken bones and relieve pain.
It’s important for patients to work with their healthcare team to create a pain plan that’s just right for them. A specialist says, “Good pain management is not just about treating pain. It’s about making the patient feel better overall.”
“Pain is whatever the experiencing person says it is, existing whenever they say it does.”
| Pain Management Strategy | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Medications | Analgesics, including opioids and non-opioids | Effective for managing various levels of pain |
| Radiation Therapy | Targeted radiation to shrink tumors | Reduces pain by decreasing tumor size |
| Bisphosphonates | Drugs to strengthen bones | Reduces pain and risk of fractures |
Symptom 2: Pathological Fractures
Bone metastases can weaken bones to the point of fracture, a condition known as pathological fracture. This happens when cancer cells in the bone cause significant destruction. It leads to a loss of structural integrity.
Why Bone Metastases Increase Fracture Risk
Bone metastases increase the risk of fractures by replacing normal bone tissue with cancer cells. This weakens the bone structure. The risk is higher in weight-bearing bones like the femur and spine.
Several factors contribute to this increased risk. These include the size and location of the metastatic lesion, as well as the type of primary cancer. For instance, lytic lesions, which are bone destruction, are more likely to result in fractures.
| Risk Factor | Description | Impact on Fracture Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Size of Metastatic Lesion | Large lesions are more likely to weaken the bone. | High |
| Location of Lesion | Lesions in weight-bearing bones are more risky. | High |
| Type of Primary Cancer | Cancers like breast and lung cancer often metastasize to bone. | Variable |
Surgical Interventions for Fractures
Surgical intervention is often necessary to stabilize pathological fractures and restore function. The goal is to alleviate pain, improve mobility, and enhance the patient’s quality of life.
Various surgical techniques are employed. These include internal fixation with rods or plates, and in some cases, joint replacement. The choice of procedure depends on the location and extent of the fracture, as well as the patient’s overall health.
“Surgical stabilization of pathological fractures is critical for improving patient outcomes and reducing morbidity.”
Preventive Measures and Supportive Devices
Preventing pathological fractures is a critical aspect of managing patients with bone metastases. This involves identifying patients at high risk and implementing appropriate preventive measures.
Supportive devices such as orthopedic braces and canes can help reduce the risk of fractures. They provide additional support and stability. In some cases, prophylactic surgery may be considered to stabilize bones at risk of fracture.
We emphasize the importance of a multidisciplinary approach to managing bone metastases. This includes regular monitoring and timely intervention to prevent complications like pathological fractures.
Symptom 3: Limited Mobility and Movement
Cancer in the bones can really hurt a person’s ability to move around. It makes bones weak, causes pain, and limits how far you can go. Even simple things like walking or getting dressed can be hard.
Impact on Daily Activities
Having trouble moving because of bone cancer can change your life a lot. Simple tasks like walking or even taking a bath can become hard. This can make you feel like you’re losing your independence and need more help from others.
Patients face many challenges, including:
- Difficulty in performing routine tasks
- Reduced ability to participate in social activities
- Increased fatigue due to the extra effort required for daily tasks
Physical Therapy Approaches
Physical therapy is key in helping people move better when they have bone cancer. A special physical therapy plan can help make muscles stronger and more flexible. This helps you move better.
Some ways physical therapy can help include:
| Therapy Type | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Strengthening Exercises | Exercises to make muscles around the affected bones stronger | Stronger bones, better mobility |
| Flexibility Exercises | Stretching to keep or improve flexibility | More movement, less stiffness |
| Aerobic Exercises | Low-impact activities like walking or swimming | Healthier heart, better overall feeling |
Assistive Devices and Home Modifications
Using special devices and making changes at home can also help a lot. These things can make it easier to move around and live on your own. They help prevent falls and injuries too.
Examples of these include:
- Canes, walkers, or wheelchairs for support
- Grab bars and non-slip mats in bathrooms
- Removing tripping hazards and improving lighting in the home
By using physical therapy, assistive devices, and making home changes, people with bone cancer can stay more independent and happy.
Symptom 4: Spinal Cord Compression
When cancer spreads to bones, one scary symptom is spinal cord compression. This is a medical emergency that needs quick action. It happens when a tumor or bone piece presses on the spinal cord. This can cause serious damage and harm if not treated right away.
Recognizing This Medical Emergency
The signs of spinal cord compression can be different for everyone. But common symptoms include severe back pain, numbness or tingling in the hands and feet, and weakness in the legs or arms. In the worst cases, you might lose control over your bladder or bowels.
It’s very important to catch these symptoms early. The success of treatment depends a lot on how fast you get help. If you have cancer and notice any of these symptoms, get medical help right away.
Immediate Treatment Approaches
Treating spinal cord compression often involves a team effort. This might include surgery, radiation therapy, and corticosteroids to reduce swelling. Surgery might be needed to remove the tumor or stabilize the spine. Radiation therapy helps shrink tumors that are pressing on the spinal cord.
The right treatment depends on many things. These include the type of cancer, how much the spinal cord is compressed, and the patient’s health. We work with each patient to create a treatment plan that fits their needs.
Long-term Management Strategies
After the initial treatment, managing the condition long-term is key. This includes physical therapy to improve strength and mobility, regular check-ups, and ongoing treatment for the cancer. We also focus on supportive care to enhance the patient’s quality of life.
This care includes managing pain, providing nutritional support, and counseling. Our goal is to help patients live better lives despite their condition.
Symptom 5: Hypercalcemia (Elevated Calcium Levels)
When cancer spreads to the bones, it can cause high calcium levels in the blood. This happens because the cancer releases calcium from the bones into the blood.
Symptoms of High Calcium Levels
The signs of high calcium levels can vary. They often include fatigue, confusion, and muscle weakness. In severe cases, it can cause nausea, vomiting, and constipation. It’s important to notice these symptoms early.
Medical Interventions for Hypercalcemia
Doctors treat high calcium levels with hydration and medicine. Intravenous fluids help remove extra calcium. Bisphosphonates slow down bone breakdown. Sometimes, calcitonin or corticosteroids are used too.
Dietary Considerations
Eating right is key in managing high calcium levels. Patients should eat less calcium-rich foods and drink lots of water. They should also avoid vitamin D supplements unless a doctor says it’s okay.
Knowing the symptoms and how to manage them helps patients deal with high calcium levels caused by bone metastasis.
Symptom 6: Localized Swelling and Inflammation
Bone metastases can cause swelling and inflammation. This is a sign that you need to see a doctor right away. Cancer in the bones can lead to swelling and inflammation in the affected area.
Distinguishing Metastatic Swelling
Swelling from bone metastases can be different from other causes. We use clinical evaluation and imaging studies to tell them apart. We look at the swelling’s location and how bad it is, along with symptoms like pain or trouble moving.
- Location: Swelling from bone metastases usually happens near the bone affected.
- Severity: The swelling can be mild or very severe, causing a lot of pain or trouble moving.
- Associated Symptoms: Pain, warmth, or redness in the affected area can happen with swelling.
Anti-inflammatory Approaches
It’s important to manage swelling and inflammation to improve comfort and outcomes. We use different ways to do this, including:
- Medications: NSAIDs or corticosteroids can help reduce swelling and pain.
- Radiation Therapy: Sometimes, radiation therapy is used to shrink tumors and reduce inflammation.
- Supportive Care: Elevating the affected limb, using cold compresses, and supportive devices can help.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
It’s important for patients to know when to get help right away. We tell patients to seek urgent care if they have:
- Severe Pain: Sudden or severe pain in the affected area.
- Increased Swelling: Swelling that gets worse fast or is with other symptoms like fever or redness.
- Neurological Symptoms: Numbness, tingling, or weakness in the affected limb.
Understanding and managing swelling and inflammation from bone metastases is key. It helps patients get the care they need quickly, improving their quality of life.
Symptom 7: Unexplained Weight Loss and Fatigue
When cancer spreads to the bones, it can cause unexplained weight loss and fatigue. These symptoms make daily life hard. They affect a person’s quality of life greatly.
Systemic Effects of Bone Metastases
Bone metastases can mess with the body’s normal functions. This leads to weight loss and fatigue. Cancer cells in the bones can change how the body uses energy, lower appetite, and cause pain.
These changes make it hard to keep weight on. The body also uses more energy to fight cancer and fix bones. This results in constant tiredness.
Nutritional Support Strategies
To tackle unexplained weight loss and fatigue, nutrition is key. Here are some tips:
- Eat foods high in calories and nutrients to stay healthy.
- Drink nutritional supplements to get enough calories.
- Have small meals often to keep energy up and manage hunger.
| Nutritional Element | Recommended Foods |
|---|---|
| Protein | Lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy products |
| Calories | Nuts, dried fruits, avocados |
| Vitamins and Minerals | Fruits, vegetables, whole grains |
Energy Conservation Techniques
To fight fatigue, saving energy is important. Here are ways to do it:
- Focus on important tasks and save energy for them.
- Take breaks to rest and get your energy back.
- Do gentle exercises like yoga or short walks to stay active without getting too tired.
Using these energy conservation and nutritional support tips can help. They improve life quality for those with bone metastases.
Symptom 8: Anemia and Immune System Changes
Cancer spreading to bones can affect the body in many ways. It can change how blood cells are made and how the immune system works. When cancer reaches the bones, it can mess up the bone marrow’s job of making blood cells.
Blood Cell Production Impact
Bone metastases can lower the number of healthy red blood cells. This leads to anemia. Symptoms of anemia include feeling tired, weak, and short of breath. Cancer cells in the bone marrow make it hard to make new blood cells.
Also, bone metastases can lower white blood cell production. White blood cells help fight infections. With fewer white blood cells, patients are more likely to get sick, making their health worse.
Medical Interventions for Blood Health
To fix anemia and blood issues from bone metastases, doctors use different treatments. These include:
- Blood transfusions to boost red blood cell count
- Medicines that help the bone marrow make more blood cells
- Supplements like iron, vitamin B12, and folate to help blood cell production
These treatments aim to ease symptoms and improve life quality.
| Medical Intervention | Purpose | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Blood Transfusions | Increase red blood cell count | Alleviates anemia symptoms, improves energy levels |
| Medications (e.g., Erythropoietin) | Stimulate bone marrow to produce blood cells | Enhances red blood cell production, reduces anemia |
| Nutritional Supplements | Support blood cell production | Corrects deficiencies, supports overall health |
Infection Prevention Strategies
Preventing infections is key when bone metastases weaken the immune system. Ways to do this include:
- Practicing good hygiene, like washing hands often
- Avoiding close contact with sick people
- Getting all recommended vaccinations
By following these steps, patients can lower their infection risk and stay healthy.
Managing anemia and immune system changes is tough. But with the right medical care and prevention, patients can handle these symptoms better. This improves their life quality.
Conclusion
It’s key to know the signs of cancer spreading to bones for good care. We talked about eight common symptoms. These include bone pain, fractures, and trouble moving.
Managing these symptoms needs a full plan. This includes medical help, changes in lifestyle, and support care. Early treatment can really help patients with bone stage 4 cancer live better.
Spotting the signs of bone metastases early is vital. This way, patients can get the right care. It helps them feel better and stay independent. A team of doctors and nurses is important for this care.
We aim to give top-notch healthcare to patients from around the world. Understanding and managing cancer in bones is key. This way, we can make patients’ lives better and improve their health.
FAQ
What are bone metastases?
Bone metastases happen when cancer cells spread to the bones. This leads to secondary bone cancer. It causes various symptoms and problems.
What are the common symptoms of cancer spreading to bones?
Symptoms include constant bone pain and fractures. You might also feel stiff, have spinal cord issues, or experience swelling. Other signs are unexplained weight loss and anemia.
How are bone metastases diagnosed?
Doctors use X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans, and bone scans to find bone metastases. They also check blood for biomarkers and might do a bone biopsy.
What is the difference between osteolytic and osteoblastic metastases?
Osteolytic metastases destroy bone tissue. Osteoblastic ones form new bone. Some people have both, known as mixed lesions.
How is metastatic bone pain managed?
Doctors use pain meds, radiation, and other treatments to ease pain. This improves life quality.
What is spinal cord compression, and how is it treated?
Spinal cord compression is a serious issue. It happens when cancer presses on the spinal cord. Treatment includes radiation, steroids, and sometimes surgery.
How can hypercalcemia be managed?
Hypercalcemia is treated with bisphosphonates, hydration, and diet changes. This lowers calcium levels and relieves symptoms.
What are the systemic effects of bone metastases?
Bone metastases can cause weight loss, fatigue, anemia, and immune system changes. These affect overall health and life quality.
How can patients with bone metastases conserve energy?
Patients can pace activities, take breaks, and use devices to reduce fatigue. This helps them stay independent.
What are the treatment options for pathological fractures?
Treatments include surgery to stabilize or rebuild bones. Preventive measures like bracing and devices are also used.
How can bone metastases affect blood cell production?
Bone metastases can lower blood cell production, causing anemia. Medical treatments can help manage these issues.
What is the role of nutritional support in managing bone metastases?
Nutritional support is key to maintaining health, managing symptoms, and supporting treatment for bone metastases.
REFERENCES
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). (n.d.). Bone Metastasis (StatPearls Publishing). NBK507911. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507911/