Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
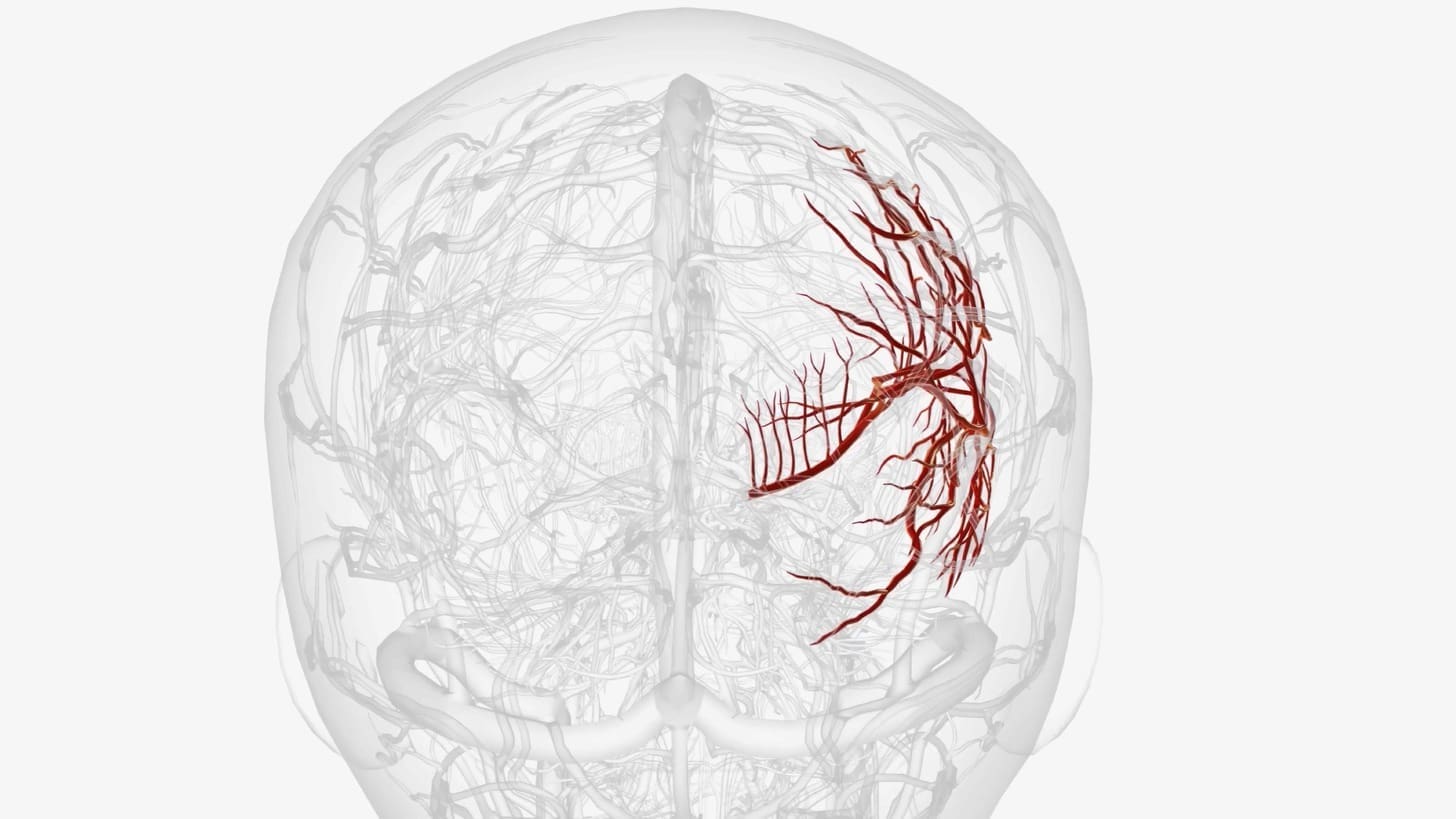
At Liv Hospital, we know how complex venous malformations in the brain can be. This condition can quietly affect brain health or bring on severe symptoms.
Venous malformation, or cerebral venous anomaly, is when veins in the brain form in abnormal clusters. These can cause headaches and seizures among other neurological symptoms.
It’s important to understand these vascular anomalies for those looking for medical help. In this article, we’ll dive into the main facts about venous malformation. We’ll look at its symptoms, causes, and how it can be treated.
The brain’s blood vessels can sometimes form venous malformations. These are also known as cerebral venous malformations or venous anomaly brain. They are abnormal veins in the brain that can affect patients in different ways.
Venous malformations are a tangle of abnormal veins in the brain. They are usually not harmful but can cause other problems. Cerebral venous malformations are present at birth but might not be found until later.
These malformations have a unique structure. They have dilated veins that look like a “caput medusae” around a central vein. This structure is key for diagnosis and understanding the risks.
It’s important to know the difference between venous malformations and other brain vascular problems. Unlike arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), venous malformations are less likely to bleed.
Here’s a comparison table to help understand the differences:
| Characteristics | Venous Malformations | Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs) | Cavernous Malformations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vessel Involvement | Veins only | Arteries and Veins | Abnormal vascular cavities |
| Risk of Hemorrhage | Generally Lower | Higher | Variable |
| Symptoms | Often Asymptomatic | Variable, can be severe | Variable, can include seizures |
| Treatment Approach | Conservative management often recommended | Various treatments, including surgery and embolization | Monitoring or surgical intervention |
Knowing these differences is key for correct diagnosis and treatment. While venous malformations are usually harmless, they can sometimes be linked to other brain vascular problems. This means they need careful evaluation and monitoring.
Looking at the demographics and prevalence of venous malformations in the brain helps us grasp their impact on public health. These vascular anomalies can greatly affect a patient’s quality of life.
Research shows that venous malformations are common among cerebral vascular malformations. They affect about 2-3% of the general population. In the U.S., this means a large number of people might have these malformations.
Thanks to better imaging technologies, we’re finding more cases. This is helping us understand and treat them better.
Venous malformations can appear at any age, but they’re often found in adults between 20 and 40. There’s no clear gender preference, affecting both men and women equally.
When symptoms show up or when they’re found by chance during imaging, is when they’re usually diagnosed.
Most venous malformations are congenital, meaning they’re present at birth. But they might not be found until later in life. The exact cause is not known, but it’s thought to happen during fetal development.
Acquired cases are rarer and might be linked to other health issues or factors that affect blood vessels.
Understanding venous malformations better helps us improve how we diagnose, treat, and manage them.
It’s important to know the symptoms of cerebral venous malformation to get timely treatment. These malformations can affect brain function and structure in many ways.
Neurological symptoms come from abnormal venous drainage. These can include cognitive difficulties, weakness, or numbness in parts of the body. Symptoms can vary a lot among patients.
Some people might have visual disturbances or difficulty with speech. This depends on where the malformation is. We’ll look into these symptoms more to understand their impact.
Headaches are common in those with cerebral venous malformations. They can be caused by pressure effects or venous congestion. The type of headache can differ, from localized to generalized.
Seizures can happen in patients with cerebral venous malformations, if the malformation is near important brain areas. It’s key to watch and manage these patients closely.
Seizures from cerebral venous malformations can be focal or generalized. Treatment might include antiepileptic drugs. Knowing how the malformation and seizures are linked is vital for treatment.
In some cases, cerebral venous malformations can cause swelling or visible venous distension. These signs are more common in superficial malformations.
Seeing these signs can help in diagnosing, as they might make patients seek medical help. Yet, many malformations are asymptomatic or have non-specific symptoms, making diagnosis harder.
Asymptomatic venous malformations in the brain are often found by accident. This raises questions about their importance and how to manage them. These malformations are usually found during imaging studies for other reasons.
Asymptomatic venous anomalies are often seen during MRI or CT scans. These scans are not meant to find these malformations but can spot them.
Patients getting imaging for other reasons should know they might find venous malformations. Knowing about these findings is key to deciding what to do next.
People with asymptomatic venous malformations should get regular check-ups. These check-ups usually involve imaging studies.
The timing of these check-ups depends on the malformation’s size, location, and the patient’s health. It’s important to follow the check-up schedule set by your doctor.
| Monitoring Frequency | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Initial Diagnosis | Baseline imaging and clinical assessment |
| 6-12 months after diagnosis | Follow-up imaging to assess stability |
| Annually or as recommended | Ongoing monitoring based on initial findings and patient health |
While many asymptomatic venous malformations are not a big worry, some signs might mean you should be concerned. We suggest keeping an eye out for any changes in your condition, like new symptoms or a bigger malformation.
Key indicators that may warrant further action include:
If you notice any of these signs, it’s time to talk to your doctor. They can help figure out what to do next.
Understanding vein malformations in the brain is key to managing them. These malformations are complex and can affect brain function.
Genetics play a big role in vein malformations. Some genetic mutations can raise the risk. For example, genes involved in blood vessel development are linked to these malformations.
Vein malformations start in fetal development. Problems with blood vessel formation during this time can cause them. Maternal health and environmental factors also play a part.
Some medical conditions increase the risk of vein malformations. For instance, conditions that affect blood vessels or involve genetic mutations can raise the risk. Syndromes like:
Research is ongoing on environmental factors and vein malformations. It suggests that certain exposures during pregnancy might increase risk. These include:
Diagnosing enlarged vessels in the brain uses top-notch imaging and careful checks. Getting it right is key to the right treatment and better health.
Top imaging methods are key for spotting enlarged brain vessels. These include:
The clinical check-up is also vital. It includes:
It’s important to tell enlarged vessels apart from other issues. This means looking at:
| Condition | Characteristics | Diagnostic Clues |
|---|---|---|
| Venous Malformation | Abnormal venous structures | Shows up on scans without arteriovenous shunting |
| Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM) | Abnormal connections between arteries and veins | Shows arteriovenous shunting on scans |
| Cavernous Malformation | Large blood vessel cavities | Looks like “popcorn” on MRI |
By using advanced imaging, careful exams, and smart diagnosis, doctors can spot enlarged brain vessels. They can then plan the best treatment.
It’s important to know the complications and risks of venous brain bleeds. These can be severe and even life-threatening. Understanding them helps in managing and treating the condition effectively.
The risk of hemorrhage is a big concern with venous malformations. Doctors look at the malformation’s size, location, and how it affects the brain. Advanced imaging techniques help a lot in this assessment. They give detailed info about the malformation and its impact on the brain.
Complications can lead to serious neurological problems. These can range from mild cognitive issues to severe motor problems. Quick and right medical action is key to reduce long-term damage and improve outcomes.
The long-term outlook for patients with venous brain bleeds depends on several things. These include the severity of the initial bleed, how well treatment works, and any underlying conditions. Regular monitoring and follow-up care are vital to manage the condition well and catch any new symptoms or complications.
A swollen vessel in the brain can cause changes over time. These changes can affect the vessel and the brain tissue around it. They can lead to more problems, like increased pressure, more bleeding, or worsening symptoms. It’s important to understand these changes to plan effective treatment.
By fully understanding the risks and complications of venous brain bleeds, doctors can create better treatment plans. This helps improve patient outcomes and lowers the risk of long-term neurological damage.
There are many ways to treat venous malformations. These range from simple, non-invasive methods to more complex surgeries. The right treatment depends on the malformation’s size, location, and symptoms. It also depends on the patient’s health.
For small or symptom-free venous malformations, doctors often suggest conservative management. This means watching the malformation with regular imaging studies. Compression therapy can help with pain or swelling.
For more active treatments, doctors might use sclerotherapy or embolization. Sclerotherapy involves injecting a solution to shrink the malformation. Embolization blocks blood flow to it using special materials.
Surgery is sometimes needed for large or symptomatic malformations. The goal is to remove the malformation. But, the risks and possible complications must be considered carefully.
Medicines can help manage symptoms like pain or inflammation. Pain relief medications and anti-inflammatory drugs are common choices. Sometimes, medicines can also help shrink the malformation or prevent problems.
In summary, treating venous malformations needs a tailored approach. Healthcare providers and patients work together to find the best treatment plan. This plan considers the unique details of each case.
Living with a venous malformation is a complex journey. It involves medical, emotional, and social aspects. Patients’ experiences show that managing this condition needs a broad approach.
Having a venous malformation can really affect someone’s life. Pain, swelling, and neurological problems can make everyday tasks hard. It’s key to tackle these issues to help patients.
Key Factors Affecting Quality of Life:
Support groups and communities are essential for those with venous malformations. They offer emotional support, share experiences, and give practical advice.
Types of Support:
Some lifestyle changes can help manage venous malformation symptoms. It’s important to talk to a healthcare provider about these changes to fit them to your needs.
| Lifestyle Change | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Regular Exercise | Improves circulation and overall health |
| Balanced Diet | Supports vascular health |
| Stress Management | Reduces symptom exacerbation |
Regular check-ups and care are key to managing venous malformations. This care helps catch problems early and adjust treatments as needed.
Components of Follow-up Care:
Understanding the challenges of living with venous malformations is important. With the right support and resources, patients can improve their quality of life.
Understanding venous malformations in the brain is key for patients. This knowledge helps them make smart choices about their care. We’ve covered the basics, like how common they are, their symptoms, causes, and how to diagnose and treat them.
For managing venous malformations, knowing a lot is important. We stress the need to talk to doctors to find the best treatment. New research keeps bringing hope to those affected.
To make good choices about care, patients need to know a lot about venous malformations. By staying informed and working with doctors, they can feel sure about their treatment plans.
The main aim of venous malformation care is to better patients’ lives. We’re dedicated to top-notch healthcare for all, including international patients. Our goal is to help them make the best decisions for their care.
A venous malformation in the brain is an abnormal cluster of veins. It can cause various neurological symptoms. It’s important for patients to understand these malformations when seeking medical care.
Venous malformations are different from other vascular issues like AVMs or cavernous malformations. Their unique characteristics are key for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Venous malformations can be either present at birth or develop later in life. Research suggests they are often present at birth but can also appear later due to various factors.
Common symptoms include headaches, seizures, and vein swelling in the head. Recognizing these symptoms is vital for both patients and healthcare providers.
Yes, some venous malformations may not show symptoms and are found by chance during imaging for other reasons. It’s important to monitor these silent malformations to know when to be concerned.
The causes and risk factors include genetic predisposition, developmental issues during fetal growth, and certain medical conditions or syndromes. Environmental factors also play a role, as research shows.
Advanced imaging like MRI or CT scans is used to diagnose enlarged vessels in the brain. A clinical evaluation and differential diagnosis help distinguish venous malformations from other conditions.
Complications include a risk of hemorrhage, neurological deficits, and long-term prognosis factors. These can be influenced by the presence of a swollen vessel in the brain.
Treatment options include conservative management, interventional procedures, and surgery. Medication may also be used to manage symptoms. The choice depends on various factors.
Patients can improve their quality of life through lifestyle changes and regular monitoring. Support resources and communities are also helpful in managing the condition effectively.
Regular monitoring is key for patients with venous malformations. It helps detect changes or complications early, allowing for timely intervention and adjustments to treatment plans.
Venous malformations can impact quality of life in different ways. The severity of symptoms, treatment approaches, and individual experiences all play a role. This highlights the importance of holistic care and support.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!