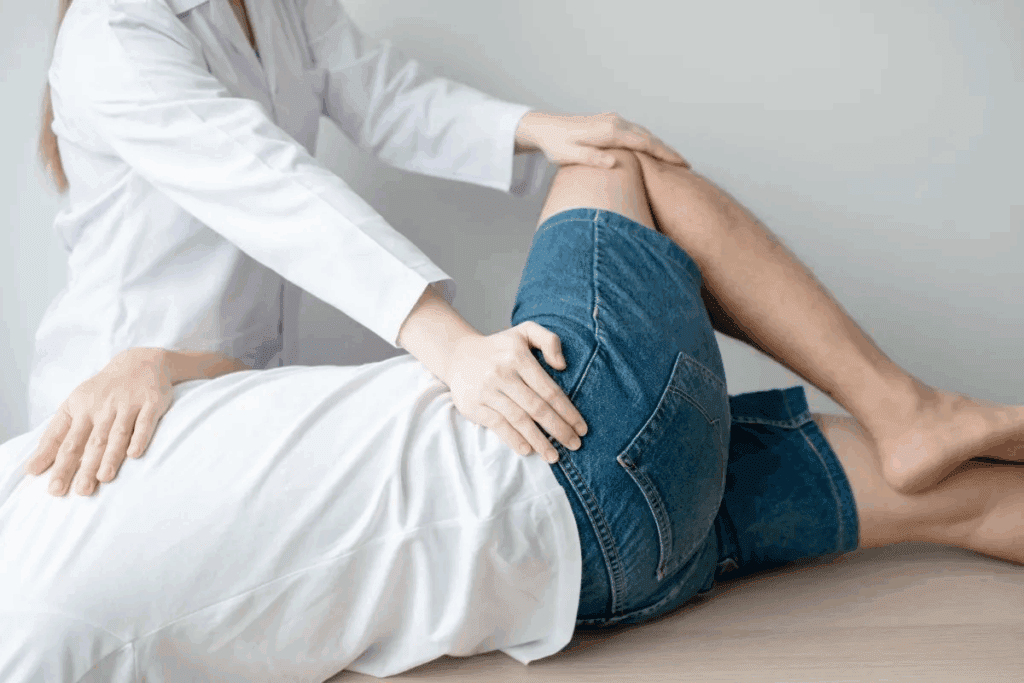
Perianal fistulas can really affect a person’s life. Treatment options are key to managing this issue well. Seton placement is a precision-focused solution that top hospitals like Liv Hospital trust. They value its advanced care and focus on the patient.
This surgery puts a seton in a strategic place to help healing. It also keeps the anal sphincter strong. With a success rate of 94.4 percent, it’s a trusted treatment. Our guide will show you how it works, its benefits, and why it’s important.
Key Takeaways
- Seton placement surgery is a highly effective treatment for perianal fistulas.
- The procedure involves the strategic placement of a seton to facilitate healing.
- Preserving anal sphincter integrity is a key benefit of this surgery.
- A success rate of 94.4 percent makes it a reliable treatment option.
- Leading hospitals trust seton placement surgery for its advanced protocols.
Understanding Perianal Fistulas and Their Management
Perianal fistulas are a complex issue that needs careful management. These abnormal connections between the anal canal and skin can really affect a person’s life. It’s important to know what they are, how they work, and how to treat them.
Definition and Pathophysiology
Perianal fistulas are abnormal tracts from the anal canal to the skin around it. They often start with an infection or inflammation in the anal glands. This can lead to abscesses and fistulas. Knowing this helps doctors choose the right treatment.
Classification Systems for Perianal Fistulas
There are different ways to classify perianal fistulas. The most common is the Parks classification. It divides fistulas into four types: intersphincteric, transsphincteric, suprasphincteric, and extrasphincteric. This helps doctors plan the best treatment.
| Classification Type | Description |
| Intersphincteric | Fistula tract passes between the internal and external anal sphincters |
| Transsphincteric | Fistula tract passes through both the internal and external anal sphincters |
| Suprasphincteric | Fistula tract passes above the puborectalis muscle |
| Extrasphincteric | Fistula tract passes outside the external anal sphincter |
Overview of Treatment Approaches
Treating perianal fistulas can involve different methods. These range from non-surgical options to surgery. The choice depends on the fistula’s type, the patient’s health, and the doctor’s opinion. Seton placement is often used for complex cases. It helps drain the fistula and lowers the chance of it coming back.
There are several ways to treat fistulas:
- Non-surgical methods like antibiotics and pain relief
- Surgery, including seton placement, fistulotomy, and flap procedures
- Other treatments like fibrin glue injection
Knowing about these options is key to effectively managing perianal fistulas. It helps improve patient outcomes.
The Role of Seton Placement Surgery in Fistula Management

Seton placement surgery is a key step in treating perianal fistulas. It helps with drainage and healing. A seton is inserted to keep the fistula open, allowing for continuous drainage and reducing abscess risk.
Mechanism of Action
The surgery keeps the fistula tract open. This allows for the drainage of infectious material. Continuous drainage reduces inflammation and promotes healing.
Types of Setons: Loose vs. Cutting
There are two main types of setons: loose and cutting. Loose setons are made of soft materials like silicone or rubber. They are used to control sepsis before surgery. Cutting setons aim to close the fistula tract by cutting through it. The choice depends on the patient’s condition and the surgeon’s preference.
| Type of Seton | Material | Purpose |
| Loose Seton | Silicone or Rubber | Maintain drainage, control sepsis |
| Cutting Seton | Non-absorbable suture material | Gradually cut through the fistula tract, promote fibrosis |
Indications and Contraindications
Seton placement is for complex or recurrent fistulas, and those with sepsis or abscesses. It’s also for patients not ready for definitive repair due to infection. But, it’s not for simple fistulas or when a patient’s health doesn’t allow surgery.
Choosing seton placement surgery needs careful thought. It depends on the patient’s situation and the fistula’s details.
Preoperative Assessment and Planning
Getting ready for surgery is key for seton placement in patients with perianal fistulas. This step makes sure the surgical team is ready to handle the patient’s needs well.
Clinical Evaluation
A detailed clinical evaluation is the first step. It includes a full history and physical exam. This helps figure out the fistula’s complexity and the patient’s health.
- Looking at the fistula’s location and how complex it is
- Checking if the patient can control their bowel movements
- Finding out if any other health issues might affect the surgery
Imaging Studies
Imaging tests are very important before surgery. They show the fistula’s path and how it relates to nearby areas.
Common imaging tests include:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) for spotting fistula tracts and abscesses
- Endoanal Ultrasound for detailed views of the anal sphincters and fistula tracts
- Fistulography, used in some cases
Patient Preparation and Counseling
Preparing the patient and talking to them is a big part of getting ready for surgery. It makes sure the patient knows what to expect and any possible risks.
Important parts of patient counseling are:
- Talking about the surgery and seton placement
- Explaining possible complications and how they are handled
- What to do after surgery and what recovery will be like
Equipment and Materials Required for Seton Placement
The success of seton placement surgery depends on the right equipment and materials. Surgical teams need the right tools and materials. They also need a well-prepared operating room.
Surgical Instruments
The tools needed for seton placement include:
- Probes for finding and checking the fistula tract
- Lacrimals or fistula probes for moving through the fistula
- Sutures or ties to keep the seton in place
- Surgical scissors for cutting the seton to the right length
- Forceps for handling the seton and tissues
These tools are key for accurately finding and managing the fistula. They help place the seton correctly.
Types of Seton Materials
The type of seton material used is very important. Common materials are:
- Silk or nylon sutures for loose setons
- Vessel loops for their strength and ease of use
- Rubber or silicone materials for their flexibility and comfort
Each material has its own benefits. The choice depends on the patient’s needs and the surgeon’s preference.
Operating Room Setup
The operating room setup is key for seton placement surgery success. The room should have:
- Standard surgical lighting to light the area
- Surgical tables for adjusting patient position
- Monitoring equipment for patient vital signs
- Anesthesia equipment for general or regional anesthesia
A well-organized operating room helps the surgical team work better. This reduces the risk of problems.
Anesthesia Options for Seton Placement Surgery
Anesthesia is key in seton placement surgery, with many options for patients. The right anesthesia choice affects comfort and procedure success.
General Anesthesia
General anesthesia is often used for seton placement, mainly for complex cases or anxious patients. It keeps the patient asleep and pain-free during surgery. But, it needs careful monitoring for side effects.
Regional Anesthesia
Regional anesthesia, like spinal or epidural, is a good alternative. It numbs the lower body, reducing pain and letting the patient stay awake if they want. It’s great for managing pain after surgery.
Local Anesthesia with Sedation
Local anesthesia with sedation is also an option, best for simpler fistulas or those at risk for general anesthesia. This method numbs the area and sedates the patient to relax. It helps in quicker recovery and lowers risks of invasive anesthesia.
Choosing anesthesia for seton placement surgery depends on the patient’s condition, fistula complexity, and surgeon’s preference. A detailed talk between the patient, surgeon, and anesthesiologist is essential to pick the best anesthesia plan.
Step-by-Step Seton Placement Surgery Procedure
The success of seton placement surgery depends on careful steps. It starts with the right patient positioning. This is key for managing perianal fistulas well.
Patient Positioning
Getting the patient in the right position is critical. They are placed in the lithotomy position. This means their legs are up and in stirrups. It gives the surgeon the best view of the perianal area.
Examination Under Anesthesia
After positioning, an examination under anesthesia (EUA) is done. This is important for checking the fistula’s complexity. It also helps find any hidden tracts or abscesses.
Fistula Tract Identification
During the EUA, the surgeon finds the fistula’s openings. A probe is used to follow the fistula’s path. This helps understand its relation to the sphincter muscles.
Probing the Fistula
Probing the fistula is a precise step. It’s done carefully to avoid damage. The probe helps the surgeon plan the seton’s placement.
| Step | Description | Key Considerations |
| Patient Positioning | Placing the patient in lithotomy position | Optimal access, patient comfort |
| Examination Under Anesthesia | Assessing fistula complexity and identifying additional tracts or abscesses | Fistula anatomy, possible complications |
| Fistula Tract Identification | Locating internal and external openings of the fistula | Accuracy, avoiding tissue damage |
| Probing the Fistula | Gently tracing the fistula’s path | Precision, understanding fistula anatomy |
Variations in Seton Placement Techniques
Seton placement surgery for perianal fistulas uses different techniques. Each has its own benefits and things to consider. The choice depends on the fistula’s complexity, the patient’s health, and the surgeon’s preference.
Single vs. Multiple Setons
The choice between a single seton and multiple setons is a topic of debate. Single seton placement is often chosen for simpler fistulas. It causes less tissue damage and helps with healing. On the other hand, multiple setons are needed for more complex fistulas with many tracts.
- Single seton: Suitable for simple fistulas, reduces tissue damage.
- Multiple setons: Used for complex fistulas with multiple tracts.
Sequential Tightening for Cutting Setons
Cutting setons help heal fistulas by cutting through them from the inside. Sequential tightening is a method where the seton is tightened at regular times. This helps the healing process.
- The seton is initially placed loosely around the fistula tract.
- It is then tightened at scheduled follow-ups to gradually cut through the tissue.
- This method allows for healing to occur as the seton cuts through.
Combined Approaches with Partial Fistulotomy
In some cases, combining seton placement with partial fistulotomy is beneficial. This method involves surgically opening a part of the fistula tract. A seton is used for the rest.
This combined technique is useful for complex fistulas. It allows for a treatment plan tailored to the patient’s needs.
Immediate Postoperative Care
After seton placement surgery, taking care of the patient right away is key. It helps with recovery and prevents problems. Good care during this time is important for the best results and comfort.
Pain Management
Managing pain is a big part of postoperative care after seton placement surgery. Adequate analgesia is needed to control pain well. This can be done with medicine and other methods.
Adequate pain control is vital for the patient’s overall health.
Doctors might give out NSAIDs or opioids for pain. It’s important to stick to the pain plan and tell the doctor if pain isn’t managed right.
Wound Care Instructions
Keeping the wound clean and dry is essential for healing and avoiding infection. Patients need to know how to care for their wound. Gentle hygiene practices are recommended around the wound.
Sitz baths may be suggested to ease discomfort and aid in healing. It’s important to follow the doctor’s specific wound care instructions to avoid problems.
Activity Restrictions
Limiting activities is important to prevent complications and help healing. Patients might be told to avoid heavy lifting, bending, or hard work for a while. Gradual return to normal activities should be guided by the healthcare provider’s advice.
Resting and avoiding hard activities can lower the risk of issues like bleeding or seton displacement.
Dietary Recommendations
What you eat can help with recovery after surgery. A high-fiber diet might be suggested to prevent constipation. Drinking enough water is also important.
Patients should be told about easy-to-digest foods. These can help keep bowel movements regular and reduce the chance of complications.
Long-term Management of Patients with Seton Drains
Managing patients with seton drains long-term is key for successful treatment. This phase includes several important steps. Healthcare providers must manage these steps carefully for the best patient outcomes.
Follow-up Schedule
A good follow-up schedule is vital. It helps monitor the patient’s condition and the seton drain’s effectiveness. Follow-up visits are usually every few weeks. They check the fistula’s progress and watch for complications.
Seton Adjustment and Replacement
Seton drains may need adjustments or replacements over time. This happens during follow-up visits. The decision to adjust or replace the seton depends on the patient’s symptoms and the fistula’s response to treatment.
Monitoring for Complications
Long-term management also means watching for complications. This includes infections, abscesses, or seton migration. Finding these issues early is important for effective management.
Timing for Definitive Treatment
This phase also involves planning for the fistula’s definitive treatment. This might mean deciding when to remove the seton or when to do more surgery.
Key considerations in long-term management include keeping the patient comfortable. It’s also important to reduce the risk of complications and find the best time for definitive treatment.
Potential Complications and Their Management
Seton placement surgery helps manage perianal fistulas but comes with risks. It’s important to know these issues to care for patients well.
Infection and Abscess Formation
Infection and abscesses are big problems after seton placement. Prompt treatment is key to avoid more harm. Doctors usually use antibiotics and may drain the abscess.
Seton Migration or Breakage
Setons can move or break, making treatment harder. Regular check-ups help catch these problems early. Doctors might need to adjust or replace the seton.
Persistent Drainage
Drainage that won’t stop can lower a patient’s quality of life. Doctors may change the seton or use other treatments to stop the drainage.
Fecal Incontinence
Fecal incontinence is a serious issue, though rare. Picking the right patients and using the right surgical methods can reduce this risk.
In summary, seton placement surgery is a good option for perianal fistulas but comes with risks. Knowing and managing these complications well is key to better patient outcomes.
Outcomes and Success Rates of Seton Placement Surgery
Seton placement surgery is a top choice for treating perianal fistulas. It has shown great success rates. This method helps manage complex fistulas, boosting patient outcomes and quality of life.
Short-term Results
Right after surgery, seton placement helps drain fistulas. This reduces pain and discharge. Studies show a high success rate in the short term. For example, a Journal of Surgery study found a 90% success rate.
“The use of seton placement has changed how we treat perianal fistulas,” says a leading surgeon. “It offers a reliable solution to a tough condition.”
Long-term Efficacy
Seton placement surgery also shows promise for long-term relief. Proper care and follow-up are key for long-term success. This ensures the seton works well over time.
A study showed patients with seton placement had fewer fistula recurrences. This is compared to other treatments.
Factors Affecting Success Rates
Several things can affect how well seton placement works. These include the fistula’s complexity, how well the patient follows instructions, and the surgeon’s skill. Choosing the right patient and using careful surgical techniques are vital.
- Complexity of the fistula
- Patient compliance
- Surgeon’s experience
Quality of Life Considerations
Seton placement surgery greatly improves quality of life. It manages symptoms well, reducing hospital visits. Improving quality of life is a big part of the procedure’s success.
One patient said, “After the surgery, I could do my daily activities without pain. It was a big relief.”
In summary, seton placement surgery is a highly effective treatment for perianal fistulas. It offers significant improvements in both short-term and long-term outcomes, as well as quality of life.
Conclusion
Seton placement surgery is a key treatment for perianal fistulas. It offers a high success rate and improves life quality. This surgery uses a seton, a thread, to drain the fistula and aid healing.
This surgery has many benefits. It reduces symptoms, improves comfort, and lowers the risk of complications. Knowing about setons helps doctors treat perianal fistulas effectively.
Managing perianal fistulas needs a full approach. This includes checking the patient before surgery, doing the surgery, and caring for them after. Seton placement is a big part of this process.
In short, seton placement surgery is a vital treatment for perianal fistulas. It offers a reliable solution for patients. By using this surgery, doctors can better help patients and improve their lives.
FAQ
What is seton placement surgery for perianal fistula?
Seton placement surgery is a treatment for perianal fistulas. It involves placing a thread or rubber material through the fistula. This helps drain the infection and aids in healing.
How is a seton placed in a fistula?
To place a seton, the fistula is first identified and probed under anesthesia. Then, the seton is carefully placed to ensure proper drainage and healing.
What are the different types of setons used in seton placement surgery?
There are two main types of setons. Loose setons allow for drainage. Cutting setons are tightened over time to cut through the fistula tract.
What is the role of seton placement in managing perianal fistulas?
Seton placement helps manage perianal fistulas. It provides drainage, reduces infection, and promotes healing. It’s often a first step before more definitive treatments.
What are the indications for seton placement surgery?
Seton placement is indicated for complex or recurrent fistulas. It’s also used for high fistulas or those with significant infection or abscesses.
What are the possible complications of seton placement surgery?
Complications can include infection, abscesses, and seton migration or breakage. Other issues are persistent drainage and fecal incontinence.
How is pain managed after seton placement surgery?
Pain is managed with analgesics, sitz baths, and other postoperative care. These measures help reduce discomfort.
What is the follow-up schedule after seton placement surgery?
Follow-up involves regular check-ups. These monitor healing, adjust or replace the seton, and address complications.
Can seton placement surgery improve quality of life for patients with perianal fistulas?
Yes, it can. By reducing symptoms, promoting healing, and minimizing complications, it significantly improves quality of life.
What are the success rates of seton placement surgery?
Success rates vary. They depend on fistula complexity, patient health, and surgical technique. But, seton placement is often effective.
What is the difference between a loose seton and a cutting seton?
Loose setons are for drainage. Cutting setons are tightened to gradually cut through the fistula tract, promoting closure.
How long does it take to recover from seton placement surgery?
Recovery time varies. Most patients can return to normal activities within a few days to weeks. Ongoing follow-up is needed to monitor healing.
References
Park, S., et al. (2024). Associations of cholecystectomy with metabolic health: A large population-based retrospective cohort study. Scientific Reports, 14, 12345. Retrieved from
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-53161-6



































