Last Updated on November 25, 2025 by Ugurkan Demir
At LivHospital, we know that coronary artery disease (CAD) can sneak up on you. It often shows up without the usual chest pain, called angina pectoris. CAD happens when the heart’s blood supply arteries get clogged with plaque.Learn what coronary artery disease without angina means, how it’s diagnosed, and the symptoms to watch for.
This is scary because it can go unnoticed until it’s too late. We focus on finding CAD early, even without symptoms. Our goal is to protect your heart before you even feel anything wrong.
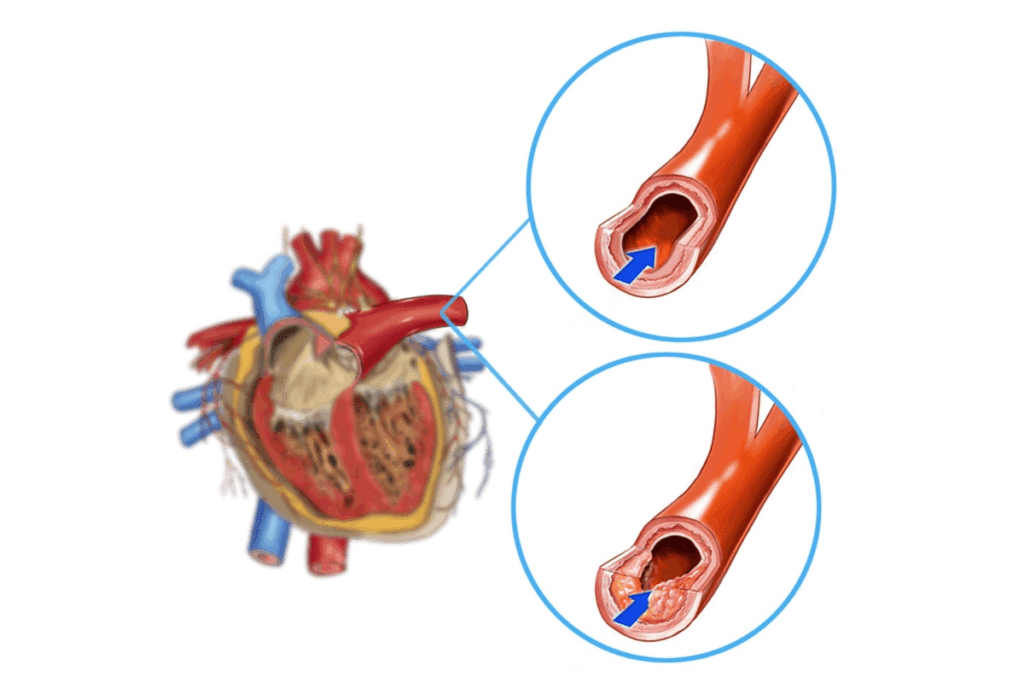
Knowing about coronary artery disease is key to keeping your heart healthy. CAD happens when the heart’s blood supply arteries get hard and narrow. This is called atherosclerosis.
This narrowing is because of cholesterol and other stuff building up on the artery walls. This buildup is called plaque.
Coronary artery disease without angina pectoris is when the original heart arteries get affected but don’t cause chest pain. The disease’s cause is complex. It involves the artery wall, blood, and cells working together.
The plaque buildup causes inflammation and damage to the artery lining. This leads to the artery getting narrower.
This disease can quietly get worse without symptoms until a big blockage happens. This is why it’s called coronary artery disease without angina pectoris.
| Stage | Description | Clinical Implication |
| Early Stage | Initial plaque formation | Often asymptomatic |
| Intermediate Stage | Narrowing of the artery | May lead to reduced exercise tolerance |
| Advanced Stage | Significant blockage or occlusion | High risk of myocardial infarction |
Coronary arteries are vital for the heart. They supply oxygen and nutrients to the heart muscle. When CAD affects these arteries, the heart’s function is at risk.
The heart needs the coronary arteries to work well. Any blockage can cause heart problems, like ischemia or infarction.
Key Functions of Coronary Arteries:
Understanding coronary arteries’ role in heart function is important. It shows why diagnosing and treating CAD is so critical.
The phrase “without angina pectoris” means people with heart disease who don’t feel chest pain. This makes diagnosing and treating heart disease harder.
Angina pectoris is chest pain or discomfort from reduced blood flow to the heart. It’s a sign of heart disease, feeling like a squeeze or pressure in the chest. This pain can spread to the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach.
Angina usually happens when you’re stressed or active and goes away with rest or medicine. But, not having angina doesn’t mean your heart arteries are okay.
Silent ischemia is when the heart muscle doesn’t get enough blood, but you don’t feel pain. This is a silent danger for people with heart disease because they don’t get warning signs.
Silent ischemia is as risky as angina because it can cause a heart attack without warning. About 1 in 20 adults over 20 have heart disease, and many don’t know until it’s too late.
There are many reasons for silent ischemia, like nerve damage, how people feel pain, and other health issues. These can make it hard to diagnose.
It’s important to understand and spot heart disease without chest pain early. We’ll look at how to diagnose and manage it next.
Many people don’t know they have coronary artery disease until it’s too late. They might have a heart attack. This shows how dangerous CAD without angina is for heart health around the world.
Studies show that about 42 percent of middle-aged adults have plaque buildup without symptoms. This highlights how common CAD without angina is. It also shows how the disease can quietly progress.
Not having symptoms doesn’t mean the disease is harmless. It often means the disease is missed until a serious heart event happens.
There are many reasons why some CAD patients don’t feel chest pain. It can depend on how each person feels pain, other health issues like diabetes, and how well the heart is connected.
Silent ischemia is when the heart muscle doesn’t get enough oxygen. This can happen without pain, making it hard to diagnose CAD without angina.
It’s important to understand why CAD without angina happens. We need to find better ways to screen and prevent it. Recognizing coronary artery disease without angina as a major health issue is key to managing it.
“Coronary artery disease involving native heart without angina pectoris” refers to disease in the original coronary arteries. These original blood vessels are key to heart health. They supply blood to the heart muscle.
Native coronary arteries are the intrinsic blood flow from the aorta to the heart. They branch out to different heart areas. They’re vital for the heart’s oxygen and nutrient supply.
It’s important to tell native coronary arteries apart from grafted ones in heart disease. Native arteries are the original ones. Grafted arteries are transplanted vessels used in CABG surgery.
Knowing the difference is key for diagnosing and treating heart disease, even without symptoms. This helps doctors create the right treatment plans for each patient.
It’s important to know the risk factors for silent coronary artery disease. This helps us find and help people at risk early on.
Traditional risk factors for coronary artery disease (CAD) are key in silent CAD. These include:
Some specific factors can also lead to silent coronary artery disease. These include:
Knowing these risk factors helps doctors spot people at high risk for silent CAD. They can then take steps to prevent it.
Coronary artery disease without angina pectoris is very dangerous. It often goes unnoticed until a heart attack happens. This makes it key for doctors to find those at risk early through screenings.
Silent CAD is often overlooked. This is because people without chest pain or angina pectoris don’t usually go to the doctor until it’s too late. Also, old risk assessment tools might not catch silent CAD.
Key factors contributing to the missed diagnosis of silent CAD include:
Screening early is vital to find silent CAD. Advanced tests help doctors spot coronary artery disease before a heart attack.
| Screening Method | Description | Benefit |
| Electrocardiogram (ECG) | Measures the electrical activity of the heart | Detects abnormal heart rhythms |
| Stress Testing | Evaluates heart function under stress | Identifies ischemia or coronary artery disease |
| Coronary Calcium Scoring | Quantifies calcium deposits in coronary arteries | Assesses risk of coronary artery disease |
Early detection through proactive screening can significantly improve outcomes for patients with silent CAD.
By tackling the challenges in diagnosing CAD without angina pectoris, we can better find and manage those at risk.
We use many non-invasive tests to find coronary artery disease in people without symptoms. These tests help spot CAD early, so we can treat it quickly.
An Electrocardiogram (ECG) checks the heart’s electrical activity. It can show signs of CAD like arrhythmias or ischemia. Stress testing is done with an ECG. It watches how the heart works when you exercise, like on a treadmill. This test shows if the heart has issues related to CAD.
Echocardiography uses sound waves to see the heart. It shows how well the heart works and its structure. It can spot areas of the heart affected by CAD, like parts that don’t move well.
Nuclear cardiac imaging uses tiny amounts of radioactive tracers to see the heart’s function. It finds areas where blood flow to the heart muscle is low, which means CAD. It checks how well the heart works under stress and at rest, helping diagnose and manage CAD.
These non-invasive tests are key for finding coronary artery disease in people without symptoms. By using ECG, stress testing, echocardiography, and nuclear cardiac imaging, doctors can find CAD in people who don’t show symptoms. Then, they can start the right treatment.
Advanced imaging has changed how we diagnose coronary artery disease. It helps find problems in the heart and arteries, even when people don’t have angina. This lets doctors diagnose and treat CAD better.
Coronary calcium scoring is a test that looks for calcium in the heart’s arteries. It uses CT scans. Finding calcium shows if there’s atherosclerosis and if heart problems might happen. It’s great for checking risk in people who don’t have symptoms.
Coronary CT angiography gives clear pictures of the heart’s arteries. It uses CT scans and dye to see blockages. This test is key for finding CAD and planning treatment.
Cardiac MRI is a non-invasive test that shows the heart’s details. It uses magnetic fields and radio waves. It checks the heart’s structure, function, and tissue health. MRI is great for complex heart issues, like CAD without angina.
These imaging methods have greatly helped diagnose and manage coronary artery disease. They give detailed info on the heart’s arteries. This helps doctors create better treatment plans and improve patient care.
It’s important to find people at risk for silent coronary artery disease (CAD) early. We need to know who is more likely to get CAD without chest pain.
Some people are more at risk for silent CAD. These include those with a family history of heart disease, smokers, and people with diabetes or high blood pressure. We should focus on these groups for early screening.
Other high-risk groups include:
Screening for silent CAD depends on age and risk level. We suggest screening for those with several risk factors, even if they don’t show symptoms.
| Age Group | Risk Profile | Screening Recommendation |
| 40-49 years | Low risk | No routine screening |
| 40-49 years | High risk | Consider stress testing or coronary calcium scoring |
| 50-59 years | Moderate risk | Consider stress testing or coronary CT angiography |
| 60 years and above | High risk | Strongly consider advanced imaging techniques like cardiac MRI |
Understanding what does without angina pectoris mean is key in CAD. It means having heart disease without chest pain. Screening for this is critical to prevent heart problems.
By identifying high-risk groups and using the right screening methods, we can catch silent CAD early. This helps prevent heart attacks and other serious issues.
Coronary artery disease without angina pectoris needs a detailed treatment plan to avoid serious issues. This plan includes medical treatments, procedures, and lifestyle changes. These steps help lower the risk of heart problems.
Medical care is key in treating coronary artery disease without angina. It aims to lower risk factors and slow the disease’s growth.
Some patients might need procedures to improve blood flow to the heart.
| Procedure | Description | Benefits |
| Angioplasty | A minimally invasive procedure to open blocked arteries. | Restores blood flow, reduces symptoms. |
| Stenting | Placement of a stent to keep the artery open. | Prevents re-narrowing, improves outcomes. |
| Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) | Surgical procedure to bypass blocked arteries. | Improves survival, reduces angina. |
Lifestyle changes are vital in managing coronary artery disease without angina. These changes help lower risk factors and boost heart health.
Dietary Changes: Eating a heart-healthy diet can lower cholesterol and blood pressure.
Physical Activity: Regular exercise, like walking or swimming, improves heart fitness and helps manage weight.
By using medical treatments, procedures when needed, and lifestyle changes, we can manage coronary artery disease well. This approach improves patient outcomes.
The way we manage CAD is changing. New biomarkers, AI tools, and personalized risk plans are helping. These changes are making it easier to spot and treat CAD, even when there’s no chest pain.
Biomarkers are key in diagnosing and treating CAD. New biomarkers are being found. For example, high-sensitivity troponin tests can find small heart damage. Other markers like lipoprotein(a) and genetic tests help understand a patient’s risk.
Using these biomarkers in healthcare can lead to early detection and better risk planning. This means we can act sooner and possibly improve health outcomes.
AI is changing cardiology, focusing on CAD detection. AI looks at lots of data from tests and patient info. It finds patterns that doctors might miss.
AI tools are being made to improve CAD diagnosis and treatment. For example, AI can analyze CT scans to spot plaque and predict heart risks.
Personalized medicine is key in CAD management. It looks at each person’s risk factors and health. This way, doctors can create plans that work better and have fewer side effects.
Personalized risk assessment uses advanced stats and AI. It predicts who might get CAD or have a heart event. This helps in planning prevention and treatment, leading to better health.
In summary, new biomarkers, AI, and personalized plans are changing CAD management. These changes help patients with CAD without chest pain. They allow for earlier detection and more focused treatments.
It’s key to understand coronary artery disease without angina to prevent and manage it well. This condition is a big health risk. It can quietly damage the heart without any symptoms until it’s too late.
We’ve looked into the details of coronary artery disease, even when there are no symptoms. Silent ischemia shows we need to screen more, mainly for those at high risk.
By knowing the risk factors and using new tests, we can spot and treat coronary artery disease without angina better. This helps doctors give better care, leading to better health and fewer heart problems.
As we get better at finding and treating coronary artery disease, focusing on personal care and healthy living is vital. This way, we can lower the risks and keep our hearts healthy.
Coronary artery disease (CAD) without angina means the heart’s arteries are sick. But, the person doesn’t feel the usual chest pain. This can be very dangerous because it might not be caught until it’s too late.
“Without angina pectoris” means the person with CAD doesn’t have chest pain. This makes finding the disease harder. Chest pain is often what makes people go to the doctor.
Native coronary arteries are the heart’s original blood suppliers. They’re key to keeping the heart working right. Disease here can cause big heart problems.
Doctors use many tests to find silent CAD. These include ECG, stress tests, and echocardiography. They also use nuclear imaging, calcium scoring, CT angiography, and MRI.
Risk factors for silent CAD include high blood pressure and high cholesterol. Diabetes and smoking also increase risk. Family history and lifestyle choices play a part too.
People with high-risk factors should get checked for silent CAD. This includes those with family history, high blood pressure, and diabetes. Age and risk level guide screening.
Treatments for CAD without angina include medicine and procedures like angioplasty. Lifestyle changes like diet and exercise are also key.
New ways to find and treat CAD include biomarkers and AI. Personalized risk checks help tailor treatments to each person’s needs.
Some CAD risks can’t be changed, like family history. But, many can be managed with a healthy lifestyle. This includes diet, exercise, and not smoking.
To lower CAD risk, live a healthy lifestyle. Eat well, exercise, don’t smoke, and manage stress. Regular doctor visits can also catch risks early.
Shams, P. (2024). Silent Myocardial Ischemia. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK536915/
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!