Atrial fibrillation (AFib) is a common heart rhythm problem. It can cause symptoms, lower quality of life, and raise stroke risk. Pacemakers are key in managing AFib, mainly for those with slow heart rates or other heart issues.
Dealing with AFib can be tough, but new pacemaker tech offers hope. At Liv Hospital, we use the latest care methods. We aim to improve your symptoms and life quality.
Find out can a pacemaker help AFib, how it works to regulate heartbeat, and when it’s needed for atrial fibrillation.
Key Takeaways
- Pacemakers help with AFib and slow heart rates or conduction disorders.
- AFib can lower quality of life and increase stroke risk.
- New pacemaker tech improves symptom control and life quality.
- Liv Hospital offers a patient-focused approach with the latest care.
- We provide tailored care for complex AFib cases.
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)
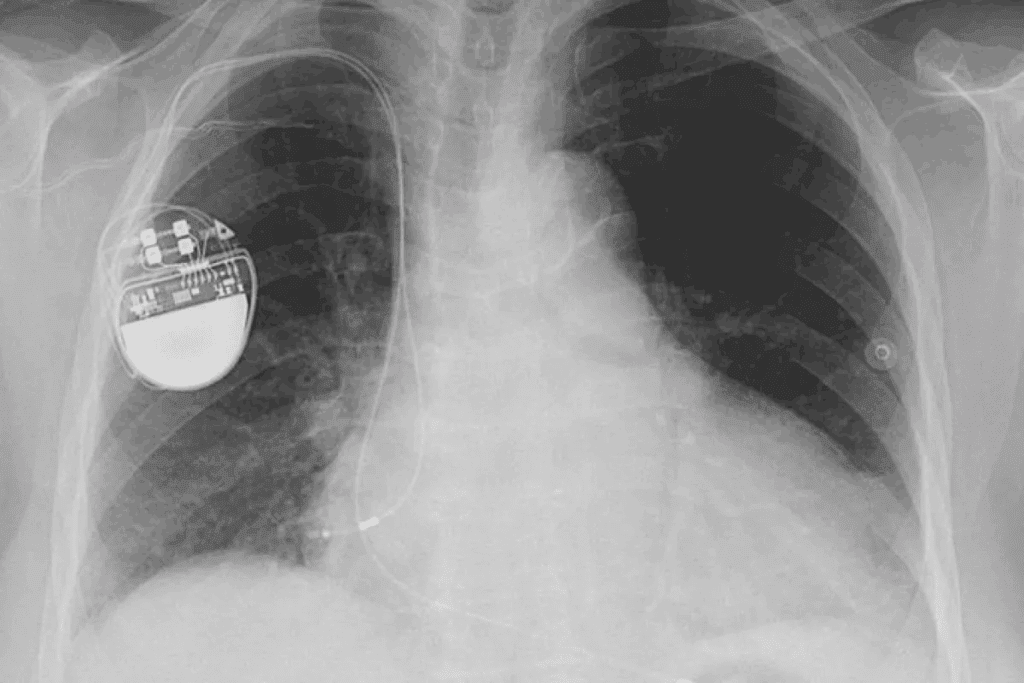
It’s important to know about atrial fibrillation (AFib) to take care of your heart and health. AFib is a heart rhythm problem that makes the upper heart chambers beat in a chaotic way.
AFib makes the upper heart chambers beat too fast and irregularly. This can cause symptoms like palpitations, shortness of breath, and fatigue. It can also make the heart less efficient, leading to more problems.
What Happens in the Heart During AFib
In a normal heart, the atria and ventricles work together well. But in AFib, the atria quiver instead of beating right. This can cause blood to pool in the atria, raising the risk of clots and stroke.
Common Symptoms and Complications
AFib symptoms can vary a lot. Some people might feel palpitations, dizziness, or chest discomfort. Others might not notice anything. But AFib can lead to serious problems like stroke, heart failure, and other heart issues.
“Atrial fibrillation is a serious condition that requires proper management to prevent complications such as stroke and heart failure.”
Impact on Quality of Life and Stroke Risk
AFib can really affect your daily life, causing symptoms that make it hard to do things. It also raises the five-fold risk of stroke. So, it’s key to manage AFib well to lower this risk.
Knowing about AFib and its effects on the heart helps manage it better. This can include lifestyle changes, medicines, and sometimes a pacemaker.
The Basics of Cardiac Pacemakers
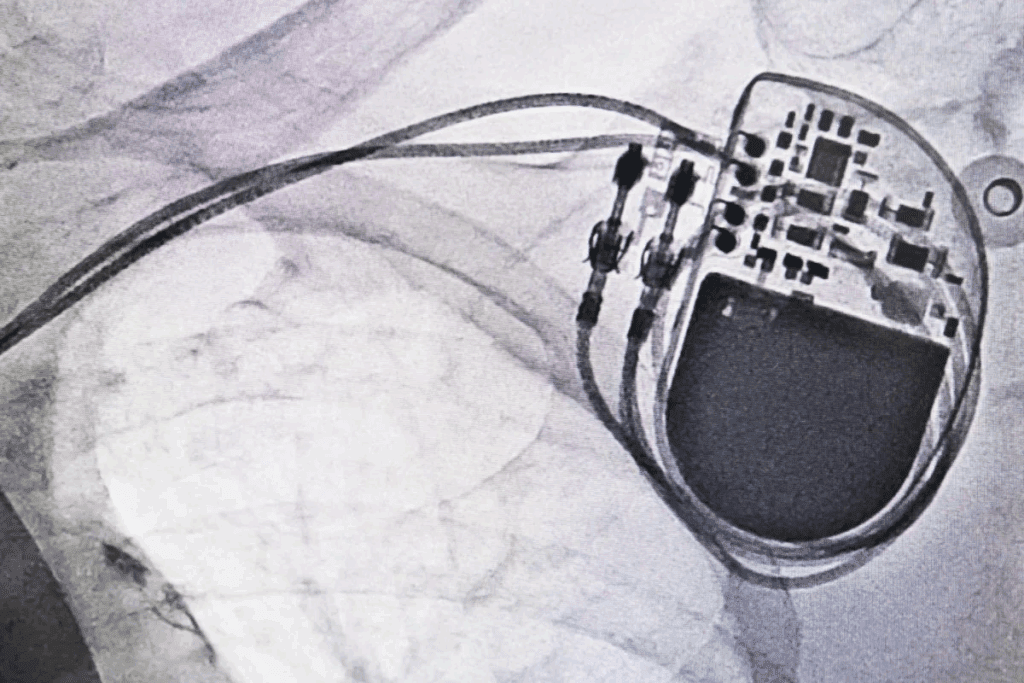
Understanding pacemakers is key for managing heart conditions like AFib. A pacemaker is a small, battery-powered device. It prevents the heart from beating too slowly. The Medical organization says pacemakers keep the heart’s rhythm regular.
How Pacemakers Function
Pacemakers send electrical impulses to the heart. This makes it beat at a regular rate. They are programmed to fit the patient’s needs, adjusting the heart rate based on activity.
Types of Pacemakers Available Today
There are many types of pacemakers, each for different needs. The main types are:
- Single-chamber pacemakers
- Dual-chamber pacemakers
- Biventricular pacemakers
| Type of Pacemaker | Description | Typical Use |
| Single-Chamber | One lead is used, typically placed in the right atrium or ventricle. | Patients who require pacing in one chamber. |
| Dual-Chamber | Two leads are used, one in the right atrium and one in the right ventricle. | Patients who need pacing in both chambers for a more natural heartbeat. |
| Biventricular | Used in cardiac resynchronization therapy, pacing both ventricles. | Patients with certain types of heart failure. |
The Implantation Procedure and Recovery
The implantation procedure involves a small incision in the chest. The pacemaker is placed under the skin. Leads are guided through a vein into the heart. Recovery usually includes a short hospital stay for monitoring.
Key aspects of the recovery process include:
- Monitoring for complications
- Adjusting the pacemaker settings as needed
- Follow-up appointments to check the device’s function
Can a Pacemaker Help AFib?
Pacemakers might help some patients with AFib, but it depends on their heart condition and symptoms. We’ll look at how pacemakers manage AFib, their limits, and common myths.
The Role of Pacemakers in AFib Management
Pacemakers don’t cure AFib, but they can help with some symptoms. They’re good for slow heart rates or when controlling heart rate is needed. They send electrical impulses to keep the heart rhythm regular, improving life quality for some.
It’s key to know pacemakers are part of a bigger treatment plan for AFib. They’re often used with other treatments like medicines or lifestyle changes.
What Pacemakers Can and Cannot Do for AFib
Pacemakers can control heart rate and ease symptoms like fatigue and shortness of breath. But, they don’t fix the root cause of AFib or stop it from getting worse.
Not everyone with AFib needs a pacemaker. The choice depends on the patient’s specific needs and health status.
| Pacemaker Benefits | Pacemaker Limitations |
| Controls heart rate in AFib patients | Does not cure AFib |
| Improves symptoms like fatigue and shortness of breath | Not suitable for all AFib patients |
| Enhances quality of life for certain patients | Does not prevent AFib progression |
Clarifying Common Misconceptions
Many think pacemakers can cure AFib. But, they manage symptoms, not the cause. Another myth is that pacemakers fit everyone. In fact, the choice depends on the patient’s heart condition and health.
Having a pacemaker doesn’t mean you’re stuck with it. Modern pacemakers are flexible and can be adjusted for each patient’s needs.
Understanding pacemakers’ role in managing AFib helps patients make better choices. While not for everyone, pacemakers can help some manage AFib well.
When Pacemakers Are Recommended for AFib Patients
Pacemakers are a key treatment for atrial fibrillation (AFib) patients facing certain complications. AFib can cause heart problems, and sometimes, a pacemaker is needed. We’ll look at when pacemakers are advised for AFib patients.
Bradycardia and Medication Side Effects
Bradycardia, or a slow heart rate, can happen in AFib patients. It might be due to the fibrillation itself or medication side effects. Pacemakers are very helpful in these situations. They keep the heart rate steady.
When medications like beta-blockers or anti-arrhythmic drugs slow the heart too much, a pacemaker is essential. It makes sure the heart beats safely.
Tachycardia-Bradycardia Syndrome
Tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome, or tachy-brady syndrome, makes the heart beat too fast and then too slow. It’s common in AFib patients and hard to manage with just medicine. Pacemakers can regulate the heart’s rhythm in these cases. They often work with other treatments to control the fast heart beats.
After AV Node Ablation
AV node ablation destroys the electrical pathway between the heart’s upper and lower chambers. It’s done on AFib patients to control heart rhythms. After this procedure, a pacemaker is usually put in. It’s to make sure the heart beats right, as the procedure can cause a very slow heart rate or block it completely.
Knowing how pacemakers help with these conditions helps AFib patients. They can then work with their doctors to find the best treatment for them.
The “Pace and Ablate” Strategy Explained
The “pace and ablate” strategy is a treatment plan with two steps. First, we ablate the AV node. Then, we implant a pacemaker. This method is for patients with Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) who haven’t responded to other treatments.
AV Node Ablation Process
AV node ablation uses catheters to destroy the AV node. This area between the heart’s chambers controls electrical signals. Destroying it stops the fast and irregular heartbeats of AFib.
The procedure is done under local anesthesia and sedation. We use catheters through a leg vein to reach the heart. Then, we apply energy to ablate the AV node, blocking the irregular signals.
Necessity of Pacemaker Implantation
After ablating the AV node, a pacemaker is needed. The AV node is key for electrical signals between chambers. Without it, the heart might beat too slowly or irregularly.
Implanting a pacemaker keeps the ventricles beating at the right rate. This maintains a good heart rate and improves AFib symptoms.
“The ‘pace and ablate’ strategy has been a game-changer for many patients with AFib, improving symptoms and quality of life.”
— Medical Expert, Cardiologist
Expected Outcomes and Success Rates
The “pace and ablate” strategy greatly improves symptoms and quality of life for AFib patients. Studies show it reduces AFib symptoms, improves exercise, and boosts overall well-being.
| Outcome | Success Rate |
| Symptom Improvement | 80-90% |
| Quality of Life Enhancement | 70-80% |
| Reduction in AFib Episodes | 90% |
While effective, the “pace and ablate” strategy has risks. Patients must be carefully chosen and informed about the benefits and risks.
What Happens When You Go Into AFib With a Pacemaker
It’s important to know how a pacemaker works during an AFib episode. A pacemaker can help keep your heart rhythm steady. But, how well it works depends on several things.
Modern Pacemaker Response to AFib Episodes
Today’s pacemakers can handle AFib in different ways. Some can switch to a different mode to control the heart rate. This is called mode switching. When this happens, the pacemaker can adjust to help manage your heart rate and lessen symptoms.
Here are some key features of modern pacemakers and their response to AFib:
- Rate-responsive pacing: Adjusts the heart rate in response to physical activity.
- Mode switching: Changes the pacing mode to help manage irregular heart rhythms.
- Advanced algorithms: Some pacemakers use complex algorithms to detect and respond to AFib episodes.
Symptoms You May STILL Experience
Even with a pacemaker, some people may feel symptoms during an AFib episode. These can include:
- Palpitations or irregular heartbeat
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue or weakness
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
It’s important to remember that a pacemaker can manage some AFib symptoms. But, it might not get rid of all of them.
When to Contact Your Doctor
If you’re feeling any of these, you should talk to your doctor:
- Frequent or severe AFib episodes
- Increased symptoms or new symptoms
- Concerns about your pacemaker’s function
It’s key to have regular check-ups with your doctor. This ensures your pacemaker is working right and makes any needed changes.
Benefits of Pacemaker Therapy for AFib
Pacemaker therapy greatly improves the lives of those with atrial fibrillation (AFib). It helps the heart beat more regularly. This reduces symptoms of AFib.
Symptom Improvement
Pacemakers help with symptoms like tiredness, dizziness, and fainting. The Medical organization says they can manage these issues. This makes patients feel better overall.
Rate Control Benefits
Pacemakers keep the heart rate in check for AFib patients. This is key to avoiding heart failure and stroke. It’s all about keeping the heart rhythm steady.
Quality of Life Enhancements
Pacemaker therapy boosts the quality of life for AFib patients. It increases energy and reduces fatigue. This makes daily activities easier.
It also cuts down on AFib episodes. This brings more stability and predictability to their condition. Stability is vital for long-term health.
Limitations and Considerations
Pacemakers can help manage AFib, but they have their limits. They are not a cure-all for AFib. It’s important to know the possible downsides and complications of using a pacemaker.
Pacemaker Dependency
One big thing to think about is pacemaker dependency. Some people might need their pacemaker to keep their heart beating right. This could be a problem if the pacemaker breaks or needs to be replaced.
- Pacemaker dependency can develop gradually.
- Regular check-ups are essential to monitor pacemaker function.
- Patients should discuss their dependency risk with their cardiologist.
Continued Stroke Risk and Anticoagulation Needs
Pacemakers don’t get rid of the stroke risk from AFib. Even with a pacemaker, people with AFib can face stroke risks. They often need to keep taking anticoagulation therapy.
Key points to consider:
- Anticoagulation therapy may need to continue even after pacemaker implantation.
- Regular monitoring of stroke risk factors is critical.
- Patients should work closely with their healthcare provider to manage stroke risk.
Device-Related Complications
Pacemakers can have side effects, like infections or blood clots. It’s key to know these risks before deciding on a pacemaker.
According to the Medical organization, possible complications of a pacemaker device or its surgery may include:
“Infection, blood clots, and damage to blood vessels or nerves are among the possible complications.”
Talking to your doctor about these risks is important. It helps you understand the pros and cons of using a pacemaker for AFib.
Advanced Pacing Technologies for AFib
Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) treatment has made big strides with new pacing technologies. These advancements aim to better manage heart rhythms and improve life quality for AFib patients.
Rate-Responsive Algorithms
Today’s pacemakers use rate-responsive algorithms. They adjust heart rate based on the body’s activity. For example, they speed up during exercise to meet blood and oxygen needs.
This tech helps patients keep a proper heart rate during activities. It boosts physical performance and comfort.
Some pacemakers can sense physical activity and adjust the heart rate. This is great for AFib patients, as it helps manage symptoms and boosts exercise ability. The Medical organization notes that some pacemakers can increase heart rate during exercise, helping patients stay active.
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) is a key technology for heart failure, often seen with AFib. It uses a pacemaker to sync the left and right ventricles, boosting heart efficiency and reducing heart failure symptoms.
CRT makes ventricles beat in sync, improving heart function and exercise ability. It also lowers hospitalization risks for heart failure. It’s a vital part of treatment for some heart failure patients.
Emerging Pacing Strategies and Research
The pacing technology field is always growing, with new research and devices. New technologies include leadless pacemakers and pacemakers with advanced algorithms for arrhythmia management.
These new strategies promise less invasive implantation, longer device life, and better AFib treatment. As research advances, we’ll see more advanced devices for AFib patients.
The Doctor-Patient Decision Process
Exploring treatment options for AFib means understanding the role of a pacemaker. It’s key to work with your doctor to make a decision. This way, you’ll be well-informed and ready for pacemaker therapy if needed.
Evaluating If You’re a Good Candidate
To see if you’re a good fit for a pacemaker, your doctor will check your health and AFib details. They’ll look at your symptoms, heart rhythm, and how AFib affects your daily life.
Key factors that influence pacemaker candidacy include:
- Symptoms and their impact on your quality of life
- Heart rate and rhythm during AFib episodes
- Response to previous treatments
- Presence of other heart conditions
Questions to Ask Your Cardiologist
Being an active participant in your healthcare means asking the right questions. When talking about pacemaker therapy, ask:
- What are the benefits of a pacemaker for my condition?
- How will a pacemaker change my daily life and activities?
- What are the risks and complications of pacemaker implantation?
- How will my condition be monitored after the pacemaker is implanted?
It’s also important to discuss your lifestyle, preferences, and any concerns you may have.
Preparing for the Procedure
If a pacemaker is right for you, there are steps to prepare. These include:
- Undergoing necessary tests to ensure you’re ready for the implantation
- Discussing any medications you’re currently taking and whether they need to be adjusted
- Understanding the details of the procedure, including what to expect on the day of the implantation
- Arranging for post-procedure care and follow-up appointments
By working closely with your healthcare team and being well-prepared, you can make the most of your pacemaker therapy. This will improve your quality of life.
Conclusion
Pacemakers are key in managing AFib, helping the heart beat regularly and easing symptoms. They are useful tools for both patients and doctors to consider. This helps in making the right choice for treating AFib.
Pacemakers can really help with AFib, making life better for those affected. The “pace and ablate” method, which includes a pacemaker and AV node ablation, works well. It helps control AFib symptoms effectively.
Even though pacemakers don’t cure AFib, they are a big part of treatment plans. They keep the heart rhythm steady and reduce symptoms. This way, pacemakers help people with AFib live active and happy lives, supporting their heart health.
As we move forward in cardiac care, pacemakers will likely become even more important in treating AFib. They offer new chances for patients and doctors to improve heart health.
FAQ
Does a pacemaker cure atrial fibrillation?
No, a pacemaker doesn’t cure atrial fibrillation (AFib). But, it can manage symptoms and control heart rate for some patients.
Can a pacemaker help with AFib symptoms?
Yes, pacemakers can ease symptoms like palpitations, shortness of breath, and fatigue. They help by making the heart rhythm more regular.
When are pacemakers recommended for AFib patients?
Pacemakers are suggested for AFib patients with bradycardia, tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome, or after AV node ablation.
What happens when you go into AFib with a pacemaker?
Modern pacemakers can adjust their pacing during AFib episodes. But, some symptoms might remain. Always contact your doctor for persistent or severe symptoms.
Are pacemakers used for AFib treatment?
Yes, pacemakers are part of the treatment for some AFib patients. This includes those with conduction disorders or after AV node ablation.
Can a pacemaker prevent AFib episodes?
Pacemakers can’t stop AFib episodes. But, they can control heart rate during an episode. This improves symptoms and quality of life.
What is the “pace and ablate” strategy for AFib?
The “pace and ablate” strategy involves ablating the AV node and implanting a pacemaker. It’s for AFib patients who haven’t responded to other treatments.
How does AV node ablation work?
AV node ablation destroys the abnormal electrical pathway between the heart’s upper and lower chambers. A pacemaker is then needed to maintain a regular heartbeat.
What are the benefits of pacemaker therapy for AFib?
Pacemaker therapy can improve symptoms and provide rate control benefits. It also enhances quality of life for AFib patients.
Are there any limitations to pacemaker therapy for AFib?
Yes, pacemaker therapy has limitations. These include pacemaker dependency, continued stroke risk, and device-related complications.
Can advanced pacing technologies improve AFib management?
Yes, advanced pacing technologies like rate-responsive algorithms and cardiac resynchronization therapy aim to better manage AFib and improve patient outcomes.
How do I know if I’m a good candidate for a pacemaker?
To see if you’re a good candidate for a pacemaker, talk to your cardiologist. Discuss your medical history, symptoms, and treatment goals. This will help decide if pacemaker therapy is right for you.
References
- Kreimer, F., et al. (2024). Pacemaker-induced atrial fibrillation reconsidered: mechanisms, associations and prevention. [Article].https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11217490/
- Parkkari, E., et al. (2023). The incidence of atrial fibrillation, new oral anticoagulation, and outcomes in patients with dual-chamber pacemakers. [Article]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352906723001380
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) is a common heart rhythm problem. It can cause symptoms, lower quality of life, and raise stroke risk. Pacemakers are key in managing AFib, mainly for those with slow heart rates or other heart issues.
Dealing with AFib can be tough, but new pacemaker tech offers hope. At Liv Hospital, we use the latest care methods. We aim to improve your symptoms and life quality.
Key Takeaways
- Pacemakers help with AFib and slow heart rates or conduction disorders.
- AFib can lower quality of life and increase stroke risk.
- New pacemaker tech improves symptom control and life quality.
- Liv Hospital offers a patient-focused approach with the latest care.
- We provide tailored care for complex AFib cases.
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)
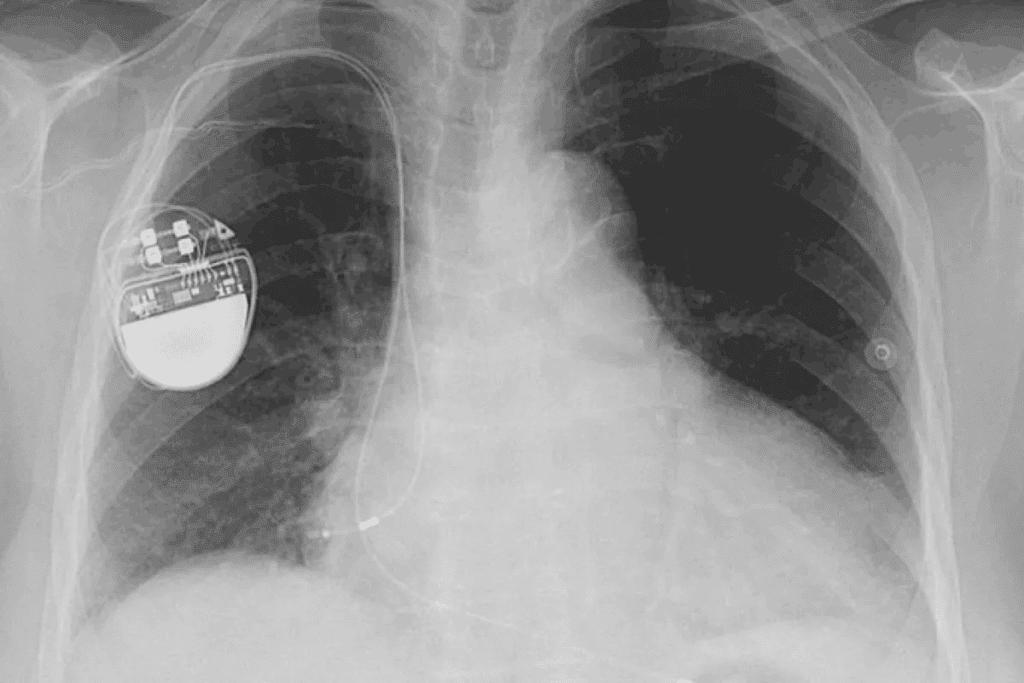
It’s important to know about atrial fibrillation (AFib) to take care of your heart and health. AFib is a heart rhythm problem that makes the upper heart chambers beat in a chaotic way.
AFib makes the upper heart chambers beat too fast and irregularly. This can cause symptoms like palpitations, shortness of breath, and fatigue. It can also make the heart less efficient, leading to more problems.
What Happens in the Heart During AFib
In a normal heart, the atria and ventricles work together well. But in AFib, the atria quiver instead of beating right. This can cause blood to pool in the atria, raising the risk of clots and stroke.
Common Symptoms and Complications
AFib symptoms can vary a lot. Some people might feel palpitations, dizziness, or chest discomfort. Others might not notice anything. But AFib can lead to serious problems like stroke, heart failure, and other heart issues.
“Atrial fibrillation is a serious condition that requires proper management to prevent complications such as stroke and heart failure.”
Impact on Quality of Life and Stroke Risk
AFib can really affect your daily life, causing symptoms that make it hard to do things. It also raises the five-fold risk of stroke. So, it’s key to manage AFib well to lower this risk.
Knowing about AFib and its effects on the heart helps manage it better. This can include lifestyle changes, medicines, and sometimes a pacemaker.
The Basics of Cardiac Pacemakers
Understanding pacemakers is key for managing heart conditions like AFib. A pacemaker is a small, battery-powered device. It prevents the heart from beating too slowly. The Medical organization says pacemakers keep the heart’s rhythm regular.
How Pacemakers Function
Pacemakers send electrical impulses to the heart. This makes it beat at a regular rate. They are programmed to fit the patient’s needs, adjusting the heart rate based on activity.
Types of Pacemakers Available Today
There are many types of pacemakers, each for different needs. The main types are:
- Single-chamber pacemakers
- Dual-chamber pacemakers
- Biventricular pacemakers
| Type of Pacemaker | Description | Typical Use |
| Single-Chamber | One lead is used, typically placed in the right atrium or ventricle. | Patients who require pacing in one chamber. |
| Dual-Chamber | Two leads are used, one in the right atrium and one in the right ventricle. | Patients who need pacing in both chambers for a more natural heartbeat. |
| Biventricular | Used in cardiac resynchronization therapy, pacing both ventricles. | Patients with certain types of heart failure. |
The Implantation Procedure and Recovery
The implantation procedure involves a small incision in the chest. The pacemaker is placed under the skin. Leads are guided through a vein into the heart. Recovery usually includes a short hospital stay for monitoring.
Key aspects of the recovery process include:
- Monitoring for complications
- Adjusting the pacemaker settings as needed
- Follow-up appointments to check the device’s function
Can a Pacemaker Help AFib?
Pacemakers might help some patients with AFib, but it depends on their heart condition and symptoms. We’ll look at how pacemakers manage AFib, their limits, and common myths.
The Role of Pacemakers in AFib Management
Pacemakers don’t cure AFib, but they can help with some symptoms. They’re good for slow heart rates or when controlling heart rate is needed. They send electrical impulses to keep the heart rhythm regular, improving life quality for some.
It’s key to know pacemakers are part of a bigger treatment plan for AFib. They’re often used with other treatments like medicines or lifestyle changes.
What Pacemakers Can and Cannot Do for AFib
Pacemakers can control heart rate and ease symptoms like fatigue and shortness of breath. But, they don’t fix the root cause of AFib or stop it from getting worse.
Not everyone with AFib needs a pacemaker. The choice depends on the patient’s specific needs and health status.
| Pacemaker Benefits | Pacemaker Limitations |
| Controls heart rate in AFib patients | Does not cure AFib |
| Improves symptoms like fatigue and shortness of breath | Not suitable for all AFib patients |
| Enhances quality of life for certain patients | Does not prevent AFib progression |
Clarifying Common Misconceptions
Many think pacemakers can cure AFib. But, they manage symptoms, not the cause. Another myth is that pacemakers fit everyone. In fact, the choice depends on the patient’s heart condition and health.
Having a pacemaker doesn’t mean you’re stuck with it. Modern pacemakers are flexible and can be adjusted for each patient’s needs.
Understanding pacemakers’ role in managing AFib helps patients make better choices. While not for everyone, pacemakers can help some manage AFib well.
When Pacemakers Are Recommended for AFib Patients
Pacemakers are a key treatment for atrial fibrillation (AFib) patients facing certain complications. AFib can cause heart problems, and sometimes, a pacemaker is needed. We’ll look at when pacemakers are advised for AFib patients.
Bradycardia and Medication Side Effects
Bradycardia, or a slow heart rate, can happen in AFib patients. It might be due to the fibrillation itself or medication side effects. Pacemakers are very helpful in these situations. They keep the heart rate steady.
When medications like beta-blockers or anti-arrhythmic drugs slow the heart too much, a pacemaker is essential. It makes sure the heart beats safely.
Tachycardia-Bradycardia Syndrome
Tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome, or tachy-brady syndrome, makes the heart beat too fast and then too slow. It’s common in AFib patients and hard to manage with just medicine. Pacemakers can regulate the heart’s rhythm in these cases. They often work with other treatments to control the fast heart beats.
After AV Node Ablation
AV node ablation destroys the electrical pathway between the heart’s upper and lower chambers. It’s done on AFib patients to control heart rhythms. After this procedure, a pacemaker is usually put in. It’s to make sure the heart beats right, as the procedure can cause a very slow heart rate or block it completely.
Knowing how pacemakers help with these conditions helps AFib patients. They can then work with their doctors to find the best treatment for them.
The “Pace and Ablate” Strategy Explained
The “pace and ablate” strategy is a treatment plan with two steps. First, we ablate the AV node. Then, we implant a pacemaker. This method is for patients with Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) who haven’t responded to other treatments.
AV Node Ablation Process
AV node ablation uses catheters to destroy the AV node. This area between the heart’s chambers controls electrical signals. Destroying it stops the fast and irregular heartbeats of AFib.
The procedure is done under local anesthesia and sedation. We use catheters through a leg vein to reach the heart. Then, we apply energy to ablate the AV node, blocking the irregular signals.
Necessity of Pacemaker Implantation
After ablating the AV node, a pacemaker is needed. The AV node is key for electrical signals between chambers. Without it, the heart might beat too slowly or irregularly.
Implanting a pacemaker keeps the ventricles beating at the right rate. This maintains a good heart rate and improves AFib symptoms.
“The ‘pace and ablate’ strategy has been a game-changer for many patients with AFib, improving symptoms and quality of life.”
— Medical Expert, Cardiologist
Expected Outcomes and Success Rates
The “pace and ablate” strategy greatly improves symptoms and quality of life for AFib patients. Studies show it reduces AFib symptoms, improves exercise, and boosts overall well-being.
| Outcome | Success Rate |
| Symptom Improvement | 80-90% |
| Quality of Life Enhancement | 70-80% |
| Reduction in AFib Episodes | 90% |
While effective, the “pace and ablate” strategy has risks. Patients must be carefully chosen and informed about the benefits and risks.
What Happens When You Go Into AFib With a Pacemaker
It’s important to know how a pacemaker works during an AFib episode. A pacemaker can help keep your heart rhythm steady. But, how well it works depends on several things.
Modern Pacemaker Response to AFib Episodes
Today’s pacemakers can handle AFib in different ways. Some can switch to a different mode to control the heart rate. This is called mode switching. When this happens, the pacemaker can adjust to help manage your heart rate and lessen symptoms.
Here are some key features of modern pacemakers and their response to AFib:
- Rate-responsive pacing: Adjusts the heart rate in response to physical activity.
- Mode switching: Changes the pacing mode to help manage irregular heart rhythms.
- Advanced algorithms: Some pacemakers use complex algorithms to detect and respond to AFib episodes.
Symptoms You May STILL Experience
Even with a pacemaker, some people may feel symptoms during an AFib episode. These can include:
- Palpitations or irregular heartbeat
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue or weakness
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
It’s important to remember that a pacemaker can manage some AFib symptoms. But, it might not get rid of all of them.
When to Contact Your Doctor
If you’re feeling any of these, you should talk to your doctor:
- Frequent or severe AFib episodes
- Increased symptoms or new symptoms
- Concerns about your pacemaker’s function
It’s key to have regular check-ups with your doctor. This ensures your pacemaker is working right and makes any needed changes.
Benefits of Pacemaker Therapy for AFib
Pacemaker therapy greatly improves the lives of those with atrial fibrillation (AFib). It helps the heart beat more regularly. This reduces symptoms of AFib.
Symptom Improvement
Pacemakers help with symptoms like tiredness, dizziness, and fainting. The Medical organization says they can manage these issues. This makes patients feel better overall.
Rate Control Benefits
Pacemakers keep the heart rate in check for AFib patients. This is key to avoiding heart failure and stroke. It’s all about keeping the heart rhythm steady.
Quality of Life Enhancements
Pacemaker therapy boosts the quality of life for AFib patients. It increases energy and reduces fatigue. This makes daily activities easier.
It also cuts down on AFib episodes. This brings more stability and predictability to their condition. Stability is vital for long-term health.
Limitations and Considerations
Pacemakers can help manage AFib, but they have their limits. They are not a cure-all for AFib. It’s important to know the possible downsides and complications of using a pacemaker.
Pacemaker Dependency
One big thing to think about is pacemaker dependency. Some people might need their pacemaker to keep their heart beating right. This could be a problem if the pacemaker breaks or needs to be replaced.
- Pacemaker dependency can develop gradually.
- Regular check-ups are essential to monitor pacemaker function.
- Patients should discuss their dependency risk with their cardiologist.
Continued Stroke Risk and Anticoagulation Needs
Pacemakers don’t get rid of the stroke risk from AFib. Even with a pacemaker, people with AFib can face stroke risks. They often need to keep taking anticoagulation therapy.
Key points to consider:
- Anticoagulation therapy may need to continue even after pacemaker implantation.
- Regular monitoring of stroke risk factors is critical.
- Patients should work closely with their healthcare provider to manage stroke risk.
Device-Related Complications
Pacemakers can have side effects, like infections or blood clots. It’s key to know these risks before deciding on a pacemaker.
According to the Medical organization, possible complications of a pacemaker device or its surgery may include:
“Infection, blood clots, and damage to blood vessels or nerves are among the possible complications.”
Talking to your doctor about these risks is important. It helps you understand the pros and cons of using a pacemaker for AFib.
Advanced Pacing Technologies for AFib
Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) treatment has made big strides with new pacing technologies. These advancements aim to better manage heart rhythms and improve life quality for AFib patients.
Rate-Responsive Algorithms
Today’s pacemakers use rate-responsive algorithms. They adjust heart rate based on the body’s activity. For example, they speed up during exercise to meet blood and oxygen needs.
This tech helps patients keep a proper heart rate during activities. It boosts physical performance and comfort.
Some pacemakers can sense physical activity and adjust the heart rate. This is great for AFib patients, as it helps manage symptoms and boosts exercise ability. The Medical organization notes that some pacemakers can increase heart rate during exercise, helping patients stay active.
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) is a key technology for heart failure, often seen with AFib. It uses a pacemaker to sync the left and right ventricles, boosting heart efficiency and reducing heart failure symptoms.
CRT makes ventricles beat in sync, improving heart function and exercise ability. It also lowers hospitalization risks for heart failure. It’s a vital part of treatment for some heart failure patients.
Emerging Pacing Strategies and Research
The pacing technology field is always growing, with new research and devices. New technologies include leadless pacemakers and pacemakers with advanced algorithms for arrhythmia management.
These new strategies promise less invasive implantation, longer device life, and better AFib treatment. As research advances, we’ll see more advanced devices for AFib patients.
The Doctor-Patient Decision Process
Exploring treatment options for AFib means understanding the role of a pacemaker. It’s key to work with your doctor to make a decision. This way, you’ll be well-informed and ready for pacemaker therapy if needed.
Evaluating If You’re a Good Candidate
To see if you’re a good fit for a pacemaker, your doctor will check your health and AFib details. They’ll look at your symptoms, heart rhythm, and how AFib affects your daily life.
Key factors that influence pacemaker candidacy include:
- Symptoms and their impact on your quality of life
- Heart rate and rhythm during AFib episodes
- Response to previous treatments
- Presence of other heart conditions
Questions to Ask Your Cardiologist
Being an active participant in your healthcare means asking the right questions. When talking about pacemaker therapy, ask:
- What are the benefits of a pacemaker for my condition?
- How will a pacemaker change my daily life and activities?
- What are the risks and complications of pacemaker implantation?
- How will my condition be monitored after the pacemaker is implanted?
It’s also important to discuss your lifestyle, preferences, and any concerns you may have.
Preparing for the Procedure
If a pacemaker is right for you, there are steps to prepare. These include:
- Undergoing necessary tests to ensure you’re ready for the implantation
- Discussing any medications you’re currently taking and whether they need to be adjusted
- Understanding the details of the procedure, including what to expect on the day of the implantation
- Arranging for post-procedure care and follow-up appointments
By working closely with your healthcare team and being well-prepared, you can make the most of your pacemaker therapy. This will improve your quality of life.
Conclusion
Pacemakers are key in managing AFib, helping the heart beat regularly and easing symptoms. They are useful tools for both patients and doctors to consider. This helps in making the right choice for treating AFib.
Pacemakers can really help with AFib, making life better for those affected. The “pace and ablate” method, which includes a pacemaker and AV node ablation, works well. It helps control AFib symptoms effectively.
Even though pacemakers don’t cure AFib, they are a big part of treatment plans. They keep the heart rhythm steady and reduce symptoms. This way, pacemakers help people with AFib live active and happy lives, supporting their heart health.
As we move forward in cardiac care, pacemakers will likely become even more important in treating AFib. They offer new chances for patients and doctors to improve heart health.
FAQ
Does a pacemaker cure atrial fibrillation?
No, a pacemaker doesn’t cure atrial fibrillation (AFib). But, it can manage symptoms and control heart rate for some patients.
Can a pacemaker help with AFib symptoms?
Yes, pacemakers can ease symptoms like palpitations, shortness of breath, and fatigue. They help by making the heart rhythm more regular.
When are pacemakers recommended for AFib patients?
Pacemakers are suggested for AFib patients with bradycardia, tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome, or after AV node ablation.
What happens when you go into AFib with a pacemaker?
Modern pacemakers can adjust their pacing during AFib episodes. But, some symptoms might remain. Always contact your doctor for persistent or severe symptoms.
Are pacemakers used for AFib treatment?
Yes, pacemakers are part of the treatment for some AFib patients. This includes those with conduction disorders or after AV node ablation.
Can a pacemaker prevent AFib episodes?
Pacemakers can’t stop AFib episodes. But, they can control heart rate during an episode. This improves symptoms and quality of life.
What is the “pace and ablate” strategy for AFib?
The “pace and ablate” strategy involves ablating the AV node and implanting a pacemaker. It’s for AFib patients who haven’t responded to other treatments.
How does AV node ablation work?
AV node ablation destroys the abnormal electrical pathway between the heart’s upper and lower chambers. A pacemaker is then needed to maintain a regular heartbeat.
What are the benefits of pacemaker therapy for AFib?
Pacemaker therapy can improve symptoms and provide rate control benefits. It also enhances quality of life for AFib patients.
Are there any limitations to pacemaker therapy for AFib?
Yes, pacemaker therapy has limitations. These include pacemaker dependency, continued stroke risk, and device-related complications.
Can advanced pacing technologies improve AFib management?
Yes, advanced pacing technologies like rate-responsive algorithms and cardiac resynchronization therapy aim to better manage AFib and improve patient outcomes.
How do I know if I’m a good candidate for a pacemaker?
To see if you’re a good candidate for a pacemaker, talk to your cardiologist. Discuss your medical history, symptoms, and treatment goals. This will help decide if pacemaker therapy is right for you.
References:
- Kreimer, F., et al. (2024). Pacemaker-induced atrial fibrillation reconsidered: mechanisms, associations and prevention. [Article].https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11217490/
- Parkkari, E., et al. (2023). The incidence of atrial fibrillation, new oral anticoagulation, and outcomes in patients with dual-chamber pacemakers. [Article]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352906723001380








