Last Updated on November 25, 2025 by Ugurkan Demir

Atherosclerosis is a serious condition where plaque builds up in arteries. It can start early in life and often goes unnoticed until it’s too late.
View the average artery blockage by age chart and understand plaque buildup risks.
At Liv Hospital, we understand how important it is to know when atherosclerosis starts. Studies show that atherosclerosis can begin as early as childhood. The risk grows as we get older.
Knowing how artery blockage progresses is key to preventing it. In this article, we’ll share 7 important facts about plaque buildup. These facts are vital for managing lifelong cardiovascular risk.
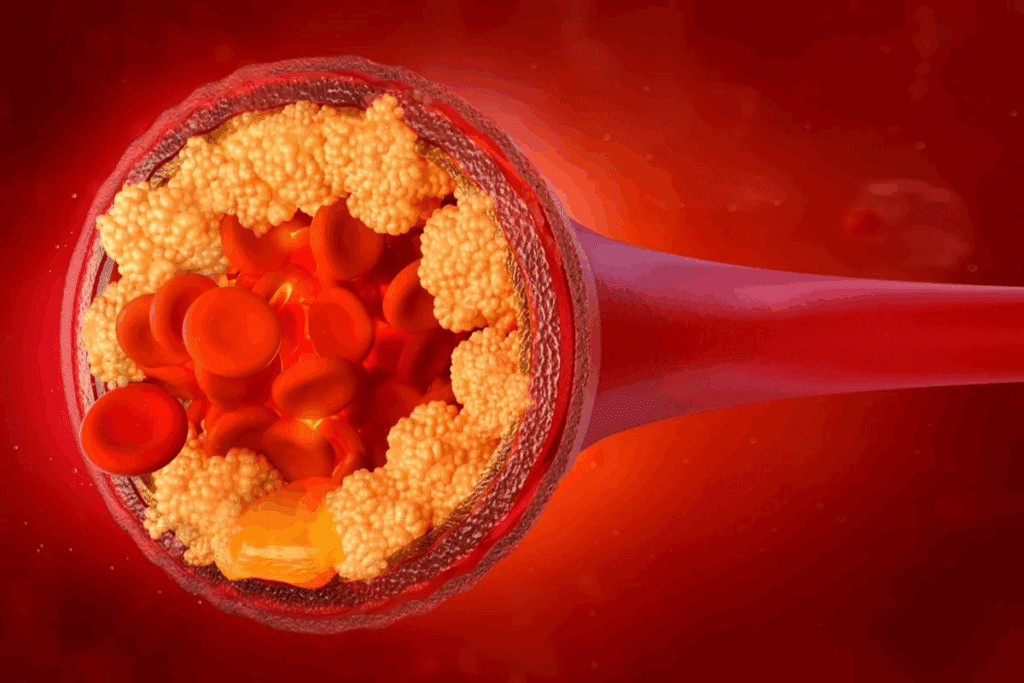
Atherosclerosis starts early and quietly, with plaque building up in artery walls. It’s a big reason for heart diseases, which kill many people. Knowing how it starts and where it happens is key to stopping it.
When arteries block, plaque builds up inside the walls. This plaque is made of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and more from the blood. Over time, it makes arteries hard and narrow, cutting off blood to important parts of the body.
This starts with damage to the artery’s inner layer. High blood pressure, smoking, or high cholesterol can cause this. Once damaged, plaque starts to grow, blocking the artery more and more.
Plaque can build up anywhere, but it often picks certain spots. The coronary arteries are a common place, as they supply blood to the heart. Other spots include the carotid arteries in the neck and the peripheral arteries in the legs.
These areas get more plaque because of blood flow and the shape of the arteries. Turbulent flow and bends in the arteries stress the walls, making them more prone to damage and plaque.
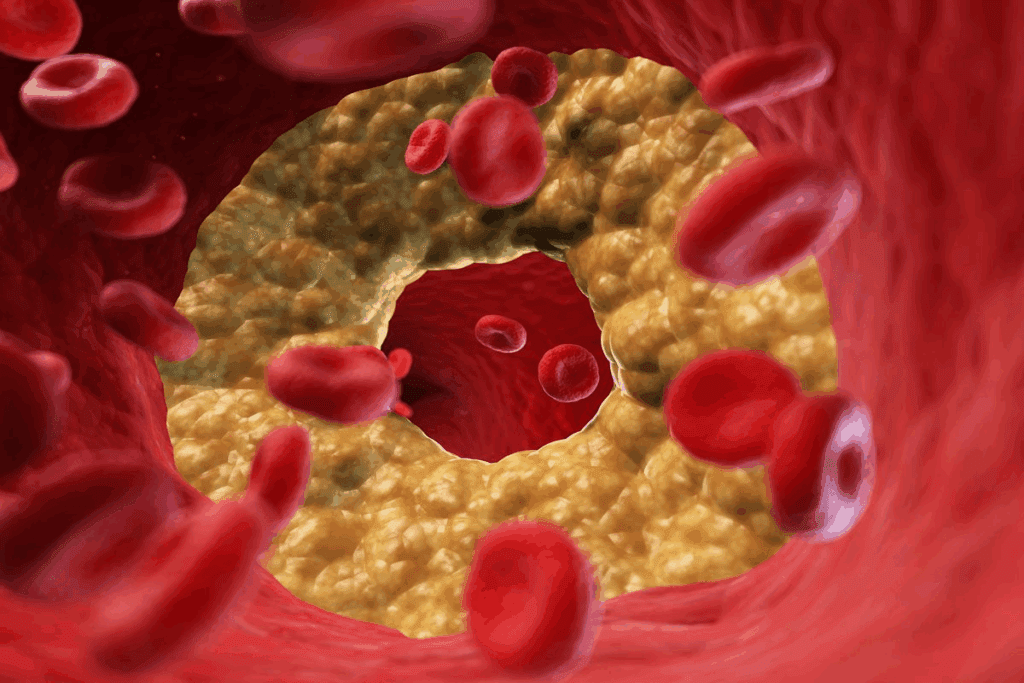
The average artery blockage by age chart gives us important insights. It shows how atherosclerosis changes with age. This helps us understand artery blockage better across different age groups.
Artery blockage is measured by calcium scores. These scores show how much plaque is in the arteries. A higher score means more plaque and a higher risk of heart problems.
A calcium score of 0 means no plaque. But a score over 400 means a lot of plaque and a high risk of heart events. Doctors use these scores to plan treatments to lower risk.
Studies show artery blockage gets worse with age. After 40, the risk of significant blockage increases. By the 60s, many people have some blockage.
From the 20s to the 60s, plaque buildup increases gradually. This shows why early prevention and monitoring are key to slowing atherosclerosis.
Doctors use tests like coronary artery calcium scans and angiograms. These tests show detailed images of the arteries. They help doctors see how much plaque there is and where it is.
By combining these test results with clinical checks, doctors can accurately measure blockage. This helps them create effective treatment plans. It also means better care for patients.
Atherosclerosis starts early, with fatty streaks in young arteries. This shows that heart diseases aren’t just for adults. They often start in childhood and teens.
Studies find fatty streaks in kids’ and teens’ arteries. These are lipid deposits on artery walls, the start of plaque.
Fatty streaks are not harmless. They signal the start of plaque buildup. This means we need to act early to stop it.
Several factors lead to early plaque in young people. These include:
It’s important to tackle these risk factors early to stop atherosclerosis from getting worse.
Preventing heart disease early is vital. Healthy habits from a young age can greatly lower the risk of atherosclerosis.
Prevention strategies include eating well, staying active, and keeping a healthy weight. It’s also key to manage high blood pressure and cholesterol.
By understanding atherosclerosis starts early and taking action, we can help kids and teens grow into healthier adults. This reduces their risk of heart disease later on.
Young adulthood is a key time for heart health. Many changes happen in the arteries during the 20s and 30s. Various factors can affect how plaque forms in arteries.
In many young adults, early atherosclerosis shows as minimal atherosclerotic changes. These early signs include fatty streaks in the arteries. Though they might not cause big blockages right away, they can lead to more plaque over time.
These early signs are often hard to spot and don’t always cause symptoms. That’s why regular health checks are so important.
There’s a worrying rise in coronary artery disease among young adults. Lifestyle choices, genetics, and obesity play big roles. It’s key for young people to know their risks and act early to lower them.
Peripheral artery disease in young adults is becoming a big worry. It’s usually seen in older people but is now showing up in the young. Smoking, diabetes, and other risks are to blame. Catching it early and treating it is vital to avoid serious damage.
Figuring out what’s normal plaque in young adults is tricky because everyone is different. Minimal plaque is usually okay for this age group. But, it’s vital to keep an eye on it and live a healthy lifestyle to stop plaque from getting worse.
By knowing these trends and taking steps now, young adults can lower their risk of serious heart problems later.
The years between 40 and 50 are key for heart health. This is when plaque buildup often speeds up. Many factors come together to raise the risk of blockages in arteries.
Research shows a sharp rise in plaque deposits after 40. This is due to lifestyle changes, hormonal shifts, and aging.
Some important facts include:
Hormonal changes, like those in menopause, can speed up artery blockage. Metabolic changes, like less insulin sensitivity, also play a part.
Key changes include:
Lifestyle choices greatly speed up artery blockage between 40 and 50. These include:
To slow down artery blockage, several steps can be taken:
Knowing why artery blockage speeds up between 40 and 50 helps people take action. They can keep their heart healthy.
The senior years bring unique challenges for artery health, after 60. The risk of artery blockage increases with age. It’s important to know the common patterns and implications of this condition.
In older adults, artery blockage often shows up in specific ways. Carotid artery blockage is a big concern as it can cause stroke. Studies show that carotid artery disease becomes more common with age.
Here are some key statistics about artery blockage in older adults:
Knowing the average carotid artery blockage by age is key for assessing risk. Research shows that:
Arteriosclerosis, or the hardening of arteries, can vary from mild to severe. Mild arteriosclerosis may not cause symptoms right away but can worsen over time. On the other hand, severe arteriosclerosis can lead to serious cardiovascular events.
The impact of hardening arteries on life expectancy is a big concern. Studies show that those with severe arteriosclerosis face a higher risk of death. Factors that affect life expectancy include:
Understanding these aspects can help manage cardiovascular health in older adults. This can potentially improve life expectancy and quality of life.
Atherosclerosis, or artery blockage, starts earlier than most people think. There are several important facts about this condition. Understanding its progression and impact is vital for keeping our hearts healthy. We will explore seven key facts about the early beginnings, progression, and factors influencing artery blockage.
Research shows that atherosclerosis can start in childhood. Fatty streaks appear in young people’s arteries. This early start highlights the need for a healthy lifestyle from a young age to prevent or slow the disease.
By the 40s, many adults have plaque in their arteries. Studies show that about half of adults in this age group have plaque. This emphasizes the importance of regular check-ups and preventive measures.
Even a little plaque at a young age can raise the risk of heart problems later. It’s important for those with early signs to work with their doctors to manage risk factors.
The years between 40 and 50 see the most plaque buildup. Hormonal changes, lifestyle factors, and metabolic shifts during this time speed up atherosclerosis.
To continue, the next three facts will explain more about artery blockage. They provide a full understanding of this condition.
Lifestyle choices, like diet, exercise, and smoking, greatly affect artery blockage. Healthy choices can lower an individual’s risk.
Those with a family history of heart disease are at higher risk. Knowing your genetic predisposition helps tailor preventive strategies.
Early detection and management through screenings and strategies can greatly improve outcomes. This shows the importance of proactive healthcare.
In conclusion, knowing these 7 critical facts about artery blockage empowers people to take control of their heart health. Recognizing the early onset and factors influencing atherosclerosis helps make informed decisions to prevent or manage the condition.
Reducing artery blockage risk starts with healthy habits and medical care. Knowing what causes blockage and acting early can lower heart disease risk.
Healthy choices are key in preventing and managing artery blockage. Some top changes include:
Medical help is also vital in managing artery blockage. This includes:
It’s important to work with your doctor to find the right treatment for you.
Knowing when to see a doctor is critical. Your age, family history, and health can affect when you need treatment. Those at higher risk may need to see doctors more often.
Combining healthy living with medical care can manage artery blockage and lower heart disease risk.
Artery blockage starts early and gets worse with age. Knowing how it progresses is key to keeping your heart healthy. It’s important to understand the factors that lead to plaque buildup.
To manage your artery health, make lifestyle changes and consider medical help when needed. Eating right, staying active, and not smoking can lower your risk of blockage. These steps are essential for your heart’s health.
Preventing and managing artery blockage can lower your risk of heart problems. Regular health checks can spot risks early. This allows for quick action to keep your arteries healthy.
It’s vital to take charge of your health. Knowing your risks and working with your doctor can help you keep your arteries in good shape. This way, you can prevent artery blockage and stay healthy.
Atherosclerosis can start early, often with fatty streaks in the arteries during childhood or adolescence.
Young adults may have minimal atherosclerotic changes. But, significant plaque buildup is not normal at any age.
Doctors use tests like angiography and ultrasound. They measure blockage as a percentage of the artery’s diameter.
Risk factors include family history, high cholesterol, hypertension, smoking, and an unhealthy diet.
Coronary artery disease can start to worry people in their 20s and 30s, with risk factors.
Peripheral artery disease is becoming more common in young adults, with risk factors like smoking and diabetes.
Changes include a healthy diet, regular exercise, quitting smoking, and managing stress.
Medical help is needed based on risk factors, blockage degree, and overall heart health.
Brain artery hardening can greatly reduce life expectancy and quality of life. It raises the risk of stroke and dementia.
Yes, atherosclerosis can be prevented or managed with lifestyle changes, medical help, and regular checks.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!