Last Updated on November 25, 2025 by Ugurkan Demir

As men get older, worries about fertility grow. People often wonder if men keep making sperm as they age. They also ask how sperm quality changes over time when does a guy stop producing sperm.
Men usually keep making sperm as they age, but the quality of sperm goes down. Male fertility starts to drop around age 35. It gets worse after 40. Even though most men keep making sperm, the quality can affect their ability to have kids.
At Liv Hospital, we take male fertility seriously. Our team offers care that focuses on the patient, supporting men at every life stage.

The link between male fertility and aging is complex and often misunderstood. As we get older, our bodies go through changes that can affect our ability to have children. Knowing about these changes is key for planning a family.
Many men think their fertility stays the same as they age, but that’s not true. Men don’t stop being fertile like women do with menopause. But, their ability to have children does decrease with age.
Some believe men can father children at any age without risks. But, research shows men over 35 have lower fertility. The risk of pregnancy problems also goes up with age. For example, older dads are more likely to have children with genetic issues.
Men keep making sperm as they age, but the quality and amount go down. Studies show that sperm count, how well they move, and their shape get worse with age. This can make it harder to have a child and increase the chance of genetic problems.
Here’s some data on how sperm changes with age:
| Age Group | Average Sperm Count (million/ml) | Sperm Motility (%) |
| 20-24 | 720 | 55 |
| 25-29 | 740 | 54 |
| 30-34 | 680 | 52 |
| 40-44 | 450 | 45 |
| 45-49 | 380 | 42 |
The table shows sperm count and motility drop a lot with age. Knowing this can help men make better choices about their fertility.
It’s important for men to understand what affects their fertility as they age. Things like lifestyle, health, and what they’re exposed to can all impact sperm quality.
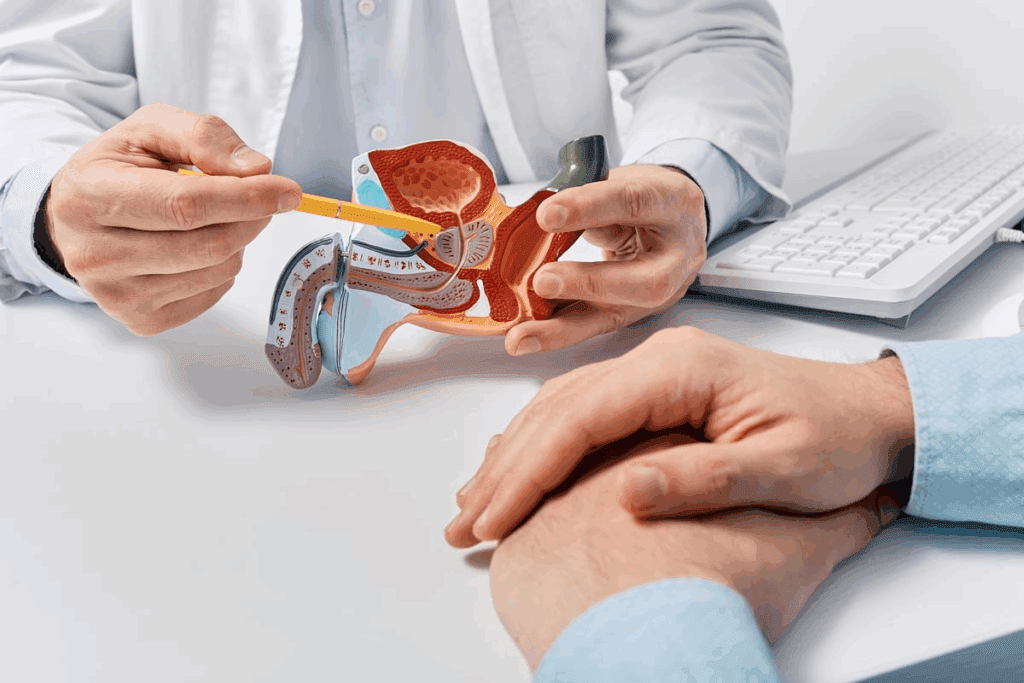
It’s important to know how the male reproductive system works. This system is made up of organs and hormones that help make sperm. It also supports fertility.
The male reproductive system has key parts, each with a special job. The testes make sperm and testosterone. The epididymis helps sperm grow and get ready. The vas deferens carries sperm to the ejaculatory ducts.
There, sperm mixes with fluids from the seminal vesicles and prostate gland.
| Structure | Function |
| Testes | Produce sperm and testosterone |
| Epididymis | Stores and matures sperm |
| Vas deferens | Transports sperm to ejaculatory ducts |
| Seminal vesicles | Produce seminal fluid |
| Prostate gland | Produces additional seminal fluid |
Spermatogenesis is how immature cells in the testes become sperm. It goes through stages like mitosis, meiosis, and spermiogenesis. Hormones like testosterone and FSH control this process.
Hormones play a big role in making sperm. Testosterone from the testes is key. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) from the pituitary gland helps too. The right balance of these hormones is important for sperm production.
As men get older, hormone levels change. This can affect sperm quality. Knowing about these changes helps us understand male fertility and aging better.
Men’s ability to make sperm changes with age. Sperm production starts at puberty and goes on until old age. But, how well and how much sperm is made changes over time.
Spermatogenesis starts at puberty, around 12-14 years old. It keeps going into old age. But, the quality and amount of sperm made isn’t the same all the time.
Peak sperm production usually happens in the late twenties to early thirties.
As men get older, many things can affect sperm production. Lifestyle, health, and hormonal changes play a role. Even though many men stay fertile into their older years, sperm quality and quantity can decrease, affecting fertility.
Men usually have their peak fertility in their late twenties and early thirties. During this time, sperm count, motility, and shape are usually the best. This increases the chances of getting pregnant.
Research shows that men in their twenties and thirties have higher sperm counts and better quality sperm. This makes it the best time for men to have children from a biological standpoint.
Men’s sperm production declines gradually with age, unlike women’s sudden stop at menopause. Most men don’t stop making sperm completely, even in old age.
But, how fast sperm production declines can vary a lot. Health, lifestyle, and environmental factors can affect this rate.
Knowing the timeline of sperm production helps men plan for their reproductive health and family. While age is important, it’s not the only thing that affects fertility.
Men’s sperm quality changes a lot as they age, affecting their ability to have kids. As we get older, our bodies go through changes that can hurt our reproductive health. We’ll look at how age affects sperm quality, including count, motility, and DNA health.
One big change with age is a drop in sperm count and semen volume. Studies show that sperm concentration and total count go down as men get older. This can start in the late 30s or early 40s and keeps going.
Several factors cause this drop. These include:
Sperm motility, or how well sperm move, also goes down with age. As men get older, fewer sperm can move well, making it harder to fertilize an egg. This decline is a big reason why older men have trouble getting pregnant.
Several things can cause this decline. These include:
DNA fragmentation, or DNA breaks, increases with age in men. High levels of DNA fragmentation can lead to lower fertility, higher miscarriage risk, and genetic problems in kids. Keeping sperm DNA intact is key for successful fertilization and healthy development.
To fight age-related sperm quality changes, men can try:
As men get older, their hormones change a lot. This affects their health and ability to have children. Hormones like testosterone, FSH, and LH play a big role in this. Knowing about these changes is key to staying healthy and dealing with aging issues.
Testosterone is very important for men. It helps with sperm, sex drive, and being masculine. It peaks in the teens and early twenties, then goes down as we get older. This drop can cause symptoms like less sex drive, tiredness, and less muscle.
Things that can affect testosterone levels include:
FSH and LH are important hormones made by the pituitary gland. They help the testicles work right. FSH helps make sperm, and LH helps make testosterone. As men age, how much of these hormones they make can change.
This change can affect fertility and health. Knowing about these changes helps men and doctors make better choices for health.
Some men might need hormone treatments because of aging. Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is one option. It helps with symptoms of low testosterone. But, it’s not without risks and should be thought about carefully.
Changing your lifestyle and treating health problems can also help. Regular health checks and screenings are important. They help find and manage hormonal changes that come with aging.
As men age, the prostate gland grows, which can cause health problems. The prostate gland is key to male reproductive health. It changes with age, and the risk of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) increases.
BPH is common in older men, where the prostate gland gets bigger. This can cause trouble with urination, like starting slowly or often. Hormonal changes with age are thought to cause BPH.
Symptoms of BPH can really affect a man’s life. These symptoms include:
BPH mainly affects urination but can also impact reproductive health. Research shows that BPH and its treatments can affect sexual function and fertility. For example, some treatments might cause erectile dysfunction or lower libido.
The link between BPH and reproductive health is complex. Men with BPH might see a decline in sexual function. This could be due to the condition or its treatments. So, it’s important for men with BPH symptoms to talk to their doctor about their reproductive health.
There are many ways to manage BPH, from watchful waiting to surgery. The right treatment depends on how bad the symptoms are and how they affect daily life.
| Treatment Option | Description | Benefits |
| Watchful Waiting | Monitoring symptoms without immediate intervention | Avoids unnecessary treatment |
| Medications | Alpha-blockers and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors | Relieves symptoms, slows disease progression |
| Surgical Interventions | TURP, laser surgery, and other procedures | Effective for severe symptoms, improves quality of life |
It’s important for men with BPH to know about treatment options. Talking to a healthcare provider can help find the best treatment. This depends on the individual’s health and needs.
Women go through menopause, but men face different hormonal changes as they age. The idea of a male version of menopause has become more popular. We’ll look at the differences between andropause and menopause, and the symptoms men experience as they age.
Andropause and menopause are both linked to aging, but they impact men and women differently. Menopause is when a woman stops having periods due to a drop in estrogen. Andropause is when testosterone levels in men slowly decrease with age.
Key differences between andropause and menopause include:
Men’s hormonal changes happen slowly over decades. This slow drop in testosterone can cause symptoms like lower sex drive, tiredness, and mood swings.
| Hormonal Change | Menopause | Andropause |
| Rate of Decline | Abrupt | Gradual |
| Symptoms | Hot flashes, cessation of menstruation | Decreased libido, fatigue, mood changes |
| Reproductive Impact | End of fertility | Decline in fertility, but not necessarily the end |
Andropause symptoms can be hard to spot and vary. Common signs include lower sex drive, trouble getting an erection, and mood swings. Spotting these symptoms early is key to managing hormonal aging.
Many things can make sperm production go down faster. Lifestyle choices, health issues, and what we’re exposed to in our environment all matter. They all play big roles in how fertile a man can be.
What we do every day can really affect our sperm. Smoking and drinking too much alcohol can hurt how many sperm we have and how well they move. A study in Human Reproduction showed that smoking can mess up sperm DNA. This can lead to more genetic problems in kids.
Being at a healthy weight and eating right is also key. Being too heavy can lower testosterone and make sperm quality worse. But, eating foods full of antioxidants like vitamins C and E can help protect sperm from damage.
“A healthy lifestyle is fundamental to maintaining optimal sperm health. Simple changes, such as quitting smoking and adopting a balanced diet, can make a significant difference.”
Some health problems can make sperm production go down faster. For example, varicocele, which is when veins in the scrotum get too big, can hurt sperm quality. Infections and inflammation, like epididymitis or orchitis, can also harm the reproductive system and lower fertility.
Chronic illnesses, like diabetes, can hurt sperm health by causing oxidative stress and damaging blood vessels to the testes. Hormonal imbalances, like low testosterone, can also lower sperm production.
| Medical Condition | Impact on Sperm Health |
| Varicocele | Impaired sperm quality due to increased scrotal temperature |
| Diabetes | Oxidative stress and vascular damage affecting sperm production |
| Infections (e.g., epididymitis) | Damage to the reproductive tract, potentially causing scarring and blockages |
Being around certain chemicals and working in hot places can also hurt sperm health. Pesticides, heavy metals, and other chemicals can lower sperm count and motility. Men who work in very hot places might also have lower fertility because of how it affects sperm production.
Knowing about these factors is important for men worried about their fertility. By making smart lifestyle choices and being careful about environmental and health risks, men can protect their reproductive health.
Men’s health is important, and it’s key to focus on lifestyle and diet. As men get older, many factors can affect their fertility. It’s vital to adopt healthy habits to keep fertility and overall health in check.
Eating a balanced diet is essential for sperm health. Foods rich in antioxidants like vitamins C and E, zinc, and selenium protect sperm from damage.
Medical Expert, a top fertility expert, says, “A healthy diet is key for sperm quality and reproductive health.”
“Nutrition is vital for spermatogenesis and reproductive system health.”
| Nutrient | Food Sources | Benefit to Sperm Health |
| Vitamin C | Citrus fruits, berries | Antioxidant properties |
| Zinc | Oysters, beef, chicken | Essential for sperm production |
| Selenium | Brazil nuts, fish | Protects sperm from oxidative damage |
Regular exercise boosts health, including reproductive well-being. It can improve sperm quality by reducing stress and balancing hormones.
Recommended exercises include:
Managing stress and getting enough sleep are key for reproductive health. Chronic stress can harm hormone balance, and poor sleep affects overall health.
Effective stress management techniques include:
Good sleep and a regular sleep schedule also support reproductive health.
As men get older, their ability to have children decreases. But, there are medical ways to help with this. Men’s fertility also changes with age, and new treatments offer hope.
Fertility tests are key for men as they age. They help find problems and decide on treatments. Tests include semen analysis, hormone checks, and genetic tests.
Semen analysis looks at sperm health. Hormone tests check for balance. Genetic tests find issues that might affect fertility.
There are many ways to tackle fertility issues in older men. These include lifestyle changes, medical treatments, and advanced reproductive technologies.
Healthy habits like good weight, not smoking, and less drinking can boost sperm quality. Hormone therapy and special medications can also help.
| Treatment Option | Description | Benefits |
| Lifestyle Modifications | Dietary changes, exercise, stress reduction | Improved overall health, enhanced sperm quality |
| Hormone Therapy | Treatment for hormonal imbalances | Regulates hormonal levels, potentially improving fertility |
| Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART) | IVF, ICSI, other advanced fertility treatments | High success rates for achieving pregnancy, when combined with other treatments |
Men facing fertility issues should talk to a reproductive specialist. These experts offer personalized advice and help choose the right tests and treatments.
If you’re over 40 and trying to have a child, or if you’ve been trying for over a year, seek help. A specialist can guide you on your fertility journey.
The path to becoming a father can be long, even for those who decide later in life. It’s important to look at the risks and considerations of fatherhood at an older age. This topic has many sides to it.
Having children later in life can increase the risk of genetic problems. Studies show that older dads are more likely to pass on genetic mutations. It’s key for older men to talk to a doctor about these risks.
Genetic conditions like achondroplasia and Apert syndrome are more common with older dads. Knowing these risks helps men and women make better choices about having children.
Age can affect a man’s fertility, but many older men can father children. Yet, the chances of conceiving naturally may drop. Older men might also take longer to conceive.
Even though the chances of conceiving naturally decrease with age, it’s not impossible. Men in their 50s, 60s, and 70s have become fathers. But the chances of success get lower as men get older.
For men who struggle to conceive naturally, ART offers hope. IVF and ICSI can boost the chances of successful conception.
Older dads thinking about ART should know the costs, success rates, and health risks. Talking to a fertility specialist is a smart first step to figure out the best option.
Men keep making sperm as they age, but the quality goes down. It’s key for men to understand how aging affects their reproductive health. By knowing what affects sperm, men can take steps to keep their reproductive health good.
Aging doesn’t just affect sperm quality. It also changes hormone levels and overall health. Men should be aware of these changes. They can make lifestyle changes, get medical help, and do fertility tests to tackle age-related fertility issues.
Men can take charge of their reproductive health by staying informed. This helps them make smart choices about their future and the risks of older fatherhood. We urge men to focus on their reproductive health and get expert advice when needed.
Men don’t stop making sperm completely, but the quality and amount go down with age. There’s no exact age when sperm production stops. But, it drops a lot after 40.
Yes, a man’s age can really affect his sperm quality. As men get older, their sperm count, how well they move, and DNA health can get worse. This can make it harder to have kids.
Men are usually most fertile between their late teens and early 30s. After that, sperm quality starts to go down.
Yes, things like diet, exercise, stress, and toxins can affect sperm health in older men. These factors can impact fertility.
Men don’t have a direct menopause like women do. But, some may see a slow drop in testosterone levels. This is called andropause or late-onset hypogonadism.
As men age, testosterone levels often go down. There can also be changes in other hormones like FSH and LH. These changes can affect reproductive health.
Older dads face higher risks of genetic problems and health issues in their kids. They may also have lower fertility.
Yes, medical help like fertility tests and treatments can help with age-related fertility issues. This includes things like assisted reproductive technologies (ART).
Men can keep their reproductive health up by living healthy. This means eating right, exercising, managing stress, and avoiding harmful things.
Men should see a reproductive specialist if they’re having trouble getting pregnant or are over 40. They can get advice and support.
BPH is when the prostate gland gets bigger. It’s common in older men and can affect both urinary and reproductive health.
Problems with the prostate, like BPH, can affect reproductive function. This is true if they’re not treated or managed well.
National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2025). When Does a Man Stop Producing Sperm as. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3253726/
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!