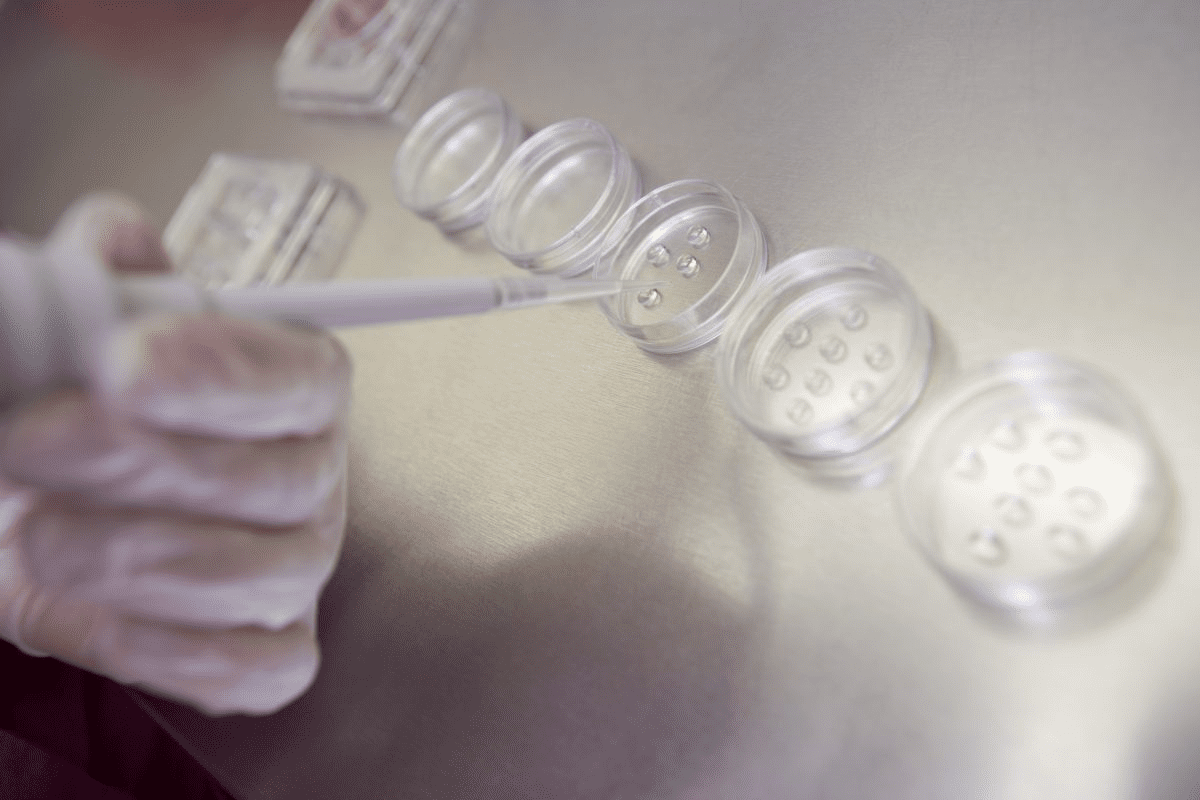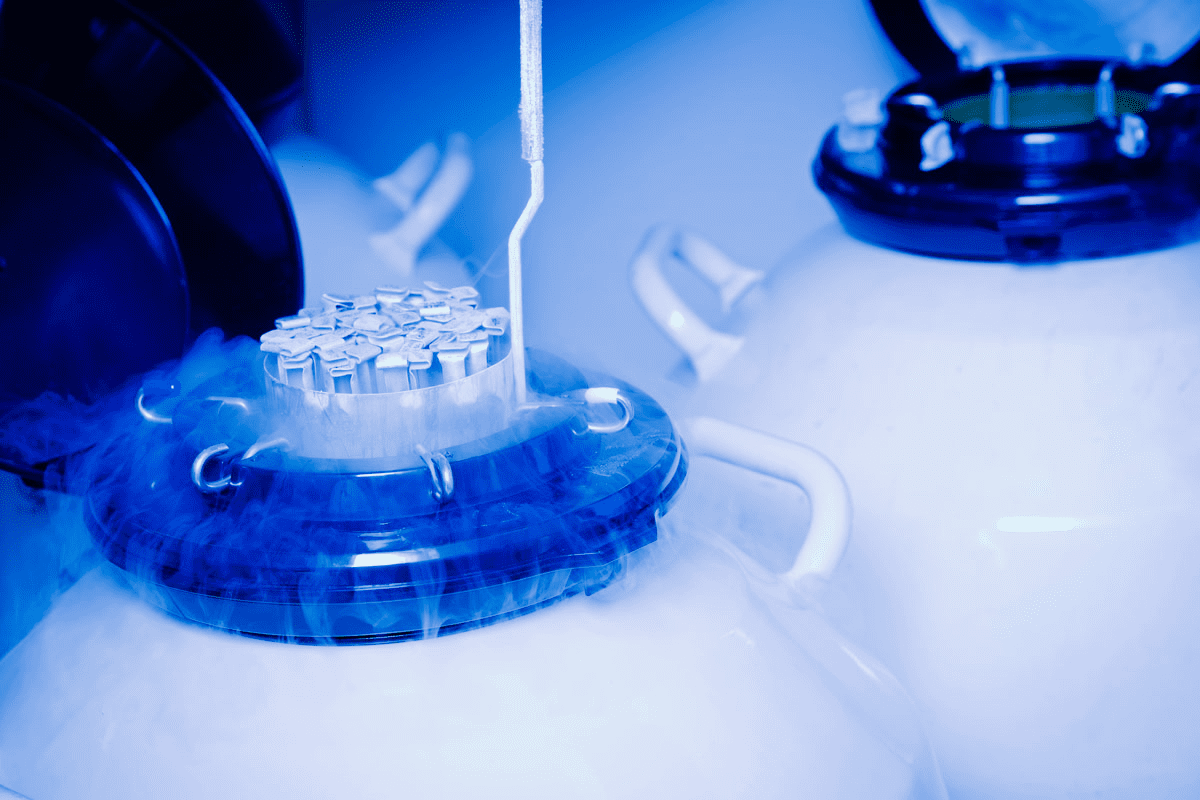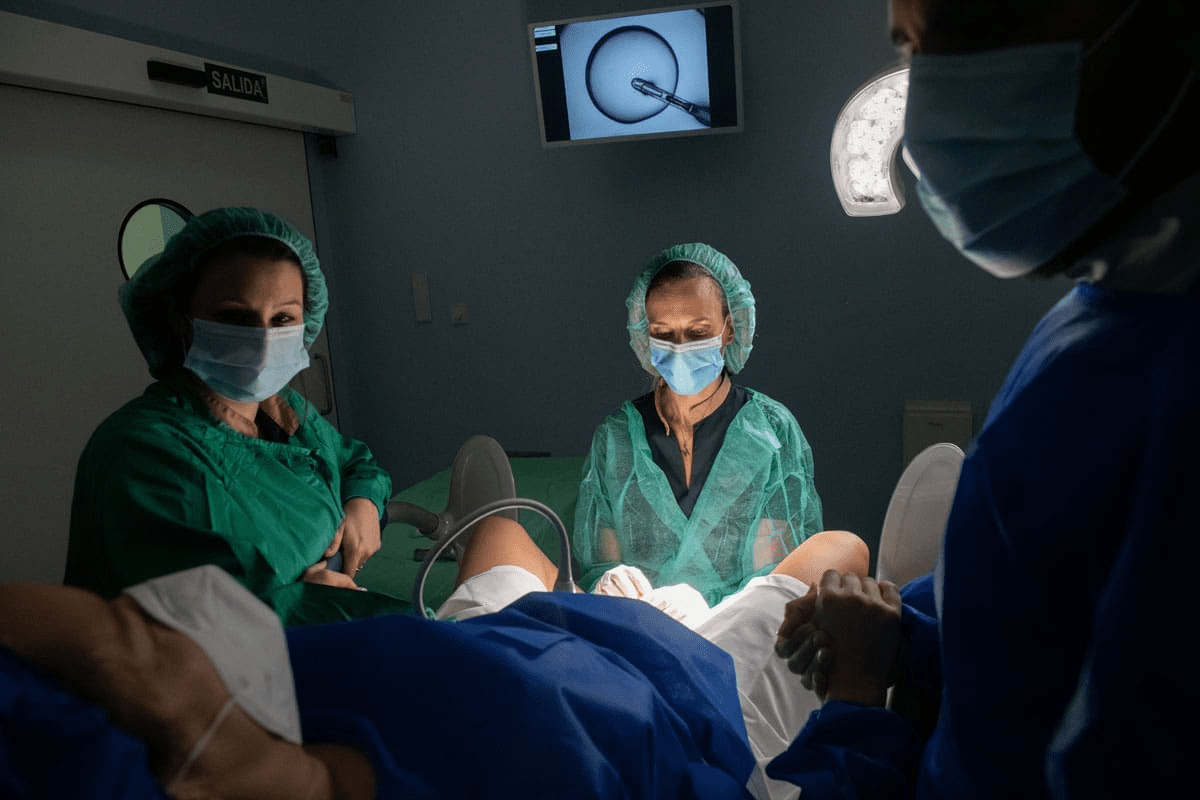
For those on the journey of fertility treatment, knowing about in vitro fertilization (IVF) is key. IVF has changed reproductive medicine, helping many conceive. It involves creating and saving embryos.
These tiny structures, about one-tenth of a millimeter, promise new life. Their look under a microscope shows their quality and chance of success. Learning about embryos in IVF gives us insight into the treatment.
More than 12 million babies have been born thanks to IVF and other ARTs. We’ll look into how embryo quality affects fertility treatment success.
Key Takeaways
- IVF involves the creation and preservation of embryos, which are key for success.
- The look of embryos under microscopes shows their quality and implantation chance.
- Over 12 million babies have been born through IVF and other ARTs worldwide.
- Knowing about embryo quality is vital for choosing fertility treatment options.
- Embryos are about one-tenth of a millimeter in size.
Understanding Embryos in IVF Treatment

Embryos are key in IVF, and their traits greatly affect success. In IVF, eggs meet sperm in a lab to form embryos. These embryos are then checked for quality before being placed in the uterus.
The Role of Embryos in Fertility Treatment
Embryos are vital in fertility treatments, helping those with fertility issues. Embryo transfers are good for those with damaged tubes, ovulation problems, or other issues. Knowing about embryos helps patients understand IVF better.
IVF is a complex and emotional journey. We guide patients with care, making sure they know about their embryos.
Physical Characteristics of Human Embryos
The look of human embryos shows their quality and chance to grow. By day 3, good embryos have 6 to 10 cells, called blastomeres. They should be the same size and have little damage.
Knowing these traits helps patients see the detailed work in IVF. By looking at cell count and damage, experts pick the best embryos. This increases the chance of a successful pregnancy.
The Embryo Development Process
[Add image here]
Understanding how an embryo develops is key for those going through IVF. The journey from fertilization to becoming a blastocyst is complex. It involves many stages.
From Fertilization to Day 3 Development
The first step is fertilization, where a sperm meets the egg. This creates a zygote. The zygote then divides into many cells, called blastomeres, without growing much. By Day 3, the embryo has 6-8 cells and is getting ready to divide more.
Key characteristics of a Day 3 embryo include:
- The number of cells (blastomeres)
- The evenness of cell division
- The presence or absence of fragmentation
Embryologists look at these factors to see if the embryo can grow.
Blastocyst Formation: Day 5-6 Development
By Day 5 or 6, the embryo becomes a blastocyst. A blastocyst has two main parts: the inner cell mass and the trophectoderm. The inner cell mass will become the fetus, and the trophectoderm will form the placenta and other tissues needed for pregnancy.
“By day 5 to day 6, embryos reach the blastocyst stage, developing two distinct cell types: the inner cell mass that becomes the fetus and the trophectoderm that forms pregnancy tissues like the placenta.”
Reaching the blastocyst stage is a big step. It shows the embryo is likely to implant well.
We know the journey of embryo development is complex and emotional for those trying IVF. Our team is here to support and care for you every step of the way.
Day 3 Embryos: Appearance and Characteristics
Day 3 embryos are a key moment in IVF. They show if an embryo might implant well. At this point, embryos have divided several times. Their looks tell us a lot about their health and chance of success.
Cell Division and Blastomere Formation
By day 3, embryos have 6-10 cells called blastomeres. How these cells divide is very important. Uniform cell size and shape are good signs of a healthy embryo. We watch the cells closely to see if the embryo is likely to grow well.
Identifying Quality Indicators in Day 3 Embryos
Good day 3 embryos have 6 to 10 cells that are all the same size and shape. They should have little to no fragmentation. Little fragmentation means a better chance of implantation. We look at how much fragmentation there is and if the cells are even to judge the embryo’s quality.
“The quality of day 3 embryos is a significant predictor of successful IVF outcomes. Embryos with optimal characteristics have a higher chance of implantation.”
Common Fragmentation Patterns
Embryos can have different kinds of fragmentation. Some common ones are:
- Minor fragmentation: Small fragments that don’t hurt the embryo’s quality much.
- Major fragmentation: Bigger fragments that might harm the embryo’s chances.
- Localized fragmentation: Fragments all in one spot of the embryo.
Knowing these patterns helps us guess how well an embryo might develop. The embryo transfer, which happens on day 3 or 5, is quick, like a pap smear. Whether to transfer on day 3 or 5 depends on the embryo’s quality and the patient’s needs.
Blastocyst Stage: Structure and Appearance
Reaching the blastocyst stage is a key moment in IVF treatment. It shows a higher chance of genetic normalcy and successful implantation. This stage usually happens on day 5 of embryo development, but can extend beyond that. At this point, the embryo has grown and differentiated significantly, making it a critical time for evaluation.
Inner Cell Mass vs. Trophectoderm
A blastocyst has two main cell groups: the inner cell mass (ICM) and the trophectoderm. The inner cell mass will form the fetus. The trophectoderm will become the placenta and other supporting tissues. The health of these cells is key to the embryo’s viability.
“The inner cell mass and trophectoderm work together for a healthy embryo,” say embryologists. The ICM is dense and tightly packed. The trophectoderm forms a clear outer layer around a fluid-filled cavity.
Visual Markers of Healthy Blastocysts
A healthy blastocyst looks like a fluid-filled sphere, like a balloon with a ping-pong ball inside. Key signs of health include a clear inner cell mass, a cohesive trophectoderm layer, and a well-expanded blastocoel cavity. The blastocoel is the fluid-filled space inside the blastocyst, showing its health and viability.
Expansion Stages and What They Mean
Blastocysts go through different expansion stages, showing their growth. These stages range from early blastocysts with a small cavity to fully expanded ones with a large cavity. The size of the cavity is important for judging the embryo’s quality and readiness for transfer.
- Early blastocysts have a small blastocoel cavity.
- Fully expanded blastocysts have a large blastocoel cavity that occupies the entire embryo.
- Hatching blastocysts are in the process of emerging from their zona pellucida.
The expansion stage tells us about the embryo’s growth and implantation chances. By looking at these signs, embryologists can pick the best embryos for transfer. This improves the chances of a successful IVF outcome.
Frozen Embryo Photos: What You’re Actually Seeing
Embryologists use powerful microscopes to check embryos before and after freezing. This gives them key info for IVF treatments. The images from these microscopes are called frozen embryo photos.
Microscopy Techniques Used in Embryology
Embryologists use special microscopy techniques. They use inverted microscopes to look at embryos in dishes without messing with them. These tools have advanced optics and cameras for clear embryo images.
They use different microscopy types, like brightfield and DIC, to look at embryo details. DIC microscopy is great for seeing embryo structure closely.
Interpreting Embryo Images for Non-Specialists
For those going through IVF, embryo images can be hard to understand. Embryologists grade embryos based on their look under the microscope. They check cell number, fragmentation, and shape.
Knowing a bit about embryology can help patients understand their treatment better. For example, cell count on Day 3 can show if an embryo might implant well.
Real Examples of Embryo Photos at Different Stages
Let’s look at some real examples of frozen embryo photos
At the blastocyst stage (Day 5-6), embryos show an inner cell mass and a fluid-filled area. These signs are key for their health. Knowing these stages shows how complex embryo growth is.
Frozen embryo transfer costs can be from $3,000 to $6,000. It’s a big expense but a vital step for many wanting to start a family through IVF.
Embryo Grading Systems Explained
Embryo grading systems are key in IVF treatment. They help check embryo quality. This is important for picking the best embryo for transfer.
Day 3 Embryo Grading Criteria
On Day 3, embryos are graded by cell number, cell regularity, and fragmentation.
- Cell Number: A good Day 3 embryo usually has 8 or more cells.
- Cell Regularity: Uniform cell size and shape mean better quality.
- Fragmentation: Fewer fragments are better. Fragmentation percentage is key in grading.
Blastocyst Grading: Understanding the A-D Scale
Blastocysts, on Day 5 or 6, get a more detailed grading. They look at the inner cell mass (ICM), trophectoderm (TE), and the blastocyst cavity’s expansion. The scale goes from A to D for each part.
- Inner Cell Mass (ICM) Grading: A tightly packed ICM is Grade A. A loose ICM is Grade D.
- Trophectoderm (TE) Grading: A cohesive TE with many cells is Grade A. Few or loose cells are Grade D.
- Expansion Status: The cavity’s expansion is graded from 1 (early) to 6 (fully hatched).
How Embryologists Evaluate Quality
Embryologists look at many factors to judge embryo quality. This includes Day 3 and blastocyst-stage criteria. They use:
- Microscopic examination for morphological features.
- Time-lapse imaging to watch development.
- Preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) for genetic checks.
Studies show frozen embryo transfers work better than fresh ones. This is mainly because of genetic screening. By grading embryos well, embryologists boost IVF success rates.
The Freezing Process and Its Effect on Embryo Appearance
Embryo freezing is key in modern fertility treatments. It uses precise methods to keep embryos alive. This is vital for people going through IVF, as it lets them save embryos for later.
Vitrification vs. Slow Freezing Methods
There are two main ways to freeze embryos: vitrification and slow freezing. Vitrification freezes quickly, stopping ice crystals from forming. This helps protect the embryo. Slow freezing freezes the embryo slowly, but it’s less common now.
Vitrification is now the top choice because it works better. It’s better at avoiding ice crystal damage to the embryo.
| Freezing Method | Description | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Vitrification | Rapid freezing method | Reduces ice crystal formation, preserves embryo integrity |
| Slow Freezing | Gradual temperature reduction | More traditional, but less effective than vitrification |
Visual Changes Before and After Freezing
Freezing can change how embryos look. Before freezing, they’re checked for quality. After vitrification, they might look a bit different because of the cryoprotectants and freezing.
Frozen embryos can stay viable for over ten years. This is thanks to better freezing methods.
Storage Conditions for Frozen Embryos
Frozen embryos are kept in liquid nitrogen at very low temperatures. Keeping them at the right temperature is key to their survival. They’re stored in special containers that keep the temperature low.
When it’s time to transfer a frozen embryo, estrogen and progesterone are used. This gets the uterus ready for the embryo. It’s a careful process to make sure everything goes smoothly.
Frozen Embryo Transfer Success Factors
Understanding what affects frozen embryo transfer success is key for both patients and doctors. A successful frozen embryo transfer depends on several important factors.
Correlation Between Embryo Appearance and Outcomes
The look of an embryo is a big clue to its implantation chances. Embryologists check embryos for cell division, fragmentation, and health. Studies show that embryos with the best look have better implantation rates. But, it’s important to remember that looks alone don’t decide success.
Beyond Appearance: Other Factors Affecting Success
While embryo quality is key, other things also matter a lot. Uterine receptivity is very important, as the uterus must be ready for the embryo. The thickness of the uterine lining and any uterine issues can affect this. Also, doctor skill is very important, as the transfer technique can change the outcome.
Modern Advances in Embryo Selection
New technology has made picking embryos better for frozen embryo transfers. Preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) helps find embryos without genetic problems, boosting success chances. Time-lapse imaging lets us watch embryo growth, giving us insights into their health.
Thanks to new techniques, frozen embryo transfer success has gotten better. By looking at embryo look, uterine readiness, and doctor skill, and using new embryo selection tech, we can help more patients succeed with frozen embryo transfers.
Conclusion: The Journey from Microscopic Embryo to Baby
The journey of embryos from creation to birth is complex and fascinating. At Pacific Fertility Center of Los Angeles, we’ve seen the impact of understanding this journey. We’ve helped patients in over 75 countries for 30 years.
Understanding embryo development helps patients grasp their IVF journey. It shows how an embryo becomes a baby. This knowledge demystifies IVF and empowers patients to make informed decisions.
The path from embryo to baby is remarkable. It involves detailed biological processes and advanced medical technology. We hope this exploration has given valuable insights into IVF and embryo development. It supports those on their path to parenthood.
FAQ
What do frozen embryos look like?
Frozen embryos are tiny, microscopic cells. They are about 0.1-0.2 millimeters in size. Their appearance changes based on their stage and quality.
How are embryos created for IVF treatment?
Embryos are made through in vitro fertilization (IVF). Eggs are retrieved and fertilized with sperm in a lab. Then, they are cultured for a few days before being transferred or frozen.
What is the significance of embryo appearance in determining their quality?
An embryo’s look is key to its quality and success. Embryologists check cell number, fragmentation, and other traits to judge viability.
What is the difference between a day 3 embryo and a blastocyst?
A day 3 embryo has 6-8 cells and is early in development. A blastocyst, around day 5/6, has a fluid-filled cavity and two cell types.
How are frozen embryo photos taken?
Photos of frozen embryos are taken with special microscopy. Techniques like brightfield or DIC microscopy help see the embryos’ details.
What is the grading system used for embryos?
Embryos are graded by their shape and structure. Day 3 embryos are judged by cell count and fragmentation. Blastocysts are evaluated by expansion, inner cell mass, and trophectoderm quality.
How does the freezing process affect embryo appearance?
Freezing, like vitrification, might change an embryo’s look. It can make the cytoplasm darker or more granular. But these changes usually don’t affect viability.
What factors influence the success of frozen embryo transfers?
Success in frozen embryo transfers depends on many things. These include embryo quality, uterine readiness, and the skill of the doctor. Timing with the woman’s natural cycle also matters.
Can I see pictures of embryos at different stages?
Yes, many IVF clinics and labs share embryo pictures. These images help people understand the development process and what to expect during IVF.
How do embryologists evaluate the quality of embryos?
Embryologists look at morphology, including cell count, fragmentation, and other traits. They also consider developmental stage and growth rate.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Frozen Embryo Appearance: IVF Photography Explained. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10842100/