Last Updated on October 20, 2025 by
We are seeing a big leap in gene therapy for young kids. Gene therapy is a new way to use genes to fight or stop diseases.
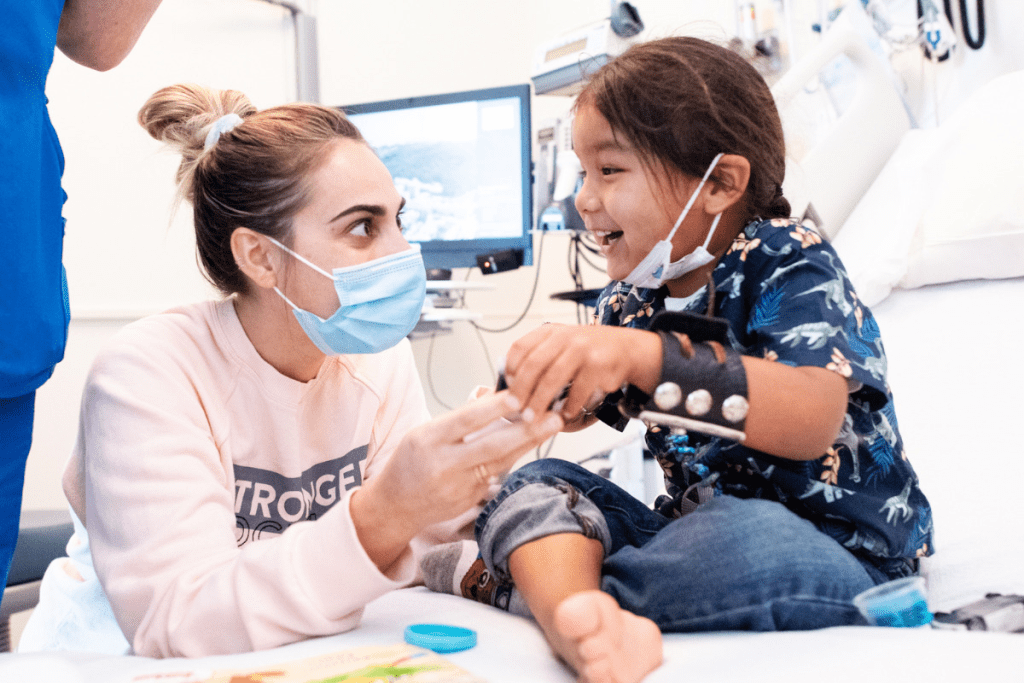
A four-year-old named KJ got a special CRISPR treatment for CPS1 deficiency. This is a rare and dangerous metabolic disorder. It’s a big step forward in genetic treatment.
how does gene therapy work by changing a person’s genes to treat or cure diseases. It often uses vectors, like modified viruses, to deliver healthy genes into a patient’s cells. These new genes can replace faulty ones, block harmful genes, or help cells function properly, targeting diseases at their genetic root
The first time gene therapy was tried on a human was in 1990. A four-year-old girl named Ashanthi had severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID).
KJ, a four-year-old, made history with the world’s first CRISPR-based treatment. This breakthrough is a big step forward in technique aimed at correcting mutated genes that cause human disease. Scientists used CRISPR to create a therapeutic gene for KJ’s specific genetic condition.
KJ’s case is special because it deals with CPS1 deficiency, a rare genetic disorder. This disorder makes it hard for the body to remove ammonia from the blood. The CRISPR treatment was made to fix this by editing the faulty gene.
This groundbreaking procedure has opened new doors for treating similar genetic disorders.
KJ’s treatment has shown promising results with no serious side effects. The main outcomes include:
These results are not just good for KJ but also for gene therapy as a whole. The FDA has approved gene therapies for Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) in young children. This shows how fast we’re moving in personalized gene therapy. Treatments like KJ’s are likely to become more common, giving hope to those with severe genetic conditions.
It’s key to understand genetic disorders in kids to help them live better lives. These disorders can really hurt a child’s health and growth. They need special and new care.
Genetic disorders in kids come from changes in their genes, often passed down from parents. These changes can really affect a child’s health and life. For example, Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID) weakens the immune system, making kids very sick.
Rare metabolic conditions, like CPS1 deficiency, are caused by specific genetic changes. These changes mess up how the body works. They can make the body build up harmful substances, causing health problems. Knowing the genetic cause is key to finding the right treatment.
The Mayo Clinic says gene therapy is a hopeful treatment. It tries to fix the genetic problem that causes disease. “Gene therapy is an experimental technique that uses genes to prevent or treat diseases.”
The genetics of inherited diseases is very important. It helps us understand how these diseases are passed down. Inherited diseases can come from one gene problem or from a mix of genes and environment.
Knowing the genetic cause of these diseases is vital for finding good treatments. Gene therapy is one such treatment. It aims to fix the genetic problem in a patient’s cells. This could greatly improve the health and life of kids with genetic disorders.
Key aspects of gene therapy include:
Gene therapy can really help kids with genetic disorders. It offers a new chance for better treatment and care.
Gene therapy is changing how we treat genetic diseases. It targets the disease at its source. This offers hope to those with diseases that were once untreatable.
CRISPR gene editing is a key tool in science. It lets scientists make precise changes to DNA. CRISPR-Cas9 is the most used system. It finds a DNA sequence, cuts it, and then adds a new gene.
“The precision of CRISPR gene editing represents a significant advancement in our ability to treat genetic disorders.”
The process involves several steps. First, scientists design a guide RNA. Then, they deliver the CRISPR-Cas9 system to cells. Lastly, they check if the edit worked. This technology is showing great promise in treating severe genetic diseases.
Getting genetic treatments to the right cells is key. Viral vectors are often used. They are safe and effective. Viral vectors can target specific cells, reducing side effects.
Other methods include electroporation and microinjection. Each has its own benefits and challenges. The choice depends on the disease and the cells involved.
As we improve these methods, gene therapy is becoming a common treatment. It holds promise for many genetic disorders.
Gene therapy has been a game-changer in medicine for decades. It started taking shape in the late 20th century. This was thanks to big leaps in genetics and new tech.
Gene therapy has made huge strides. The first trial was in 1990 on a girl named Ashanthi with SCID. This trial was a big step forward for medicine.
Gene therapy began in the late 20th century. The first human trial was in 1990. It has grown a lot, with new tech and understanding of genetics.
The story of gene therapy shows our drive for medical progress. New methods like CRISPR have changed the game.
Gene therapy has been a big hope for kids with severe genetic diseases. It has greatly improved their lives. It has also opened doors to treating diseases that were once thought untreatable.
Children treated with gene therapy have made amazing progress. Kids with genetic disorders have grown and developed in ways thought impossible. This shows the power of gene therapy in treating childhood diseases.
Key Milestones in Gene Therapy:
Personalized medicine is changing gene therapy. It offers treatments made just for each patient’s genes. This could lead to much better results by fixing the root cause of a patient’s problem.
Personalized gene therapy uses viruses to carry genes into cells. Viral therapy is a method that shows great promise. It can fix or lessen the harm of bad genes.
By making treatments for each person, we can tackle their specific genetic issues. This is a big step up from old treatments that didn’t fit everyone.
New gene editing tools have made it faster to go from finding a problem to fixing it. This is key for genetic diseases, where quick action is very important.
The pros of gene therapy include its ability to fix genetic problems for good. As these technologies get better, we’ll see treatments come faster. This brings hope to those with genetic diseases.
We’re getting closer to treating genetic diseases better, thanks to personalized gene therapy. This field keeps growing, promising better care for people all over the world.
Toddlers and young children treated with gene therapy are seeing amazing results, thanks to recent clinical trials. They are making big strides in development, bringing hope to families with severe genetic conditions.
Children with genetic disorders like Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) are getting better. They can walk and do daily tasks more easily. This is a big step forward in their health and happiness.
Gene editing tools like CRISPR are making precise changes to genes. This has led to remarkable recoveries in young patients. They were once expected to face big developmental hurdles.
Figuring out if gene therapy works involves looking at several things. We check if the genetic problem is fixed, if symptoms improve, and if the child’s quality of life gets better. We use clinical checks, patient feedback, and tests to measure these.
By looking at these areas, we can see how well gene therapy works for toddlers and young children. This helps us move forward in treating genetic diseases.
Gene therapy has great promise, but we must consider its risks and benefits. As we move forward, keeping safety in mind is key, even more so for kids.
Gene therapy aims to fix genes to treat or cure diseases. For kids with genetic disorders, this can be a game-changer. But, it’s vital to watch for any bad side effects.
The FDA keeps a close eye on gene therapy trials to make sure they’re safe and work well. We need to keep watching, even more so for kids, to catch any problems early. This means regular check-ups to make sure the treatment isn’t causing harm.
Adverse effects can be anything from mild to serious. They might include immune reactions, inflammation, or even changes to the genes. By watching patients closely, we can act fast if something goes wrong.
For rare diseases, the benefits of gene therapy often outweigh the risks. These diseases are often very severe and gene therapy might be the only hope. We need to think about how bad the disease is, how much the treatment could help, and what risks it carries.
Germline therapy, which changes genes that can be passed on, brings up more complex issues. These are important to consider as we develop gene therapy further.
By carefully looking at the risks and benefits, we can make sure gene therapy is used wisely and safely. This means keeping a close eye on patients and doing more research to make treatments better and safer.
Gene therapy is a technique aimed at correcting mutated genes that cause human disease. It raises big ethical questions. As we push forward in this field, we must think about the moral and societal impacts of genetic changes.
There’s a big difference between somatic and germline gene therapy. Somatic therapy changes non-reproductive cells, affecting only the treated person. Germline therapy changes reproductive cells, impacting future generations.
Somatic gene therapy is more common and has helped treat genetic disorders in kids. For example, a child with a rare genetic disorder can get somatic gene therapy. This has shown great promise in clinical trials, giving hope to families.
Germline therapy, though, brings up more serious ethical concerns. It could prevent inherited diseases but also carries unknown risks. This makes it a more complex issue.
Regulatory bodies and oversight are key to handling these ethical challenges. They make sure gene therapy follows ethical standards and protects patient rights.
Worldwide, regulatory agencies are setting up rules for gene therapy. They focus on safety and effectiveness through strict testing and monitoring.
As we advance, it’s vital to keep talking between scientists, ethicists, and lawmakers. This ensures gene therapy is developed and used responsibly.
Pediatric gene therapy is set to change how we treat genetic disorders. It’s moving fast, thanks to ongoing research and new technologies. These advancements aim to make gene therapies better and safer.
The benefits of gene therapy are clear, and they’re big. It’s helping kids with rare genetic diseases. Gene therapy can fix or lessen the effects of certain genetic problems, giving hope where there was none before.
At first, gene therapy was mainly for metabolic disorders. But now, it’s being used for many other genetic conditions. Scientists are looking into treating diseases of the immune system, muscles, and nervous system in kids.
New gene editing tools, like CRISPR, and better ways to deliver treatments are key. They help make gene therapy more precise and effective.
The future of pediatric gene therapy depends on new technologies. Better gene editing, vector design, and delivery systems are important. The idea of is there a winning gene is becoming more important as therapies aim to fix specific genetic issues.
As we learn more about the genetics of diseases, gene therapy can treat more conditions. We’re excited about the future of pediatric gene therapy and its ability to change how we treat genetic diseases in children.
Gene therapy is changing how we treat childhood genetic diseases. We’ve seen big steps forward in this field, starting from 1990.
The process of gene therapy, which fixes or lessens genetic problems, looks promising. Our knowledge of genetics and gene editing is growing. This means gene therapy could help more children and families with genetic issues.
Looking ahead, the future of gene therapy is exciting. We aim to provide top-notch healthcare and support to patients worldwide. Gene therapy is a key part of our mission.
Gene therapy is a medical method. It uses genes to treat or prevent diseases. It aims to fix the genetic problems at the root.
CRISPR gene editing uses a guide RNA to find a specific DNA sequence. The Cas9 enzyme then cuts it. This allows a corrected gene to be inserted.
Gene therapy is promising for treating severe genetic conditions in kids. It could lead to better health, developmental progress, and a better quality of life.
Gene therapy might have risks, like side effects. It’s important to watch for these and weigh the benefits against the risks, mainly in kids.
Somatic gene therapy changes non-reproductive cells. Germline therapy changes cells that can pass on traits to future generations.
Gene therapy started in 1990 with the first human trial. It has grown a lot over the years.
Personalized medicine in gene therapy means treatments are made for each patient. They are based on the patient’s genetic makeup. This makes treatments more effective and targeted.
Pediatric gene therapy is quickly changing. New uses, technologies, and treatments for more genetic conditions are on the horizon.
Viral vectors are key in gene therapy. They help deliver genes to patients. This is how genetic disorders are treated.
Success in gene therapy is measured in many ways. It includes fixing the genetic defect, improving symptoms, and bettering the patient’s quality of life.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!