Last Updated on November 25, 2025 by Ilayda Cengizhan
Getting a CT Scan of the Eye, also known as an orbital CT scan, is key for diagnosing eye and orbital diseases. This test uses X-rays and computer technology to show detailed images of the eye sockets and bones around them. A CT Scan of the Eye offers fast, accurate visuals that help detect a wide range of conditions early.
We’ll show you how to get ready for the CT Scan of the Eye. You’ll learn what to expect during it and how to take care of yourself afterward. The prep steps might change based on the scan type, and you might need to adjust your diet.
A CT Scan of the Eye, or orbital CT scan, uses X rays to show detailed images of the eye and its surroundings. This tool has transformed how we diagnose and treat eye and orbital diseases. The CT Scan of the Eye allows for thorough multiplanar scanning.
A CT Scan of the Eye is a non-invasive test. It uses computer technology and X-rays to create clear images of the orbital area. CT technology works by showing how different tissues absorb X-rays at different rates. This helps create highly detailed cross-sectional images.
During a CT Scan of the Eye, you lie on a table that moves into the CT scanner. The scanner rotates around your head, taking multiple X-ray images from different angles. A computer then reconstructs these into detailed orbital images.
There are two main types of CT Scan of the Eye procedures: contrast and non-contrast. For some scans, you might need an iodine-based contrast dye. This dye highlights blood vessels and structures to produce clearer orbital images.
A CT Scan of the Eye is essential for diagnosing many orbital and ocular conditions. It provides detailed images that help detect issues quickly and accurately.
A CT Scan of the Eye is especially useful after trauma. It shows the extent of fractures, bleeding, or foreign bodies, guiding treatment plans.
A CT Scan of the Eye can identify tumors or abnormal masses in the orbital region. It helps determine the tumor size, structure, and location.
With a CT Scan of the Eye, inflammatory conditions like orbital cellulitis can be visualized clearly through swelling or abnormal tissue changes.
Foreign objects in the orbit are easily located with a CT Scan of the Eye, which is crucial for surgical planning.
Condition | CT Scan Findings | Clinical Significance |
Eye Trauma | Fractures, foreign bodies | Guides surgical intervention |
Orbital Tumors | Masses, lesions | Aids in diagnosis and treatment planning |
Inflammatory Conditions | Swelling, increased density | Helps in assessing severity and guiding treatment |
Foreign Bodies | Presence and location of foreign bodies | Critical for surgical planning |
In conclusion, CT scans of the eye are very important for diagnosing many eye problems. They give us the detailed images we need to accurately diagnose and treat eye and orbital conditions.
To make sure your CT scan goes smoothly, follow these steps. Getting ready right is important for clear images. These images help doctors diagnose and plan treatments.
Before your scan, share your medical history with your doctor. Include any surgeries, allergies, and health issues. Remember to tell your doctor about any medicines you’re taking.
If you’re getting a CT scan with contrast, you might need to change your diet. Some places might let you drink water if needed. Always follow the diet instructions from your doctor or the imaging center.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you’re taking. This includes supplements and over-the-counter drugs. Your doctor might ask you to stop or adjust some medicines before the scan.
Wear comfy clothes on the day of your scan. Avoid jewelry or metal items. Bring your medical records, insurance info, and a list of your medicines to your appointment.
We’ll walk you through the steps of a CT orbital scan. This can help ease any worries you might have. Knowing what to expect can make the process less scary and more straightforward.
The first thing you’ll do is register. You’ll need to show your ID and share your medical history. Our team will then ask you a few questions about your health and any allergies.
After the initial questions, you’ll lie down on the CT scanner table. For an orbital scan, you’ll lie on your back with your head in a headrest. This helps keep everything steady. Our technologist will make sure you’re comfy and in the right spot.
If contrast is needed, a small needle will be put in your arm or hand. After it’s in, the needle comes out. You might feel a warm feeling or taste something metallic. These feelings are short-lived and go away fast.
The scanning itself is quick, lasting just a few minutes. You’ll need to stay very quiet and might be asked to hold your breath. This helps get clear pictures of your orbital area.
Step | Description | Duration |
Registration | Providing identification and medical history | 5-10 minutes |
Positioning | Getting into position on the CT scanner table | 2-5 minutes |
Contrast Administration | Receiving contrast injection (if applicable) | 1-2 minutes |
Scanning | The actual CT scan process | 2-5 minutes |
Knowing the steps of a CT orbital scan helps you prepare. It lets you know what to expect at each step.
Getting ready for your eye CT scan? Knowing what to expect can ease your worries. This scan is non-invasive and quick, usually taking 15 to 30 minutes.
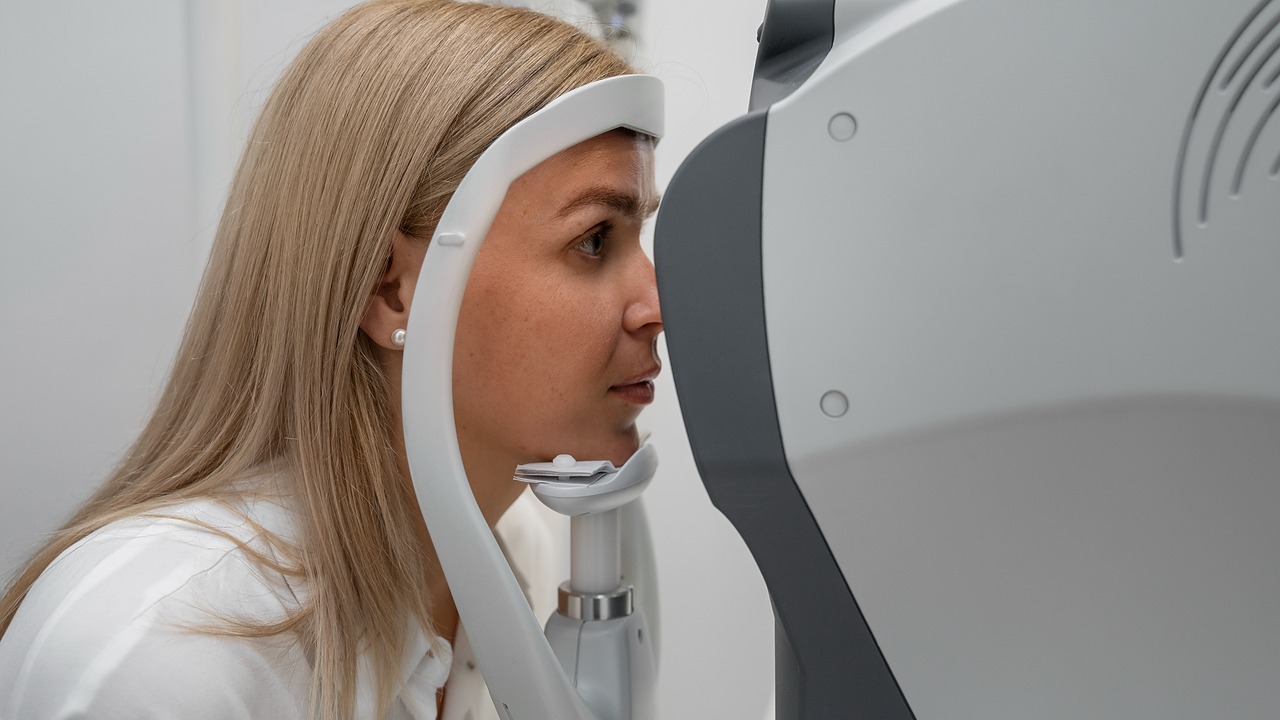
The whole process, from start to finish, takes about 30 to 60 minutes. The actual scanning part is shorter, lasting 15 to 30 minutes.
You might feel some sensations during the scan, like a hot feeling or a metallic taste. This is because of the contrast injection. The table will move slowly, and you might hear some sounds.
You can talk to the technologists through an intercom during the scan. They’ll tell you when to hold your breath or stay very quiet.
Feeling anxious or claustrophobic? Talk to your doctor about it before the scan. They might suggest relaxation methods or even mild sedation to help you relax.
Aspect | Description |
Procedure Time | 15 to 30 minutes |
Total Visit Time | 30 to 60 minutes |
Sensations During Scan | Hot feeling, metallic taste (if contrast is used) |
After your CT orbital scan, our team will help you with the next steps. You might have questions about what to do next after the scan.
We’ll give you instructions right after the scan. Drink lots of water for 48 hours to stay hydrated. This helps your body get rid of any dye used during the scan.
Your CT eye scan results will come in a few hours to days. This depends on how complex the scan was and our radiologist’s schedule. We’ll let you know when to expect them and what to do next.
You might need to see your doctor after the scan to talk about the results. We’ll help you understand what the findings mean and what to do next.
If dye was used in your scan, you might feel some side effects. These are usually mild and short-lived. We’ll show you how to handle any discomfort and keep an eye on your health.
CT scans of the eye have some risks and safety steps. They are usually safe, but knowing these helps patients make better choices.
One big worry with CT scans is radiation. They use X-rays to see the eye and orbital structures. The radiation is small, but it slightly raises cancer risk.
Some CT scans of the eye use contrast dye for better images. Some people might react to it, from mild hives to serious issues. Those with allergies or kidney problems should talk to their doctor.
If you’re pregnant or might be, tell your doctor before a CT scan orbital. The risk to the baby is low, but they take extra care.
To keep you safe, they follow these steps:
Knowing these risks and safety steps makes patients more confident for a CT scan of the eye. Always talk to your healthcare provider about any worries or questions.
Getting the results of a CT scan of the eye can be tricky. We’ll guide you through what the images mean, common findings, and how to talk to your doctor about them.
CT images of the eye are very detailed. A radiologist will look closely at them for any signs of problems. The ct scan of the eye shows the orbital structures clearly, helping in making a diagnosis.
An eye ct scan might show trauma, tumors, or inflammation. We’ll explain what these mean and how they might affect your health.
A radiologist is key in reading your ct of the orbit images. They’ll give a detailed report to your doctor, pointing out important findings and suggesting next steps.
After your doctor gets the radiologist’s report, they’ll talk to you about it. This is your chance to ask questions and understand what’s next. Knowing your orbital ct scan results helps you make informed decisions about your treatment.
There are other ways to look at the eye and orbital area, aside from CT scans. These options are good when CT scans can’t be used or aren’t available.
MRI is a great tool for seeing the eye and orbit clearly. It doesn’t use harmful radiation. It’s best for soft tissue and safe for some patients where CT scans are not.
Ultrasound is safe and doesn’t use radiation. It’s good for many patients, including pregnant women and kids. It can spot issues like retinal detachment and tumors inside the eye.
X-rays can show some orbital problems, like fractures. Other tools like OCT are used for eye diseases, like those affecting the retina.
Choosing an imaging method depends on the patient’s health and what’s being looked for. For example, MRI might be better than CT for pregnant women or when soft tissue details are needed.
Imaging Modality | Key Features | Preferred Use |
MRI | No radiation, excellent soft tissue detail | Soft tissue characterization, pregnant women |
Ultrasound | Non-invasive, no radiation | Retinal detachment, intraocular tumors, children |
X-Ray | Quick, widely available | Fractures, initial assessment |
Finding the right place for your eye CT scan is key to getting a good diagnosis and treatment. There are important things to look for to make sure you get the best care.
Specialized eye imaging centers focus on eye imaging. They have the latest technology and skilled staff. This means your CT scan of the eye will be done with great care and detail.
Hospitals and outpatient centers both do CT scan orbital services. Hospitals can handle more complex cases but may have longer waits and higher costs. Outpatient centers are often quicker and cheaper, making them a good choice for many.
The quality of the equipment and technology is very important. Look for the latest CT scanners for better images and faster scans. This can also mean fewer repeat scans and more accurate diagnoses.
When picking a place for your CT of the orbit, ask important questions. Find out about the staff’s qualifications, the equipment used, and patient care. Also, ask about wait times for results and how you’ll get them.
Medical experts say choosing the right imaging center is as important as the procedure itself. By asking the right questions, you can have a smooth and successful experience.
“The quality of the imaging facility directly impacts the accuracy of the diagnosis and the effectiveness of the subsequent treatment plan.”
Medical Expert, Radiologist
By considering these points and doing your homework, you can find a top-notch ct scan orbital facility.
A CT scan of the eye, or orbital CT scan, is a key tool for diagnosing eye issues. It gives detailed images of the eye and nearby tissues. This helps doctors spot problems like trauma, tumors, and inflammation.
This guide aims to explain the CT scan process for the eye. It covers preparation, the scan itself, and what to do after. Knowing this helps patients feel more ready for their scan.
The results from an eye CT scan are vital for treatment plans. Choosing a trusted facility with modern CT tech ensures accurate diagnoses and care.
If you’re facing eye trauma or think you might have an orbital tumor, a CT scan can help. If you’re set for a scan, ask questions and get support from your healthcare team.
A CT scan of the eye, also known as an orbital CT scan, is a non-invasive test. It uses X-rays to create detailed images of the eye and its surroundings. This helps diagnose various eye conditions.
To prepare, share your medical history and follow any dietary restrictions. Tell your doctor about your medications and wear comfortable, metal-free clothing.
You’ll lie on a table that slides into a CT scanner. The technologist will guide you through the process. This may include contrast administration and scanning.
A CT scan of the eye usually takes a few minutes to about 30 minutes. The exact time depends on the scan’s complexity and if contrast is used.
CT scans of the eye are generally safe but involve radiation. Some people may react to contrast dye. Medical professionals manage these risks carefully.
Alternatives include MRI, ultrasound, and X-rays. These might be preferred when avoiding radiation is important or for specific conditions.
Understanding your results involves reading the images with a radiologist. They’ll identify any abnormalities and provide a diagnosis. Then, you’ll discuss it with your doctor to decide what to do next.
Look for specialized eye imaging centers. Check the technology and equipment used. Also, consider if it’s a hospital or outpatient center. Ask about their experience and protocols.
A contrast CT scan uses dye to highlight areas or structures. A non-contrast CT scan does not use dye. The choice depends on the condition being diagnosed.
If you’re pregnant, tell your doctor. CT scans involve radiation. Alternative imaging methods may be considered to protect the fetus.
To manage claustrophobia, discuss your concerns with your doctor or technologist. They may offer relaxation techniques, sedation, or an open CT scanner to help you feel more comfortable.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!