Cancer involves abnormal cells growing uncontrollably, invading nearby tissues, and spreading to other parts of the body through metastasis.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Overview and Definition
Cancer is not just one disease, but a group of related diseases. In every type of cancer, some cells in the body start dividing uncontrollably and can spread into nearby tissues. Normally, our cells grow and divide as needed, and old or damaged cells die off to make room for new ones. Cancer interrupts this process. Abnormal cells may survive when they should die, and new cells may form when they are not needed. These extra cells can keep dividing and may form lumps called tumors. Tumors can be benign (not cancer) or malignant (cancer). Cancer can begin almost anywhere in the body, which is made up of trillions of cells.
Staging describes how much cancer is in the body, including the size of the tumor and whether it has spread to other areas. Staging is important because it helps doctors decide on the best treatment and understand the outlook. For example, Stage I means early cancer, while Stage IV means it has spread.
Our center is recognized as a Comprehensive Cancer Center. We offer advanced radiation therapy with equipment like TrueBeam STx and MR-Linac, comfortable chemotherapy infusion centers, and a nuclear medicine department with PET-CT scans. We focus on precision medicine, using genetic testing of tumors to choose the best targeted treatments.
The most common way to stage cancer is called the TNM system. T stands for the size of the tumor, N shows if cancer has spread to lymph nodes, and M means metastasis, or spread to other parts of the body. This system helps doctors understand how far the cancer has progressed.
Cancer can affect the body by pressing on organs, which may cause pain or even organ problems. Treatments like chemotherapy target fast-growing cells, so they attack cancer but can also affect healthy cells, leading to side effects like hair loss, tiredness, or nausea. Immunotherapy works by boosting the immune system, which can sometimes cause symptoms similar to the flu.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.

Several factors can increase the risk of cancer. Genetics, such as inherited mutations like BRCA, are important, but lifestyle choices matter a lot too. Smoking, being overweight, drinking alcohol, and too much sun are major risks that can be prevented. Age is the biggest risk factor, since DNA damage builds up over time. Some infections, like HPV or Hepatitis, can also cause certain cancers.
Diagnosing cancer begins with imaging tests like MRI, CT, or PET-CT scans to find the tumor. The final diagnosis is made by taking a tissue sample, called a biopsy, which is examined by pathologists. Genetic testing of the tumor can also find specific mutations that help doctors choose targeted treatments.
The Medical Oncologist is the main doctor who plans and coordinates your cancer care. They manage treatments like chemotherapy and immunotherapy. They also work closely with Surgical Oncologists, who remove tumors, and Radiation Oncologists, who use targeted beams, to make sure all aspects of your treatment are covered.
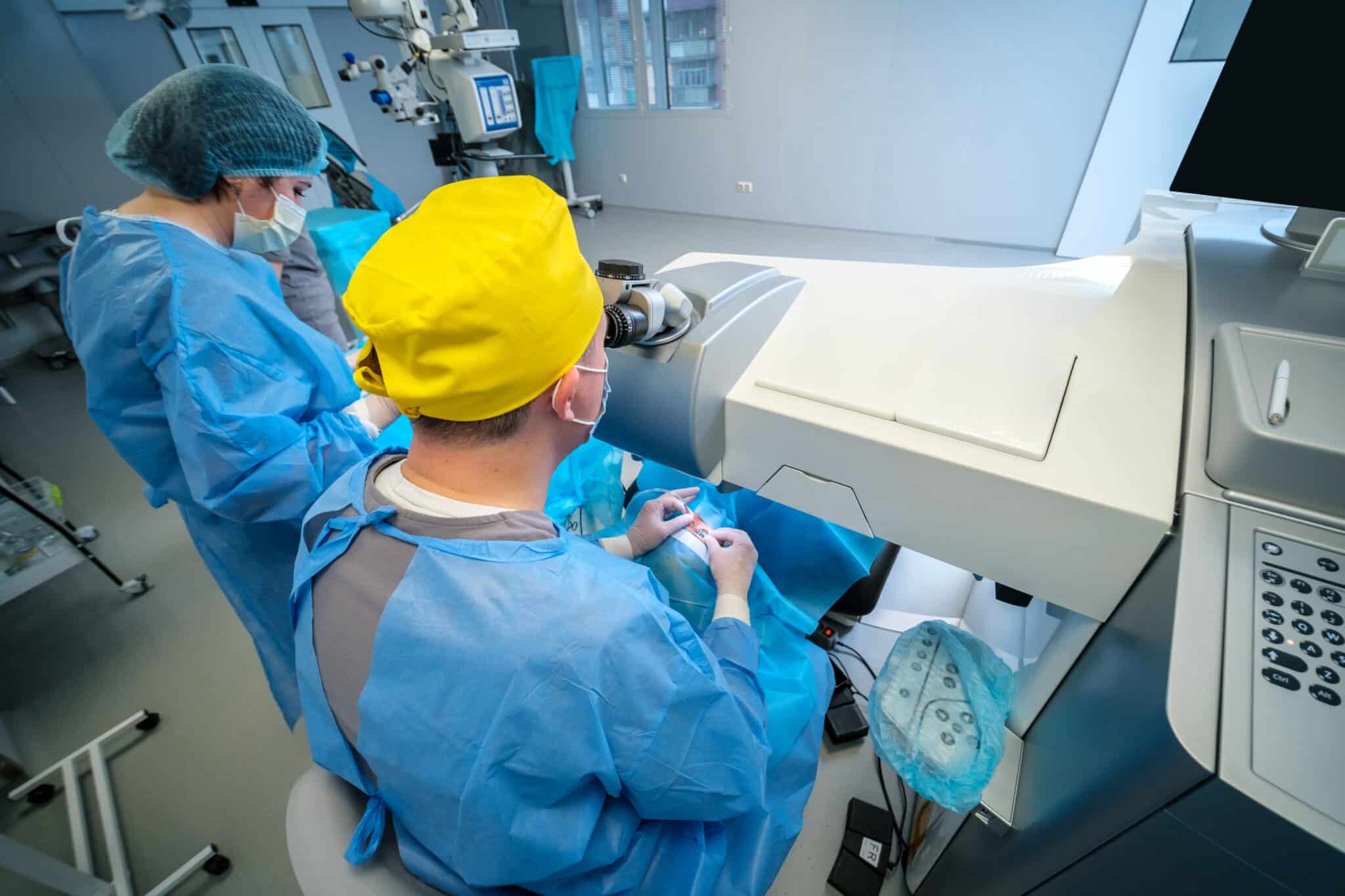
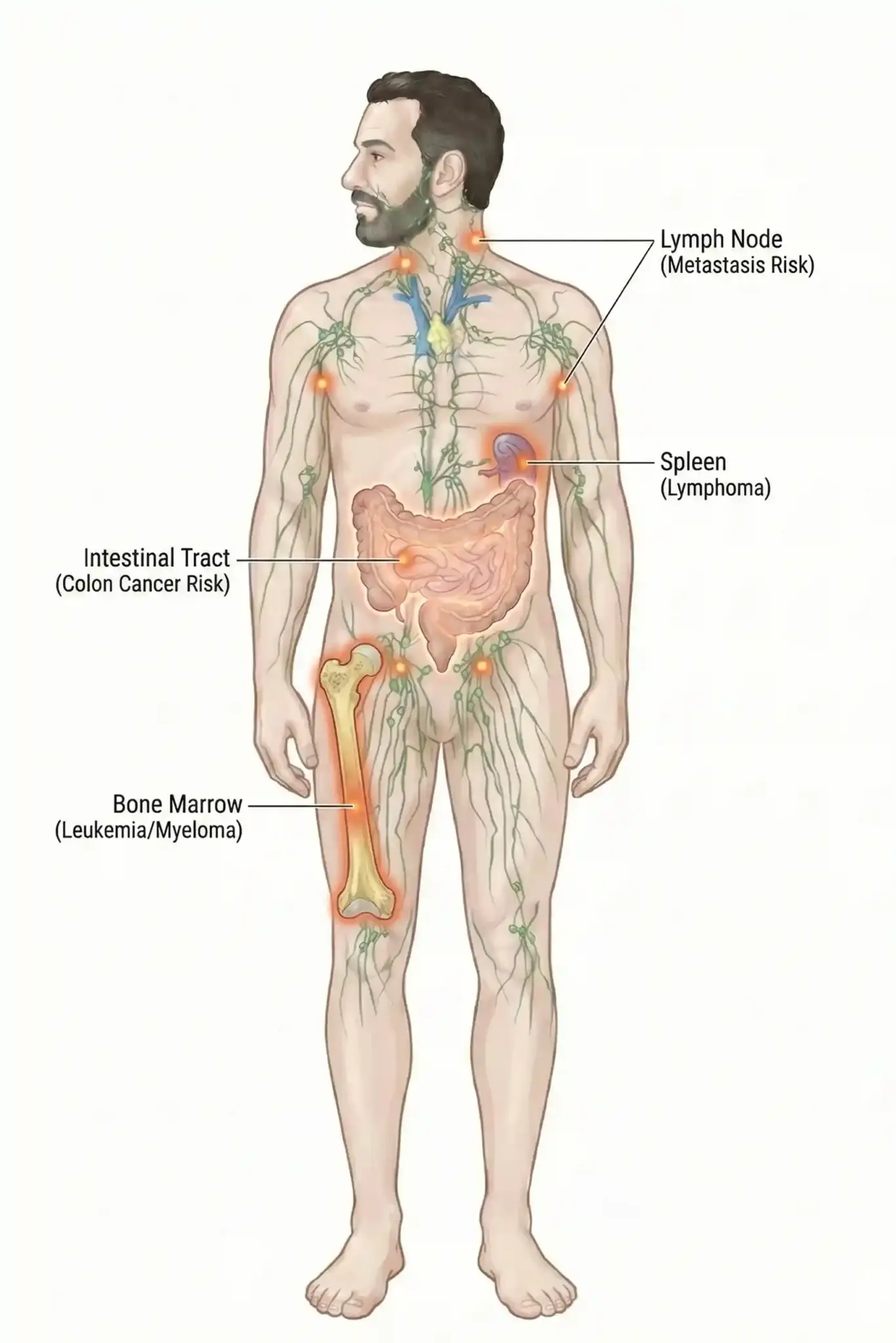

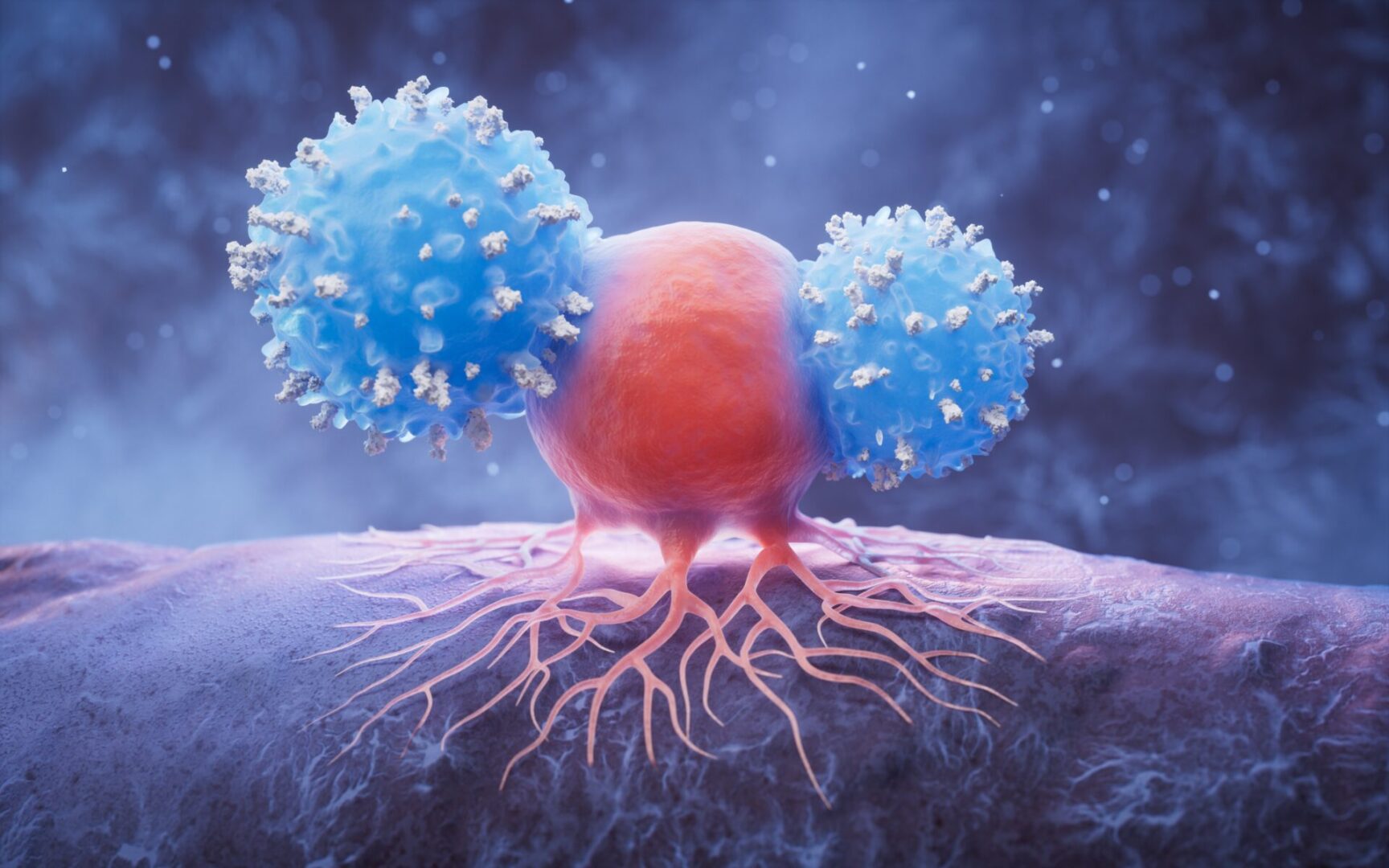
Cancer treatment is now tailored to each person, rather than using the same approach for everyone. Doctors choose treatments based on the tumor’s genetic features. Options include surgery to remove the tumor, radiation therapy, chemotherapy drugs, targeted therapy that blocks certain cancer genes, and immunotherapy to help the immune system fight cancer.
After diagnosis, your case is reviewed by a Tumor Board. Treatment usually follows a sequence, such as starting with therapy to shrink the tumor, then surgery, and finally more therapy to remove any remaining cancer cells. Regular scans check your progress, and supportive care like pain management and nutrition is provided throughout.

In the 21st century, the definition of cancer has evolved to include the tumor’s molecular profile. Genetic mutations drive the disease’s behavior.
Precision medicine involves analyzing tumor DNA to identify specific targets. This allows therapies designed to target cells with those particular mutations.
This approach moves beyond simply knowing the organ of origin. It focuses on the biological pathways that allow the tumor to thrive.
Before starting treatment, patients should talk to their doctor about fertility preservation if it applies to them. Dental check-ups are often recommended. It’s also important to prepare mentally—joining a support group or relying on family support can help. Knowing about possible side effects ahead of time makes them easier to manage.
After treatment ends, the focus turns to regular check-ups to watch for any return of cancer and to manage any long-term side effects. Many people find a new normal, where healthy habits like good nutrition and exercise help prevent cancer from coming back. Our hospital offers ongoing support through survivorship clinics.
Benign tumors are noncancerous growths that do not spread to other parts of the body, whereas malignant tumors are cancerous and have the potential to invade nearby tissues and metastasize.
Specific inherited gene mutations can increase the likelihood of developing particular cancers, but somatic mutations acquired during a lifetime due to environmental factors also play a significant role.
Staging determines the extent of the disease, including tumor size and whether it has spread to lymph nodes or other organs, which is essential for planning the most effective treatment.
Cancers like ovarian or pancreatic are often called silent because they grow and spread without causing specific or noticeable symptoms until they reach an advanced stage.
The lymphatic system serves as a transport network for immune cells, but cancer cells can also use it to spread from the primary tumor site to other parts of the body.


Did you know that traumatic experiences can change the brain’s structure and function? Studies show that people who have gone through trauma might have different





Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)