Most Common Childhood Infections: What Parents Should Know
Parents often worry about their children falling ill frequently. On average, a young child will experience 8 to 10 colds annually. This is because their immune systems are not fully developed yet, and this makes them more vulnerable to childhood infections. Most common childhood infections spread easily in schools, playgrounds, and daycare centers, which is why frequent illnesses are a normal part of early development.
It’s a normal part of growing up to be exposed to many germs. Knowing which childhood infections are common can help parents protect their kids. It also helps them know when to see a doctor.
As caregivers, we aim to give our children the best care. Learning about pediatric infection statistics and common childhood illnesses is key. This knowledge helps us face the challenges of parenting and ensure our kids get the care they need.
Key Takeaways
- Young children are highly susceptible to infections due to their immature immune systems.
- The average child experiences 8 to 10 colds per year.
- Understanding common pediatric infections can help in prevention and treatment.
- Being informed about childhood infection prevalence aids in better childcare.
- Knowledge of pediatric infections supports parents in making informed decisions.
Understanding Childhood Infections
It’s important to know about childhood infections to stop them from spreading. This helps keep kids healthy. These infections are common and can really affect a child’s health.
What Are Childhood Infections?
Childhood infections happen when harmful germs like bacteria, viruses, and fungi grow inside a child. These germs can cause many illnesses, from mild to serious. They can affect different parts of the body.
Common types of childhood infections include respiratory infections, ear infections, skin infections, and gastrointestinal infections. Each one is caused by different germs and shows different symptoms.
How Do Infections Spread Among Children?
Infections can spread among kids in several ways:
- Direct Contact: Touching an infected child or their things.
- Indirect Contact: Touching things that have germs on them.
- Droplet Transmission: Breathing in droplets when someone coughs or sneezes.
- Airborne Spread: Breathing in germs that are floating in the air.
Children are more likely to get infections because their immune systems are not fully grown. They also spend a lot of time together in schools and daycare.
Symptoms to Watch For
Childhood infections can show up in many ways. It’s key to know the signs to look out for. As parents or caregivers, spotting these symptoms early can help get your child the right care fast.
Common Signs of Infection
Common child infections often have symptoms like fever, coughing, runny nose, and rash. These signs can change based on the infection and the child’s health. For example, respiratory infections might cause trouble breathing or a long cough. Gastrointestinal infections could lead to vomiting or diarrhea.
Watch for serious symptoms too. These include high fever lasting days, severe headache, or confusion. Some infections can cause serious problems, like ear infections or skin infections, which need doctor’s care.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If your child has severe symptoms, like difficulty breathing, excessive sleepiness, or refusal to drink fluids, get medical help right away. Also, look out for dehydration signs, like fewer wet diapers or no tears when crying. Medical check-ups are needed then, especially since some childhood infections can worsen quickly if not treated on time.
It can be tough to know when to get help. But, if you’re unsure about your child’s symptoms or health, always talk to a doctor. They can give advice based on your child’s symptoms and medical history. This ensures your child gets the right care and helps prevent complications from childhood infections. Staying informed and seeking help early is one of the best ways to protect children from the risks associated with childhood infections.
Ear Infections: A Frequent Challenge
Ear infections are a common health issue affecting children worldwide. According to pediatric health statistics, ear infections are among the most frequent reasons for doctor visits and are often linked to childhood infections that weaken or irritate the immune system. We will explore the causes and treatment options for ear infections to help parents understand and manage their child’s condition, especially since ear infections are one of the most recognizable childhood infections parents encounter.
What Causes Ear Infections?
Ear infections are often caused by bacteria or viruses. The infection can be triggered by a cold or allergies. This blocks the Eustachian tube, causing fluid buildup in the middle ear. This condition is more common in children because their Eustachian tubes are smaller.
- Colds and respiratory infections
- Allergies
- Anatomical issues, such as a smaller Eustachian tube
- Exposure to smoke
How Are Ear Infections Treated?
Treatment for ear infections typically involves antibiotics to combat bacterial infections, which are a common result of childhood infections that affect the ears and respiratory system. Pain management is also key to alleviate discomfort. In some cases, doctors may recommend waiting to see if the infection resolves on its own before starting antibiotics, especially because many ear problems linked to childhood infections can improve naturally as the immune system responds.
- Antibiotics to treat bacterial infections
- Pain relief medication, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen
- Ear drops to help alleviate pain and inflammation
By understanding the causes and treatment options for ear infections, parents can better manage their child’s condition. They can seek appropriate medical care when needed.
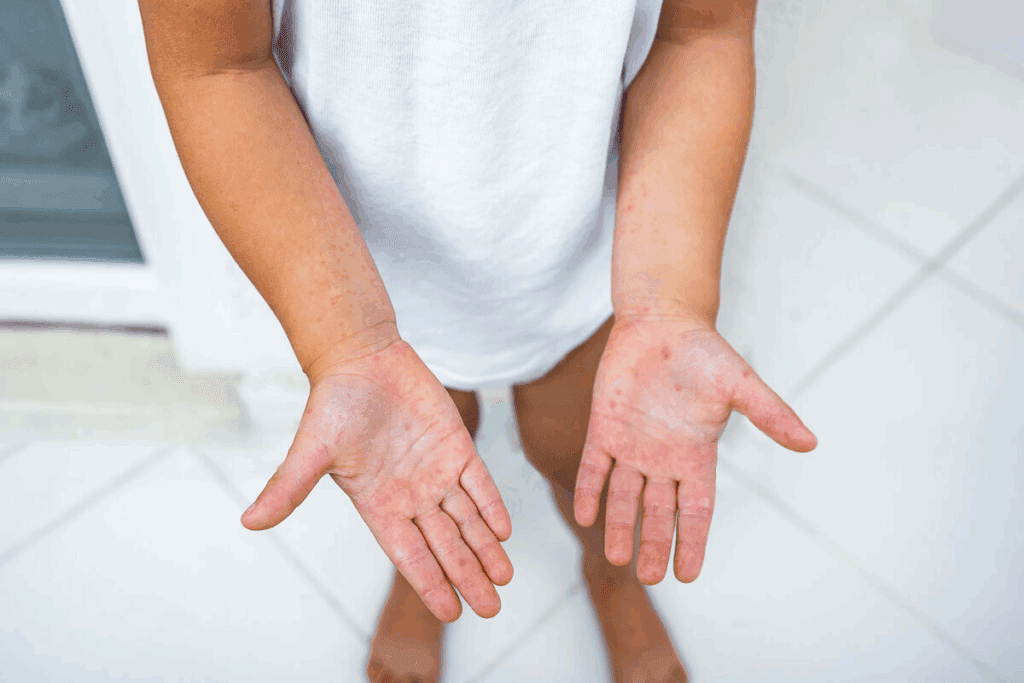
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is a common viral infection that affects children worldwide. It’s important for parents and caregivers to know its symptoms and how to prevent it.
This disease is caused by viruses, like coxsackievirus A or enterovirus 71. It spreads easily through direct contact with an infected person’s:
- Nose and throat secretions
- Saliva
- Fluid from blisters or rash
- Feces
Symptoms of Hand, Foot, and Mouth
The symptoms of hand, foot, and mouth disease can vary. They often include:
- Fever
- Sore throat
- Mouth sores or ulcers
- Rash or blisters on the hands and feet
A pediatric infection survey shows most children with this disease have mild symptoms. But, some may face serious complications like:
- Viral meningitis
- Encephalitis
Prevention Strategies
To prevent hand, foot, and mouth disease, good hygiene is key. We suggest:
- Frequent handwashing with soap and water
- Avoiding close contact with anyone infected
- Cleaning and disinfecting surfaces regularly
- Avoiding sharing utensils, towels, or other personal items
Health experts say, “Good hygiene practices are key to stopping hand, foot, and mouth disease.” By understanding childhood disease patterns and taking steps to prevent it, we can keep our children safe.
The Role of Vaccinations
Vaccines play a key role in keeping children safe from childhood infections. They help lower the number of pediatric disease prevalence. By making sure kids get all their shots, we protect them from serious illnesses and help everyone’s health by reducing the spread of childhood infections.
Essential Vaccines for Children
There are many vaccines that kids need. They protect against serious diseases. Here are some:
- DTaP Vaccine: Keeps kids safe from diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis.
- MMR Vaccine: Stops measles, mumps, and rubella.
- Polio Vaccine: Prevents poliomyelitis.
- Hepatitis B Vaccine: Protects against hepatitis B infection.
- Varicella Vaccine: Stops chickenpox.
Doctors give these vaccines on a schedule. This schedule helps kids stay safe from infection rates children.
How Vaccines Prevent Infections
Vaccines introduce a small piece of a pathogen to the body. This triggers the immune system to make antibodies. These antibodies fight the disease if the child is exposed later, preventing infection. Studies show vaccines have greatly reduced diseases, as seen in childhood infections studies.
A study in a pediatric journal found vaccines cut disease rates by up to 90% in some groups. A health expert said, “Vaccines are a huge step forward in medicine. They save lives and prevent suffering from diseases.” These findings highlight how essential vaccination is in lowering childhood infections and protecting communities. By strengthening immunity early, vaccines continue to reduce the global burden of childhood infections.
“Vaccination is a fundamental right and a key step in protecting not just individual children, but communities as a whole.”
| Vaccine | Disease(s) Prevented | Typical Age of Administration |
| DTaP | Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis | 2, 4, 6, and 15-18 months |
| MMR | Measles, Mumps, Rubella | 12-15 months and 4-6 years |
| Polio | Poliomyelitis | 2, 4, 6-18 months, and 4-6 years |
Stomach Bugs and Gastroenteritis
Gastroenteritis, or a stomach bug, is common in kids all over the world. It causes symptoms like diarrhea, vomiting, and stomach pain. These symptoms are a big worry for parents. We’ll look at the signs of gastroenteritis and how to prevent it.
Common Symptoms of Gastroenteritis
The signs of gastroenteritis can differ but often include:
- Diarrhea, which can cause dehydration if not treated
- Vomiting, which can make dehydration worse
- Stomach cramps or pain
- Fever, though not always there
Spotting these symptoms early is key to managing them well. Pediatric infection research shows early detection can lessen the infection’s impact.
Tips for Prevention
To stop gastroenteritis, keep things clean and avoid being too close to sick people. Here are some good ways to do it:
- Frequent Handwashing: Teach kids to wash their hands with soap and water, after using the bathroom and before eating.
- Avoiding Close Contact: Keep kids away from sick people to stop the infection from spreading.
- Proper Food Handling: Make sure food is handled and cooked right to avoid contamination.
By using these tips and knowing about common pediatric infections, parents can lower their child’s chance of getting gastroenteritis. Looking at kids health data can also help understand and manage gastroenteritis in kids.
Chickenpox and Its Impact
Chickenpox is a common illness in kids that spreads easily. It causes a rash and fever. Knowing how to care for your child with chickenpox is important.
Symptoms of Chickenpox
The first signs of chickenpox are fever, headache, and feeling sick. Then, a rash appears. The rash starts as small, itchy blisters that crust over later. Spotting these signs early helps manage the illness better.
Common symptoms include:
- Fever
- Headache
- Rash with itchy blisters
- Loss of appetite
Managing Chickenpox
When your child gets chickenpox, it’s important to manage symptoms and prevent complications. Keep them comfortable by making sure they drink lots of water and rest. Over-the-counter meds can help with fever and itching.
| Symptom | Management Strategy |
| Fever | Administer acetaminophen (if advised by a doctor) |
| Itching | Use antihistamines or calamine lotion |
| Dehydration | Encourage fluid intake |
By knowing the symptoms and how to manage them, parents can help their child feel better. It’s also important to watch for serious complications and get medical help if needed.
Respiratory Infections: Colds and Flu
Colds and flu are common in kids all over the world. It’s important to know how to tell them apart and how to handle them. Learning about pediatric infectious diseases helps us keep our kids healthy.
Differences Between Cold and Flu
Colds and flu are both caused by viruses, but they’re different. A cold is usually mild, while the flu can be serious and even dangerous for young kids.
Symptoms can help tell them apart. Colds cause a runny nose, sneezing, and a mild cough. The flu, on the other hand, brings high fever, tiredness, and body aches, along with respiratory issues.
| Symptom | Cold | Flu |
| Fever | Rare | Common, can be high |
| Cough | Mild to moderate | Often severe |
| Fatigue | Mild | Significant |
| Body Aches | Mild | Common, often severe |
How to Reduce the Risk of Infection
To lower the risk of respiratory infections, practice good hygiene and make lifestyle changes. For flu, getting vaccinated is key. Washing hands often with soap and water is a top way to stop viruses.
- Encourage kids to wash their hands often, after coughing or sneezing.
- Teach kids not to touch their eyes, nose, and mouth.
- Support a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet and exercise to boost immunity.
- Get vaccinated against flu every year, as doctors advise.
Knowing the difference between colds and flu and taking steps to prevent them can greatly reduce their impact. Staying up-to-date with kids illness statistics and being proactive helps us care for our children better.
Preventing the Spread of Infections
With more kids getting sick, it’s key to know how to stop infections from spreading. We’ve talked about how common childhood illnesses can hurt a child’s health. Simple steps can help keep kids healthy.
Importance of Hygiene Practices
Good hygiene is key to stopping infections. Frequent handwashing is a top way to stop illnesses. Kids should wash their hands with soap and water for 20 seconds. This is important after using the bathroom, before eating, and after blowing their nose, coughing, or sneezing.
Also, teach kids to stay away from sick people. And tell them not to share things like utensils, towels, or drinking glasses. This helps lower the chance of getting sick.
Role of Nutrition and Immune Health
Eating well is important for a strong immune system. Adequate nutrition helps kids fight off sickness better. Foods full of vitamins C and D, zinc, and iron are good for the immune system.
Pediatric health stats show kids who eat right get sick less often. Make sure your child eats a variety of fruits, veggies, whole grains, and lean proteins. This helps their immune system stay strong.
“A healthy diet is key for a strong immune system, which fights off infections.”
– American Academy of Pediatrics
Good hygiene and a healthy diet can greatly lower the chance of infections in kids. This approach not only keeps your child safe but also helps the whole community stay healthy.
- Encourage frequent handwashing with soap and water.
- Teach children to avoid close contact with anyone who is sick.
- Provide a well-balanced diet rich in essential nutrients.
Dental Infections in Children
Keeping teeth clean is key to stop dental infections in kids. These infections come from bacteria and can cause pain and swelling. This can really hurt a child’s life. So, it’s important to take them to the dentist often and teach them to brush their teeth well.
Signs of Dental Issues
Spotting dental problems early is very important. Look out for toothache, sensitivity, and swollen gums or face. Kids might also get upset or eat less because of tooth pain. If you see these signs, don’t wait to see a dentist.
Some common dental problems in kids are:
- Tooth decay
- Gum disease
- Abscesses
These can hurt a lot and get worse if not treated.
Effective Treatment Options
Fixing dental infections in kids needs both dentist visits and home care. First, a dentist will check how bad the infection is.
Treatment might include:
| Treatment | Description |
| Antibiotics | Prescribed to combat bacterial infections |
| Dental Fillings | Used to repair tooth decay |
| Root Canal Therapy | Performed to save a severely infected tooth |
Also, keeping teeth clean at home is very important. This means brushing, flossing, and not eating too much sugar.
Knowing about dental infections helps us protect our kids’ teeth. Regular dentist visits and good oral care at home are the best ways to avoid these problems.
Skin Infections: Impetigo and Beyond
Children are more likely to get skin infections like impetigo because their immune systems are not fully developed. These infections can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. It’s important to know how to manage them.
Causes of Common Skin Infections
Skin infections in kids, like impetigo, are often caused by Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes. These bacteria get into the body through cuts or scrapes. Impetigo is very contagious and can spread easily.
Things like poor hygiene and crowded living can make kids more likely to get skin infections. Spotting the early signs of skin infections is key to stopping them from spreading and getting them treated right away.
Treatment and Prevention
Doctors usually treat skin infections with antibiotics. For impetigo, they might start with a cream, and for worse cases, pills. Keeping the area clean and using warm compresses can also help.
To prevent skin infections, good hygiene is essential. Washing hands often and keeping cuts clean can help a lot. Also, staying away from others with skin infections can stop it from spreading.
By knowing the causes and how to prevent and treat them, we can protect kids from the pain and problems of skin infections like impetigo. Our aim is to give parents the knowledge and tools to keep their child’s skin healthy and free from infections.
Conclusion: Keeping Your Child Healthy
It’s important to know about common childhood infections and how to prevent them. By understanding the symptoms and patterns of these diseases, parents can help keep their kids healthy. This proactive approach can reduce the risk of infections.
Understanding Infection Patterns
Research from pediatric infection surveys reveals that some infections are more common at certain times of the year. Knowing these patterns helps parents and caregivers take the right steps to protect their children.
Resources for Healthy Parenting
There are many resources available for parents and caregivers looking to manage and prevent infections. By staying informed about pediatric disease patterns and prevention, we can all work together. This way, we can ensure children stay healthy and happy.
FAQ
What are the most common childhood infections?
Common childhood infections include ear infections and hand, foot, and mouth disease. Gastroenteritis, chickenpox, and respiratory infections like colds and flu are also common.
How do infections spread among children?
Infections spread through direct and indirect contact, droplets, and airborne ways. Knowing these helps parents prevent them.
What are the common symptoms of childhood infections?
Symptoms include fever, cough, sore throat, and runny nose. Diarrhea, vomiting, and rash are also common. Spotting these early can prevent worse problems.
How can I prevent my child from getting ear infections?
To lower ear infection risk, avoid smoke and get flu and pneumococcus vaccines. Good hygiene is also key.
What is hand, foot, and mouth disease, and how can it be prevented?
Hand, foot, and mouth disease causes mouth sores and rash on hands and feet. Prevent it with good hygiene and avoiding sick kids.
Are vaccinations important in preventing childhood infections?
Yes, vaccines are vital. They protect against serious diseases and stop infections from spreading.
How can I reduce the risk of gastroenteritis in my child?
To lower gastroenteritis risk, wash hands often and ensure food and water safety. Avoid sick people too.
What should I do if my child gets chickenpox?
Keep your child comfy and prevent scratching to avoid infections. Follow your doctor’s advice for symptom management.
How can I differentiate between a cold and flu in my child?
Colds and flu are both respiratory infections. But flu is more severe and can cause complications. Look for high fever, body aches, and fatigue for flu.
What role does nutrition play in preventing infections?
Nutrition is key for a healthy immune system. Eat fruits, veggies, whole grains, and lean proteins to boost immunity and fight infections.
How can I prevent dental infections in my child?
Prevent dental infections with good oral hygiene. Brush and floss regularly, limit sweets, and visit the dentist often.
What are the common skin infections in children, and how can they be treated?
Common skin infections include impetigo, ringworm, and eczema. Treat them with antibiotics, antifungals, or other meds as directed. Good hygiene is also important.
How can I keep my child healthy and reduce the risk of infections?
Keep your child healthy with good hygiene, a balanced diet, and regular vaccines. Stay informed about common infections and how to prevent them.









