
Autoimmune conditions are a wide range of chronic diseases. They happen when the immune system attacks the body’s own tissues. Studies show that about 15 million people in the United States suffer from these diseases.Providing a complete autoimmune disease list of over 50 conditions and a quick guide to their primary characteristics.
It’s hard to spot these diseases because they are so varied. Knowing all the autoimmune disease list is key for doctors and patients. It helps get the right diagnosis and treatment.

Autoimmune diseases are becoming more common worldwide. They happen when the body’s immune system attacks its own cells and tissues. This is due to a mix of genetic, environmental, and immune system issues.
Autoimmune reactions are caused by genetics, environment, and hormones. Genetic predisposition is a big factor, with some genes making you more likely to get an autoimmune disease. Environmental factors like infections and toxins can also start an autoimmune response.
In autoimmune diseases, the immune system gets confused and attacks healthy tissues. This leads to inflammation and damage. For example, in rheumatoid arthritis, the immune system attacks the joints, causing pain and swelling.
Both environment and genetics play a role in autoimmune diseases. Environmental triggers include viruses and certain chemicals. Genetic factors involve genes that can make you more likely to get an autoimmune disease. Knowing these factors helps in finding ways to prevent and treat these diseases.
|
Factor |
Description |
Examples |
|---|---|---|
|
Genetic |
Predisposition due to genetic markers |
HLA genes, CTLA4 |
|
Environmental |
Triggers that can initiate autoimmune responses |
Viral infections, toxins, dietary components |
|
Hormonal |
Influence of hormones on immune function |
Estrogen, testosterone |
The number of people with autoimmune diseases is growing fast. It’s increasing by 19.1 percent every year. This shows we need more research and better treatments for these diseases.
Autoimmune disorders are becoming a big problem for health and research. These diseases affect a lot of people worldwide. It’s estimated that 5 to 10 percent of people in industrial countries have them.
There are over 50 different autoimmune diseases. They are common and affect many people. Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis are among the most common.
Studies show that autoimmune diseases are widespread. For example, about 8% of people in the U.S. have one. This shows we need more research and awareness.
|
Autoimmune Disease |
Estimated Prevalence |
|---|---|
|
Rheumatoid Arthritis |
1% of global population |
|
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) |
20-150 per 100,000 people |
|
Multiple Sclerosis |
2.3 million people worldwide |
Women are more likely to get autoimmune diseases. In fact, 80 percent of cases are in women. This is true for diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus.
“The gender disparity in autoimmune diseases is a critical area of study, as understanding the underlying causes could lead to more targeted and effective treatments.” – Medical Expert, Autoimmune Researcher
This shows we need to study why women get these diseases more. Hormones, genes, and the environment might play a role.
Autoimmune diseases cost a lot to manage. They need long-term care, which is expensive. This includes medicines, hospital stays, and other services.
A study found that these diseases cost a lot more than others. The costs are not just for healthcare but also for families and individuals.
As more people get autoimmune diseases, we must find ways to handle the costs. This is important for healthcare systems and economies everywhere.
It’s important to know the common symptoms of different autoimmune diseases. This helps in early detection and better management. Autoimmune conditions happen when the body’s immune system attacks its own tissues.
Early signs of autoimmune diseases can be hard to spot. They often include fatigue, fever, joint pain, and skin rashes. These symptoms are not specific, making it tough to diagnose early.
Rheumatoid arthritis starts with joint pain and swelling. Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) shows a butterfly-shaped rash on the face, among other signs.
Many autoimmune diseases cause inflammation all over the body. This can lead to muscle pain, swelling, and feeling unwell.
|
Symptom |
Possible Autoimmune Conditions |
|---|---|
|
Joint Pain and Swelling |
Rheumatoid Arthritis, Lupus |
|
Skin Rashes |
Psoriasis, Lupus, Dermatomyositis |
|
Muscle Weakness |
Myasthenia Gravis, Polymyositis |
If you have symptoms that last a long time or are very bad, see a doctor. Early treatment can greatly improve life for those with autoimmune diseases.
If you have chronic fatigue, recurring fevers, or unexplained pain, see a healthcare professional. They can figure out what’s wrong and suggest the right treatment.
Rheumatic and inflammatory autoimmune diseases affect millions worldwide. They happen when the immune system attacks the body’s own tissues. This leads to inflammation and various symptoms.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder. It mainly affects the joints, causing pain, swelling, and damage. It can also harm other body systems like the skin, eyes, and heart.
Early diagnosis and treatment are key. They help prevent long-term damage and improve life quality.
Systemic lupus erythematosus, or lupus, is a complex autoimmune disease. It can affect many organs, including the skin, joints, and kidneys. Symptoms range from mild to severe.
Managing lupus involves medications to control symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
Sjögren’s syndrome mainly affects the glands that produce tears and saliva. This leads to dry eyes and mouth. It can also affect other parts of the body, like the skin and joints.
Treatment aims to relieve symptoms. It may include medications to help with tear and saliva production.
Ankylosing spondylitis is a type of arthritis that mainly affects the spine. It causes inflammation that can lead to severe pain and discomfort. In advanced cases, this can cause the vertebrae to fuse together.
Treatment focuses on reducing symptoms and maintaining mobility.
These diseases show how autoimmune conditions can affect people differently. Understanding them is important for effective management and treatment.
Neurological autoimmune diseases are complex disorders. They happen when the immune system attacks the nervous system by mistake. These diseases can severely affect a person’s quality of life, impacting both the central and peripheral nervous systems.
There are several debilitating conditions in this group. Each has its own unique characteristics and challenges in diagnosis and treatment. It’s important to understand these diseases to develop effective treatments.
Multiple sclerosis is a chronic condition that affects the central nervous system. The immune system attacks the protective covering of nerves. This disrupts communication between the brain and the rest of the body.
Symptoms can vary widely among patients. They may include vision problems, muscle weakness, and coordination issues.
Treatment approaches for multiple sclerosis focus on managing symptoms. They also aim to reduce disease activity and slow disease progression. Disease-modifying therapies are key in managing the disease.
Guillain-Barré Syndrome is an acute condition where the immune system attacks the peripheral nerves. This leads to muscle weakness and sometimes paralysis. It often follows a viral or bacterial infection and can progress rapidly.
The diagnosis of Guillain-Barré Syndrome involves clinical evaluation and nerve conduction studies. Treatment includes plasmapheresis and intravenous immunoglobulin. These treatments aim to reduce the severity and duration of the condition.
Myasthenia Gravis is characterized by muscle weakness and rapid fatigue. It occurs when the immune system disrupts communication between nerves and muscles. Symptoms can include drooping eyelids, double vision, and difficulty swallowing.
Treatment for Myasthenia Gravis often involves medications that improve neuromuscular transmission. It also includes immunosuppressive drugs to reduce antibody production.
Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy (CIDP) is a condition that involves progressive weakness. It affects the myelin sheaths of peripheral nerves due to the immune system’s attack.
The diagnosis of CIDP is based on clinical presentation, electrodiagnostic tests, and sometimes nerve biopsy. Treatment typically involves corticosteroids, plasmapheresis, or intravenous immunoglobulin. These treatments aim to reduce inflammation and modulate the immune response.
Gastrointestinal autoimmune disorders are complex conditions that affect the digestive system. They happen when the immune system mistakenly attacks the gut. This leads to inflammation, damage, and various symptoms.
Celiac disease is an autoimmune reaction to gluten. It damages the small intestine. Symptoms include diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fatigue. A strict gluten-free diet is the main treatment.
Key aspects of celiac disease include:
Crohn’s disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). It can affect any part of the gut. It causes chronic inflammation, leading to symptoms like abdominal pain, diarrhea, and weight loss.
Management strategies for Crohn’s disease include:
Ulcerative colitis is another form of IBD that mainly affects the colon. It causes chronic inflammation and ulcers in the colon lining. Symptoms include bloody stools and urgency.
|
Condition |
Primary Affected Area |
Common Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
|
Celiac Disease |
Small intestine |
Diarrhea, abdominal pain, fatigue |
|
Crohn’s Disease |
Any part of the GI tract |
Abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss |
|
Ulcerative Colitis |
Colon |
Bloody stools, urgency, abdominal pain |
Autoimmune hepatitis is a condition where the immune system attacks the liver. This leads to inflammation and can cause liver damage. Symptoms include jaundice, fatigue, and abdominal discomfort.
Treatment for autoimmune hepatitis typically involves:
When the immune system attacks the endocrine system, it can cause serious health problems. The endocrine system has glands that make hormones. These hormones help control how our body grows, develops, and works.
When the immune system fights these glands, it can mess up hormone production. This leads to different health issues.
Type 1 diabetes happens when the immune system attacks the pancreas’ beta cells. These cells make insulin. Without enough insulin, people need to take insulin shots to control their blood sugar.
It’s important to catch and treat type 1 diabetes early to avoid serious problems.
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes can come on fast. They include feeling very thirsty and tired, and seeing things blurry. Seeing a doctor right away is key to start treatment and avoid serious issues like diabetic ketoacidosis.
Graves’ disease is an autoimmune disorder that makes the thyroid gland produce too many hormones. This is because the immune system makes antibodies that tell the thyroid gland to make more hormones. There are treatments like medicines, radioactive iodine, and surgery.
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an autoimmune condition that affects the thyroid gland. It makes the gland not make enough hormones. Symptoms can start slowly and include feeling very tired, gaining weight, and dry skin.
Addison’s disease is a rare autoimmune condition. It happens when the immune system destroys the adrenal glands. This leads to not enough cortisol and aldosterone hormones. Symptoms include feeling very tired, weak muscles, and skin color changes. Treatment is to replace the missing hormones.
The following table summarizes key aspects of these endocrine system autoimmune conditions:
|
Condition |
Primary Effect |
Common Symptoms |
Treatment Approach |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Type 1 Diabetes |
Insulin deficiency |
Increased thirst, fatigue |
Insulin therapy |
|
Graves’ Disease |
Thyroid hormone overproduction |
Weight loss, anxiety |
Medications, radioactive iodine, surgery |
|
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis |
Thyroid hormone underproduction |
Fatigue, weight gain |
Thyroid hormone replacement |
|
Addison’s Disease |
Cortisol and aldosterone deficiency |
Fatigue, muscle weakness |
Hormone replacement therapy |
It’s important to understand these autoimmune conditions to diagnose and manage them early. Recognizing symptoms and causes helps healthcare providers give the right treatment. This improves patient outcomes.
The skin and connective tissue often face autoimmune attacks, causing many diseases. These diseases can make life hard for those who have them.
There are many autoimmune diseases that affect the skin and connective tissue. Each has its own signs and treatments. Knowing about these diseases helps doctors give better care.
Psoriasis is a long-lasting disease that makes the skin inflamed and grow too fast. This leads to thick, scaly patches on the skin, which can be itchy and sore.
Treatment approaches for psoriasis include creams, light therapy, and medicines. These aim to reduce inflammation and slow skin cell growth.
Scleroderma is an autoimmune disease that makes the connective tissue thick and fibrous. It can also harm internal organs, making it serious.
Scleroderma causes the skin to tighten, joints to hurt, and can affect the stomach. Early diagnosis is key to managing the disease and avoiding serious problems.
Dermatomyositis is an inflammatory disease that causes a rash and muscle weakness. It’s considered an autoimmune disease, but its exact cause is unknown.
Treatment for dermatomyositis usually includes corticosteroids and other medicines to fight inflammation and muscle damage.
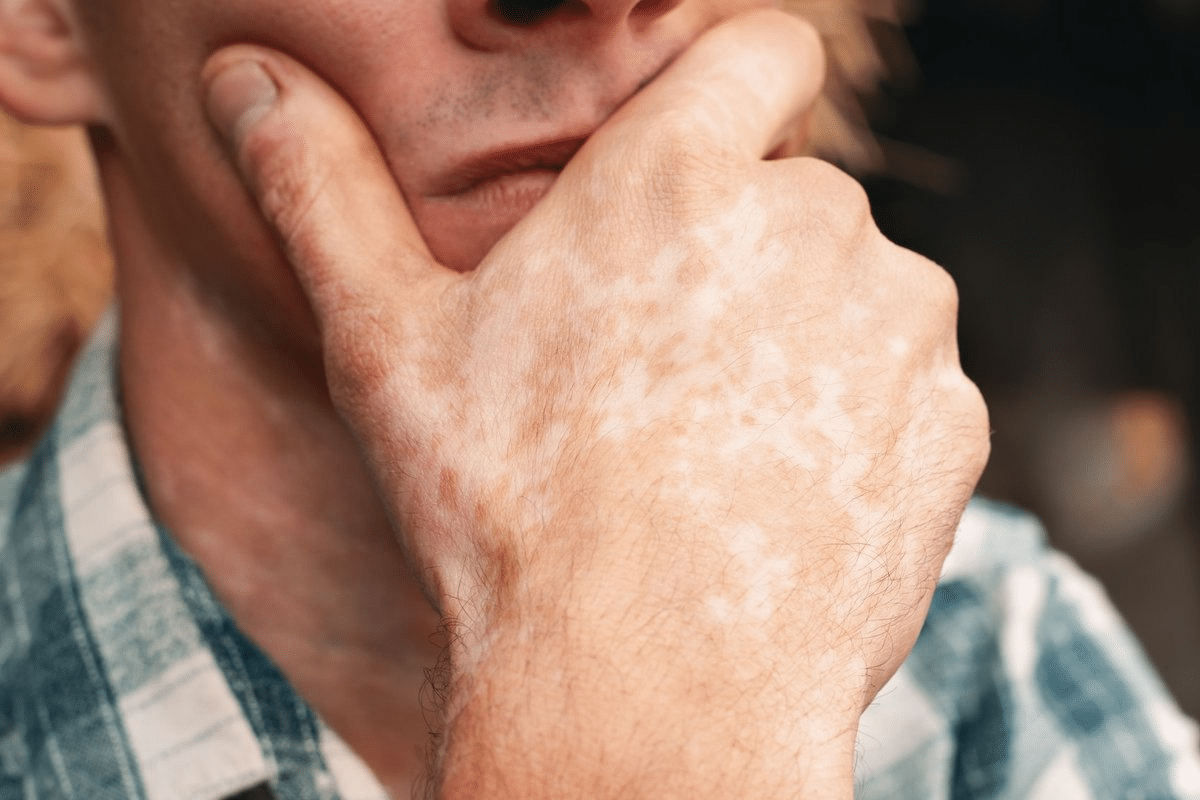
Vitiligo is an autoimmune disease that makes skin lose pigment, causing white patches. It can affect just one area or spread all over.
There’s no cure for vitiligo, but there are ways to manage it. These include creams, light therapy, and skin grafts.
Blood and vascular autoimmune disorders are complex conditions. They can greatly affect patient outcomes if not managed well. These disorders happen when the immune system attacks the body’s own blood vessels and cells.
Autoimmune diseases in the blood and vascular system are hard to diagnose and treat. They show different symptoms and affect the vascular system in complex ways. Healthcare providers need to understand these conditions to manage them effectively.
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is marked by antiphospholipid antibodies and symptoms like thrombosis. APS can cause serious health problems, like recurrent miscarriages or severe blood clots.
Key Features of Antiphospholipid Syndrome:
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA) happens when the immune system attacks the patient’s red blood cells. This leads to severe anemia and needs quick treatment.
Diagnosis of AIHA involves:
Immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) is an autoimmune condition with low platelet count. It can cause bruising, petechiae, and serious bleeding.
|
Condition |
Primary Symptoms |
Diagnostic Tests |
|---|---|---|
|
Antiphospholipid Syndrome |
Thrombosis, recurrent miscarriages |
Antiphospholipid antibody tests, thrombosis history |
|
Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia |
Anemia, jaundice, fatigue |
Direct Coombs test, blood smear, CBC |
|
Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura |
Bruising, petechiae, bleeding |
Platelet count, bone marrow biopsy |
Vasculitis is inflammation of the blood vessels. It can damage the vascular walls and cause problems like aneurysms or organ damage. Vasculitis is linked to many autoimmune conditions.
Managing blood and vascular autoimmune disorders needs a detailed approach. This includes accurate diagnosis, proper treatment, and ongoing monitoring. These steps help prevent complications and improve patient outcomes.
Rare autoimmune diseases affect fewer people but have a big impact on their lives. We need to understand their causes and symptoms better. These diseases are hard to diagnose and treat, needing special care.
Behçet’s disease is a rare condition that causes inflammation in blood vessels. It leads to mouth sores, genital sores, skin rashes, and eye inflammation. The exact cause is unknown, but it’s thought to be a mix of genetics and environment.
Goodpasture syndrome is a very rare autoimmune disorder. It affects the lungs and kidneys. The immune system mistakenly attacks the basement membrane, causing lung bleeding and kidney inflammation. Early treatment is key to managing it.
Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (GPA) is a rare autoimmune disorder. It affects small- and medium-sized blood vessels. It mainly harms the respiratory tract and kidneys, causing inflammation and damage. Treatment includes immunosuppressive medications.
Stiff Person Syndrome (SPS) is a rare neurological disorder. It causes muscles to become stiff and rigid, making it hard to move. It’s believed to be an autoimmune condition, with antibodies attacking nervous system proteins. Medications help manage symptoms and improve life quality.
It’s important to understand rare autoimmune diseases and emerging conditions. This helps us provide the right care and support. More research is needed to find effective treatments and improve patient outcomes.
Medical research has made big strides in diagnosing and treating autoimmune diseases. Finding the right diagnosis can be tough because symptoms can look like other health issues. Doctors use a mix of clinical checks, lab tests, and sometimes biopsies to figure out what’s going on.
It’s hard to diagnose autoimmune diseases because they can show up in many ways. Laboratory tests, like blood tests for autoantibodies, are key. For example, tests for antinuclear antibodies (ANA) help spot systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
New discoveries in genetics and molecular diagnostics have helped us understand these diseases better. Genetic testing can show if someone is more likely to get certain autoimmune diseases. This means doctors can start treatment early.
|
Diagnostic Tool |
Description |
Common Autoimmune Diseases Diagnosed |
|---|---|---|
|
Blood Tests |
Detect autoantibodies and inflammatory markers |
Rheumatoid Arthritis, SLE |
|
Biopsy |
Examine tissue for inflammation or damage |
Celiac Disease, Autoimmune Hepatitis |
|
Genetic Testing |
Identify genetic predispositions |
Type 1 Diabetes, Rheumatoid Arthritis |
Treatment for autoimmune diseases usually includes medicines and lifestyle changes. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and corticosteroids help lower inflammation.
There’s always new research into autoimmune diseases. Biologic therapies target the immune system and have helped with conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis.
The future looks bright with personalized medicine and new treatments. Stem cell therapy and gene therapy might offer new ways to treat these diseases soon.
Living with autoimmune diseases needs a full plan. This includes medical care, lifestyle changes, and support. It’s important to understand and manage these diseases to improve life quality.
Managing autoimmune diseases well means following treatments, eating right, and staying active. Education and support for patients are also key. They help people deal with their conditions better.
More research on autoimmune diseases is vital for better care. Understanding these conditions helps doctors find better treatments. This leads to better care for patients.
By taking a whole-person approach to autoimmune diseases, people can face their challenges. This way, they can improve their well-being and life quality through effective disease management.
Autoimmune diseases happen when the body’s immune system attacks itself. This can affect different parts of the body. There are over 50 known types.
Autoimmune reactions come from genetics, environment, and hormones. These factors lead to an immune system that doesn’t work right.
Common diseases include Rheumatoid Arthritis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). Type 1 Diabetes, Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis, and Psoriasis are also common.
Symptoms vary but often include fatigue and joint pain. Skin rashes and gastrointestinal issues are also common.
Doctors use medical history, physical exams, and lab tests to diagnose. Imaging studies may also be used.
Treatments include medicines to reduce inflammation and lifestyle changes. Alternative therapies help manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
While some can be managed well, a cure is rare. Treatment aims to control symptoms and prevent complications.
Yes, rare diseases include Behçet’s Disease and Goodpasture Syndrome. Stiff Person Syndrome is another rare one, needing special care.
These diseases can greatly affect life, causing chronic symptoms and disability. But, with proper care, many people can stay active.
Autoimmune diseases are costly for healthcare systems. This includes medication, hospital stays, and lost work time.
Yes, new treatments like biologics and gene therapy are being researched. They offer hope for managing these diseases.
Managing it requires a whole approach. This includes taking medicine, making lifestyle changes, managing stress, and seeing doctors regularly.
Common diseases include Rheumatoid Arthritis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). Sjögren’s Syndrome and Ankylosing Spondylitis are also common.
Neurological diseases include Multiple Sclerosis and Guillain-Barré Syndrome. Myasthenia Gravis and Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy are examples too.
Gastrointestinal disorders include Celiac Disease and Crohn’s Disease. Ulcerative Colitis and Autoimmune Hepatitis are also part of this group.
Government Health Resource. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://www.jci.org/articles/view/178722/ga
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!