Gout can cause severe pain in joints, lasting about seven days without treatment. Knowing how to use NSAIDs like ibuprofen safely can greatly improve your life.nsaids and goutShoulder Pain and bursitis and shoulder Explained
At Liv Hospital, we offer expert care and tailored treatment for gout. NSAIDs are a key part of treating gout quickly, easing pain and swelling.
We know how important it is to use NSAIDs right to ease gout symptoms. By learning how to use these drugs safely, you can manage your gout better and feel better overall.
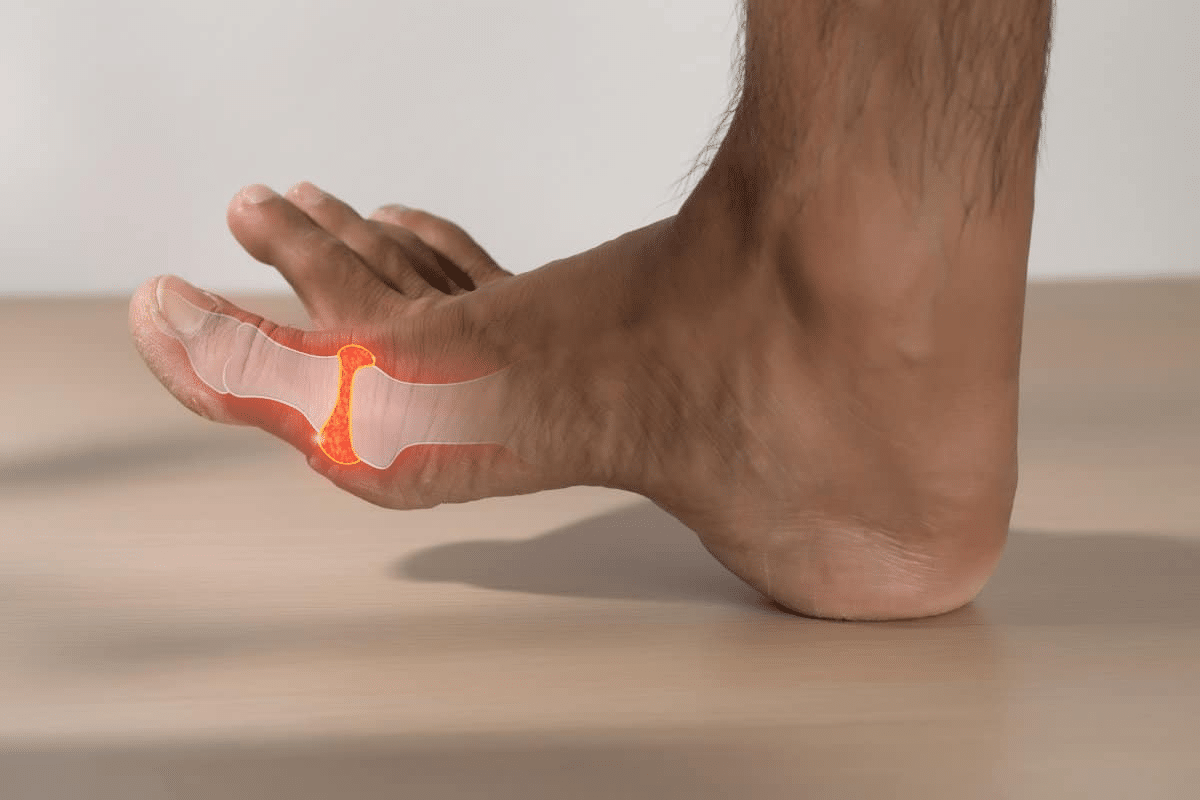
It’s important to know about gout and its painful attacks to manage them well. Gout is a type of arthritis that causes sudden, severe pain and swelling in one or more joints. It often affects the big toe.
Gout happens when there’s too much uric acid in the blood. This excess uric acid forms sharp crystals in joints or tissues. These crystals cause pain, inflammation, and swelling.
Uric acid buildup can come from making too much uric acid or not getting rid of it well enough. Many things can raise your risk of getting gout, like your genes, diet, being overweight, and certain health conditions. Eating foods high in purines, like red meat and seafood, can also lead to more uric acid.
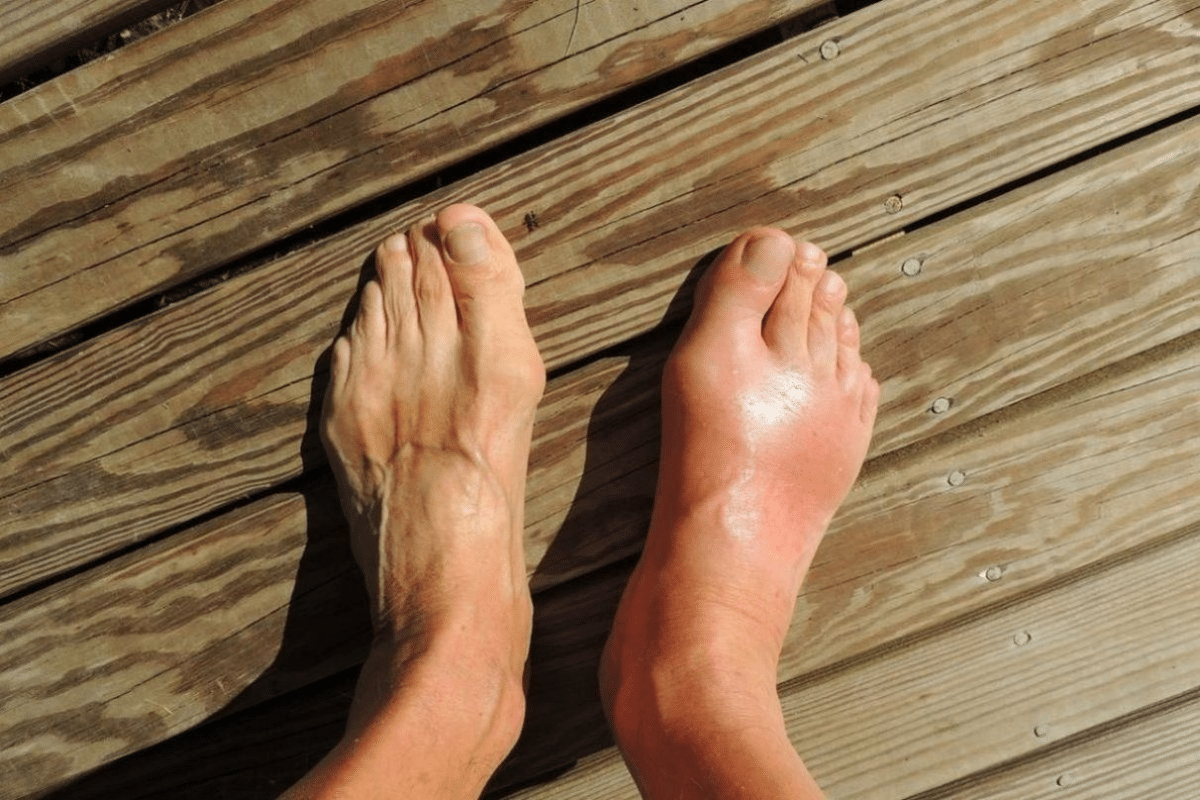
A gout flare can start suddenly and usually affects one joint, but can hit multiple joints too. You’ll know it’s happening if you feel intense pain, see redness, swelling, and warmth around the joint.
The pain from a gout flare is very intense and feels like a burning or pressure feeling. Spotting these signs early is key to getting the right treatment and feeling better fast.
It’s vital to treat a gout flare quickly to ease pain, reduce swelling, and protect the joint from damage. Waiting too long can make the pain last longer and increase the risk of serious problems.
Starting treatment early can also help stop future gout attacks by keeping uric acid levels in check. Good treatment plans can greatly improve life for people with gout.
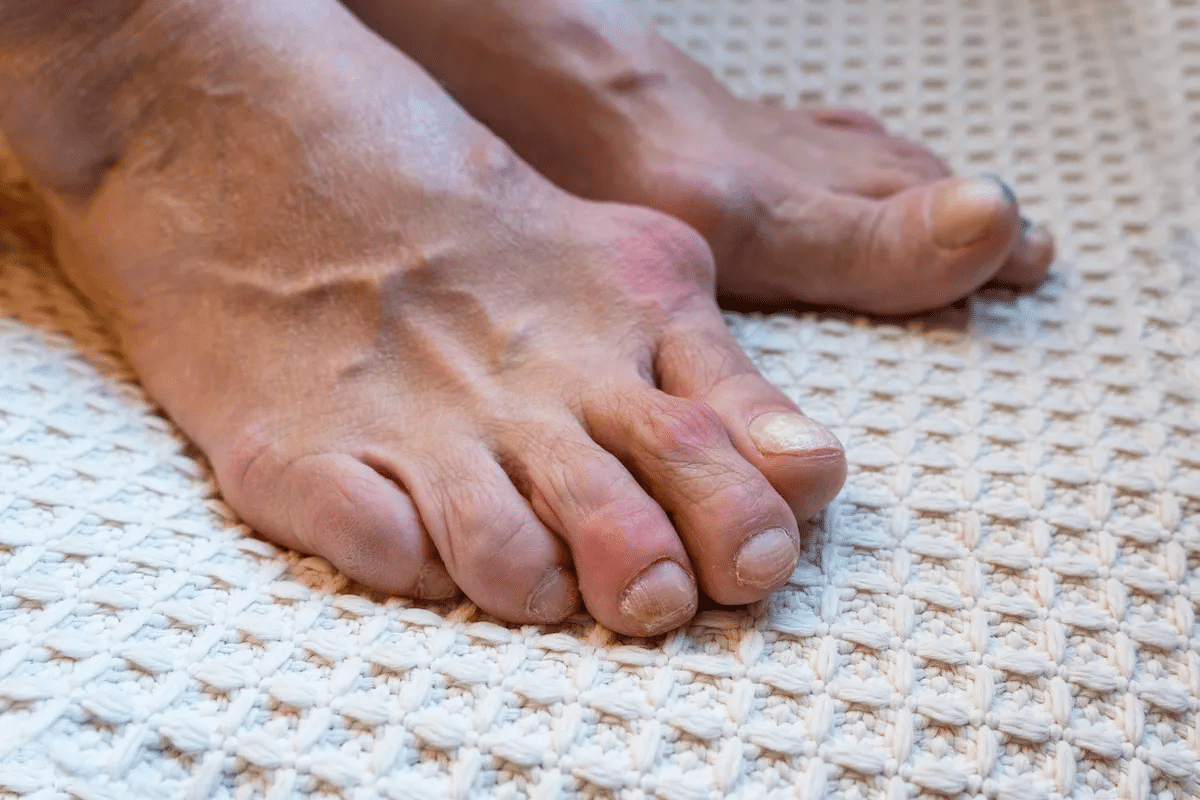
NSAIDs are a strong solution for gout pain relief. Gout is a type of arthritis that causes sudden, severe pain and swelling in joints. NSAIDs are key in treating gout attacks because they reduce inflammation.
NSAIDs block the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX), which makes prostaglandins. Prostaglandins cause inflammation and pain. By stopping their production, NSAIDs lessen gout’s pain and swelling.
Key benefits of NSAIDs for gout include:
Many studies show NSAIDs are effective against gout attacks. They offer pain relief similar to glucocorticoids. This makes NSAIDs a top choice for treating gout.
Clinical evidence supporting NSAIDs includes:
NSAIDs are often preferred over other gout treatments like colchicine and corticosteroids. They work fast and are effective. But, the best treatment depends on the patient’s health and how they react to side effects.
A comparison of gout treatments reveals:
|
Treatment |
Onset of Action |
Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
|
NSAIDs |
Rapid |
Gastrointestinal risks |
|
Colchicine |
Moderate |
Gastrointestinal side effects |
|
Corticosteroids |
Rapid |
Systemic side effects |
Several NSAIDs are good for managing gout. The right choice depends on how bad the symptoms are, the patient’s health, and possible side effects.
Ibuprofen is a top pick for gout relief. It’s easy to find over-the-counter and works well to reduce inflammation. Studies show it can cut down on pain and swelling from gout attacks. But, it’s key to take it as directed and talk to a doctor to avoid side effects.
For gout attacks, taking ibuprofen at the highest dose is best. This helps symptoms go away fast and improves life quality. Starting treatment within 24 hours of symptoms is best for results.
Naproxen is another NSAID used for gout. It lasts longer in the body than ibuprofen, giving longer relief. Naproxen works well for those needing ongoing anti-inflammatory help. Like ibuprofen, it should be used with a doctor’s advice to avoid risks.
Research backs naproxen for gout attacks. It greatly reduces pain and swelling, helping patients feel better. You can get naproxen by prescription or over-the-counter, giving patients options.
For really bad gout, stronger NSAIDs might be needed. These are more potent and work better for those not helped by over-the-counter meds. These stronger NSAIDs are usually used for short periods during attacks, as they can have more side effects.
Examples include indomethacin and celecoxib. Doctors pick these based on how well they work, the patient’s health, and other meds they take. It’s important for patients to work with their doctors to find the best treatment.
In summary, many NSAIDs can help with gout, giving patients choices. Knowing about these options helps doctors create treatment plans that fit each patient’s needs.
Many people wonder if ibuprofen can help with gout. Gout is a type of arthritis that causes sudden, severe pain and swelling. Ibuprofen, an NSAID, is often used to ease these symptoms.
Studies show that ibuprofen can manage gout symptoms well. Clinical studies have shown it reduces pain and swelling. For example, a study in a medical journal found ibuprofen improved pain scores in gout patients.
The time it takes for ibuprofen to work can vary. Ibuprofen starts to work in 30 minutes to an hour. The full effect is seen in 2-3 hours. It’s important to take the right dose to get the best results and avoid side effects.
Ibuprofen works well for many, but not all gout cases. For severe attacks, other treatments may be needed. This could include other NSAIDs, colchicine, or corticosteroids. Some people may need to use ibuprofen carefully or avoid it due to health conditions or medications.
In summary, ibuprofen can help with gout by reducing pain and inflammation. But, it’s important to know its limits, mainly for severe cases, to manage gout effectively.
NSAIDs are key in treating gout flares. Their success depends on quick use. We’ll cover how to use NSAIDs for gout, focusing on when to start, how much to take, and for how long.
For NSAIDs to work best, start them within 24 hours of symptoms. Early action can lessen flare severity and duration. Waiting too long can make symptoms worse and last longer.
To tackle a gout flare, use NSAIDs at their highest dose. For instance, ibuprofen can be up to 800 mg three to four times a day. The right dose depends on the NSAID, your health, and how well your kidneys and stomach handle it.
NSAIDs for gout flares usually last from a few days to a week. It’s important to find the right balance between pain relief and avoiding NSAID side effects like stomach problems.
|
Aspect |
Recommendation |
|---|---|
|
Timing of Treatment |
Start within 24 hours of symptom onset |
|
Dosing Strategy |
Maximum anti-inflammatory dose |
|
Treatment Duration |
Until flare resolves, typically 3-7 days |
By sticking to these NSAID use tips, you can better manage your gout symptoms. It’s important to work with your doctor to find the best treatment for you.
NSAIDs are good for managing gout symptoms. But, they have risks that need attention. It’s important to watch for these risks to avoid problems.
When you take NSAIDs, watch out for stomach upset, nausea, and dizziness. It’s key to keep an eye on these side effects to stop them from getting worse.
NSAIDs can cause stomach problems like ulcers and bleeding. Using proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) can help lower these risks.
|
Gastrointestinal Risk Factors |
Protective Measures |
|---|---|
|
History of ulcers or gastrointestinal bleeding |
Use of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) |
|
Concomitant use of corticosteroids or anticoagulants |
Consider alternative therapies or gastroprotective agents |
|
Age over 65 |
Lower doses or alternative treatments |
NSAIDs can harm the kidneys, more so in those with kidney disease. It’s vital to check kidney function regularly, even with long-term use.
Some people should not take NSAIDs because of health risks. This includes those with severe kidney disease, a history of NSAID-induced asthma, and active peptic ulcers.
Knowing these safety tips helps both patients and doctors decide if NSAIDs are right for managing gout.
NSAIDs are often used to help with gout pain. But, they can also raise concerns about heart health. It’s important to look at the latest studies and guidelines on this topic.
Recent studies have looked into the heart risks of NSAIDs in gout patients. They found that some NSAIDs might increase the chance of heart attacks and strokes. This is more likely in people who already have heart problems.
A study in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology found a link. It said NSAIDs could raise heart event risks in gout patients, even more so for those with heart disease history.
“The cardiovascular safety profile of NSAIDs is a critical consideration for gout patients, particularlly those with cardiovascular risk factors.”
– Medical Expert, Cardiologist
Not all NSAIDs are the same when it comes to heart risks. Some might be safer than others.
|
NSAID |
Cardiovascular Risk Level |
|---|---|
|
Ibuprofen |
Moderate |
|
Naproxen |
Lower |
|
Indomethacin |
Higher |
The table shows naproxen might have a lower heart risk compared to others like indomethacin.
For those with heart issues, using NSAIDs for gout needs extra care. Always talk to a doctor to find the safest option.
People with heart conditions should watch for signs of heart problems. This includes chest pain or trouble breathing while taking NSAIDs for gout.
Knowing the heart safety of NSAIDs and taking the right steps can help gout patients. They can manage their condition without risking their heart health.
Finding the safest gout medication means looking at each patient’s unique needs and risks. Gout is a complex condition that needs a personalized management plan. This plan considers many factors, like other health issues, medication interactions, and the patient’s health history.
It’s important to do a personalized risk assessment for each patient. This means looking at the patient’s overall health, including any existing conditions. For example, patients with a history of bleeding in the stomach should avoid certain NSAIDs that could make this risk worse.
It’s key to find a balance between how well a treatment works and its safety. While NSAIDs are good for quick gout attacks, they can have long-term risks, like for those with certain health issues. So, it’s important to weigh the good against the bad and choose other treatments when needed.
Key considerations include:
The way we treat gout changes depending on if it’s for a quick attack or long-term. For quick attacks, NSAIDs are often safe and effective when used right. But for long-term, we focus on lowering uric acid levels and making lifestyle changes to prevent future attacks.
It’s important to teach patients about:
Managing gout often requires a multi-step approach. Using NSAIDs with other treatments helps to reduce symptoms and prevent future attacks. We’ll look at how NSAIDs can be paired with other medications for better gout management.
Colchicine is a common gout treatment. Combining NSAIDs with colchicine can be more effective for some. But, it’s important to watch for side effects like stomach problems. Adjusting dosages based on patient response is key to balance benefits and risks.
Corticosteroids are strong anti-inflammatory drugs for gout attacks. Sometimes, NSAIDs and corticosteroids are used together for severe flares. This combo can offer quick relief, but considering the patient’s health and possible risks is vital.
Combining NSAIDs with other treatments like colchicine or corticosteroids raises drug interaction risks. Knowing these interactions is critical for safe treatment. For instance, NSAIDs can affect blood thinners and increase bleeding risk. Healthcare providers must closely watch patients on these combinations to avoid problems.
Uric acid lowering medications are key in managing gout long-term. NSAIDs help with sudden attacks, but these meds tackle the root cause. They lower uric acid levels in the blood.
Uric acid treatment tablets, like allopurinol and febuxostat, work by blocking uric acid production. They are vital for stopping gout attacks from coming back and for managing chronic gout.
Allopurinol starts at a low dose and goes up as needed. Febuxostat is a good choice for those who can’t take allopurinol.
Starting uric acid therapy is advised for those with frequent gout attacks, tophaceous gout, or kidney disease. The choice depends on the patient’s specific needs and risks.
Talking to your doctor about the pros and cons of these meds is important. They can help decide what’s best for you.
Checking serum urate levels regularly is key to seeing if the therapy is working. The goal is to keep levels under 6 mg/dL.
Medication doses might need to change based on how well you’re doing with the treatment.
|
Medication |
Starting Dose |
Target Serum Urate Level |
|---|---|---|
|
Allopurinol |
100 mg daily |
< 6 mg/dL |
|
Febuxostat |
40 mg daily |
< 6 mg/dL |
Using uric acid lowering meds wisely can greatly help manage gout. It can also cut down on how often gout attacks happen.
To prevent gout attacks, understanding medication and lifestyle changes is key. Gout prevention goes beyond just treating symptoms. It’s about reducing flare-ups through a complete approach.
Effective gout management needs long-term medication plans. Uric acid-lowering therapy (UALT) is a mainstay in preventing gout attacks. Drugs like allopurinol and febuxostat lower blood uric acid levels. This stops urate crystals from forming, which cause gout.
We suggest patients work with their healthcare provider to find the right medication. It’s important to regularly check uric acid levels and adjust medications as needed.
Diet is a big part of managing gout. Some foods can trigger attacks, while others can help prevent them. Dietary modifications are key to a gout prevention plan.
Making these dietary changes can greatly help manage gout. We recommend patients talk to a dietitian or healthcare provider to create a personalized diet plan.
Other lifestyle factors also play a role in managing gout. Maintaining a healthy weight is important, as extra weight can raise uric acid levels. Regular exercise improves health and lowers the risk of other conditions.
Also, cutting down on alcohol, like beer and liquor, can prevent gout attacks. We advise patients to be aware of these lifestyle factors and make necessary changes to support their medication.
Combining long-term medication, dietary changes, and lifestyle adjustments can effectively manage gout. We are dedicated to helping our patients through every step of their gout management journey.
We’ve looked at how NSAIDs help manage gout attacks. They quickly reduce pain and swelling. Knowing how to use them safely is key to handling gout flares.
Managing gout goes beyond just NSAIDs. It also includes lifestyle changes and sometimes lowering uric acid levels. It’s important to find the right balance between treatment and safety for each person.
Using NSAIDs with other treatments and making smart lifestyle choices can help. This approach can make gout attacks less frequent and less severe. We suggest working with your doctor to create a personalized plan.
With the right strategy, you can control your gout better. This improves your life quality. Effective management is essential for living well with gout.
Advil, or ibuprofen, is often used to ease gout symptoms. It works by reducing inflammation and pain. But, always follow the dosage and talk to a doctor, even if you have other health issues or take other meds.
The safest gout medication depends on your health and how severe your gout is. NSAIDs are good for quick relief, but for long-term, uric acid lowering meds might be better. A doctor will choose the best option for you.
Yes, you can take ibuprofen for gout. It’s good at easing pain and swelling. Just remember to follow the dosage and watch out for side effects, mainly with long-term or high doses.
For gout, NSAIDs like ibuprofen or naproxen are usually the best. They help reduce pain and swelling. If NSAIDs don’t work, colchicine or corticosteroids might be suggested.
NSAIDs block enzymes that cause inflammation and pain. This helps relieve symptoms during a gout attack. They’re often the first choice for treating acute gout.
NSAIDs can cause stomach problems, kidney issues, and heart risks. Always talk to a doctor about these risks, even if you have other health conditions.
NSAIDs are usually for short-term use during gout attacks. For long-term, uric acid lowering therapy is often recommended. But, some might need to keep taking NSAIDs under a doctor’s watch.
Uric acid lowering meds help prevent gout attacks by lowering blood uric acid levels. They’re for long-term management and can greatly reduce flare-ups.
Preventing gout involves medication, diet changes, and lifestyle tweaks. Uric acid meds, avoiding certain foods and drinks, staying hydrated, and keeping a healthy weight are key.
Yes, NSAIDs can interact with other gout meds like colchicine or corticosteroids. Always tell your doctor about all your meds to avoid bad interactions.
To manage gout, try dietary changes, like eating less of certain foods and drinking less alcohol. Stay hydrated, exercise, and keep a healthy weight. These can help with medication and reduce attacks.
Starting uric acid therapy depends on how often and severe your gout attacks are, and your health. A doctor will decide when to start based on your specific situation.
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8656463/
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!