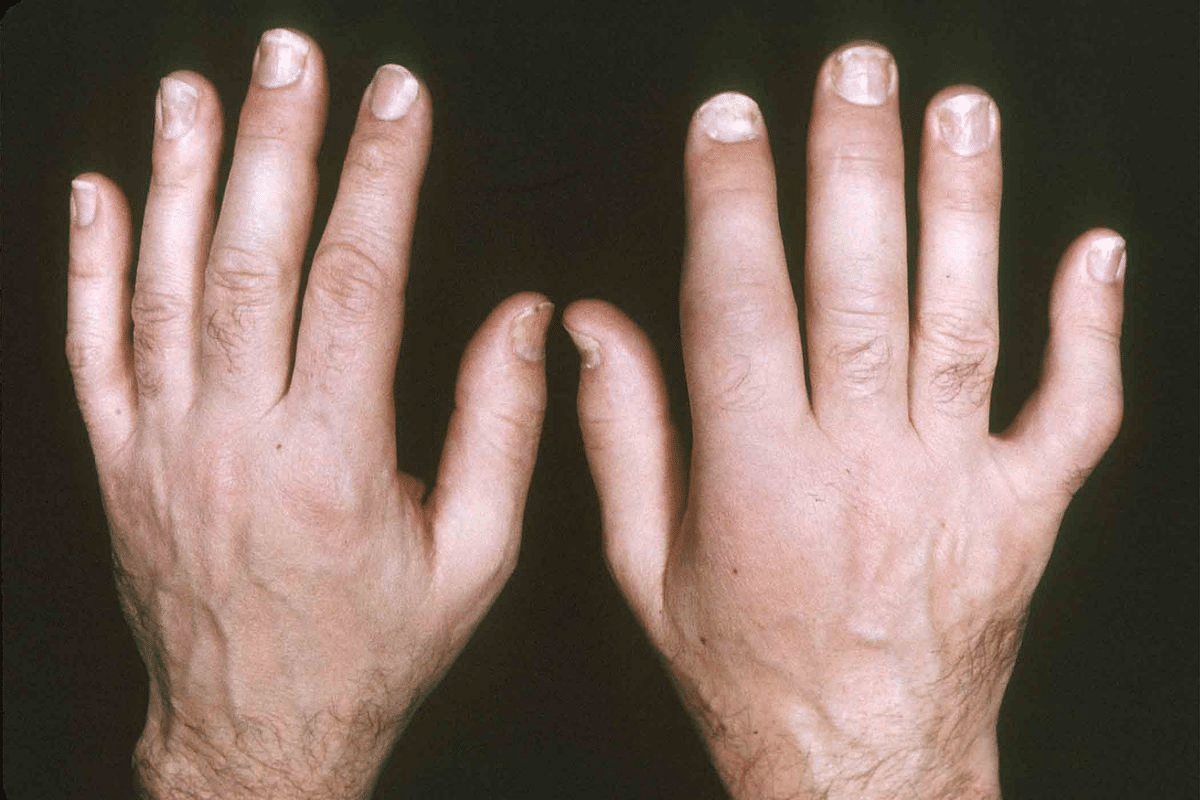
Arthritis is a chronic condition that affects millions globally. It’s often linked to joint pain, but muscle aches and pain are also common. At Liv Hospital, we focus on treating the complex link between arthritis and muscle issues.can arthritis cause muscle achesArthritis In Fingers And Hands
Studies show that arthritis can cause muscle aches and pain. This happens through inflammation and muscle weakening from lack of use. Knowing this helps manage both joint and muscle symptoms better.
It’s important to understand arthritis to manage its effects on daily life. It affects nearly 40 million Americans. Arthritis is not just one disease but over 100 conditions that impact joints and tissues.
Arthritis causes inflammation and pain in the joints. This leads to stiffness, swelling, and less mobility. It gets more common with age, affecting people of all ages.
Recent stats show nearly 1 in 5 adults in the U.S. has arthritis. Osteoarthritis is one of the most common types.
Key statistics on arthritis prevalence include:
The most common types of arthritis include:
Each type of arthritis has its own symptoms and affects different parts of the body.
The main symptoms of arthritis include joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and less range of motion. The areas affected vary by type of arthritis. For example, osteoarthritis often hits the hips, knees, and spine. Rheumatoid arthritis can affect many joints at once.
Common symptoms and affected areas:
It’s important to understand how joints and muscles work together. This is key to seeing how arthritis affects our bodies. The musculoskeletal system is a complex network of joints, muscles, and bones. It helps us move and stay upright.
The musculoskeletal system is a delicate balance of bones, joints, and muscles. Joints connect bones, allowing for movement. Muscles make movement happen by contracting and relaxing.
When a muscle contracts, it pulls on tendons, moving the joint. This system is supported by nerves that control muscle movement. Any problem, like arthritis, can cause pain and make it hard to move.
The relationship between joints and muscles is key to understanding arthritis. Joints provide structure, while muscles move us. Arthritis in a joint can cause inflammation, pain, and less mobility. This can also affect the muscles around it.
In conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, joint inflammation can weaken muscles. This is due to direct effects of inflammation on muscles and less mobility.
Arthritis in a joint doesn’t just affect the joint. It can also harm the muscles around it. Inflammation and pain can cause muscle spasms and tightness. The body tries to protect the joint by tightening muscles.
|
Effect on Muscles |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Muscle Spasms |
Involuntary contractions of muscles around the affected joint, leading to pain and stiffness. |
|
Muscle Weakness |
Reduced strength in muscles due to pain, inflammation, and reduced mobility. |
|
Muscle Wasting |
Loss of muscle mass due to chronic inflammation and reduced use of the affected limb. |
It’s vital to understand these connections for effective treatment. Treating not just the joint but also the muscles can improve outcomes for those with arthritis.
Arthritis can cause more than just joint pain. It can also affect muscles, leading to aches and pain. This is because arthritis can spread beyond the joints, impacting the whole musculoskeletal system.
Arthritis can harm muscles in two ways. Directly, it can cause inflammation that affects muscles. Indirectly, it can lead to muscle strain and weakness due to pain and reduced mobility.
Direct Effects: Inflammatory arthritis, like rheumatoid arthritis, can directly harm muscles. This is because it releases inflammatory cytokines that cause pain and weakness.
Indirect Effects: Arthritis can also cause muscle atrophy and increased pain sensitivity. This is because patients often have reduced mobility.
Research shows a strong link between arthritis and muscle pain. Studies found that people with rheumatoid arthritis have higher pain sensitivity and weaker muscles than healthy individuals.
“Patients with rheumatoid arthritis often report muscle pain and weakness, highlighting the complex interplay between joint inflammation and muscle health.”
— Medical Expert, Rheumatologist
|
Study |
Findings |
|---|---|
|
Research on Rheumatoid Arthritis |
Higher pressure pain sensitivity and reduced muscular strength in patients |
|
Osteoarthritis Study |
Compensatory muscle strain around affected joints, leading to muscle pain |
Many people with arthritis experience muscle aches and pain. This greatly affects their quality of life. A large number of patients with arthritis have muscle-related symptoms.
Understanding the link between arthritis and muscle pain helps healthcare providers. They can create better treatment plans that address both joint and muscle health.
Arthritis and muscle pain are linked by inflammation. Arthritis causes joint inflammation, but it also affects muscles. This leads to pain and discomfort.
Arthritis flare-ups lead to the production of inflammatory proteins. These proteins break down muscle proteins. This can cause muscle wasting, leading to weakness and pain.
Inflammatory cytokines are key in this process. Cytokines are proteins that cells release. In arthritis, they increase inflammation and muscle pain.
“The production of pro-inflammatory cytokines is a hallmark of arthritic conditions, and these molecules can directly influence muscle metabolism, leading to muscle wasting and pain.”
Cytokines like TNF-alpha and IL-6 are high in arthritis. They cause muscle breakdown by degrading muscle proteins.
Systemic inflammation in arthritis harms skeletal muscle. It causes muscle protein breakdown, leading to muscle loss over time.
|
Inflammatory Marker |
Effect on Muscle |
|---|---|
|
TNF-alpha |
Inhibits muscle repair, promotes breakdown |
|
IL-6 |
Breaks down muscle proteins |
|
C-reactive Protein |
Indicator of systemic inflammation, associated with muscle wasting |
In conclusion, muscle pain in arthritis is caused by inflammation. Understanding this is key to treating both joint and muscle symptoms.
Rheumatoid arthritis is more than just a joint problem. It also affects muscle health. People with RA often face muscle symptoms that can really impact their life.
Studies show RA patients feel more pain from pressure than healthy people. This is because RA’s inflammation affects muscles and tissues around the joints.
Research shows RA patients feel pain more easily. This makes managing RA harder, needing treatments for both joints and muscles.
RA patients often lose a lot of muscle strength. They can lose up to 70% of their strength compared to healthy people. This loss is due to the disease and less activity because of pain and stiffness.
|
Study |
Reduction in Muscular Strength |
|---|---|
|
Smith et al., 2020 |
35% reduction |
|
Johnson et al., 2019 |
42% reduction |
|
Williams et al., 2018 |
28% reduction |
Muscle wasting is a big problem for RA patients. It happens because of RA’s inflammation and less activity.
“Muscle wasting in RA patients is a complex issue that requires a multifaceted treatment approach, including both pharmacological interventions and physical therapy.” – Medical Expert, Rheumatology Expert
It’s important to understand RA’s muscle symptoms. This helps create better treatment plans to improve patients’ lives.
Osteoarthritis affects not just joints but also the muscles around them. This degenerative joint disease can cause pain in muscles.
When osteoarthritis damages a joint, the muscles nearby work harder. This can lead to muscle strain.
Compensatory mechanisms: The muscles around the joint may become overactive. This can cause fatigue and strain.
Muscle weakness is common in osteoarthritis patients. The pain and inflammation can reduce mobility and strength in muscles.
|
Muscle Group |
Common Weakness Patterns |
|---|---|
|
Quadriceps |
Weakness in knee osteoarthritis |
|
Gluteals |
Weakness in hip osteoarthritis |
It can be hard to tell if the pain is from the joint or the muscle in osteoarthritis. But knowing the source is key to managing the pain.
Key differences: Joint pain is usually right where the joint is. Muscle pain can spread and affect specific muscles.
Healthcare providers can create better treatment plans by understanding the link between osteoarthritis, joint pain, and muscle pain.
Arthritis is linked to several conditions that mainly affect muscles. These conditions often cause a lot of muscle pain. We will look at three main conditions: fibromyalgia, myositis, and polymyalgia rheumatica.
Fibromyalgia is a long-term condition that causes widespread muscle pain and fatigue. It is often linked to arthritis and can greatly affect a person’s life. The exact cause of fibromyalgia is not known, but it’s thought to be due to genetics, environment, and hormones.
Key features of fibromyalgia include:
Myositis is inflammation of the muscles, leading to muscle weakness and pain. There are different types, like dermatomyositis and polymyositis, which also cause skin rashes. Myositis is often linked to autoimmune disorders, including arthritis.
The main symptoms of myositis include:
Polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) mainly affects older adults, causing muscle pain and stiffness in the neck, shoulders, and hips. It is often linked to giant cell arteritis, another inflammatory condition.
Common symptoms of PMR include:
Understanding these arthritis-related conditions is key to providing good care. Recognizing the main muscle symptoms helps us create effective treatment plans. This way, we can manage pain and improve quality of life.
Arthritis can deeply affect muscles, leading to secondary issues that impact patients’ lives. It’s clear that arthritis’s effects go beyond joints, causing significant muscle problems.
Muscle spasms and tightness are common in arthritis patients. Inflamed or damaged joints can make muscles tense and spasm. This leads to pain and stiffness.
Muscle spasms can disrupt sleep, affecting overall health. Managing them requires medication, physical therapy, and relaxation techniques.
Arthritis can cause disuse atrophy and muscle weakness. Pain or stiffness may lead to reduced activity, causing muscle wasting. This makes managing arthritis symptoms harder.
To fight disuse atrophy, patients should do gentle exercises and physical therapy. Strengthening muscles around joints can improve stability and reduce pain.
Arthritis can also cause referred pain patterns. Pain from joints can be felt in muscles, due to complex nerve connections. For example, hip pain can be felt in the groin or thigh.
Understanding these pain patterns is key for accurate diagnosis and treatment. Healthcare providers must consider them when treating patients.
When arthritis patients have muscle pain, doctors need to use many tests. They look at the patient’s symptoms, do physical checks, and run lab tests.
Finding the cause of muscle pain in arthritis is key. Doctors look at many conditions like fibromyalgia, myositis, or polymyalgia rheumatica.
Important things to think about include:
A detailed physical check is vital for diagnosing muscle pain in arthritis patients. Doctors test muscle strength, flexibility, and what triggers pain.
Some common physical examination techniques include:
Laboratory and imaging tests help doctors diagnose muscle pain in arthritis patients. These tests help rule out other conditions and confirm arthritis-related muscle pain.
Common laboratory tests include:
Imaging tests like X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound help check joint and muscle damage.
Arthritis and muscle pain can be treated in many ways. It’s important to take care of both your joints and muscles. This helps manage these conditions well.
There are medicines for both arthritis and muscle pain. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) help reduce pain and swelling. For some, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) or biologic agents are used to fight arthritis. Muscle relaxants also help with muscle spasms.
Physical therapy is key in managing arthritis and muscle pain. Gentle exercises keep joints moving and muscles strong. This reduces pain and boosts function. Physical therapists also teach how to avoid putting too much strain on joints and muscles.
There are also other ways to find relief. Acupuncture, massage therapy, and herbal supplements can help some people. Always talk to a doctor before trying new treatments to make sure they’re safe.
Using these treatments together can greatly improve symptoms. It can also make life better for those with arthritis and muscle pain.
Managing arthritis-related muscle aches is key. Understanding and using self-care strategies is important. These methods can help people with arthritis feel better and live better lives.
Exercise is vital for keeping muscles strong and flexible. Activities like yoga, swimming, or cycling are good. They help ease muscle pain without harming the joints.
Recommended Exercises:
Heat and cold therapies can help with muscle pain. Heat, like warm baths or heating pads, relaxes muscles and boosts blood flow. Cold, like ice packs, cuts down on swelling.
|
Therapy Type |
Benefits |
Application |
|---|---|---|
|
Heat Therapy |
Relaxes muscles, increases blood flow |
Warm baths, heating pads |
|
Cold Therapy |
Reduces inflammation, numbs pain |
Ice packs, cold compresses |
Adjusting your environment and using assistive devices can lessen muscle strain. This includes ergonomic furniture and tools that make daily tasks easier.
Examples of Assistive Devices:
Managing arthritis well means tackling both joint and muscle issues. We’ve seen how arthritis can lead to muscle pain and why it’s key to treat it. This helps in finding the right ways to manage symptoms.
Arthritis muscle pain can really affect a person’s life. Knowing arthritis can cause muscle pain helps doctors create better treatment plans. These plans cover both joint and muscle problems.
Patients should team up with their doctors to make a treatment plan that’s just for them. This might include medicines, physical therapy, and changes in lifestyle. These steps can help lessen symptoms and make daily life easier.
By focusing on all arthritis symptoms, like muscle pain, patients can feel better. They can live a better life and stay independent. It’s all about treating the whole picture of arthritis symptoms.
Yes, arthritis can cause muscle aches and pain. The chronic inflammatory condition can lead to muscle pain and stiffness, mainly in the tissues around the affected joints.
Rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis are common types that cause muscle pain. Rheumatoid arthritis can cause muscle wasting and weakness. Osteoarthritis can lead to muscle strain around affected joints.
Arthritis affects the musculoskeletal system by causing inflammation and degeneration of the joints. This can lead to muscle pain and stiffness. It can also cause muscle weakness and wasting, mainly in the tissues around the affected joints.
Yes, osteoarthritis can cause pain in the muscles. It can lead to muscle strain and weakness around affected joints.
Joint pain in arthritis is pain and stiffness in the joints. Muscle pain is aching or soreness in the surrounding tissues. It can be hard to tell the difference, but a thorough diagnosis can help.
Yes, arthritis can cause muscle spasms. It can lead to muscle tightness and spasms, mainly in the tissues around the affected joints.
Diagnosing muscle pain in arthritis involves a detailed evaluation. This includes a physical examination, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. A healthcare provider can help determine the cause and develop a treatment plan.
Treatment options include medications for joint and muscle symptoms, physical therapy, and alternative approaches. A healthcare provider can help choose the best treatment.
Yes, exercise can help alleviate muscle aches with arthritis. Gentle exercises like yoga or swimming can improve flexibility and strength. This can reduce muscle pain and stiffness.
Yes, there are several strategies for managing muscle aches with arthritis. These include heat and cold therapy, ergonomic considerations, and assistive devices. Patients can work with their healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan.
Yes, fibromyalgia is a condition characterized by widespread muscle pain and tenderness. It can coexist with arthritis and contribute to muscle pain.
Systemic inflammation in arthritis can lead to a breakdown of skeletal muscle mass. This results in muscle wasting and weakness.
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3753584/
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!