
Obesity is a complex medical condition that affects millions worldwide. The biggest indicator of obesity is an elevated Body Mass Index (BMI). We rely on BMI as a key metric to understand and address this growing issue, making it a priority health concern for communities and healthcare systems globally. According to the CDC, adult obesity prevalence was 40.3% in the U.S. from 2021-2023. This alarming statistic shows the need for effective management strategies. As we explore the role of BMI in obesity, it’s clear that innovative, multidisciplinary healthcare approaches are essential. Understanding obesity through current data highlights why we need effective healthcare solutions to address this urgent priority health challenge.
Key Takeaways
- BMI is the biggest indicator of obesity.
- Adult obesity prevalence in the U.S. was 40.3% from 2021-2023.
- Innovative healthcare approaches are necessary to address obesity.
- Understanding obesity indicators is key to effective management.
- BMI plays a significant role in measuring and addressing obesity globally.
Understanding Obesity as a Global Health Crisis

The World Health Organization sees obesity as a big cause of non-communicable diseases worldwide. It’s a big health problem that affects millions, so we need to understand it well. This includes knowing what it is, how widespread it is, and how to measure it.
The Definition and Scope of Obesity
Obesity is defined by the World Health Organization using Body Mass Index (BMI). It tells us who is overweight or obese. This is key to seeing how obesity affects health worldwide.
According to the WHO, obesity increases the risk of diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and some cancers. It’s not just a personal problem. It’s influenced by genetics, environment, and lifestyle.
Why Accurate Obesity Measurement Matters
Measuring obesity accurately is important for finding at-risk individuals and creating effective plans. BMI is a main indicator of obesity, helping us compare across different groups. But we also need to look at waist size and body composition for a full health picture.
By understanding obesity’s scope and measuring it accurately, we can tackle it better. For more on global efforts to fight obesity, check out the WHO’s page on controlling global obesity.
Measuring obesity accurately is more than just spotting a health problem. It’s about finding a way to live healthier. By recognizing obesity’s complexity and its wide effects, we can all help reduce its impact on health worldwide.
Body Mass Index (BMI): The Primary Indicator of Obesity

The Body Mass Index (BMI) is a key tool for spotting obesity. It’s simple and works well for sorting people by weight and height. Doctors all over the world rely on BMI to check for obesity.
How BMI is Calculated and Interpreted
To find your BMI, divide your weight in kilograms by your height in meters squared (kg/m). This gives a number that shows if you’re underweight, normal, overweight, or obese. Here’s how we see it: under 18.5 is underweight, 18.5-24.9 is normal, 25-29.9 is overweight, and 30 or more is obese.
BMI Classification Categories for Adults and Children
BMI helps both adults and kids, but kids’ results are different because they grow. Adults fit into the same categories everywhere. Kids get a BMI percentile from growth charts, showing if they’re underweight, normal, overweight, or obese.
Strengths and Limitations of BMI as a Screening Tool
BMI is great because it’s easy and doesn’t hurt anyone. But, it can’t tell how much body fat you have or if it’s muscle or fat. Even so, BMI is a big help in fighting obesity because it’s easy to use and everyone knows it.
We know BMI isn’t perfect, but it’s the best we have for now. Learning about BMI helps us understand obesity better. This way, we can find the right ways to help people.
Alarming Obesity Statistics and Trends
Obesity is a big health problem worldwide that needs quick action. Looking at the numbers, it’s clear that obesity is not just a personal issue. It’s a big problem that affects many people, leading to air hunger and other breathing issues.
U.S. Obesity Prevalence: 40.3% of Adults (2021-2023)
In the U.S., obesity among adults is very high. Between 2021 and 2023, 40.3% of adults were obese. This is very worrying for young people, as obesity can harm their health for a long time. It’s important to know how obesity affects adolescents to help them.
Global Obesity Crisis: 2.11 Billion Overweight or Obese Adults
Worldwide, the situation is just as bad. In 2021, over half of all adults were overweight or obese, with 2.11 billion affected. This has big effects on how long people live and their quality of life. Obesity can shorten life span and raise the risk of serious diseases.
World Obesity Federation’s Projection: 115% Increase by 2030
The World Obesity Federation says obesity will rise by 115% by 2030 if things keep going as they are. This shows we really need to work on preventing and managing obesity. We must act fast to stop this health crisis and its serious effects.
Secondary Indicators That Support BMI Assessment
While BMI is key for spotting obesity, other signs give a fuller picture of health risks. Studies show that genes, environment, and behaviour all play a part in obesity. For example, feeling insecure about one’s body can lead to binge eating, making things worse.
Waist Circumference and Waist-to-Hip Ratio
Measuring waist size and waist-to-hip ratio is important. Too much fat around the waist is linked to heart disease and diabetes. These measurements help doctors see more than just BMI.
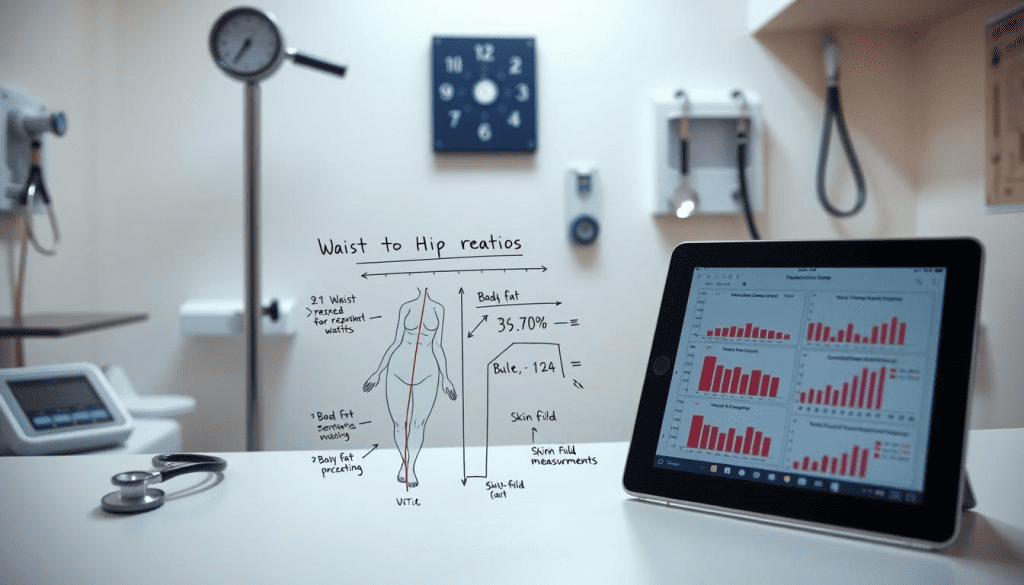
Body Composition Analysis Methods
Tools like DXA and BIA give a detailed look at body fat and muscle. They show who has too much fat, even if the BMI looks okay. This info helps doctors tailor health plans.
Clinical Assessments and Laboratory Markers
Tests like blood pressure and lipid profiles add to the health picture. They spot risks like high blood pressure and bad cholesterol. Mixing these with BMI and other signs helps doctors understand and treat health better.
Using these extra signs in health checks helps doctors see more clearly. They can then make better plans to prevent and treat obesity.
Obesity as a Priority Health Issue: Causes and Consequences
Obesity is a big health problem that needs our urgent attention. It affects people all over the world. We must understand its causes and how it impacts communities.
The Deadly Impact: 1.6 Million Premature Deaths Annually
Obesity is linked to many health issues. It leads to about 1.6 million premature deaths each year. This shows how critical it is to manage obesity well.
By knowing how obesity affects death rates, we can tackle this problem better. This helps us understand obesity’s role in public health.
Genetic, Environmental, and Behavioural Contributors
Obesity comes from genetics, environment, and behaviour. Genetics can make some people more likely to gain weight. The environment affects us too, like easy access to unhealthy food and not enough exercise.
Behaviour also plays a big part, like what we eat and how active we are. Knowing these factors helps us create better ways to prevent and treat obesity.
By understanding these causes, we can make plans to help people. This way, we can fight obesity more effectively.
Best Practices in Obesity Management: The Livhospital.com Approach
Managing obesity well needs a mix of medical care, lifestyle changes, and support. At Livhospital.com, we use a team approach. This includes custom diet plans, exercise advice, and therapy.
Our goal is to give patients the skills to manage their weight. With the right treatment and lifestyle changes, people can live healthier lives.
Conclusion: Addressing the Obesity Epidemic Through Comprehensive Assessment
We stress that a full assessment is vital to tackle the obesity crisis. By mixing Body Mass Index (BMI) with other signs, doctors can craft solid plans. BMI is the main tool, giving a basic view of someone’s weight.
Using infographics can show the many reasons behind obesity, making it clearer. These include genetics, environment, and behavior. These must be looked at when making treatment plans.
Healthcare teams can make tailored plans by understanding obesity’s many sides. They use tools like waist size and body fat analysis. This detailed method is key to better health and fighting obesity.
Good plans, backed by data and checks, can lower obesity’s dangers. This includes the high number of early deaths. A thorough assessment helps fight obesity and boosts health globally, using tools like mdes for treatment choices.
FAQ’s:
What is the biggest indicator of obesity?
The biggest indicator of obesity is Body Mass Index (BMI). It’s a widely used metric. It calculates an individual’s weight in kilograms divided by their height in meters squared.
How is BMI calculated?
BMI is calculated by dividing an individual’s weight in kilograms by their height in meters squared. This gives a numerical value. It helps categorize individuals into different weight status categories.
What are the limitations of using BMI as a screening tool?
While BMI is useful, it has limitations. It can’t distinguish between lean body mass and body fat. It’s also not accurate for athletes or those with a muscular build.
What is considered a healthy BMI range?
A healthy BMI range is between 18.5 and 24.9. Those below 18.5 are underweight. Those with a BMI of 25 or higher are overweight or obese.
What are some secondary indicators that support BMI assessment?
Secondary indicators include waist circumference and body composition analysis. Clinical assessments like blood pressure and lipid profiles also support BMI assessment. These indicators give a more complete view of health risks.
What is the significance of waist circumference in assessing obesity?
Waist circumference is key in assessing obesity-related health risks. It measures central obesity and visceral fat. These are linked to an increased risk of chronic diseases.
How does body composition analysis contribute to obesity assessment?
Body composition analysis provides detailed information on body fat percentage and lean body mass. It helps healthcare professionals develop targeted interventions and monitor progress.
What are the consequences of obesity?
Obesity increases the risk of cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers. It can lead to premature mortality, causing significant economic and social burdens.
What is the role of genetics in obesity?
Genetics plays a big role in obesity. Certain genetic variants affect appetite regulation, metabolism, and body weight. But, environmental and behavioural factors also contribute to obesity.
What is a subset of the population that is particularly vulnerable to obesity?
Adolescents are very vulnerable to obesity. This stage of life sees significant physical, emotional, and social changes. These changes can impact eating habits and physical activity levels.
What is meant by the term “air hunger” in the context of obesity?
Air hunger, or dyspnea, is a symptom of obesity. It’s difficulty breathing or feeling like you can’t catch your breath. It’s related to reduced lung capacity and increased respiratory effort.
How does insecurity relate to obesity?
Insecurity, like food insecurity, can lead to obesity. People may overeat or make poor food choices. They might rely on high-calorie, high-fat foods that are more affordable.
What does it mean to define something objectively in the context of obesity?
Objectively defining obesity means using measurable criteria like BMI or body fat percentage. It’s about using quantifiable data, not personal opinions.
What is the MDES in the context of obesity research?
The Minimal Detectable Effect Size (MDES) is a statistical concept. It helps determine the smallest effect size detectable in research. It’s important in obesity research to evaluate intervention effectiveness.
What is the meaning of “no healthy upstream” in the context of obesity prevention?
“No healthy upstream” means many factors contributing to obesity are not being addressed. This makes it hard to prevent or manage obesity.
How do gender symbols relate to the discussion of obesity?
Gender symbols are relevant in obesity discussions. There are differences in body composition, fat distribution, and health risks between men and women. These differences should be considered in assessing and managing obesity.
What is the significance of “leading” in the context of obesity management?
Leading in obesity management means guiding individuals towards healthy behaviours. This includes healthy eating and regular physical activity. It helps them achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
What is meant by “overall shorts” in the context of obesity?
“Overall shorts” is not directly related to obesity. It might refer to shortcomings in current approaches to obesity prevention and management.
What is the definition of binge in the context of eating behaviours?
Binge eating is excessive food consumption. It’s often accompanied by feelings of loss of control, guilt, or shame. It can lead to weight gain and obesity.
What is the life span of an individual with obesity?
Obesity can reduce an individual’s life span due to increased risk of chronic diseases. But, effective management and healthy lifestyle changes can improve health outcomes and increase life expectancy.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2022). About Adult BMI. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/healthyweight/assessing/bmi/adult_bmi/index.html









