Last Updated on November 26, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
Ovarian cancer is a major health concern for women worldwide. Ovarian cancer body location refers to the ovaries, which are located in the female pelvis. A surprising fact is that 1 in 78 women will get ovarian cancer in their lifetime. Knowing when ovarian cancer usually starts is key for catching it early and treating it well.
The chance of getting ovarian cancer changes with age. Knowing about ovarian cancer age statistics helps women and doctors act fast. Most ovarian cancer is found in women over 50, making it very important to be aware and get checked.
Looking into the average age for ovarian cancer diagnosis is very important. It helps women make better health choices and get better results.
Key Takeaways
- Ovarian cancer risk increases with age, with most cases diagnosed in women over 50.
- Understanding ovarian cancer age statistics is vital for early detection.
- Awareness and screening are key for good treatment and better results.
- The average age for ovarian cancer diagnosis varies, but knowing helps women take care of their health.
- Ovarian cancer is a big health issue worldwide, affecting women of all ages.
Understanding Ovarian Cancer Basics
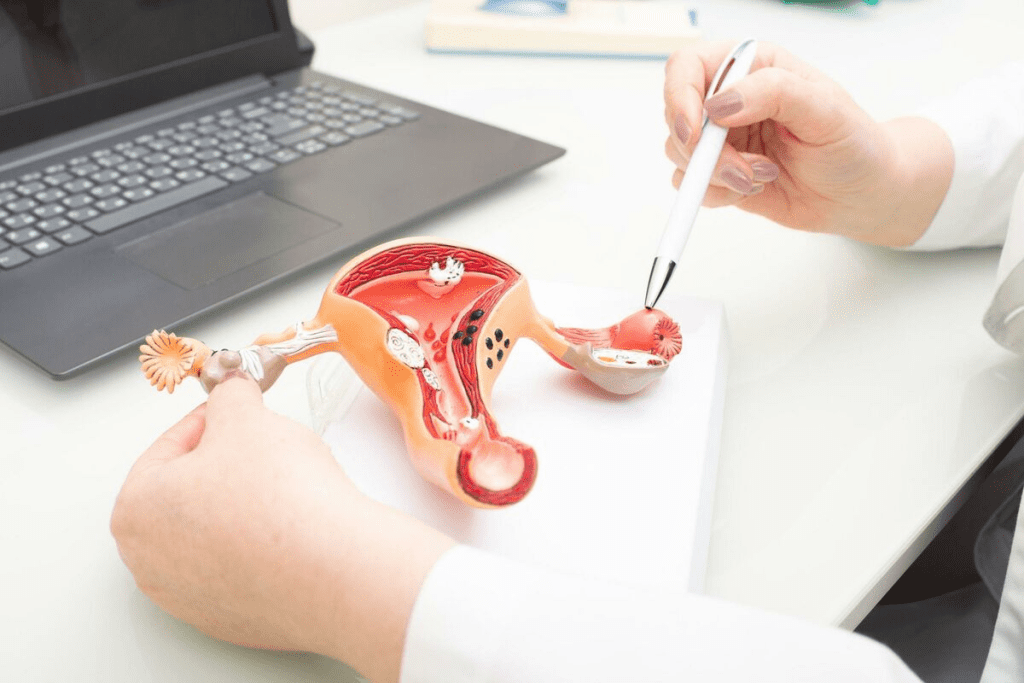
To understand ovarian cancer, we need to look at its basics. This includes types, symptoms, and warning signs. Ovarian cancer is a complex disease with different types, each with its own traits.
Types and Classifications of Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer is mainly split into types based on where it starts. The main types are:
- Epithelial ovarian cancer, which starts in the outer layer of the ovary
- Germ cell ovarian cancer, from the cells that make eggs
- Sex cord-stromal ovarian cancer, from the tissue that holds the ovary together
Knowing these types helps doctors choose the right treatment.
| Type of Ovarian Cancer | Origin | Frequency |
| Epithelial | Outer layer of the ovary | 85-90% |
| Germ cell | Cells that produce eggs | 5-10% |
| Sex cord-stromal | Connective tissue of the ovary | 1-2% |
Common Symptoms and Warning Signs
It’s important to know the symptoms of ovarian cancer for early detection. Common symptoms include:
- Pelvic or abdominal pain
- Bloating or swelling in the abdomen
- Difficulty eating or feeling full quickly
- Urinary urgency or frequency
These symptoms can be similar to other conditions. But, if they last or get worse, see a doctor.
Knowing these signs can help women get medical help fast. This could lead to better outcomes.
Average Age Ovarian Cancer Patients in the United States
The average age of ovarian cancer patients in the US is about 63 years. Ovarian cancer body location refers to the ovaries, which are small organs located deep in the pelvis on either side of the uterus. These organs produce eggs and are the primary site where ovarian cancer begins.
Median Age at Diagnosis According to US Statistics
The median age for ovarian cancer in the US is 63 years. This means half of the patients are diagnosed at or before this age. The other half are diagnosed after. It shows why screening and awareness are so important for women in their early sixties.
Mean Age of Ovarian Cancer Patients
The mean age of ovarian cancer patients in the US is a bit different. Studies show it’s around 62-64 years. This reflects a balanced distribution of ages at diagnosis.
How US Statistics Compare Globally
Looking at the average age of ovarian cancer diagnosis in the US and worldwide shows differences. The US average is 63 years. But, globally, it ranges from 55 to 65 years. This variation is seen across different countries and regions.
| Country/Region | Average Age at Diagnosis |
| United States | 63 |
| Europe | 62 |
| Asia | 58 |
| Africa | 55 |
This comparison highlights the need for regional data. It helps us understand ovarian cancer better. It also helps tailor healthcare strategies for different areas.
Age Distribution of Ovarian Cancer Cases
Looking at how age affects ovarian cancer helps us spot trends. This knowledge guides us in making better screening and prevention plans. Ovarian cancer hits women of all ages, with its impact and traits evolving over time.
Incidence Rates by Decade of Life
Ovarian cancer rates change a lot with age. Most cases happen in women aged 55 to 64, peaking at 60. Rates are low in women under 40 but climb after 40.
Here’s a closer look:
- Women under 40: Less than 10% of ovarian cancer cases are diagnosed in this age group.
- Women between 40 and 49: The incidence starts to increase, with about 15-20% of cases diagnosed in this decade.
- Women between 50 and 59: This age group accounts for approximately 25-30% of ovarian cancer diagnoses.
- Women between 60 and 69: The highest incidence rates are observed, with around 30-35% of cases diagnosed in this age group.
Changing Trends in Age of Diagnosis Over Time
Research shows ovarian cancer is being diagnosed later in life. Recent studies indicate a shift towards diagnosing ovarian cancer at an older age. This might be because of better healthcare and changes in the population.
There are also differences in the types of ovarian cancer found in different age groups. Younger women often get borderline ovarian tumors. Older women are more likely to get epithelial ovarian cancer, which is more aggressive.
Knowing these trends is key to creating better screening and early detection plans. By focusing on age-specific risks and traits, we can improve how we diagnose and treat ovarian cancer.
Ovarian Cancer in Women Over 50
Women over 50 face a higher risk of ovarian cancer. It’s important to know the risks and how to detect it. As women get older, the risk of ovarian cancer goes up. This makes it key to tackle the challenges for women over 50.
Why Postmenopausal Women Face Higher Risk
The risk of ovarian cancer goes up with age, after menopause. Hormonal changes, aging, and genetic mutations play a role. These factors increase the risk over time.
Research shows ovarian cancer peaks in women aged 60 to 70. This age group is at the highest risk. It’s something both patients and doctors need to keep in mind.
Detection Challenges Specific to Older Women
Finding ovarian cancer in older women is hard. Symptoms like pelvic pain or bloating are often mistaken for other conditions. This can lead to delays in finding the cancer.
There are screening tools like ultrasound and the CA-125 blood test. But, they’re not perfect. They can sometimes cause unnecessary surgeries or give false hope.
| Age Group | Incidence Rate | Detection Challenges |
| 50-60 | Increasing | Symptom attribution to other age-related conditions |
| 60-70 | Peak incidence | Lack of effective screening methods |
| 70+ | High risk | Comorbidities complicating diagnosis and treatment |
It’s vital to understand these challenges to improve detection and treatment for ovarian cancer in women over 50. By recognizing the higher risk and tackling detection issues, we can improve health outcomes for this group.
Can Young Women Get Ovarian Cancer?
Ovarian cancer isn’t just for older women. Young women can also get it. Most cases happen in women after menopause. But, it’s important to know it can happen to women of all ages, even those under 40.
Ovarian Cancer Under Age 40: Incidence and Types
Ovarian cancer is rare in young women. Studies show that women under 40 make up a small part of cases. But, when it does happen, it’s often different in younger women.
Younger women are more likely to get germ cell tumors. Older women are more likely to get epithelial ovarian cancers. Knowing this helps doctors plan the best treatment.
Youngest Documented Cases in Medical Literature
There are cases of ovarian cancer in very young girls. These cases are rare but show the need for careful checks at all ages.
Medical records show cases as young as 15. This shows ovarian cancer can affect anyone, no matter their age. It’s important to get checked if symptoms show up, no matter how old you are.
Fertility Considerations for Young Patients
For young women with ovarian cancer, keeping fertility is key. The type of cancer, how far it has spread, and treatment plans all affect this. Doctors should talk about keeping fertility before starting treatment.
There are ways to keep fertility, like special surgeries and technologies. It’s vital to support young patients with these concerns. They deserve care and hope.
Age-Related Risk Factors for Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer risk is shaped by hormones and genes. These factors change as a woman ages. Knowing about these risks helps us understand how to prevent the disease.
Hormonal Influences Throughout a Woman’s Life
Hormones play a big role in a woman’s health. They affect ovarian cancer risk. Hormonal changes from puberty to menopause can raise or lower this risk.
Women who start menstruating early or stop later may face a higher risk. This is because they are exposed to estrogen for longer. Hormone therapy during menopause also increases ovarian cancer risk, but the risk is small.
Genetic Predispositions and How They Interact with Age
Genetics are a big factor in ovarian cancer risk. Mutations like BRCA1 and BRCA2 greatly increase the risk. The risk also changes with age, making it harder to predict.
Women with a family history of cancer may need to start screening early. The age when genetic risks show up can vary. But, women with high-risk genes often get ovarian cancer younger.
Looking at hormones and genes together helps us understand ovarian cancer risk better. This way, doctors can give advice and screenings based on each woman’s risk.
Ovarian Cancer After Menopause
Menopause brings many changes that can affect ovarian cancer risk. It’s important for women to understand these changes for their health.
Biological Mechanisms Behind Increased Post-Menopausal Risk
After menopause, the risk of ovarian cancer may rise. This is due to hormonal changes, like a drop in estrogen. This hormone change can affect the growth of some ovarian cancer cells.
Also, genetic mutations build up over a woman’s life. These can increase the risk of ovarian cancer after menopause.
Hormone Replacement Therapy: Risks and Considerations
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) helps with menopause symptoms. But, it can raise the risk of ovarian cancer, mainly with long-term use.
It’s important to think about HRT’s benefits and risks. We must consider each patient’s unique situation and medical history.
| Risk Factor | Description | Impact on Ovarian Cancer Risk |
| Hormone Replacement Therapy | Use of hormones to alleviate menopausal symptoms | Increased risk, specially with long-term use |
| Age | Post-menopausal age | Increased risk with advancing age |
| Genetic Mutations | Accumulation of genetic mutations over time | Contributes to increased risk |
Knowing these risk factors is key to managing ovarian cancer risk after menopause.
Average Age for Different Stages of Ovarian Cancer
Knowing when ovarian cancer is diagnosed at different stages is key for better healthcare. Ovarian cancer is staged based on how far it has spread. The age at diagnosis changes a lot between these stages.
Average Age for Stage 1 Ovarian Cancer Diagnosis
Stage 1 ovarian cancer is when the cancer is only in the ovaries. Women diagnosed at this stage are usually in their mid-to-late 50s. This is based on studies.
Finding cancer early is very important. Knowing the average age for Stage 1 helps doctors give better advice on when to screen women.
Average Age for Advanced Ovarian Cancer Diagnosis
Advanced ovarian cancer, Stages III and IV, is found in older women. The average age for this diagnosis is in the early to mid-60s.
The age gap between early and advanced stages shows we need to screen older women more. This could save lives.
| Stage at Diagnosis | Average Age |
| Stage 1 | 55-59 years |
| Stage III | 62-65 years |
| Stage IV | 63-66 years |
The table shows the average age for ovarian cancer diagnosis at different stages. It shows how age increases as the disease gets worse.
In summary, the age at diagnosis for ovarian cancer changes a lot with each stage. Knowing these differences helps doctors plan better treatments for each stage.
Age-Specific Symptoms and Diagnostic Approaches
Ovarian cancer symptoms change with age, needing different treatments. As we get older, the risk and signs of ovarian cancer shift. It’s key for doctors to know these age-specific differences.
How Symptoms Vary Across Different Age Groups
Symptoms of ovarian cancer vary by age. Younger women often feel pelvic pain and unusual vaginal bleeding. Older women might just feel bloated or uncomfortable in their belly.
Symptoms in Younger Women: Women under 40 might get germ cell tumors. These can cause sudden, severe pain from a tumor bursting or twisting.
Symptoms in Older Women: Women over 40 are more likely to get epithelial ovarian cancer. This type often shows up with vague signs like bloating, feeling full too soon, and needing to pee a lot.
Age-Appropriate Diagnostic Strategies
Diagnosing ovarian cancer should match the patient’s age. Younger women need a pelvic exam and ultrasound. Older women might need more tests, like imaging and tumor markers.
- For Younger Women: A transvaginal ultrasound and CA-125 test, along with family history, are key for early detection.
- For Older Women: A mix of ultrasound types and CT scans, plus CA-125 levels, helps diagnose and stage ovarian cancer.
Using age-specific diagnostic methods can help doctors find and treat ovarian cancer better in all age groups.
Treatment Considerations Based on Patient Age
Ovarian cancer treatment changes with the patient’s age. Healthcare providers tailor plans for different age groups. They look at the patient’s health, cancer type, and how treatment affects life quality.
Treatment Options and Approaches for Younger Patients
Younger patients face unique needs in ovarian cancer treatment. Women under 40 often want to preserve fertility. We explore fertility-sparing options like conservative surgery and targeted therapies.
Younger patients might get more aggressive treatments to fight cancer well. Yet, we also think about the long-term effects. We aim to keep treatment effective while preserving quality of life.
Treatment Approaches for Elderly Women with Ovarian Cancer
Elderly women with ovarian cancer have special challenges. They might have other health issues and can’t always handle tough treatments. We make treatment plans that focus on symptom management and improving life quality.
Our approach might include less intense chemotherapy, palliative care, and supportive therapies. In some cases, we consider hospice care for those who can’t get curative treatments. We aim to provide comfort and support.
By focusing on each patient’s needs, we can improve treatment results. This approach helps enhance the quality of life for women with ovarian cancer.
Ovarian Cancer Survival Rates by Age Group
Ovarian cancer survival rates change a lot with age. It’s key for patients, doctors, and researchers to know this. It helps in making better treatment choices.
Five-Year Survival Statistics Across Different Age Brackets
Five-year survival rates are a big clue about ovarian cancer’s outlook. Women under 40 diagnosed with ovarian cancer have a much better chance of survival. This is compared to women older than 40.
| Age Group | Five-Year Survival Rate |
| Under 40 | 70-80% |
| 40-59 | 50-60% |
| 60 and above | 30-40% |
These numbers show how vital early detection is. They also show how age affects survival chances.
Factors Affecting Prognosis Beyond Chronological Age
Age is a big factor in ovarian cancer survival, but it’s not the only one. Other important factors include:
- Overall Health: Patients with fewer health problems tend to live longer.
- Tumor Biology: The tumor’s genetic makeup can greatly affect survival.
- Treatment Response: How well a patient responds to treatment is key to survival.
- Genetic Predispositions: Having genetic mutations like BRCA1 and BRCA2 can change survival chances.
A leading oncologist, says, “It’s important to understand how age, tumor biology, and health interact. This knowledge helps improve survival rates for ovarian cancer patients.”
“The prognosis for ovarian cancer patients is not just about age. It’s a complex mix of factors that guides our treatment plans.” –
Oncologist
By looking at these factors, doctors can create more tailored treatment plans. This can lead to better survival rates for ovarian cancer patients of all ages.
Screening and Prevention Recommendations Throughout Life
Ovarian cancer prevention changes as women get older. Different screening methods work better at different ages. We’ll cover how to prevent and screen for ovarian cancer at each stage of a woman’s life.
Risk Assessment Timeline from Adolescence to Post-Menopause
Checking for ovarian cancer risk starts early. In teens, family history and genes matter. As women grow older, their reproductive history affects their risk.
Key Risk Factors by Life Stage:
- Adolescence: Family history of ovarian or breast cancer, genetic mutations (BRCA1 and BRCA2).
- Reproductive Years: Parity, use of oral contraceptives, history of endometriosis.
- Peri-Menopause and Post-Menopause: Age, history of hormone replacement therapy, obesity.
Age-Appropriate Preventive Measures and Monitoring
Preventive steps and monitoring change with age. They’re not the same for everyone.
| Age Group | Preventive Measures | Monitoring Strategies |
| 20-40 years | Risk assessment, consideration of oral contraceptives for high-risk women | Annual pelvic exams, awareness of symptoms |
| 40-60 years | Risk reduction through surgical options for high-risk women, lifestyle modifications | Regular check-ups, symptom awareness, possible transvaginal ultrasound |
| Post-Menopause | Review of hormone replacement therapy risks, maintaining a healthy weight | Continued symptom awareness, discussion of screening options with healthcare provider |
By following these age-specific tips, women can lower their ovarian cancer risk. They can also catch it early.
Special Considerations for High-Risk Age Groups
Ovarian cancer risk changes with age, making some groups more at risk. Early detection is key to better survival rates, health groups say. This means we need different ways to find and prevent ovarian cancer in different age groups.
Monitoring Protocols for Women Under 40 with Genetic Risk
Women under 40 with a genetic risk, like BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations, need close monitoring. They should get regular screening. This includes transvaginal ultrasound and CA-125 blood tests.
The American Cancer Society advises women with a strong family history or genetic risk to talk to their doctor. They might start screening earlier than others.
- Annual or biennial screening with transvaginal ultrasound
- CA-125 blood tests as recommended by healthcare providers
- Genetic counseling to understand personal risk factors
Surveillance Strategies for Post-Menopausal High-Risk Women
Post-menopausal women at high risk for ovarian cancer need special care. We stress the importance of ongoing monitoring, even after menopause. The risk of ovarian cancer doesn’t go away.
A study in the Journal of Clinical Oncology found that post-menopausal women on hormone replacement therapy face a higher risk. This shows why they need careful watching.
For post-menopausal high-risk women, surveillance might include:
- Regular pelvic exams to monitor for any abnormalities
- Transvaginal ultrasound to detect early signs of ovarian cancer
- CA-125 testing, possibly with other biomarkers
By using these specific monitoring and surveillance plans, we can catch ovarian cancer early. This can lead to better outcomes for those at high risk.
It’s vital for women in high-risk age groups to work with their healthcare providers. Together, they can create a personalized surveillance plan.
Future Trends in Ovarian Cancer Age Distribution
Ovarian cancer age distribution is on the verge of big changes. These changes are driven by many factors. It’s important to understand these shifts to prepare for future challenges in diagnosing, treating, and preventing ovarian cancer.
Changing Demographics and Public Health Implications
The demographics of ovarian cancer are changing. We see a shift in the age of patients, which affects public health. Increasing life expectancy and changes in reproductive patterns are key factors.
As the world’s population ages, ovarian cancer cases are expected to rise. This will put more pressure on healthcare systems. It highlights the need for effective screening methods and prevention strategies for different age groups.
Emerging Research on Age-Related Risk Factors
Research on age-related risk factors for ovarian cancer is growing fast. Studies are looking into how genetic predispositions and age affect cancer risk. Knowing this is key to creating targeted prevention and early detection plans.
Also, new evidence shows that hormonal influences throughout a woman’s life impact ovarian cancer risk. More research in this area could lead to new ways to assess and manage risk.
By keeping up with these trends and research, we can tackle ovarian cancer’s challenges. This will help improve outcomes for patients of all ages.
Conclusion
Our look into the average age for ovarian cancer diagnosis shows a mix of factors affecting risk and outcomes. The average age at diagnosis is about 63 years. Most cases happen in women after menopause. Yet, ovarian cancer can strike women of any age, making awareness key for all.
Knowing the average age for ovarian cancer and its risk factors is vital for early detection and treatment. Healthcare providers can better help patients by spotting symptoms early and using the right tests. Treatment plans also vary with the patient’s age, which is important for managing the disease.
We must keep spreading the word about ovarian cancer, its risks, and the need for early detection. This effort can help improve outcomes for women everywhere. By focusing on education and research, we aim to make a difference for future generations.
FAQ
What is the average age for ovarian cancer diagnosis?
Most ovarian cancer cases are found in women between 60 and 70 years old.
Can young women get ovarian cancer?
Yes, young women can get ovarian cancer, though it’s rare. Women under 40 are at risk, mainly if they have a family history.
What are the common symptoms of ovarian cancer?
Symptoms include bloating, pelvic pain, trouble eating, and needing to pee a lot. These signs can differ by age.
How does age affect the risk of ovarian cancer?
Age is a big risk factor for ovarian cancer. The risk goes up after menopause. Hormones and genes also play a part.
What is the average age for stage 1 ovarian cancer diagnosis?
Stage 1 ovarian cancer is often found in women in their 50s. This is younger than those with advanced cancer.
How does ovarian cancer survival rate vary by age?
Survival rates for ovarian cancer change with age. Younger women tend to live longer than older ones. Five-year survival rates show big differences by age.
What are the treatment considerations for ovarian cancer based on patient age?
Treatment plans vary by age. Younger patients might get more aggressive treatments. Older women might need gentler approaches due to health issues.
Are there any preventive measures for ovarian cancer?
There’s no sure way to prevent ovarian cancer. But, a risk check from teen years to after menopause can spot high-risk women. Age-based checks and monitoring can help.
How does hormone replacement therapy affect ovarian cancer risk?
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) might affect ovarian cancer risk. It’s important to think carefully about using HRT, mainly for women after menopause.
What are the special considerations for high-risk age groups?
Women under 40 with genetic risks and older women at high risk need close monitoring. Early detection is key.
What are the future trends in ovarian cancer age distribution?
Changes in demographics and new research on age and risk might change who gets ovarian cancer. This could affect public health and screening.
References
- National Cancer Institute. (2023). SEER Cancer Stat Facts: Ovarian Cancer. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/ovary.html