
Nearly 500,000 coronary angioplasty procedures happen every year in the United States. These often include the use of heart stents to keep arteries open. Answering can you feel stents in your heart (no) and explaining the procedure known as balloon angioplasty and stenting.
This procedure, known as balloon angioplasty, has changed how we treat coronary artery disease. It’s a big step away from more invasive surgeries.
By making clogged arteries wider and improving blood flow, stenting is key in heart health. It helps many people feel better.
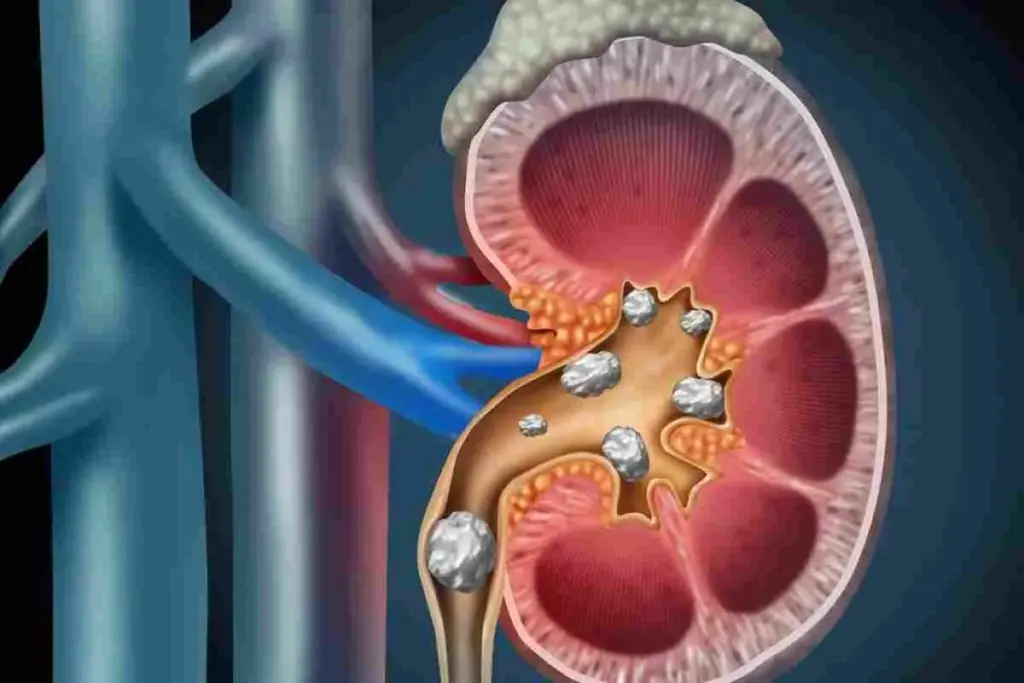
Coronary stents are small, wire mesh tubes that help keep arteries healthy. They are key in treating coronary artery disease. This disease narrows or blocks arteries due to plaque buildup.
Coronary stents keep arteries open, ensuring blood flows to the heart. They are often used with balloon angioplasty. This procedure uses a balloon to widen the artery by pushing aside plaque.
Stents are used to stop arteries from narrowing or blocking again after angioplasty. This lowers the risk of heart attacks and other coronary artery disease complications.
There are many types of coronary stents, each with its own benefits and features.
Bare-metal stents are traditional and made of metal mesh. They are cheaper but have a higher chance of causing artery narrowing.
Drug-eluting stents have a coating that prevents artery narrowing. They are more effective than bare-metal stents in preventing restenosis.
Bioabsorbable stents dissolve over time. They are a newer option designed to reduce long-term risks of traditional stents.
|
Stent Type |
Description |
Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
Bare-Metal Stents |
Made of metal mesh |
Less expensive, traditional option |
|
Drug-Eluting Stents |
Coated with medication |
Reduces risk of restenosis |
|
Bioabsorbable Stents |
Made of dissolvable materials |
Reduces long-term risks |
The development of drug-eluting stents has been a big step forward in cardiology. This shows how important it is to pick the right stent for each patient.
The balloon angioplasty and stenting process has several key steps. It’s a minimally invasive method to treat coronary artery disease.
The first step is inserting a catheter into the clogged artery. A guidewire helps guide the catheter to the blockage. Then, a balloon on the catheter is inflated to widen the artery.
Key Steps in the Procedure:
After the balloon angioplasty, a stent is placed. The stent is a small, mesh-like tube. It’s left in the artery to prevent future blockages.
Patients are awake but sedated during the procedure. Local anesthesia numbs the area where the catheter is inserted. This reduces discomfort.
After the procedure, patients are monitored for a few hours. They check for any complications. This includes watching the insertion site for bleeding and monitoring vital signs.
|
Monitoring Aspect |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Vital Signs |
Heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation are closely monitored. |
|
Insertion Site |
The area where the catheter was inserted is checked for signs of bleeding or hematoma. |
|
Cardiac Function |
ECG monitoring is used to observe heart function and detect any possible issues. |
Many patients wonder if they can feel heart stents after they’re placed. Stents are used to treat coronary artery disease. It’s a common procedure, but patients often ask if they can feel the stent.
Most people don’t feel their stents after they’re put in. But, some might feel discomfort or soreness where the catheter was inserted. This usually goes away in a few days. It’s rare for patients to directly feel the stent itself.
The stent is placed inside the artery and expands to fit. It then becomes part of the artery wall. Because it’s made of metal mesh and very small, most people don’t feel it.
Some discomfort is normal after getting a stent. But, chest pain or shortness of breath could mean a problem. It’s important to know the difference between normal feelings and those that need medical help.
Some patients might feel more aware of their stent because of anxiety or stress. This can make them think they feel the stent more than they actually do. Doctors can help by educating and reassuring patients.
In summary, while most patients don’t feel their stents, knowing about possible sensations and psychological factors helps. This knowledge can help manage expectations and reduce anxiety after the procedure.
Knowing what to expect after a stent is placed can ease worries and help with healing. The time right after the procedure is key. It ensures the stent works right and the patient gets better fully.
Right after the stent is put in, some people might feel pain in their groin or arm. This depends on where the doctor put the stent in. These feelings usually go away quickly and are treated with medicine.
It takes about two weeks for the body to adjust to the stent. During this time, the body starts to heal around the stent. The chance of problems going down. Cardiac rehabilitation programs help a lot. They offer safe exercise, teach heart-healthy habits, and help with stress.
Doctors often tell patients to avoid heavy lifting and hard activities after stenting. They also say not to drive for a while. The doctor will tell you exactly what to do based on your situation and the stent procedure.
Going back to normal life takes time and depends on your health and recovery. Most people can get back to their usual routine in a week or two. But, it’s very important to listen to your doctor’s advice to recover safely and well.
By understanding the recovery and following the doctor’s advice, patients can avoid problems and get the best results from stent placement.
Stent placement is a big deal, and knowing what comes next is key for comfort and safety. After the procedure, people might feel different things because of the stent and healing.
Many patients feel chest discomfort or pressure. This could be from the stent or how the body reacts to it. Chest discomfort is a normal part of getting better, but watching how bad it is and for how long is important.
While healing, people might feel mild pain, numbness, or like something is stuck in their chest. These feelings usually go away as the body gets better.
It’s important to tell normal feelings from serious problems. Severe chest pain, trouble breathing, or feeling dizzy mean you need to see a doctor right away. Knowing the difference can help your recovery and safety a lot.
People on meds after stent placement might feel side effects that seem like stent issues. Knowing your meds and their side effects helps avoid confusion. Always talk to your doctor if you’re not sure about any feelings.
In short, while stent placement saves lives, knowing what to expect can really help with comfort and recovery. Understanding what’s normal and what’s not lets patients feel more confident during their recovery.
Stents are usually not felt by the body. But, restenosis or stent thrombosis can cause sensations. It’s important to know about these complications and their signs.
Restenosis is when the artery narrows again after a stent is placed. You might feel chest pain or discomfort, like before the stent. If you have these symptoms, get medical help right away.
Stent thrombosis is a rare but serious issue where a blood clot forms in the stent. You might feel sudden chest pain, shortness of breath, or even have a heart attack. Getting immediate medical help is key.
Some people might have allergic reactions to stent materials. Symptoms can be mild, like skin rashes, or severe. Always tell your doctor about any allergies before getting a stent.
There are several diagnostic tests to check how well the stent is working. These include:
|
Test |
Purpose |
Frequency |
|---|---|---|
|
Angiography |
Visualize stent and artery |
As needed |
|
Stress Test |
Assess heart function under stress |
Periodic |
|
Ultrasound |
Check blood flow through stent |
Regular check-ups |
Regular check-ups and diagnostic tests are important. They help make sure the stent is working right and catch any problems early.
Having a heart stent is just the start of taking care of your heart. After the procedure, patients start a new chapter in heart health. They often wonder about the long-term effects of having a stent.
Over time, the body gets used to the stent. At first, the stent keeps the artery open for better blood flow. As it heals, the stent becomes part of the artery wall. Most patients can then do their usual activities without big problems. The stent gets covered by cells that line the artery. This reduces the risk of problems.
“The stent becomes a part of the arterial wall, and with proper care, patients can enjoy a healthy life post-procedure.”
Living with heart stents means making some lifestyle changes. These changes help the stent work right and keep your heart healthy. Changes might include:
These lifestyle changes can greatly improve life for patients with heart stents.
Patients with heart stents usually need to take medicines to stop clots. These medicines are often aspirin and P2Y12 inhibitors, like clopidogrel. How long you need these medicines depends on the stent type and your health.
|
Medication |
Purpose |
Duration |
|---|---|---|
|
Aspirin |
Prevent blood clots |
Indefinitely |
|
P2Y12 Inhibitors (e.g., clopidogrel) |
Prevent platelet aggregation |
6-12 months or longer |
Many patients have shared good experiences with heart stents. For example, a patient was back to hiking in a few weeks after his stent. “I was back on the trails in no time, feeling healthier than ever,” he said.
Living with heart stents long-term is doable with the right attitude, lifestyle changes, and following your medication. Understanding how your body adapts and making the right changes can lead to a healthy, active life.
It’s important for patients with heart stents to know when to seek urgent medical help. Most people do well with their stents. But knowing about possible complications can help get the right care quickly.
Some symptoms need immediate attention. Severe chest pain or discomfort could mean a stent problem or a new heart issue. Also, shortness of breath, dizziness, or fainting are serious signs. And don’t ignore fever, redness, or swelling at the catheter site.
Some symptoms need to be told to your doctor, not just right away. Report mild chest pain, fatigue, or any odd feelings. It’s key to know the difference between normal recovery and possible problems.
Regular check-ups with your cardiologist are key. They help keep an eye on the stent and your heart health. These visits can catch issues early and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Be active in your health by asking questions at follow-up visits. Ask things like: “What are the signs of stent failure?”, “How long will I need to take antiplatelet therapy?”, and “Are there lifestyle changes I should make for the stent’s success?”
Balloon angioplasty and stenting are key in treating heart issues and keeping the heart healthy. Knowing about these procedures helps people understand their treatment and recovery better.
Stents in arteries help blood flow, lowering heart problem risks. Most people don’t feel their stents. But knowing what’s normal and what’s not can help with recovery.
Keeping the heart healthy after stenting means making lifestyle changes, taking medicine as directed, and getting follow-up care. These steps help avoid complications and get the most from the stenting procedure.
In short, balloon angioplasty and stenting are vital for heart health. Understanding these procedures helps people make better care choices. This leads to better heart health outcomes.
Balloon angioplasty and stenting is a procedure to open blocked arteries. It uses a balloon to widen the artery and a stent to keep it open.
There are many heart stents, like bare-metal, drug-eluting, and bioresorbable stents. Each type is chosen based on the patient’s condition and medical history.
Most people don’t feel their stents after the procedure. But, some might feel chest discomfort or pressure during healing.
After stent placement, people might feel mild chest discomfort or pressure. These feelings are usually temporary and go away as the artery heals.
Recovery time varies, but most can get back to normal in a few days to a week. It’s important to follow the doctor’s instructions and attend follow-up appointments.
Severe chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness, or severe bleeding are warning signs. If you experience these, seek emergency care.
Follow-up appointments are key to check the stent’s function and heart health. The frequency depends on your condition and the doctor’s advice.
Yes, with proper care and lifestyle changes, you can live normally with a stent. Follow your doctor’s instructions, take medications, and make healthy choices.
After stent placement, you might need to change your diet, exercise regularly, manage stress, and quit smoking. Talk to your doctor about what you need.
Tests like angiograms or stress tests check the stent’s function. Attend follow-up appointments and report any symptoms or concerns to your doctor.
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28279314/
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!