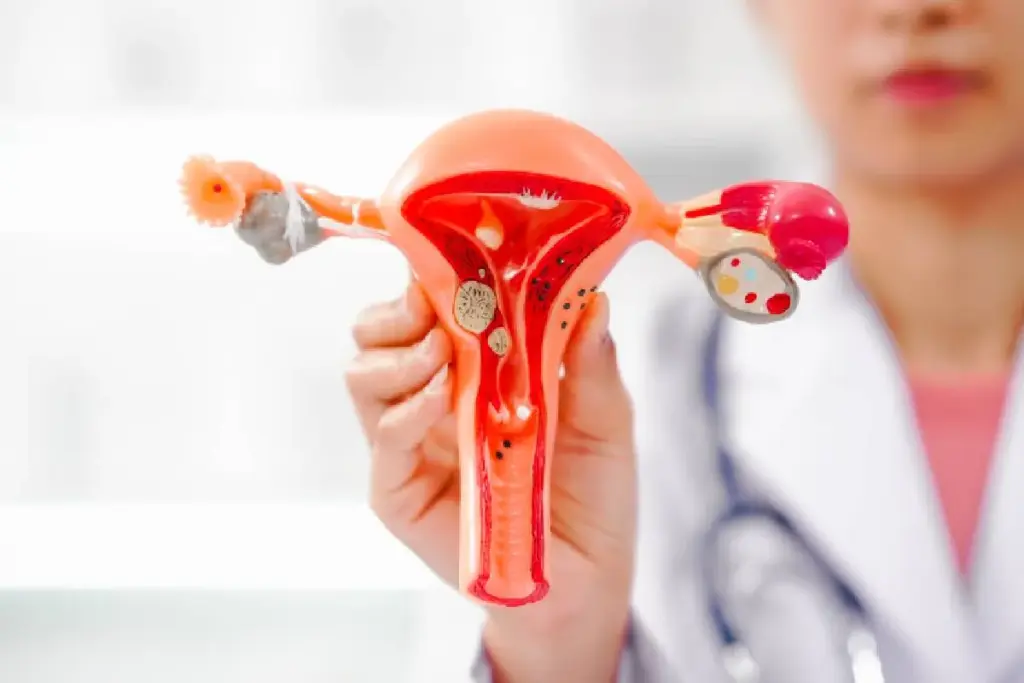
Uterine fibroids are common, affecting millions of women worldwide. Up to 80% of women get them by age 50. A 7 cm fibroid is quite large and can really affect a woman’s life.
It’s important to know the size and weight of such fibroids. This is true for both patients and doctors.
The size of a fibroid can change treatment options and health effects. While the exact weight of a 7 cm fibroid varies, knowing the average weight helps in making care decisions.
Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas, are non-cancerous tumors in the uterus. They can cause various symptoms and health problems. These growths are common in women of childbearing age and affect each person differently.
Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths in or around the uterus. They come in different sizes, numbers, and locations. A lot of women get fibroids, with up to 80% affected by age 50.
The exact reason for uterine fibroids is not known. Hormones, genetics, and environment are thought to play a role in their development.
Women with uterine fibroids may have heavy bleeding, long periods, pelvic pain, and fertility issues. These symptoms can greatly affect a woman’s life.
It’s important to know about treatment options and how to manage symptoms. This helps women make better health choices.
|
Symptom |
Description |
Prevalence |
|---|---|---|
|
Heavy Menstrual Bleeding |
Excessive bleeding during menstrual periods |
Common |
|
Pelvic Pressure/Pain |
Discomfort or pain in the pelvic region |
Frequent |
|
Fertility Issues |
Difficulty conceiving or maintaining pregnancy |
Variable |
Knowing about uterine fibroids, their symptoms, and treatment options is key. It helps women make informed health decisions.
There are many types of uterine fibroids, each with its own features and health effects. They are classified by where they are in or around the uterus. Knowing these differences helps doctors choose the best treatment.
Intramural fibroids are the most common. They grow inside the muscular wall of the uterus. Intramural fibroids can make the uterus bigger and cause heavy bleeding and pelvic pain.
Subserosal fibroids stick out from the uterus into the pelvic area. They grow on the outside and might be attached by a stalk. Posterior subserosal fibroids grow on the back and can press on nearby organs like the rectum.
Submucosal fibroids grow just under the uterine lining. They can stick into the uterine cavity. These fibroids are rare but can cause heavy bleeding and fertility problems.
Pedunculated fibroids are a special kind of subserosal or submucosal fibroid. They are attached to the uterus by a stalk. This can make the fibroid twist, causing a lot of pain.
Knowing the type of uterine fibroid is key to finding the right treatment. Each type affects the uterus differently and has its own health impact.
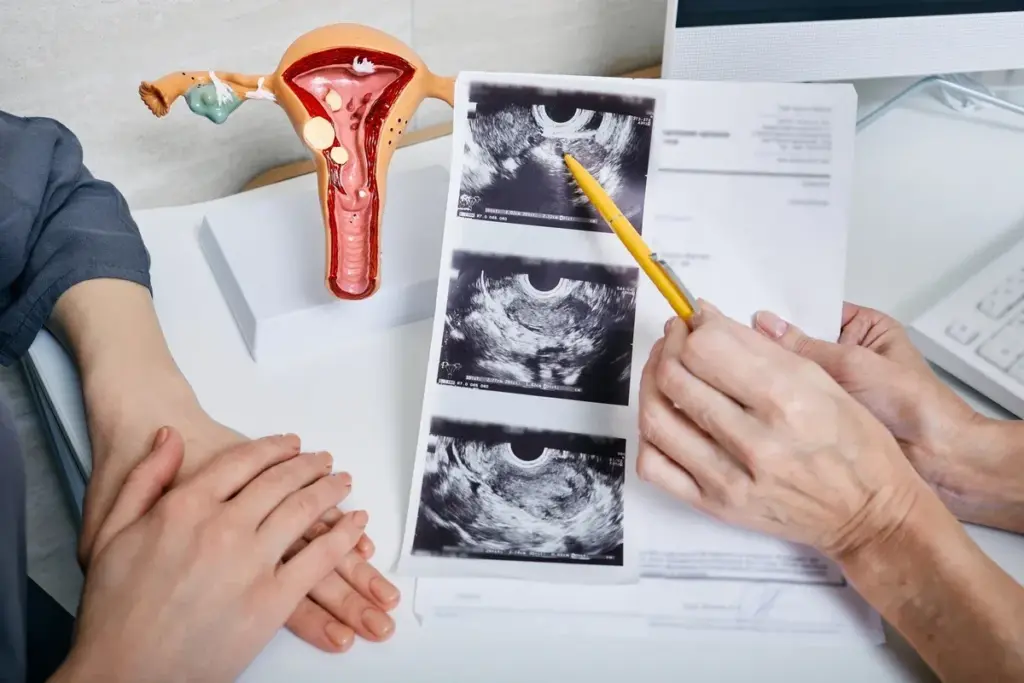
Ultrasound technology is key in measuring and diagnosing fibroids. It’s a non-invasive method that gives important info about fibroid size, location, and number. This helps doctors understand the situation better.
Ultrasound uses sound waves to create images of the uterus. It often involves a transvaginal ultrasound for clearer images. This method is better for seeing the uterine structure and fibroids.
Doctors measure the largest diameter of the fibroid. They use centimeters or millimeters. This info is key for understanding the fibroid’s size and its effect on the uterus.
Fibroids show up as distinct masses on ultrasound images. They can look hypoechoic (darker), hyperechoic (brighter), or mixed. This helps doctors identify the type and characteristics of the fibroid.
Ultrasound images also show where fibroids are in relation to the uterine cavity and other structures. This info is important for planning treatment, like surgery or other strategies.
Ultrasound technology helps doctors accurately diagnose and measure fibroids. It gives a clear picture of their size and impact. This is vital for creating a treatment plan that meets the patient’s needs.
Uterine fibroids can make the uterus bigger. But what is considered normal uterine size? Knowing the normal size of the uterus is key. It helps us see how fibroids can change its size and cause health problems.
The size of a uterus varies among women. Generally, it’s about 7-8 cm long, 5 cm wide, and 4 cm thick. In millimeters, that’s 70-80 mm long, 50 mm wide, and 40 mm thick. These sizes can change based on age, how many times a woman has given birth, and her overall health.
Fibroids can make the uterus bigger. As they grow, they push the uterus beyond its normal size. The size of enlargement depends on the fibroids’ size, number, and where they are located. For example, one big fibroid can make the uterus bigger than many small ones.
Fibroids can make the uterus vary in size, from a bit bigger to much bigger. Sometimes, the uterus gets so big it presses on other organs. This can cause pain and other issues.
The effect of fibroids on uterine size varies among women. The type of fibroid, its location, and the woman’s overall health are important. These factors determine how much the uterus will enlarge.
Knowing the size of fibroids is key for good treatment plans. Fibroids can be different sizes, and knowing their size helps decide the best treatment.
Fibroids are measured in millimeters (mm) or centimeters (cm). They come in various sizes, from small to large. These sizes help doctors understand how serious the problem is and plan the treatment.
|
Fibroid Size Category |
Size in mm |
Size in cm |
|---|---|---|
|
Small |
1-30 mm |
0.1-3 cm |
|
Medium |
31-60 mm |
3.1-6 cm |
|
Large |
61-100 mm |
6.1-10 cm |
|
Very Large |
>100 mm |
>10 cm |
The size of a fibroid affects symptoms and complications. Larger fibroids can cause more severe symptoms.
There’s no one “normal” size for fibroids. But, smaller ones usually don’t cause many problems. Fibroids over 5 cm can start to cause serious symptoms and might need surgery. Those over 10 cm are considered large and can lead to severe health issues like pain, heavy bleeding, and organ pressure.
It’s important for both patients and doctors to understand fibroid sizes and classifications. This helps make better decisions about managing and treating fibroids.
The weight of a uterine fibroid is complex. It depends on its size and other traits. Size is a big clue, but it’s not the only thing that matters.
The size of a fibroid can hint at its weight. Bigger fibroids usually weigh more than smaller ones. But, the fibroid’s density also plays a big role.
A larger fibroid with low density might weigh less than a smaller, denser one. This shows that size isn’t the only factor.
Studies have shown a link between fibroid size and weight. But, this link isn’t always straightforward. As fibroids grow, their weight can increase. But, their composition and blood flow also matter.
Many things can change a fibroid’s weight. Its makeup, where it is, and any changes it goes through are examples. For instance, fibroids with more fibrous tissue might weigh differently than those with more muscle or blood vessels.
“The weight of a fibroid is influenced by multiple factors, making each case unique.” -Gynecologist
Other factors that can affect fibroid weight include:
Understanding these factors is key for doctors. It helps them see how fibroids affect patients. And it helps them choose the best treatment options.
Knowing the weight of uterine fibroids is key for diagnosis and treatment. Fibroids come in different sizes and weights. This knowledge helps doctors choose the right treatment.
Small fibroids are lighter than bigger ones. A 1-3 cm fibroid usually weighs between a few grams and 20 grams. The exact weight depends on the fibroid’s density and makeup.
Medium fibroids, 4 to 6 cm, are heavier than small ones. They can weigh between 50 grams and 150 grams. For example, a 5 cm fibroid might weigh about 100 grams, but it can vary.
Large fibroids, 7 cm or bigger, are much heavier. A 7 cm fibroid might weigh 200 to 300 grams. A 10 cm fibroid could weigh 500 grams or more. These larger fibroids can affect the uterus and nearby organs a lot.
In summary, fibroid weight changes with size. Knowing this helps doctors diagnose and treat better.
The weight of a 7 cm fibroid can vary. It’s important to know its average weight range. This helps us understand its impact on the body.
A 7 cm fibroid is quite large and can weigh a lot. On average, it can weigh between 100 to 200 grams. This can change based on its density and if it’s alone or part of multiple fibroids.
Here are some key points about the weight of a 7 cm fibroid:
Comparing a 7 cm fibroid to everyday objects helps us understand its size and weight. It’s about the size of a large orange or a baseball. In terms of weight, it’s similar to:
Knowing the size and weight of a 7 cm fibroid is key. It helps women and healthcare providers understand its impact. They can then decide the best treatment.
Intramural fibroids grow inside the muscular wall of the uterus. They can appear in different parts of the uterine wall, including the fundus. Their effect on the uterus and health can vary a lot.
Intramural fibroids in the uterine fundus, the top part of the uterus, have special implications. The fundus is a common place for these fibroids. They can change the shape of the uterine cavity, affecting fertility and menstrual flow.
Key Considerations for Intramural Fibroids in the Fundus:
The weight of intramural fibroids can change a lot. It depends on size, location, and how dense the tissue is. Knowing these variations is key for diagnosis and treatment.
|
Size of Intramural Fibroid (cm) |
Average Weight Range (grams) |
|---|---|
|
1-3 |
5-20 |
|
4-6 |
20-50 |
|
7-10 |
50-100 |
In conclusion, intramural fibroids, like those in the uterine fundus, need careful thought. They can affect the uterus and health a lot. Knowing how their weight changes can help in managing and treating them.
Fibroids grow at different rates in different people. This is due to many factors. Fibroids are non-cancerous growths in or around the uterus. Their growth can be affected by various elements.
Fibroid tumors grow at different speeds. Knowing how fast they grow is key to finding the right treatment. Some fibroids stay small and don’t cause problems. But others can grow fast and cause a lot of symptoms.
Studies show that fibroids can grow up to 1 cm per year. But, their growth rate can change due to many factors. These include hormonal changes, genetics, and the environment.
Key factors that influence fibroid growth speed include:
Many things can affect how fast fibroids grow. Knowing these factors is important. It helps predict how a fibroid might grow and find the best treatment.
Hormonal influences are very important in fibroid growth. Estrogen, in particular, helps fibroids grow. This is why they often grow faster during times of high estrogen, like pregnancy.
Understanding what affects fibroid growth helps doctors create better treatment plans. These plans are tailored to each patient’s needs.
Fibroids vary in size, each with its own health effects. Knowing these differences is key for diagnosis and treatment.
Fibroids of different sizes have unique traits. A 5 cm fibroid is medium, while a 7 cm fibroid is bigger and may cause more symptoms. A 10 cm fibroid is large and can lead to serious health problems.
The size of a fibroid affects its symptoms and treatment. Larger fibroids often cause more severe symptoms like heavy bleeding and pelvic pain. They can also complicate pregnancy.
The weight of a fibroid depends on its size, but density also plays a role. We can estimate weight differences based on averages.
|
Fibroid Size (cm) |
Average Weight Range (grams) |
Common Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
|
5 cm |
50-100 |
Mild to moderate pelvic pressure, heavy menstrual bleeding |
|
7 cm |
150-250 |
Moderate to severe pelvic pressure, significant menstrual bleeding |
|
10 cm |
400-600 |
Severe pelvic pressure, heavy menstrual bleeding, possible pregnancy complications |
Knowing the weight differences helps us understand a fibroid’s health impact. It guides us on when medical help is needed.
Large fibroids, like those measuring 7 cm, can greatly affect a woman’s body. They can cause various physical symptoms and impact reproductive health.
A 7 cm fibroid can cause a lot of discomfort. Women may feel heavy menstrual bleeding, long periods, and pelvic pain or pressure. The size and where the fibroid is can make these symptoms worse, affecting daily life and quality of life.
When a fibroid grows to 7 cm, it can press on nearby organs like the bladder and rectum. This can cause urinary frequency, constipation, or bloating. Where the fibroid is in the uterus can affect which organs get pressed and how much.
A 7 cm fibroid can also affect fertility. Its location can block the embryo from implanting or change the shape of the uterus. Women thinking about getting pregnant should talk to their doctor about fibroids.
|
Symptom |
Possible Cause |
Effect on Quality of Life |
|---|---|---|
|
Heavy Menstrual Bleeding |
Large fibroid size (7 cm) |
Anemia, fatigue, and social anxiety |
|
Pelvic Pain or Pressure |
Pressure on surrounding organs |
Discomfort, pain during activities |
|
Urinary Frequency |
Pressure on the bladder |
Frequent urination, nocturia |
Deciding when surgery is needed for fibroids depends on their size and how they affect health. Fibroids can lead to mild discomfort or severe pain and heavy bleeding. These symptoms can greatly reduce a person’s quality of life.
Surgery is often advised for fibroids that are big enough to cause serious symptoms. Fibroids over 5 cm are usually considered for surgery. This is because they can lead to heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pressure, and discomfort.
Doctors say the size of the fibroid is key in deciding if surgery is needed. A 7 cm fibroid is considered big and may need surgery if it’s causing a lot of symptoms.
The severity of symptoms from fibroids is also important in deciding on surgery. Symptoms like severe menstrual cramps, prolonged menstrual bleeding, and anemia from heavy blood loss may require surgery.
“Surgical treatment should be considered for women with symptomatic fibroids who have failed medical management or have significant symptoms affecting their quality of life.”
In cases where fibroids cause a lot of symptoms, surgery can help. It can improve a patient’s overall health and well-being.
A 7 cm fibroid can really affect a woman’s life. Luckily, there are many ways to treat it. The right treatment depends on how bad the symptoms are, the patient’s health, and if she wants to have kids.
For some, not using surgery might be the best first step. These options include:
Minimally invasive methods are another option for 7 cm fibroids. They offer smaller cuts, less pain, and faster healing than open surgery. Choices include:
Sometimes, surgery is needed or wanted. Surgical choices are:
Each treatment has its own good points and things to think about. The best choice depends on the person’s situation. Talking to a doctor is key to finding the right treatment.
Knowing the size and weight of uterine fibroids is key to finding the right treatment. This article has covered how to measure and diagnose fibroids, focusing on 7 cm ones.
It’s clear that fibroid size and weight affect symptoms and treatment choices. A 7 cm fibroid can cause a lot of pain and might need surgery. Knowing the weight range helps women understand their condition better and make informed decisions.
In the end, knowing about fibroid size, weight, and treatment options helps women take charge of their health. Understanding a 7 cm fibroid’s implications lets people work with their doctors to find the best treatment. This improves their overall health and well-being.
A uterine fibroid is a non-cancerous growth in or around the uterus. It’s also known as a uterine myoma or leiomyoma.
Fibroids are measured using ultrasound. Their size is recorded in centimeters or millimeters.
A normal uterus is about 7-8 cm long, 4-5 cm wide, and 2-3 cm thick.
A 7 cm fibroid weighs around 100-200 grams. This is like a large orange or a small grapefruit.
Symptoms include heavy menstrual bleeding and pelvic pressure. You might also feel the need to urinate often. Discomfort or pain in the lower abdomen is common too.
Yes, large fibroids can prevent pregnancy. They can distort the uterine cavity or affect implantation.
Surgery is recommended for fibroids over 7-10 cm. It’s also considered for those causing significant symptoms or affecting fertility.
Treatment options include hormonal therapies and minimally invasive procedures like uterine artery embolization. Surgical options like myomectomy or hysterectomy are also available.
Fibroid growth rates vary. Some grow slowly over years, while others grow faster.
An intramural fibroid grows within the muscular wall of the uterus.
Fibroids can make the uterus larger. This depends on their size, number, and location.
New England Journal of Medicine. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMra1403409
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!