Last Updated on November 26, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir

Recent studies show that ovarian cancer is often diagnosed late. This makes early detection key for effective treatment. It’s important to know how doctors check for this condition.
Doctors employ different detection procedures to spot ovarian cancer. Early detection greatly boosts treatment success. Knowing these methods helps patients stay informed about their health.
Key Takeaways
- Early detection of ovarian cancer is vital for effective treatment.
- Doctors use various methods to check for ovarian cancer.
- Understanding detection procedures can improve patient awareness.
- Recent studies stress the need for ovarian cancer screening.
- Effective treatment depends on the stage of diagnosis.
Understanding Ovarian Cancer: A Brief Overview
Knowing about ovarian cancer is key to catching it early and treating it. Ovarian cancer happens when cells in the ovaries grow abnormally, forming tumors. The ovaries are important for making eggs and hormones. Finding cancer here early is hard.
Ovarian cancer is not just one disease but many. It can start in different parts of the ovary. The most common start in the outer layer, while others begin in egg-making cells or in the tissue that holds the ovary together.
Types of Ovarian Cancer
There are many types of ovarian cancer, with high-grade serous carcinoma being the most common and deadly. Other types include:
- Serous Tumors: These can be either low-grade or high-grade, with high-grade serous carcinoma being more aggressive.
- Clear Cell Carcinoma: Known for its resistance to conventional chemotherapy.
- Mucinous Tumors: These can be benign, borderline, or malignant.
- Endometrioid Tumors: Often associated with endometriosis.
| Type of Ovarian Cancer | Description | Characteristics |
| High-Grade Serous Carcinoma (HGSC) | Most common and aggressive form | Often diagnosed at an advanced stage |
| Clear Cell Carcinoma | Resistant to conventional chemotherapy | Associated with endometriosis |
| Mucinous Tumors | Can be benign, borderline, or malignant | May be large in size |
Why Early Detection Matters
Finding ovarian cancer early is vital for a good outcome. Early detection means better treatment and survival chances. Sadly, ovarian cancer often has no symptoms in its early stages. Regular screening and knowing your risk are important, even more so for those with a family history.
Early detection means timely treatment, like surgery or chemotherapy. Knowing about ovarian cancer and its importance can help women stay proactive about their health.
Common Signs and Symptoms That Prompt Screening
Knowing the signs of ovarian cancer is key. Women should get medical help fast if they notice these symptoms. Ovarian cancer symptoms are often mild and can be mistaken for other issues.
Physical Symptoms
Physical signs are often the first clue. These include:
- Abdominal bloating or swelling, which can be persistent and noticeable.
- Pelvic pain or discomfort, which may be constant or come and go.
- Difficulty eating or feeling full quickly, which can lead to weight loss.
- Urinary symptoms such as urgency or frequency.
Systemic Symptoms
Systemic symptoms affect the whole body. They can be just as telling. Common ones include:
- Fatigue or feeling unusually tired.
- Back pain, which can be a result of the cancer spreading.
- Changes in bowel habits, such as constipation.
- Weight loss, which can occur due to a decrease in appetite or difficulty eating.
When to See a Doctor
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms persistently, see a doctor. These symptoms can also be signs of other conditions. A doctor can give a proper diagnosis.
Key considerations:
- If symptoms persist for more than a few weeks.
- If you have a family history of ovarian or breast cancer.
- If you’re experiencing a combination of these symptoms.
Early detection and diagnosis are key to managing ovarian cancer. If you’re worried about your symptoms, get medical advice without delay.
Risk Factors That May Necessitate Regular Screening
Knowing your risk factors is important for ovarian cancer screening. Several factors can raise your risk of getting ovarian cancer. Understanding these can help in early detection and prevention.
Genetic Predispositions
Genetic mutations are a big deal in ovarian cancer. Mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, known for breast cancer, also up the risk of ovarian cancer. Women with a family history of ovarian or breast cancer, and those with these mutations, are at higher risk.
Women with a BRCA1 mutation face a 35-70% chance of breast cancer by age 70. Those with a BRCA2 mutation have a 25-60% chance. The risk of ovarian cancer by age 70 is about 39-46% for BRCA1 and 10-27% for BRCA2.
| Genetic Mutation | Breast Cancer Risk by Age 70 | Ovarian Cancer Risk by Age 70 |
| BRCA1 | 35-70% | 39-46% |
| BRCA2 | 25-60% | 10-27% |
Family History Considerations
A family history of ovarian or breast cancer is a big risk factor. Women with a first-degree relative (mother, daughter, or sister) diagnosed with ovarian cancer are at higher risk. The risk goes up with more affected relatives.
Women with a significant family history should talk to their healthcare provider. They might suggest genetic counseling and testing to check for harmful mutations.
Age and Lifestyle Factors
Age is a key factor, with risk increasing after 50. Lifestyle factors like obesity and hormone replacement therapy also raise the risk.
Reproductive factors, such as never having children or having a first pregnancy after 35, can also affect risk. Knowing these factors helps decide if regular screening is needed.
Women at high risk should get regular screening. This includes annual ultrasound and CA-125 blood tests for those with significant genetic or family history risk factors.
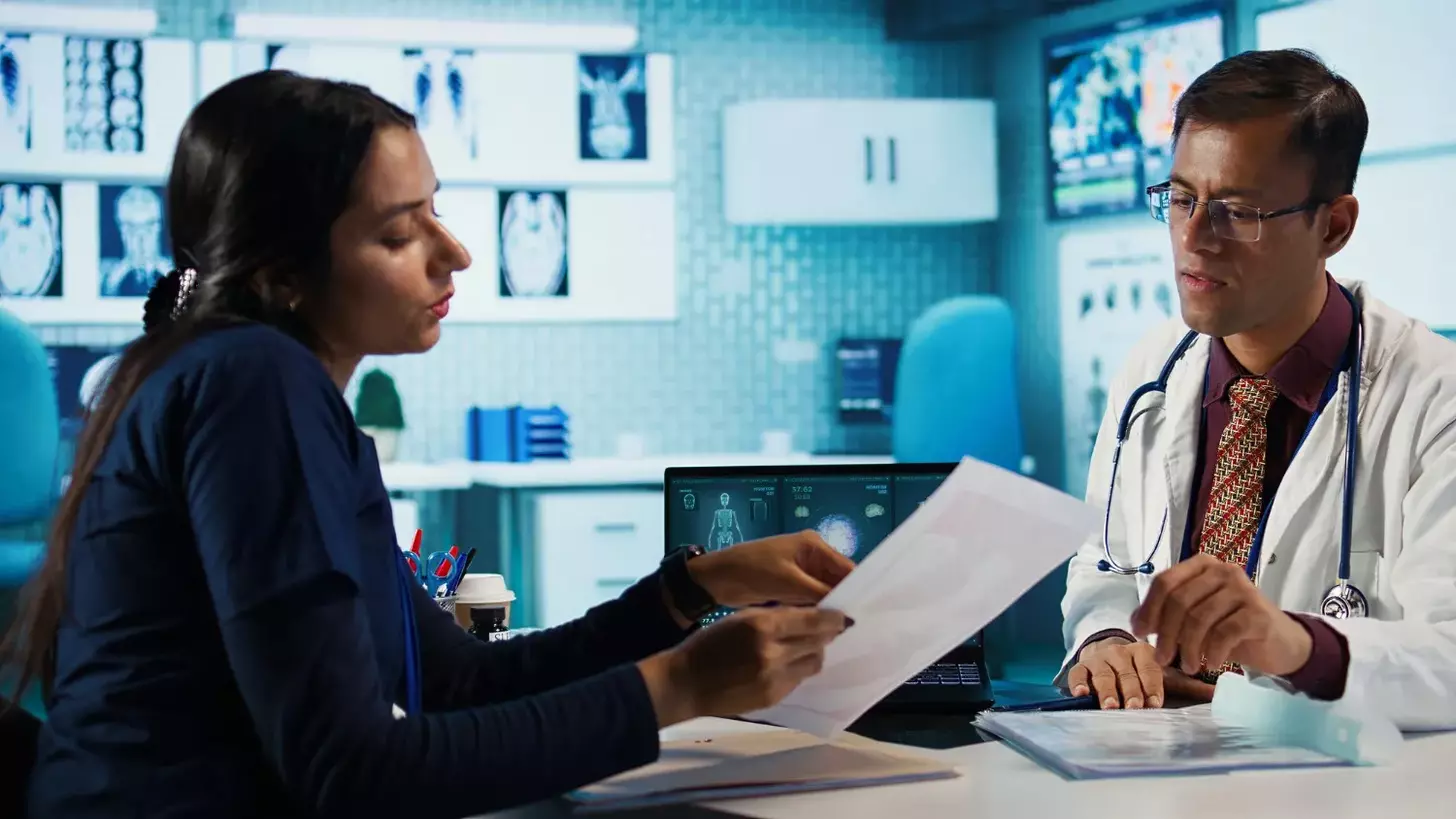
Initial Assessment: The First Doctor’s Visit

The first doctor’s visit is key in diagnosing ovarian cancer. It involves a detailed check to spot symptoms and risk factors of ovarian cancer.
Medical History Review
Looking over the patient’s medical history is vital. Doctors check past health records, surgeries, and current health issues. They also ask about family health, focusing on ovarian or breast cancer.
Symptom Evaluation
Doctors also focus on the patient’s symptoms. They ask about the symptoms’ details, how long they last, and what makes them better or worse.
Doctors carefully review the patient’s medical history and symptoms to spot ovarian cancer. The patient’s family medical history is also important in this process.
Physical Examination Procedures
Healthcare providers use specific techniques to check for ovarian cancer. A detailed physical exam is key to find signs of ovarian cancer.
Pelvic Examination Technique
A pelvic exam is vital for ovarian cancer checks. It involves looking and feeling the reproductive organs. The goal is to see and feel the ovaries’ size, shape, and if they’re tender.
Key aspects of a pelvic examination include:
- Visual inspection of the vulva, vagina, and cervix
- Manual examination to assess the ovaries and other reproductive organs
- Checking for any abnormalities, such as masses or tenderness
Abdominal Examination
An abdominal exam is done to find any oddities in the belly area. It involves feeling the abdomen for any unusual masses or tenderness.
The healthcare provider will look for signs such as:
- Abdominal distension or swelling
- Tenderness or pain upon palpation
- Presence of any masses or abnormalities
What Doctors Look For During Physical Exams
Doctors look for signs of cancer during exams. They check for oddities in the ovaries and symptoms like belly swelling or tenderness.
Doctors are trained to identify:
- Abnormalities in the size or shape of the ovaries
- Tenderness or pain in the pelvic or abdominal region
- Presence of masses or other abnormalities
By combining findings from pelvic and abdominal exams, doctors get a full picture. This helps them decide on the next steps for diagnosis and treatment.
Blood Tests for Ovarian Cancer Detection
Blood tests, like the CA-125 test, are often used to find ovarian cancer. They check for proteins in the blood that might show cancer.
CA-125 Blood Test Explained
The CA-125 blood test looks at the CA-125 protein in your blood. High levels can mean ovarian cancer, but they can also show other issues like pregnancy or endometriosis.
CA-125 testing is not definitive by itself. It’s usually used with other tests. It helps see how well treatment is working and if cancer comes back.
Other Tumor Marker Tests
There are other tests for ovarian cancer too. For example, the HE4 test looks for a protein found in some cancers.
Using many tumor marker tests might make diagnosis better. But, we need more studies to find the best mix and how well they work.
Limitations of Blood Testing
Blood tests, like CA-125, are helpful but have big downsides. They’re not just for ovarian cancer and can give wrong results.
The limits of blood tests show we need a full check-up. This includes imaging and physical exams.
Knowing these limits helps doctors and patients make better choices about tests and treatment.
Ovarian Cancer Screening Methods: Imaging Tests
Imaging tests are key in finding ovarian cancer early. They let doctors see the ovaries and nearby tissues. This helps spot any signs of cancer.
Ultrasounds are the main imaging tests for ovarian cancer. There are two types: transvaginal and abdominal. Each has its own way of working and benefits.
Transvaginal Ultrasound Procedure
A transvaginal ultrasound uses a special probe in the vagina to see the ovaries. It’s great for finding small problems because it gets a close-up view.
The good things about transvaginal ultrasound are:
- It gives clear images of the ovaries
- It can spot small issues
- It’s a gentle procedure
Abdominal Ultrasound
An abdominal ultrasound uses gel on the belly and a transducer to see the ovaries and more. It’s not as detailed as the vaginal one but is useful.
The benefits of abdominal ultrasound are:
- It’s easy and doesn’t hurt
- It looks at bigger areas, like the belly
- It’s good for finding big problems or fluid
Interpreting Ultrasound Results
Reading ultrasound results needs skill. The images show the ovaries’ size, shape, and texture. Signs of ovarian cancer include complex cysts, solid masses, and more blood vessels.
Doctors look at several things when reading results, like:
- Any oddities, like cysts or masses
- The size and type of any found issues
- The patient’s health history and risk factors
Getting ultrasound results right is very important. It helps decide what to do next for diagnosis and treatment.
Advanced Imaging Techniques for Diagnosis
Imaging technologies have changed how we diagnose and stage ovarian cancer. These advanced methods give detailed info on tumor size, location, and spread. This is key for choosing the right treatment.
CT Scan for Ovarian Cancer
A CT scan is a key imaging test for ovarian cancer. It uses X-rays to show detailed images of the abdomen and pelvis. This helps doctors spot tumors and check for cancer spread.
MRI Scan Procedures
MRI scans create detailed images of the body’s inside without harmful radiation. For ovarian cancer, MRI helps tell if a tumor is cancerous or not. It also checks if cancer has spread to nearby tissues.
PET Scan for Cancer Staging
A PET scan is great for seeing if cancer has spread to other areas. It uses a tiny amount of radioactive glucose. Cancer cells take it up, making them show up on the scan.
Together, these imaging methods give a full picture of ovarian cancer’s spread. They help doctors make the best treatment plans.
Biopsy Procedures: The Definitive Diagnosis
Diagnosing ovarian cancer often starts with a biopsy. A biopsy looks at tissue samples to find out if cancer is present, what type it is, and how far it has spread.
Types of Ovarian Biopsies
There are different ways to do an ovarian biopsy. These include:
- Fine-needle aspiration biopsy: A thin needle is used to get a cell sample.
- Core needle biopsy: A bigger needle gets a tissue core sample.
- Surgical biopsy: A surgery to remove tissue or the whole ovary for testing.
Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic surgery is a small cut method to look at ovaries and nearby tissues. It uses small cuts in the belly and a laparoscope for viewing. Surgeons can also take tissue samples during this.
Tissue Sample Analysis
After getting a tissue sample, it goes to a lab for study. Pathologists look at it under a microscope for cancer cells. They also find out the cancer type and grade, which helps decide treatment.
Looking at tissue samples involves several steps:
- Preparing the tissue sample.
- Looking at it under a microscope.
- Doing histopathological analysis to see cancer cells’ details.
Genetic Testing for BRCA Mutations
For those worried about ovarian cancer, genetic testing for BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations can be very helpful. It’s most important for people with a family history of ovarian or breast cancer.
Who Should Consider Genetic Testing
Women with a big family history of breast or ovarian cancer should think about genetic testing. This includes those with:
- A first-degree relative (mother, daughter, or sister) diagnosed with breast or ovarian cancer at a young age.
- Multiple relatives on the same side of the family diagnosed with these cancers.
- A known BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation in the family.
Talking to a healthcare provider about your family history and risk factors can help decide if genetic testing is right for you.
The Testing Process
The first step is a meeting with a genetic counselor or healthcare provider to talk about genetic testing. If you decide to get tested, a blood or saliva sample is taken. It’s then sent to a lab for analysis.
The results can show if you have a BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation, helping figure out your risk of ovarian cancer.
Interpreting Genetic Test Results
Understanding your genetic test results needs help from a genetic counselor or healthcare professional. A positive result means you have a harmful mutation. But a negative result doesn’t mean you’re not at risk.
It’s key to know what your test results mean. This helps you make choices about how to prevent cancer and watch for it.
Staging and Further Assessment
Ovarian cancer staging is key for doctors to understand the disease’s spread. Accurate staging is vital for determining the prognosis and planning the most effective treatment strategy. It looks at the tumor’s size, location, and if it has spread to other parts of the body.
The FIGO Staging System
The International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) staging system is widely used. It categorizes ovarian cancer into different stages based on the tumor’s extent. The FIGO staging system is critical for standardizing ovarian cancer classification, leading to more consistent treatments and research comparisons.
“The FIGO staging system is used to stage ovarian cancer, determining the extent of the disease,” as noted by a reputable medical source. The stages range from I, where the cancer is confined to the ovaries, to IV, where the cancer has spread to distant organs outside the peritoneal cavity.
Additional Tests for Staging
To accurately stage ovarian cancer, additional tests beyond the initial diagnosis are often necessary. These may include:
- Computed Tomography (CT) scans to assess the spread of the disease.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) for detailed images of the tumor and surrounding tissues.
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans to identify any metastatic disease.
These tests help clinicians determine the most appropriate treatment plan. Whether it involves surgery, chemotherapy, or a combination of both. The goal of accurate staging is to provide the best possible outcome for patients by tailoring the treatment to their specific disease characteristics.
Current Guidelines for Ovarian Cancer Screening
Ovarian cancer screening guidelines have changed over time. They differ for women at average and high risk. Health organizations like the American Cancer Society update these guidelines often.
Recommendations for Average-Risk Women
For women at average risk, there’s no recommended screening test for everyone. The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force says there’s not enough evidence for routine screening in asymptomatic women.
“The current evidence does not support screening for ovarian cancer in women who are not at high risk,” says the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. This is because there’s no proven test that lowers ovarian cancer death rates in the general population.
Recommendations for High-Risk Women
Women at high risk, due to genetic mutations or family history, may need more screening.
- High-risk women may need screening every 3-6 months.
- Deciding to start screening should be a personal choice, made with a healthcare provider. It depends on individual risk and the pros and cons of screening.
Frequency of Screening
How often high-risk women should be screened varies. It’s usually every 3-6 months. But, the exact timing depends on individual risk and should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
As
“Screening decisions should be individualized, considering the woman’s risk factors, the characteristics of the screening tests, and the possibility of false positives or negatives.”
This way, screening is tailored to each woman. It aims to maximize benefits while avoiding unnecessary tests.
Challenges in Early Detection of Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer is hard to catch early, even with new medical tools. It’s tough because of the limits of today’s tests and the vague signs it shows.
Limitations of Current Screening Methods
Today’s tests for ovarian cancer have big problems. The CA-125 blood test and ultrasound are not perfect. They can say you have cancer when you don’t, or miss it when you do.
- Inaccuracy in detecting early-stage cancer: Many ovarian cancers are not caught until they’re too far along.
- Lack of specificity: Tests often say you have cancer when you don’t, causing extra worry.
- Limited availability of effective screening tools: There’s no one test that can reliably find ovarian cancer.
Why Symptoms Are Often Missed
Ovarian cancer signs are often unclear and can be mistaken for other, less serious issues. Symptoms include bloating, pelvic pain, and trouble eating. These signs are easy to overlook.
- Non-specific symptoms: Signs like bloating and pain are common in many other illnesses, making it hard to spot ovarian cancer.
- Lack of awareness: Both patients and doctors might not see these symptoms as signs of ovarian cancer.
- Delayed diagnosis: Because symptoms are similar to other conditions, finding ovarian cancer can take too long.
It’s key to understand these challenges to improve finding and treating ovarian cancer. By knowing the flaws in current tests and the subtle nature of symptoms, doctors can aim for earlier detection and better care for patients.
New Developments in Ovarian Cancer Detection
New ways to find ovarian cancer are giving hope for better treatment. Scientists are working hard to spot cancer early and save lives. They’re looking into new methods to make detection more accurate.
Emerging Blood Tests
Blood tests are a big hope for finding ovarian cancer early. These tests look for special signs in the blood that show cancer is present. For example, researchers are making tests that find several proteins and molecules linked to ovarian cancer.
Advantages of Emerging Blood Tests:
- Less invasive than surgery
- Can find cancer early, helping people live longer
- Helps track how the disease is changing and how well treatments work
Innovative Imaging Technologies
New imaging tools are also helping find ovarian cancer. Better ultrasound and MRI scans are being made. These tools help doctors see cancer more clearly.
Examples of Innovative Imaging Technologies include:
- Contrast-enhanced ultrasound
- High-resolution MRI scans
- AI in image analysis
Multi-modal Screening Approaches
Using different tests together is another way to find ovarian cancer. This mix of blood tests, imaging, and doctor checks might spot cancer sooner and more accurately.
The future of finding ovarian cancer looks bright. With ongoing research, we’ll likely see better results. This will be thanks to new blood tests, imaging, and combining different tests.
Conclusion: The Future of Ovarian Cancer Screening
New screening and detection methods are on the horizon, promising better outcomes for ovarian cancer patients. The future will likely see a mix of early detection tests. These include better blood tests and advanced imaging technologies.
Scientists are working hard to find the best screening tests. New technologies are showing promise for earlier and more accurate diagnoses. These advancements could lead to more effective screening, improving patient care.
It’s vital to keep researching ovarian cancer screening. Early detection is key to treating the disease successfully. By exploring new screening methods, doctors aim to boost survival rates and quality of life for those with ovarian cancer.
FAQ
What are the different types of ovarian cancer?
Ovarian cancer comes in three main types. Epithelial ovarian cancer is the most common, making up about 90% of cases. The other types are germ cell ovarian cancer and sex cord-stromal ovarian cancer.
How do doctors check for ovarian cancer?
Doctors use several methods to check for ovarian cancer. They start with a pelvic exam and review your medical history. They also look at your symptoms.
What is the CA-125 blood test used for?
The CA-125 blood test looks for a protein that may be higher in women with ovarian cancer. It’s not a sure way to diagnose, but it can point to a higher risk.
What is a transvaginal ultrasound, and how is it used in ovarian cancer screening?
A transvaginal ultrasound uses a probe in the vagina to see the ovaries. It’s often used with a pelvic exam to check for any issues.
Who should consider genetic testing for BRCA mutations?
Women with a family history of ovarian or breast cancer should think about genetic testing. It can show if you’re at higher risk and help with prevention.
What is the FIGO staging system, and how is it used in ovarian cancer?
The FIGO staging system helps classify ovarian cancer based on how far it has spread. It’s used to predict outcomes and plan treatment.
How often should women undergo ovarian cancer screening?
Screening frequency varies based on risk. Women at average risk might not need regular screening. But those at high risk may need it more often.
What are some of the challenges in early detection of ovarian cancer?
Finding ovarian cancer early is hard. Symptoms are often not specific, and current tests have limits. Many cases are found when the cancer is advanced.
What are some emerging developments in ovarian cancer detection?
New blood tests and imaging tech are being developed. These aim to improve detection by combining different tests.
What is laparoscopy, and how is it used in ovarian cancer diagnosis?
Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgery. It lets doctors see the ovaries and nearby tissues. It’s used to diagnose and check how far the cancer has spread.
What is the role of PET scans in ovarian cancer staging?
PET scans use a radioactive tracer to find cancer cells. They help in staging and planning treatment by showing how far the cancer has spread.
Can ovarian cancer be detected through a routine pelvic exam?
A pelvic exam might find signs of ovarian cancer, but it’s not always reliable. More tests are usually needed to confirm a diagnosis.
References
- Cancer Research UK. (2025, February 23). Screening for ovarian cancer. https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/ovarian-cancer/getting-diagnosed/screening