Nearly two-thirds of cancer patients get radiation therapy as part of their treatment. This is according to the National Cancer Institute. It shows how important radiation therapy is in cancer care.
Many people often wonder at what stage of cancer is radiotherapy used and how it helps in different phases of treatment. Radiation therapy is a common treatment for cancer, and its use changes based on the cancer stage and type. Knowing when and how radiotherapy is used is key for good treatment.
Key Takeaways
- Radiation therapy is used in various cancer stages, from early-stage to advanced cancer.
- The decision to use radiotherapy depends on the type and stage of cancer.
- Guidelines for radiotherapy in cancer treatment are established by cancer research institutions.
- Radiation therapy can be used alone or in combination with other treatments.
- The goal of radiotherapy is to destroy cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy tissue.
Understanding Radiation Therapy in Cancer Treatment
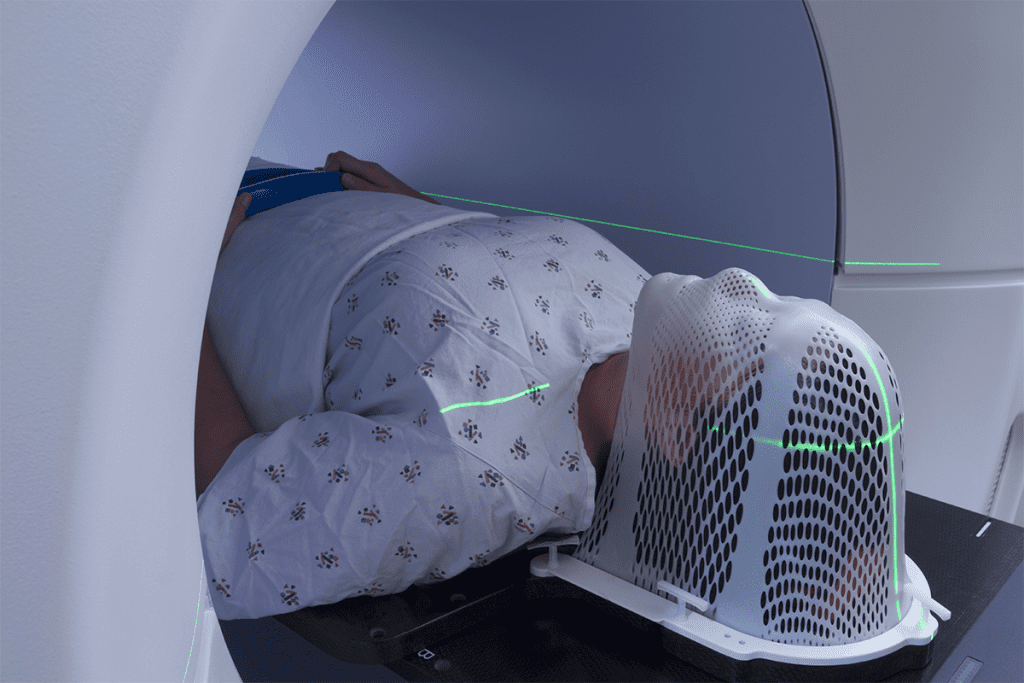
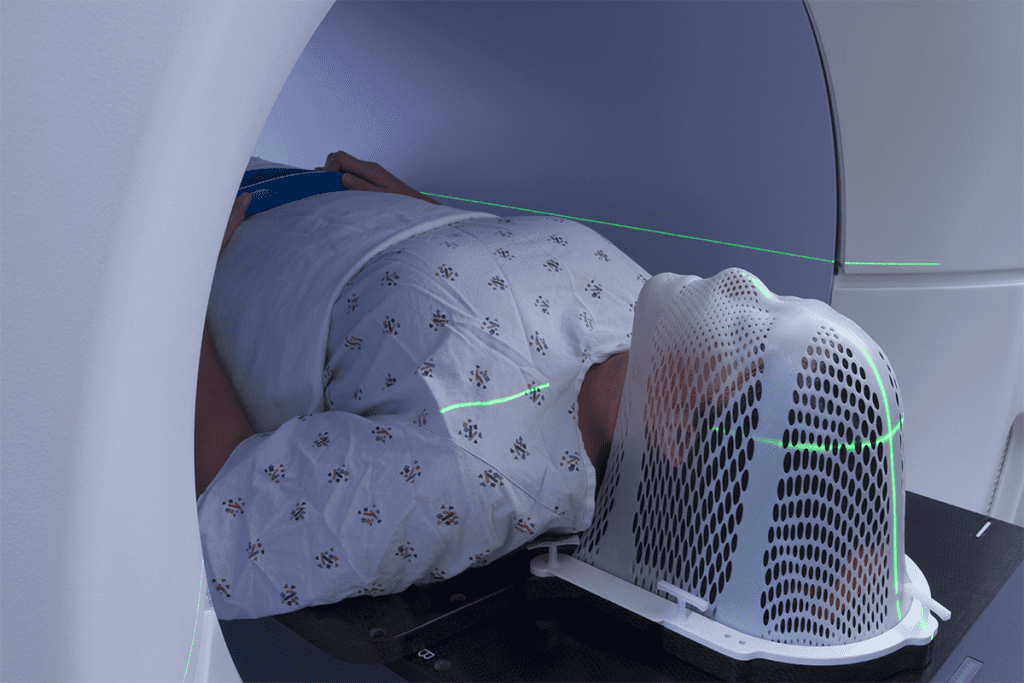
Radiation therapy is a key treatment for cancer. It targets cancer cells in a specific area of the body.
Radiation therapy damages the DNA of cancer cells. This stops them from growing and dividing. The treatment uses high-energy particles or waves to do this.
The Science Behind Radiation Therapy
The science of radiation therapy uses high-energy particles or waves to harm cancer cells. There are two main types: external beam radiation therapy and internal radiation therapy (brachytherapy). External beam radiation therapy sends radiation from outside the body to the cancer cells. Brachytherapy places a radioactive source close to or inside the tumor.
- External beam radiation therapy is common and treats many cancers.
- Brachytherapy is great for treating tumors that are close to the surface.
How Radiation Kills Cancer Cells
Radiation therapy kills cancer cells by damaging their DNA. This damage stops the cells from reproducing. The success of radiation therapy depends on the cancer type, stage, and the patient’s health.
- The dose and how often radiation is given are carefully planned. This aims to harm cancer cells while protecting healthy tissue.
- Radiation therapy can be used alone or with other treatments like surgery or chemotherapy.
At What Stage of Cancer is Radiotherapy Used
Radiotherapy is used in many ways in cancer care. It’s used for early-stage, locally advanced, and metastatic cancer. This treatment uses radiation to kill cancer cells or slow their growth. The choice to use radiotherapy depends on the cancer type, stage, and the patient’s health.
Radiotherapy can be used alone or with other treatments like surgery and chemotherapy. Its flexibility makes it a key tool in cancer management at various stages.
Early-Stage Cancer Treatment
In early-stage cancer, radiotherapy aims to cure the cancer. For example, in early-stage breast cancer, it’s used after lumpectomy to kill any remaining cells. This reduces the chance of cancer coming back. In early-stage prostate cancer, radiotherapy also offers a high chance of cure.
The American Cancer Society says radiotherapy is often used in early-stage cancers. It improves survival rates and may avoid the need for more surgery.
Locally Advanced Cancer Treatment
For cancers that have grown or spread to nearby tissues but not far away, radiotherapy is used with chemotherapy. This combo helps shrink the tumor. It makes it easier to remove surgically or treat with radiotherapy alone.
“Radiotherapy plays a key role in managing locally advanced cancers, improving local control and survival.”- A radiology expert highlights.
A study in the Journal of Clinical Oncology showed benefits of combining radiotherapy with chemotherapy. It found better outcomes than using radiotherapy alone for locally advanced cancers.
Metastatic Cancer Treatment
In metastatic cancer, where cancer has spread far, radiotherapy helps manage symptoms. For example, it can relieve pain from bone metastases or shrink tumors pressing on important structures.
| Cancer Stage | Radiotherapy Application | Goals |
| Early-Stage | Curative intent, post-surgery | Eliminate cancer, reduce recurrence |
| Locally Advanced | Combined with chemotherapy | Shrink tumor, improve local control |
| Metastatic | Palliative care | Relieve symptoms, improve quality of life |
Understanding radiotherapy’s role at different cancer stages helps patients and doctors make better treatment choices.
Goals of Radiation Therapy Across Different Cancer Stages
Radiation therapy has many roles in cancer treatment. Its goals change a lot depending on the cancer stage. It aims to cure, support other treatments, or ease symptoms.
Curative Intent: Eliminating Cancer
At early cancer stages, radiation therapy aims to get rid of the cancer. It’s used for tumors that haven’t spread. The goal is to kill cancer cells without harming healthy tissue.
Adjuvant Therapy: Preventing Recurrence
Sometimes, radiation therapy is used after surgery or chemo to stop cancer from coming back. It targets any cancer cells left behind. This is key for cancers at high risk of returning.
Palliative Care: Symptom Management
For advanced cancers, radiation therapy focuses on easing symptoms and improving life quality. It can reduce pain, shrink tumors, and manage other symptoms. This helps patients feel better.
Radiation therapy’s goals show its importance in cancer treatment. Knowing these goals helps patients and doctors choose the best treatment.
Types of Radiation Therapy Techniques
There are many types of radiation therapy, each with its own benefits. The right choice depends on the cancer type, its stage, and the patient’s health.
External Beam Radiation Therapy
External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT) is the most common. It uses beams from outside the body to kill cancer cells. Treatments are given over several sessions to let healthy cells recover.
The American Cancer Society says EBRT targets a specific area. This helps protect healthy tissues nearby.
Internal Radiation Therapy (Brachytherapy)
Brachytherapy, or internal radiation, places radioactive material close to the tumor. It delivers high doses of radiation to the tumor while protecting healthy tissues.
Brachytherapy can be temporary or permanent. Temporary brachytherapy uses radioactive material for a short time before it’s removed. Permanent brachytherapy leaves the material in place for months.
| Type of Brachytherapy | Duration | Application |
| Temporary | A few minutes to a few days | Commonly used for cancers of the cervix, prostate, and breast |
| Permanent | Until radiation is fully emitted (often a few months) | Often used for prostate cancer |
Systemic Radiation Therapy
Systemic radiation therapy uses radioactive substances given orally or by injection. These substances travel through the bloodstream to find and kill cancer cells all over the body. It’s great for cancers that have spread to many places.
The National Cancer Institute says systemic radiation therapy is effective for cancers that have spread. It’s a good option for widespread cancer.
How Radiation Therapy is Administered
Radiation therapy is a detailed treatment that needs careful planning and execution. It aims to target cancer cells effectively. The process starts with a consultation and ends with the actual radiation delivery.
The Treatment Planning Process
The planning stage is key in radiation therapy. It begins with imaging tests like CT scans, MRI, or PET scans. These tests help find the tumor’s size and location.
Next, a radiation oncologist creates a treatment plan. This plan outlines the dose and how often the therapy will be given.
Radiation Therapy Sessions and Duration
Radiation therapy sessions usually last for weeks. The number and frequency depend on the cancer type, stage, and the patient’s health. Each session is planned to target the tumor precisely, protecting healthy tissues.
Technology and Equipment Used
Modern technology and equipment are vital in radiation therapy. Linear accelerators are often used for external beam radiation therapy. Brachytherapy machines and imaging tools like cone-beam CT are also used for precise targeting.
| Technology | Use in Radiation Therapy |
| Linear Accelerators | Deliver external beam radiation therapy |
| Brachytherapy Machines | Administer internal radiation therapy |
| Cone-Beam CT | Enable precise targeting of tumors |
Radiation Therapy for Specific Cancer Types
Radiation therapy is used in different ways for various cancers, like breast, lung, and brain cancers. Each cancer type needs a special approach to radiation therapy because of its unique traits.
Breast Cancer Radiation Protocols
After a lumpectomy, radiation therapy is often used for breast cancer. It can be external beam radiation therapy (EBRT) or brachytherapy. The choice depends on the cancer’s stage and type.
A study in the Journal of Clinical Oncology showed that women with early-stage breast cancer who got radiation therapy after lumpectomy had a lower risk of cancer coming back.
| Type of Breast Cancer | Radiation Therapy Protocol |
| Early-Stage Breast Cancer | EBRT or Brachytherapy |
| Locally Advanced Breast Cancer | EBRT with Boost |
Lung Cancer Radiation Approaches
Lung cancer radiation therapy can be the main treatment or used with other treatments. Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) is often used for early-stage lung cancer. It gives a high dose of radiation in fewer sessions.
A study in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology found that SBRT helped patients with inoperable early-stage lung cancer live longer.
Brain Cancer and Radiation Masks
For brain cancer, radiation therapy often needs a radiation mask to keep the head steady. This ensures the radiation hits the tumor right on target. It also helps protect healthy tissues around it.
The National Cancer Institute says radiation therapy is a key treatment for brain tumors. Using a radiation mask is key to making the treatment work well.
| Type of Brain Cancer | Radiation Therapy Considerations |
| Glioblastoma | Use of radiation mask, EBRT |
| Meningioma | Precision radiation therapy, Stereotactic radiosurgery |
Comparing Radiation Therapy and Chemotherapy
Radiation therapy and chemotherapy are both used to fight cancer. They work in different ways and are used in different situations. Knowing their differences is key to planning effective cancer treatment.
Radiation therapy uses high-energy particles or waves to kill cancer cells. It can be given from outside the body or inside through brachytherapy. Chemotherapy, on the other hand, uses drugs to kill cancer cells. These drugs can be taken by mouth or given through an IV.
Key Differences in Treatment Mechanisms
The main difference between radiation therapy and chemotherapy is how they work. Radiation therapy targets cancer cells in a specific area. Chemotherapy, on the other hand, affects the whole body. This makes chemotherapy good for treating cancers that have spread.
| Treatment Characteristics | Radiation Therapy | Chemotherapy |
| Mechanism of Action | Localized, targets specific area | Systemic, affects whole body |
| Delivery Method | External beam or internal (brachytherapy) | Oral or intravenous drugs |
| Primary Use | Treating localized tumors | Treating systemic or metastatic cancer |
When Chemotherapy is Preferred Over Radiation
Chemotherapy is often chosen when cancer has spread to many parts of the body. It’s also used for cancers that respond well to chemotherapy. For example, some types of leukemia and lymphoma are treated with chemotherapy.
Combined Chemoradiation Approaches
In some cases, both radiation therapy and chemotherapy are used together. This is called chemoradiation. It can make treatment more effective by making cancer cells more sensitive to radiation.
For instance, using chemoradiation in treating some head and neck cancers can improve survival rates. This is compared to using radiation therapy alone.
Side Effects of Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy fights cancer but can harm healthy tissues. This can cause various side effects. These depend on the radiation dose, the body area treated, and the patient’s health.
Short-Term Side Effects
Short-term side effects happen during or right after treatment. They include:
- Fatigue
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Skin irritation, including redness and itching
These effects usually go away once treatment ends.
Long-Term Side Effects
Long-term side effects can last months to years after treatment. They include:
- Infertility
- Changes in organ function, depending on the area treated
- Increased risk of secondary cancers
- Fibrosis or scarring in the treated area
Hair Loss and Skin Reactions
Hair loss and skin reactions are visible side effects. Hair loss is usually in the treated area and can be permanent. Skin reactions can be mild or severe, like blistering or peeling.
It’s important to manage these side effects. Patients are told to follow skin care routines. They might also get medicines to help.
Managing Life During Radiation Treatment
Life during radiation treatment needs careful planning and flexibility. Patients must adapt to changes that affect their daily life and health.
Daily Routines and Adjustments
Radiation therapy can be tough on the body and mind. Patients often have to change their daily routines to fit treatment times. It’s key to plan rest and balance activity and recovery.
Making small changes, like modifying meal times or reducing strenuous activities, can help manage side effects. This makes treatment more comfortable.
Self-Care Strategies
Effective self-care strategies are vital for patients. This includes eating well, staying hydrated, and doing stress-reducing activities like meditation or yoga.
It’s also important to stay in touch with loved ones. Social support helps a lot in dealing with radiation treatment challenges.
Measuring Effectiveness of Radiation Therapy
It’s key to check if radiation therapy is working well. This treatment focuses on cancer cells in a certain body area. Doctors use different ways to see if it’s effective, like imaging tests and clinical checks.
How to Know if Radiation is Working
To see if radiation therapy is effective, doctors look at several things. Imaging tests like CT scans, MRI, and PET scans help see how tumors are doing. They also watch for signs that the treatment is helping, like smaller tumors or less pain.
“The aim of radiation therapy is to fight cancer and protect healthy tissues,” explains a radiation oncologist. Regular check-ups are vital to see how treatment is going and make changes if needed.
Follow-up Protocols and Monitoring
Follow-up care is a big part of radiation therapy. It lets doctors keep track of how treatment is doing and spot problems early. Follow-up care includes regular visits, imaging tests, and other checks. How often you need to go back depends on your cancer type and how you’re doing.
A structured follow-up plan helps manage side effects or complications. It’s also a chance for patients to talk about their treatment or any worries they have.
Decision-Making Process for Radiation Treatment
Choosing radiation treatment involves looking at many medical and personal factors. A team of healthcare experts works together to find the best treatment for each patient.
Medical Team Considerations
The medical team is key in deciding if radiation therapy is right for a patient. They consider the cancer type and stage, the patient’s health, and the therapy’s benefits and risks. They use the latest tests and scans to understand the cancer’s extent and its effects on the body.
Patient Factors in Treatment Planning
Patient factors greatly affect treatment planning. The patient’s wishes, medical history, and current health are considered to make the treatment fit their needs. This approach makes the therapy as effective as possible while reducing side effects.
Guidelines for Radiotherapy in Cancer Treatment
Guidelines for radiotherapy are based on the latest research. These guidelines help ensure patients get high-quality care. The team follows these protocols and considers each case to make informed decisions about radiation therapy.
By combining medical team considerations, patient factors, and radiotherapy guidelines, healthcare professionals can create a detailed treatment plan. This plan optimizes the use of radiation therapy in cancer care.
Innovations in Radiation Oncology
Innovations in radiation oncology are changing how we treat cancer. They bring new hope to patients. The field keeps growing with new tech and treatment methods.
Precision Targeting Technologies
Precision targeting technologies have made radiation therapy better. Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) help target cancer more accurately. This reduces harm to healthy tissues.
Reduced Side Effect Approaches
Reducing side effects in radiation therapy is key. Proton therapy and image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) are used to protect non-cancerous areas. This helps lower side effect risks.
Future Directions in Radiation Therapy
The future of radiation therapy is bright. Research in artificial intelligence (AI) and personalized medicine is underway. These advancements will make treatments more precise and effective.
Finding Radiation Therapy Services
Finding radiation therapy services may feel overwhelming, but the right information makes it easier. When you’re diagnosed with cancer, knowing your radiation therapy options is key.
Radiation Oncology Centers
Radiation oncology centers offer radiation therapy. They have the latest tech and skilled doctors. To find one near you, try these steps:
- Ask your primary care doctor for a referral.
- Check with your insurance for in-network centers.
- Look online for centers in your area.
When picking a center, look at their experience with your cancer type. Also, check their tech and staff qualifications.
| Center Characteristics | Importance | What to Look For |
| Experience with Cancer Type | High | Centers with a proven track record for your cancer type |
| Technology and Equipment | High | Latest models of linear accelerators, brachytherapy equipment |
| Staff Qualifications | High | Board-certified radiation oncologists, experienced physicists and therapists |
Questions to Ask Your Radiation Oncologist
After finding a center, ask important questions during your visit. Key questions include:
- What type of radiation therapy is recommended for my condition?
- What are the possible side effects, and how can they be managed?
- How will the treatment be planned and delivered?
- Are there any clinical trials or new treatments available?
These questions help you understand your options and make informed choices about your care.
Conclusion: The Role of Radiation in Modern Cancer Care
Radiation therapy is key in modern cancer treatment. It offers a flexible and effective way to handle different cancer stages. This shows its importance and adaptability in cancer care.
Radiation therapy has many roles, like curing cancer, helping other treatments, or easing symptoms. Thanks to new technologies, treatments are now more precise and less harsh. This means better care for patients.
The value of radiation in cancer treatment is clear. It helps patients and doctors make better choices. This leads to better results and a better life for those with cancer.
FAQ
What is radiation therapy used for in cancer treatment?
Radiation therapy kills cancer cells or slows their growth. It can be used alone or with other treatments like chemotherapy or surgery.
At what stage of cancer is radiation therapy used?
Radiation therapy is used at different cancer stages. This includes early-stage, locally advanced, and metastatic cancer. The stage depends on the cancer type, location, and the patient’s health.
How does radiation therapy work?
Radiation therapy damages cancer cells’ DNA. This stops them from dividing and growing. It leads to the death of these cells.
What are the different types of radiation therapy?
There are several types of radiation therapy. These include external beam radiation therapy, internal radiation therapy (brachytherapy), and systemic radiation therapy. Each type is used for specific cancers.
How is radiation therapy administered?
Radiation therapy involves treatment planning and sessions. Specialized technology and equipment are used. The planning ensures the radiation targets the tumor precisely.
What are the side effects of radiation therapy?
Side effects include fatigue, skin reactions, hair loss, and nausea. These depend on the radiation location and dose.
How can I manage my daily life during radiation treatment?
Adjust your routine and practice self-care during treatment. Follow your healthcare team’s advice. This helps manage side effects and keeps you well.
How do I know if radiation therapy is working?
Effectiveness is monitored through follow-up appointments and imaging tests. Your healthcare team will assess your response and adjust the plan if needed.
What is the difference between radiation therapy and chemotherapy?
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy uses drugs to target them. Both can be used alone or together, based on cancer type and stage.
How often do I need to undergo radiation therapy sessions?
Session frequency and number vary by cancer type and stage. Your radiation oncologist will guide you on the schedule.
Can radiation therapy be used for palliative care?
Yes, it can relieve symptoms and improve quality of life in advanced cancer patients.
What are the latest innovations in radiation oncology?
Innovations include precision targeting technologies and new radiation delivery techniques. These aim to improve treatment outcomes and patient care.
How can I find radiation therapy services near me?
Look for radiation oncology centers in your area. Consult with a radiation oncologist. They can discuss treatment options and help choose the best care.
References
Baskar, R., Lee, K. A., Yeo, R., & Yeoh, K. W. (2012). Cancer and radiation therapy: current advances and future directions. PMC. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3298009/