Last Updated on October 21, 2025 by mcelik

Over 1 million people in the U.S. are diagnosed with blood-related disorders each year. These conditions affect the blood, bone marrow, and lymphatic system. They can be complex and need special care. A hematologist is a healthcare expert who deals with these diseases.
The American College of Physicians says hematologists treat issues like anemia, bleeding disorders, and blood cancers. If you’re seeing a hematologist, your primary care doctor thinks you need their help. This is because they suspect a condition that needs a hematologist’s expertise.
Hematology is the study of blood and blood disorders. It’s key in healthcare. It helps us understand blood conditions and their effects on health.
Hematology is a branch of medicine focused on blood disorders. It studies blood cells and proteins involved in bleeding and clotting.
Blood is essential for our survival. It performs critical functions:
Blood has several key components with unique functions:
Knowing about these components and their roles is crucial for diagnosing and treating blood disorders.
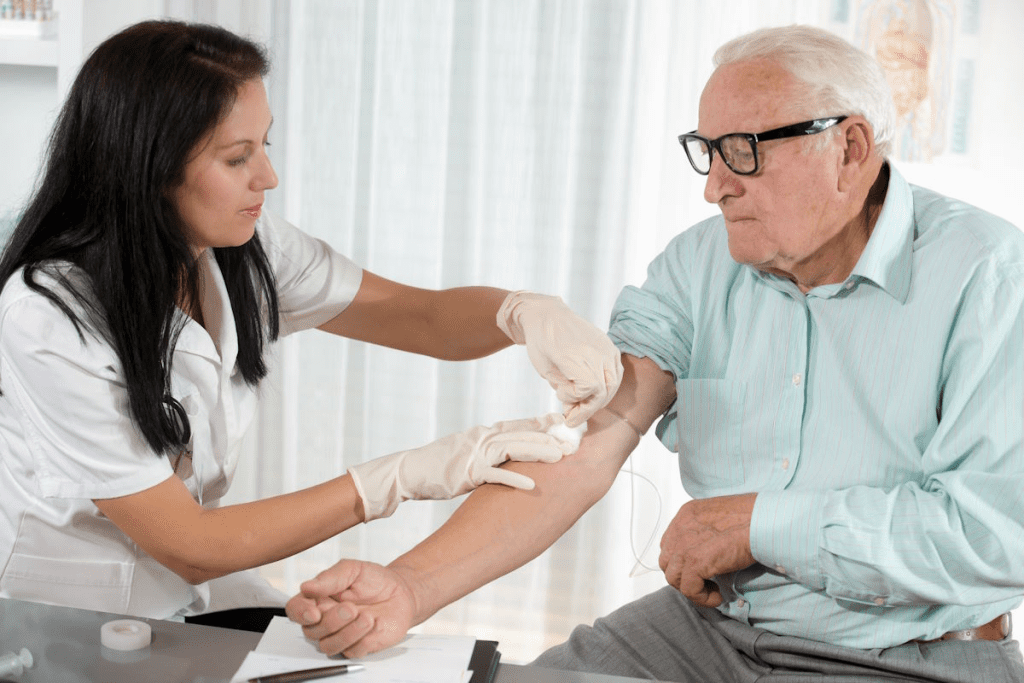
Hematologists are key in treating blood-related issues, from simple to serious. They diagnose, treat, and manage diseases that affect blood cells.
To become hematologists, they go through a lot of education and training. Here’s what they usually do:
This training helps them understand and treat complex blood disorders.
Hematology has many special areas. Some hematologists focus on:
These special areas help hematologists become experts and give better care to their patients.
Hematologists are important in the healthcare team. They work with others to give full care. Their jobs include:
| Role | Description |
| Diagnosis | They do and read blood tests and other tests. |
| Treatment | They make and carry out plans for treating blood disorders. |
| Collaboration | They work with other healthcare teams for better care. |
By teaming up with others, hematologists make sure patients get the best care for their blood issues.
If you’re being referred to a hematologist, it’s likely due to abnormal blood test results or persistent symptoms. This can be a concerning time. It’s natural to have questions about what this means for your health.
Abnormal blood test results often lead to a hematologist referral. These tests can show issues like anemia, clotting disorders, or even leukemia. If your primary care doctor finds unusual results, they might send you to a specialist for a closer look and treatment plan.
Some common blood tests that may lead to a hematologist referral include:
Persistent symptoms like fatigue, bruising, or frequent infections can also lead to a referral. These symptoms might point to a blood disorder that needs specialized care. A hematologist can investigate these symptoms, find the cause, and create a treatment plan.
Some symptoms that may lead to a hematologist referral include:
| Symptom | Possible Indication |
| Unexplained fatigue | Anemia or other blood disorders |
| Easy bruising or bleeding | Clotting disorders or platelet issues |
| Frequent infections | Immune system disorders or bone marrow issues |
The referral process starts with your primary care doctor. They will check your symptoms and test results to see if you need a specialist. If a hematologist is needed, your primary care doctor will refer you and share your medical history.
At your first visit with a hematologist, you’ll have a detailed review of your medical history and a physical exam. You might also have more tests to accurately diagnose your condition.
Understanding why you need a hematologist and what to expect can make you feel more prepared and confident. If you’re looking for a “hematologist near me” or “hematologists near me,” choose a specialist who can offer the care and support you need.
Knowing why you need to see a hematologist can help ease your worries. It’s not always a sign of a serious illness. Hematologists deal with many blood diseases, both simple and serious.
Hematological issues can be mild or very serious. Hematologists are experts in treating a wide range of blood disorders.
They handle conditions like anemia, bleeding disorders, and blood clotting issues. These can affect people differently, from mildly to severely.
Common Hematological Conditions:
| Condition | Description | Typical Treatment Approach |
| Anemia | A condition characterized by low red blood cell count or hemoglobin level. | Iron supplements, dietary changes, or addressing underlying causes. |
| Bleeding Disorders | Conditions like hemophilia that affect the blood’s ability to clot. | Replacement therapy, clotting factor concentrates, or gene therapy. |
| Blood Clotting Disorders | Conditions that lead to inappropriate blood clot formation. | Anticoagulant medications, lifestyle modifications. |
Preventive care is crucial in hematology. Regular check-ups can catch problems early. Hematologists help manage chronic conditions and prevent complications.
“Early detection and treatment of blood disorders can significantly improve patient outcomes. Regular monitoring and preventive measures are key components of hematology care.”
Not all blood disorders are serious. Hematologists can tell the difference between minor and major issues.
Mild anemia might need just diet changes and supplements. But severe cases might need transfusions or other treatments.
Understanding blood disorders and preventive care helps patients. Whether it’s a minor or major issue, hematologists are ready to help.
Hematology covers many blood disorders, each with its own challenges and treatments. Hematologists deal with conditions that affect blood production, function, and health. They diagnose and treat various blood-related issues.
Anemia means not enough red blood cells, leading to less oxygen for tissues. There are several types of anemia, like iron-deficiency and vitamin deficiency anemia. Hematologists find the cause and suggest treatments, like diet changes or supplements.
Blood clotting disorders happen when blood doesn’t clot right, causing too much bleeding, or clots too much, causing blockages. Conditions like hemophilia and von Willebrand disease are bleeding disorders. Hematologists use tests to find these disorders and plan treatments, like clotting factor replacement.
Blood cancers, like leukemia and lymphoma, affect the blood and bone marrow. Hematologists are trained to diagnose and treat these cancers with therapies like chemotherapy. Early treatment is key to managing blood cancers.
Inherited blood disorders are passed down through families, affecting blood cell production or function. Sickle cell disease and thalassemia affect hemoglobin, while hemophilia affects clotting. Hematologists help manage these conditions with monitoring, medication, and other treatments.
Understanding blood disorders needs a detailed approach. Hematologists use many tests and procedures. They aim to diagnose and manage blood-related conditions.
The first step is usually initial blood tests and screenings. These tests look for any oddities in blood cell counts and shapes. Common tests include:
These tests are key to understanding a patient’s blood health. They help decide what steps to take next.
If initial tests show a problem, more tests follow. These can be:
These tests help diagnose complex blood disorders. They shed light on their causes.
Sometimes, a bone marrow biopsy is needed. It involves taking a bone marrow sample for study. Other tests might include:
These tests give deep insights into bone marrow health. They help diagnose diseases like leukemia or lymphoma.
Genetic testing is vital for diagnosing inherited blood disorders and some cancers. It helps find genetic mutations or abnormalities. This is crucial for understanding a patient’s condition.
Genetic testing helps tailor treatments. It ensures each patient gets the best care possible.
Treating blood disorders involves many steps. These include medicines, blood transfusions, stem cell transplants, and sometimes surgery. Hematologists create treatment plans that fit each patient’s needs. They look at the condition, its severity, and the patient’s health.
Medicines are key in treating many blood disorders. For example, anticoagulants stop blood clots. Clotting factors help those with bleeding issues. Immunosuppressive drugs treat aplastic anemia by stopping the immune system from attacking the bone marrow.
Iron supplements or erythropoiesis-stimulating agents help with anemia. They boost red blood cell production. For blood cancers, chemotherapy is often used, along with other treatments.
Blood transfusions are a common treatment. They help those with severe anemia or blood loss. Patients with bleeding disorders might get clotting factors or platelets.
Using blood products is done with care to avoid risks. Modern blood banking has made transfusions safer.
Stem cell transplantation can cure some blood cancers and disorders. It replaces diseased bone marrow with healthy stem cells. These can come from the patient or a donor.
Choosing stem cell transplantation is a big decision. It depends on the risks, benefits, and the patient’s health.
Some blood disorders need surgery. For example, splenectomy helps with an enlarged spleen. Surgery can also fix blood clot complications or damaged blood vessels.
Surgical choices are made for each patient. They consider the benefits and risks, and the patient’s condition.
Your first visit to a hematologist is a big step in dealing with blood issues. Being ready is very important. You’ll get a full check-up to find out what’s causing your symptoms.
Before you go, collect all your medical info. This means your health history, what medicines you’re taking, and any test results you have. This helps your hematologist understand your situation better.
To get the most from your visit, follow these steps:
At your first visit, your hematologist will look over your medical history, do a physical check, and talk about tests or more checks you might need. They aim to understand your condition and plan your care.
Your hematologist will ask many questions to get a clear picture of your health. They’ll want to know about your symptoms, health history, and lifestyle. Being truthful helps them give you the best care.
Some questions they might ask include:
| Category | Example Questions |
| Medical History | What are your previous illnesses or conditions? |
| Symptoms | Can you describe your symptoms in detail? |
| Lifestyle | Do you have any family history of blood disorders? |
After your first visit, you’ll likely have follow-up appointments. These are to check on your health, talk about test results, and change your treatment plan if needed. Keeping up with care is key for managing blood disorders.
At follow-up visits, you can expect:
Knowing what to expect at your first hematologist visit helps you feel more ready and confident. Remember, your hematologist is there to help you manage your condition and improve your health.
Hematology and oncology work together because many blood cancers are treated by hematologists. These doctors have expertise in oncology. This is because blood cancers affect the blood, bone marrow, and lymph nodes.
Hematologic oncology deals with cancers of the blood and lymphatic system. This includes leukemias, lymphomas, and multiple myeloma. Hematologic oncologists handle both the blood and cancer aspects, offering complete care.
A leading expert says,
“The integration of hematology and oncology has revolutionized the way we approach blood cancers, allowing for more targeted and effective treatments.”
Patients with blood disorders or cancers often see both hematologists and oncologists. This team approach covers all aspects of their condition. For example, a leukemia patient might get chemotherapy from an oncologist and blood monitoring from a hematologist.
The table below shows when both specialties are needed:
| Condition | Hematologist’s Role | Oncologist’s Role |
| Leukemia | Diagnosing and managing blood-related complications | Administering chemotherapy and other cancer treatments |
| Lymphoma | Monitoring blood cell counts and managing related disorders | Coordinating cancer treatment, including chemotherapy and radiation therapy |
Collaboration between hematologists and oncologists is key for comprehensive care. This teamwork ensures patients get seamless treatment. Both specialists work together to tackle the complexities of the condition.
Collaborative care offers many benefits:
Understanding the connection between hematology and oncology helps patients. It makes them aware of the comprehensive care they receive from these specialties.
Finding a hematologist who fits your needs is key to managing your blood health. There are many things to think about. It’s important to know what to look for.
When looking for a hematologist, several important factors come into play. Specialization and experience are crucial. You want someone who has treated conditions like yours before.
Patient care approach is also vital. You need a hematologist who understands your medical needs and cares for you.
To find the right hematologist, prepare a list of questions. Some important ones include:
| Question | Why It Matters |
| What experience do you have? | Ensures they are familiar with your condition. |
| How do you stay updated? | Indicates their commitment to current best practices. |
| How do you communicate with patients? | Reflects their approach to patient care and support. |
Before making your final decision, think about insurance coverage and referral requirements. Check if the hematologist is in your insurance network. Also, understand any costs you might have to pay.
Also, find out if you need a referral from your primary care doctor. Knowing this can save you time and reduce stress.
By carefully looking at these factors and asking the right questions, you can choose a hematologist who meets your needs. This ensures you get the best care for your blood health.
Living with chronic blood disorders can be tough, but it’s possible to live well. You need the right strategies and support. Chronic blood conditions need ongoing care to avoid problems and enhance life quality.
Managing daily life with a chronic blood condition involves several important steps. Adherence to medication is key, as your hematologist prescribes. Also, a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and exercise, helps manage symptoms and boosts health.
Access to support resources and communities is crucial for those with chronic blood conditions. These resources offer emotional support, practical advice, and a sense of belonging.
Long-term monitoring and care are key to managing chronic blood conditions. Regular visits to your hematologist help adjust treatments and catch complications early.
Regular check-ups allow for monitoring your condition and adjusting treatment plans. It’s also a chance to discuss any concerns or symptoms you’re experiencing.
Making lifestyle modifications can greatly improve blood health. This includes dietary changes, avoiding harmful substances, and managing stress.
By adopting these strategies and working closely with your healthcare team, individuals with chronic blood conditions can enhance their quality of life and manage their conditions well.
Hematological symptoms can sometimes turn into emergencies. It’s important to know when to seek help right away. Some blood disorders can get worse fast, needing quick medical help to avoid serious problems.
Knowing the warning signs for emergency care is crucial. Look out for severe bleeding that won’t stop, extreme fatigue or shortness of breath, and fever or chills in people with weak immune systems.
Specific symptoms that warrant immediate attention include:
If you’re facing a hematological emergency, getting to the right place fast is key. Take the patient to the nearest emergency department or urgent care, based on how bad their symptoms are.
| Symptom | Possible Condition | Action |
| Severe bleeding | Bleeding disorder or trauma | Apply pressure and seek immediate care |
| Extreme fatigue | Anemia or leukemia | Contact hematologist or visit emergency department |
| High fever | Infection in immunocompromised patients | Seek immediate medical attention |
Good communication between emergency care and hematology teams is vital. They need to share important medical history, current treatments, and any special instructions for managing blood disorders.
Understanding the signs of hematological emergencies and how to handle them is crucial. Good communication between healthcare providers is essential for managing these conditions well.
Understanding a hematologist’s role helps patients work better with their healthcare team. This teamwork is key to managing blood disorders well.
Being proactive and asking questions is part of partnering with a hematologist. This way, patients can manage their blood health effectively. They make informed choices and handle the challenges of blood care.
Good blood health comes from accurate diagnosis, effective treatment, and ongoing care. Working closely with a hematologist ensures the best outcomes. This improves patients’ lives greatly.
We urge patients to stay involved and informed about their blood health. A strong partnership with a hematologist leads to the best results.
A hematologist is a doctor who deals with blood disorders and diseases. They diagnose, treat, and manage these conditions.
Hematologists treat blood disorders like anemia and blood cancers. They also give preventive care and manage long-term conditions.
You might see a hematologist if your blood tests show something odd. Or if you have symptoms that could mean a blood disorder. They also help with diagnosed blood conditions.
No, it’s not always serious. Hematologists handle many blood disorders. Most of these are not life-threatening.
At your first visit, expect a detailed medical history and physical exam. You might have some tests. Your doctor will also ask about your symptoms and health history.
Hematologists often diagnose anemia, blood clotting issues, blood cancers, and inherited disorders.
Look for a hematologist based on their experience and specialization. Check patient reviews and insurance coverage too.
Hematology and oncology are closely related. They work together, especially in treating blood cancers. This ensures comprehensive care.
Managing chronic conditions involves medical treatment and lifestyle changes. Your hematologist can guide you on how to manage your condition.
Seek emergency care for severe symptoms like heavy bleeding or severe pain. Your hematologist can tell you when to seek immediate help.
Hematology/oncology is a field that deals with blood disorders and cancer. It combines hematology and oncology.
Hematologists diagnose and treat blood disorders. They also provide preventive care and manage chronic conditions. They work with other healthcare professionals too.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!