Last Updated on October 21, 2025 by mcelik
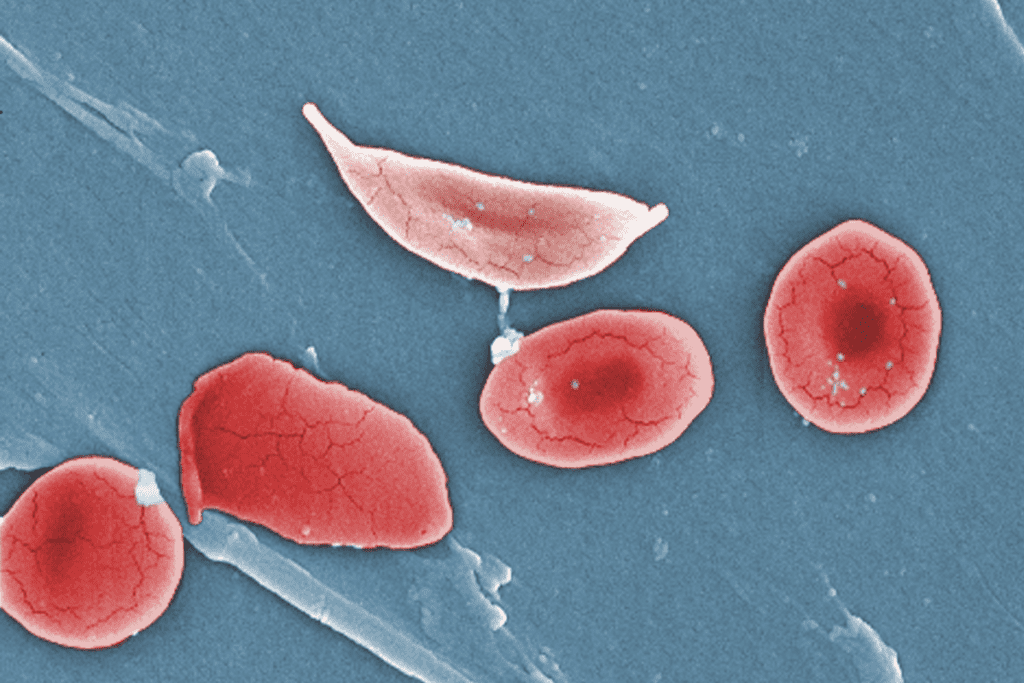
Sickle cell disease is a genetic disorder that affects how red blood cells are made. It makes these cells misshapen and prone to breaking down. The World Health Organization says about 300,000 kids are born with sickle cell disease each year globally.
We must grasp the importance of sickle cell trait symptoms. They have a big impact on people and communities. Sickle cell disease is a major health issue, especially in areas where the sickle cell gene is common.
Sickle cell disease is a condition caused by a mutation in the HBB gene. This mutation leads to the production of abnormal hemoglobin, called hemoglobin S. As a result, red blood cells become sickle-shaped, especially under certain conditions.
Sickle cell disease is caused by abnormal hemoglobin, known as hemoglobin S. This happens because of a genetic mutation. It makes red blood cells rigid and sickle-shaped, which affects their ability to carry oxygen.
“Sickle cell disease is a complex condition that affects not just the red blood cells but also the overall health of an individual,” as noted by medical professionals. The disease is caused by a mutation in the HBB gene, which codes for the beta-globin subunit of hemoglobin.
It’s important to know the difference between sickle cell disease and sickle cell trait. People with sickle cell trait are carriers of the disease. They have one normal and one mutated HBB gene. They usually don’t show symptoms but can pass the mutated gene to their children.
Understanding the difference between these two conditions is key for genetic counseling and managing health.
Sickle cell disease is a big health problem worldwide. It affects many people in different places. This genetic disorder is found in millions globally.
Sickle cell disease is very common worldwide. The World Health Organization says 300,000 to 400,000 children are born with it every year. Most of these children are in sub-Saharan Africa.
The disease is also found in the Middle East, India, and South Asia. It’s linked to malaria in some areas. The sickle cell trait helped protect against malaria, so it’s more common where malaria was once a big problem.
Some groups are more likely to have sickle cell disease because of their genes. In the U.S., it mostly affects people of African descent. But it can also be found in people from the Mediterranean, Middle East, and India.
In Africa, especially sub-Saharan Africa, the disease is a big public health issue. Countries like Nigeria, the Democratic Republic of Congo, and Uganda have a lot of children born with it. Knowing where the disease is most common helps us plan better health strategies.
Managing sickle cell disease worldwide needs a big effort. By understanding where it’s most common, we can help those most at risk.
Sickle cell disease hits hard in certain groups in the US, showing the need for specific health efforts. It’s most common among African Americans, with about 1 in 365 births affected.
The disease’s spread varies across different groups in the US. African Americans are hit the hardest, with 1 in 365 births affected. Hispanic Americans also face a higher risk, but less than African Americans. Non-Hispanic whites are less likely to have it.
Knowing these differences helps healthcare workers focus their efforts better. For example, states with big African American populations, like Mississippi and Alabama, see more cases of sickle cell disease.
Life expectancy for those with sickle cell disease has gone up in the US thanks to better medical care. Yet, there are still big gaps in healthcare access and results, especially for the poor and uninsured.
About 100,000 people in the US live with sickle cell disease. It costs a lot to care for them, with costs ranging from $10,000 to over $100,000 a year. This depends on how severe the disease is and how often complications happen.
Public health efforts to raise awareness and improve care for sickle cell disease are key. They help tackle these gaps and better the lives of those affected.
It’s important to know how sickle cell disease is passed down. This condition affects how red blood cells carry oxygen. It’s caused by a problem with hemoglobin, a key protein in these cells.
Sickle cell disease follows an autosomal recessive pattern. This means a person needs two mutated HBB genes, one from each parent, to have the disease. If someone has only one mutated gene, they might carry the trait but not show symptoms.
When both parents carry the trait, there’s a 25% chance their child will have sickle cell disease. There’s a 50% chance the child will be a carrier like the parents. And a 25% chance the child won’t have the mutated gene.
| Parental Carrier Status | Chance of Child Having Sickle Cell Disease | Chance of Child Being a Carrier | Chance of Child Not Being Affected |
| Both parents are carriers | 25% | 50% | 25% |
| One parent is a carrier, the other is not | 0% | 50% | 50% |
The mutation causing sickle cell disease happens in the HBB gene. This gene tells our bodies how to make a part of hemoglobin. The mutation leads to abnormal hemoglobin, called hemoglobin S (HbS).
Key aspects of the genetic mutation include:
Knowing about these genetic details is key for family planning. It’s especially important for families with sickle cell disease or trait history.
Most people with sickle cell trait don’t show symptoms. But, hard physical work or high altitudes can cause problems. Knowing these risks helps manage the condition better.
People with sickle cell trait usually don’t have symptoms. But, intense physical stress or high altitudes can lead to issues. These might include splenic infarction and hematuria, or blood in the urine.
It’s important for carriers to know these risks. This is especially true for those who do hard activities or go to high places. Being aware and taking steps to prevent problems can help a lot.
Symptoms in sickle cell trait carriers often show up in certain situations. For example, during tough military training or sports, athletes might get exertional rhabdomyolysis. This is when muscles break down. High altitudes can also cause problems like splenic sequestration in some cases.
Knowing these risks helps carriers take steps to avoid them. For instance, getting used to high altitudes slowly and not pushing too hard physically can help prevent issues.
It’s important to know the symptoms and complications of sickle cell disease. This genetic disorder affects how red blood cells make hemoglobin. It leads to several health problems.
People with sickle cell disease often face acute symptoms. Pain crises are a big issue. They happen when sickled red blood cells block blood vessels, cutting off blood flow and causing pain.
Common acute symptoms include:
Chronic complications are also a big concern for those with sickle cell disease. These problems come from repeated sickling and vaso-occlusion. They can damage organs over time.
Some of the chronic complications include:
Managing these symptoms and complications needs a detailed plan. This includes medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and regular check-ups. Knowing all about sickle cell disease helps healthcare providers give better care and support.
Sickle cell disease makes red blood cells sickle-shaped. This can cause them to break down early. It affects many parts of the body because of abnormal hemoglobin.
Red blood cells in sickle cell disease patients are abnormal. They break down quickly, lasting only 10-20 days. This leads to anemia, where the body doesn’t get enough oxygen.
The sickled cells also stick together, blocking blood vessels. This can cause acute pain crises and damage to organs. It’s because of poor blood flow and oxygen delivery.
Sickle cell disease affects more than just red blood cells. It can harm organs and systems across the body. Some possible problems include:
Understanding sickle cell disease’s effects is key to managing it. It helps prevent long-term problems. Healthcare providers can then create better treatment plans to help patients.
Sickle cell disease and trait can be diagnosed through specific tests. Early diagnosis is key to managing the disease and preventing complications.
Diagnosing sickle cell disease involves several blood tests. The main test is hemoglobin electrophoresis. It finds abnormal hemoglobin types, like Hemoglobin S, linked to sickle cell disease.
Other tests include:
These tests help tell the difference between sickle cell trait and the disease. They give important information to those affected and carriers.
Many countries have newborn screening programs for sickle cell disease. These programs use a simple blood test, often during routine newborn screening.
The benefits of newborn screening are:
| Benefits | Description |
| Early Detection | Identifying the condition early allows for timely medical interventions. |
| Preventive Care | Parents are educated on signs of complications, enabling preventive care. |
| Improved Outcomes | Early diagnosis and management improve the quality of life for affected children. |
Newborn screening has greatly improved outcomes for children with sickle cell disease. It allows for early intervention and better management of the condition.
The way we treat sickle cell disease has changed a lot. This brings new hope to people all over the world. We’re seeing big changes in how this condition is managed, with new and exciting methods being developed.
Old treatments for sickle cell disease focused on easing pain and preventing serious problems. Hydroxyurea is a key drug that helps reduce pain crises and may cut down on blood transfusions. Other drugs, like pain relievers and antibiotics, help manage symptoms and fight off infections.
There are also therapies to help manage the disease. Blood transfusions lower the risk of sickle red blood cells. Some patients also get physical therapy and psychological support to deal with the disease’s effects on their life.
In recent years, we’ve seen big steps forward in treating sickle cell disease. Gene therapy and CRISPR technology are being explored as possible cures. These new treatments aim to fix the genetic issue that causes the disease, offering hope for a cure.
New drugs, like crizanlizumab, have been developed to reduce pain crises. There’s also progress in using stem cell transplantation as a cure for some patients.
These new developments are a big step forward in managing sickle cell disease. They bring hope to patients and their families. As research keeps going, we’ll see even more improvements in treatments and outcomes for those with this condition.
It’s key for those with sickle cell trait to know how to manage it. This is to avoid health problems. Even though it’s not as bad as sickle cell disease, carriers need to be careful.
Carriers should know they carry the trait and follow certain steps. Staying hydrated and not doing too much extreme physical exertion are important. They should also see doctors regularly to check on their health.
It’s also vital for carriers to tell their doctors about their trait. This is especially true before surgery or starting new exercise plans. Being proactive helps reduce risks.
Carriers should take several steps to manage their trait. They should avoid very hot or cold temperatures and drink lots of water. They should also be careful when doing intense exercise or at high altitudes.
By following these tips and precautions, people with sickle cell trait can stay healthy and active. It’s all about being aware and making smart choices for their health.
People with sickle cell disease can live active lives with the right lifestyle adjustments and coping strategies. It’s key to manage the condition well to improve life quality.
Those with sickle cell disease face special challenges. But, with the right approach, they can lessen symptoms and avoid complications. We’ll look at the practical ways to live with this condition, focusing on adjustments and strategies that help a lot.
Living with sickle cell disease means making some lifestyle changes. One important one is to stay hydrated. Drinking lots of water helps prevent dehydration, which can cause sickle cell crises.
It’s also crucial to avoid extreme temperatures. Both very hot and very cold can cause crises. So, it’s important to dress right and stay away from extreme weather.
Stress management is key too. Stress can make symptoms worse. Doing things like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing can help manage stress.
| Lifestyle Adjustment | Benefit |
| Staying Hydrated | Prevents dehydration and reduces the risk of sickle cell crises |
| Avoiding Extreme Temperatures | Reduces the risk of temperature-related crises |
| Stress Management | Helps to reduce stress-related symptoms |
Along with lifestyle changes, it’s important to have good coping strategies. This means having a support network of family, friends, and healthcare professionals.
Doing regular physical activity, as allowed, can also help manage symptoms. It’s important to talk to a healthcare provider to make a safe exercise plan.
Also, staying informed about the condition and its management is empowering. This means understanding the latest treatments and therapies.
By combining lifestyle changes with effective coping strategies, people with sickle cell disease can improve their quality of life and manage their condition better.
For families with sickle cell disease history, genetic counseling is key. It helps with family planning and risk assessment. Understanding the genetic side of this condition is crucial for making good choices.
Genetic counseling gives families the info they need about sickle cell disease risks. It helps them grasp the chances of passing the disease to their kids. We guide them in making choices that fit their needs.
We look at the risk of a child having sickle cell disease or trait. We explain the genetic causes and how they’re passed down. This knowledge helps families make smart reproductive choices.
| Genetic Status | Risk of Sickle Cell Disease in Offspring | Risk of Sickle Cell Trait in Offspring |
| Both parents are carriers | 25% | 50% |
| One parent is a carrier, the other has sickle cell disease | 50% | 50% |
| One parent is a carrier | 0% | 50% |
Managing sickle cell disease is more than just medical care. It needs a full support system. Families can find counseling, support groups, and educational materials.
These resources offer emotional support, practical tips, and educational info. They help families deal with the condition. We also connect them with groups focused on sickle cell disease research and advocacy.
By offering genetic counseling and support, we help families manage sickle cell disease well. They can make informed decisions about their health and well-being.
Ongoing research into sickle cell disease is leading to new treatments and potential cures. We are learning more about the disease and finding new ways to manage and treat it.
Research into sickle cell disease is exploring many areas. Some key areas include:
Gene therapy is especially promising. It targets the disease’s root cause, aiming for a cure. Clinical trials are underway to assess the safety and efficacy of these new treatments.
New therapies for sickle cell disease are varied. They include:
| Therapy Type | Description | Potential Benefits |
| Gene Editing | Corrects the genetic mutation causing sickle cell disease | Potential cure, reduced symptoms |
| Pharmacological Interventions | New medications to manage pain crises and other complications | Improved quality of life, reduced hospitalizations |
| Stem Cell Transplantation | Replaces diseased bone marrow with healthy stem cells | Potential cure, elimination of disease symptoms |
These new therapies are both promising and a big step towards personalized treatment. As research keeps advancing, we can look forward to better outcomes for those with sickle cell disease.
As we look ahead, it’s crucial to keep supporting research and stay hopeful about treating sickle cell disease.
Sickle cell disease awareness and advocacy are key to helping those affected. We aim to raise awareness and support the needs of families. This helps improve the lives of those with this genetic disorder.
Many organizations and support groups focus on sickle cell disease. They offer educational resources, patient advocacy, and community support. For example, the Sickle Cell Disease Association of America works hard to raise awareness and support research.
Educational efforts are vital for understanding and managing sickle cell disease. These include public awareness campaigns and education for healthcare providers. They help promote early diagnosis and effective treatment.
Newborn screening programs are a big help. They catch sickle cell disease early, allowing for timely care. Workshops for healthcare providers also ensure they can manage the disease well.
We believe awareness, advocacy, and education can greatly improve lives. This is especially true for those with sickle cell disease.
Understanding sickle cell disease is key to managing it well. We’ve looked at how common it is, its causes, symptoms, and treatments. This gives us a full picture of sickle cell disease.
Sickle cell disease touches millions globally, affecting families deeply. Knowing the signs helps us catch it early. This improves life for those dealing with it.
Research and awareness are crucial in fighting sickle cell disease. We must support groups and efforts to help those with this condition.
In summary, our knowledge of sickle cell disease is growing. This lets us offer better care. Together, we can greatly improve the lives of those with sickle cell disease.
Sickle cell disease is a genetic disorder. It affects how red blood cells make hemoglobin. This makes the cells misshapen and they break down.
Sickle cell disease happens when you have two abnormal hemoglobin genes. Sickle cell trait is when you have one normal and one abnormal gene.
Symptoms include pain episodes, anemia, and infections. Organs like the spleen, kidneys, and liver can also get damaged.
Usually, people with sickle cell trait don’t show symptoms. But, they might feel effects under extreme conditions or high altitudes.
Doctors use blood tests and genetic testing to diagnose it. Newborn screening programs also help.
Treatments include medicines, blood transfusions, and other therapies. They help manage symptoms and prevent complications.
People with sickle cell trait should know their status. They should stay hydrated and avoid too much physical activity to reduce risks.
A healthy diet, staying hydrated, and managing stress are key. These lifestyle changes can help manage the disease.
There’s no cure yet, but research is ongoing. Scientists are working on new treatments and potential cures.
Genetic counseling is vital. It helps families understand the risks and implications. It aids in making informed family planning decisions.
Yes, many organizations offer support. They provide resources, education, and advocacy for those affected by sickle cell disease.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!