Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
When symptoms point to a can ct miss brain tumor, patients look for reliable answers. At Liv Hospital, we focus on patient care and use top-notch diagnostic tools. CT scans are valuable, but they can miss some tumors, like small ones or those in hard-to-reach spots.
We know that even the latest tech, like CT scans, can miss a brain tumor sometimes. The size, location, or type of tumor can affect how well it’s found. At Liv Hospital, we take a detailed approach to diagnosis. We use CT scans and other imaging methods together to get the most accurate results.
Key Takeaways
- CT scans have limitations in detecting brain tumors, like small or complex ones.
- A detailed diagnostic approach is key to accurate detection.
- Liv Hospital is dedicated to using the best diagnostic tools.
- Using CT scans with other imaging methods can improve detection accuracy.
- Factors like tumor size, location, and type can impact detection limits.
Understanding CT Scans in Brain Tumor Detection
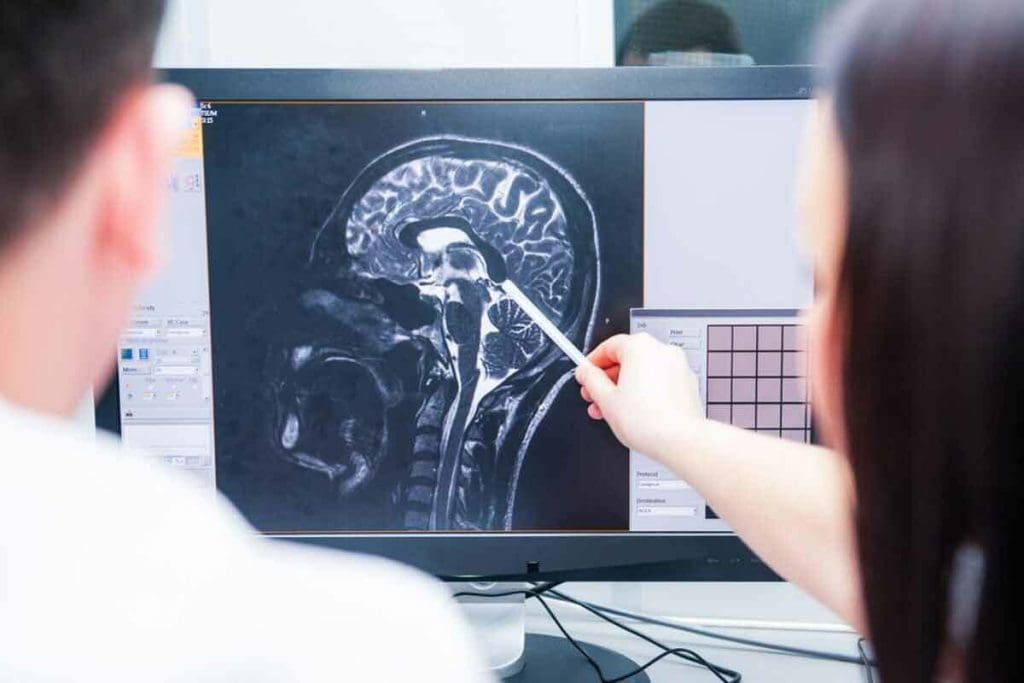
CT scans are key in finding brain tumors. They show detailed brain images. CT scans use X-rays to create detailed images of the brain, helping diagnose various conditions, including brain tumors.
How CT Scanning Technology Works
CT scanning technology uses a rotating X-ray beam and detectors. It captures images of the brain from multiple angles. These images are then made into detailed cross-sectional images, or slices, of the brain.
“The technology has revolutionized the field of neurology,” as it lets doctors see the brain in high detail. This improves how well they can diagnose.
The process starts with the patient on a table that slides into a CT scanner. This is a large, doughnut-shaped machine. The scanner rotates around the patient, capturing images. These images are then used to create a detailed view of the brain’s structures.
Role of CT Scans in Neurological Diagnosis
CT scans are key in neurological diagnosis, very important in emergencies. They are good at finding acute hemorrhages, fractures, and other urgent conditions. For brain tumors, CT scans give initial insights, but more imaging might be needed for a sure diagnosis.
CT scans are often the first line of imaging because they are quick and available. They help see how big and where tumors are, guiding further decisions.
“CT scans have become an indispensable tool in neurology, providing a fast and effective way to see the brain and diagnose various conditions.”
Understanding CT scans and their role in diagnosing brain tumors and other conditions shows their importance.
Can CT Miss a Brain Tumor? Understanding the Limitations
CT scans are not always 100% accurate in finding brain tumors. They are fast and easy to get, but knowing their limits is key. This is important for doctors and radiologists.
Statistical Overview of CT Scan Accuracy
Research shows CT scans can sometimes miss brain tumors sometimes. They are about 80% to 90% accurate in the best cases. But this means they can miss a lot of tumors.
Key statistics on CT scan accuracy include:
- Sensitivity: 80-90% in optimal conditions
- Specificity: Generally high, but can vary based on the tumor type
- False negatives: More common in small or low-grade tumors
Common Scenarios Where Tumors Go Undetected
There are a few reasons why brain tumors might not show up on CT scans:
- Small tumor size: Tumors under 5 mm are hard to spot, even with contrast.
- Low-grade tumors: Tumors that don’t show up much on scans can be tricky to find.
- Location: Tumors near bony structures or the skull base can be hard to see.
It’s important for doctors to know these limits. This helps them decide when to use MRI or add contrast to CT scans. Knowing when CT scans might miss tumors helps doctors give better care to patients.
Factors Affecting Brain Tumor Visibility on CT Scans
Many things can affect how well brain tumors show up on CT scans. How well a tumor is seen depends on its own traits and the scanning technology used.
Tumor Size and Detection Thresholds
The size of a brain tumor matters a lot for detection on CT scans. Bigger tumors are easier to spot, but smaller ones might be missed. Early detection is key because smaller tumors are often easier to treat.
Detection thresholds are the smallest size or contrast a tumor can be seen on a CT scan. Newer CT tech has raised these thresholds, letting us spot smaller tumors. But there’s a limit to how tiny a tumor can be and be seen.
Tumor Location and Anatomical Challenges
Where a brain tumor is located also impacts its visibility. Tumors in tricky spots, like the posterior fossa, are harder to find. These areas are more likely to hide small or subtle tumors.
Tumors near important brain structures or major blood vessels are also tough to spot. Being close to these areas makes detection harder and affects treatment plans.
Tumor Density and Contrast Issues
The density of a brain tumor compared to the brain around it is key for visibility on CT scans. Tumors that match the brain’s density are hard to see without contrast. Contrast enhancement makes tumors stand out by showing where the blood-brain barrier is broken.
But, some tumors don’t show up well with contrast. This makes them harder to find. The tumor’s blood flow and the blood-brain barrier’s state affect how it looks on a contrast-enhanced CT scan.
| Factor | Impact on Visibility | Clinical Consideration |
| Tumor Size | Smaller tumors are harder to detect | Early detection is key to treatment |
| Tumor Location | Complex anatomy can hide tumors | Special care is needed for tricky areas |
| Tumor Density | Isodense tumors are harder to spot | Contrast agents can help |
Types of Brain Tumors Most Commonly Missed on CT Scans
Some brain tumors are tricky to spot on CT scans. This is because of their nature and where they are in the brain. Knowing this helps doctors and radiologists get better at finding these tumors.
Low-Grade Gliomas
Low-grade gliomas are hard to find on CT scans. They blend in with the brain’s tissue because they’re similar in density.
Why are low-grade gliomas missed on CT scans include:
- They look like the brain tissue around them
- They don’t show up well with contrast
- They’re often in hard-to-reach spots
Small Metastatic Lesions
Small metastatic lesions are also hard to see on CT scans. They’re tiny and can be in spots that make them hard to image.
| Characteristics | Challenges in Detection |
| Small size | Hard to tell apart from the brain tissue |
| Variable location | Can be in tricky-to-image areas |
| Different enhancement patterns | It may not always show up well with contrast |
Posterior Fossa Tumors
Posterior fossa tumors are at the brain’s base. They’re hard to spot on CT scans because of the dense bones in that area.
It’s key to know the limits of CT scans for these tumors. While CT scans are useful, they’re not perfect. Sometimes, MRI scans are needed for a full diagnosis.
The Importance of Contrast Enhancement in CT Brain Imaging
Contrast agents are key to showing brain tumors on CT scans. They help highlight the differences between tumors and normal tissue. This has changed neuro-oncology by making tumor detection and characterization better.
How Contrast Agents Improve Tumor Detection
Contrast agents change the contrast between tissues. This makes tumors stand out from normal brain tissue. When given, they gather in areas with broken blood-brain barriers, like tumors, making them clearer on CT scans. This helps doctors spot tumors more accurately and see how big they are.
A leading neuroradiology expert says, “Contrast enhancement is key for detecting tumors on CT scans.” This shows how vital contrast agents are in medical practice.
When Non-Contrast CT Might Miss Tumors
CT scans are great for diagnosing, but non-contrast ones might miss small tumors. Contrast enhancement can greatly boost detection rates. Tumors that look the same as brain tissue are hard to spot without contrast.
Contraindications for Contrast Use
Even though contrast is powerful, there are times when it shouldn’t be used. People with allergies, severe kidney disease, or certain health issues can’t have contrast-enhanced CT scans. Healthcare providers must weigh the risks and benefits for each patient.
Knowing how contrast enhancement helps in detecting tumors is key. This knowledge helps doctors decide when to use CT scans for brain tumor diagnosis.
Radiation Exposure Risks in CT Brain Imaging
CT scans are very useful in medical tests, but they use ionizing radiation. This is something we need to think about when we use them to find brain tumors. Knowing about radiation exposure is very important.
Understanding Radiation Dose in CT Scans
The dose from a CT scan is measured in millisieverts (mSv). A head CT scan usually gives about 2 mSv of radiation.
Here’s a table to help you understand the doses from different CT scans.
| CT Scan Type | Typical Effective Dose (mSv) |
| Head CT | 2 |
| Chest CT | 7 |
| Abdomen/Pelvis CT | 10 |
Cumulative Exposure Concerns
Getting more radiation over time is a big worry. It can increase cancer risk. Kids and young adults are at higher risk because they have more years to live and their bodies are more sensitive.
Risk-Benefit Analysis for Patients
Doctors look at the good and bad of CT scans. For people with serious conditions like brain tumors, the scan’s benefits often outweigh the risks.
But it’s key for patients to talk to their doctors, even if they’ve had many scans. This helps them make smart choices about their health.
CT vs. MRI: Comparative Effectiveness in Brain Tumor Detection
It’s important to know how CT and MRI compare in finding brain tumors. These tools help us see if a tumor is there, how big it is, and where it is.
Sensitivity and Specificity Differences
CT scans use X-rays to show brain details. MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves. MRI is usually better at finding certain brain tumors than CT, like those in the back of the brain or small ones. MRI shows soft tissues better, helping to see tumor edges clearly.
A study compared CT and MRI for finding brain tumors. Here are the main differences:
| Imaging Modality | Sensitivity for Brain Tumors | Specificity for Tumor Type |
| CT | Moderate | Lower |
| MRI | Higher | Higher |
When MRI Is the Preferred Imaging Method
MRI is often the top choice for finding brain tumors. It’s best for tumors in hard-to-reach places or near important parts. MRI’s detailed images in different views help doctors plan surgery.
Cases Where CT Might Be Chosen Over MRI
Even though MRI is better, CT has its own benefits. CT is quicker and easier to get than MRI, which is good in emergencies or for people with metal implants. CT also works better for moving patients, as it’s less affected by movement.
In summary, while both CT and MRI are useful, MRI is usually the better choice for finding brain tumors. But, the right choice depends on the situation, the patient, and the need for detailed images.
The Role of Radiologist Expertise in Tumor Detection
Radiologists are key in finding and understanding brain tumors. The brain’s complex structure and tumors’ varied looks make their job very important. They help make accurate diagnoses.
Impact of Experience and Specialization
Experience and focus on certain areas are vital for radiologists. Radiologists with specialized training in neuroradiology know the brain better. This helps them spot small issues. Studies show they find tumors more often and make fewer mistakes.
Spotting tumors is not just about knowing tech. It also needs a sharp eye for details. For example, telling a tumor from a harmless condition requires skill and experience.
Common Interpretation Challenges
Even with better imaging, radiologists face tough tasks. Some common problems include:
- Telling different tumor types and grades apart
- Finding tumors in hard-to-reach spots
- Dealing with artifacts that look like tumors
To tackle these issues, radiologists must keep up with new tech and rules. Continuous education and training are key to staying accurate.
Double-Reading Practices
Having a second radiologist check scans can really help. This method:
- Reduces false negatives by catching missed tumors
- Confirms diagnoses and boosts confidence
- Offers a second opinion, which is very helpful in tricky cases
Using radiologists’ skills and double-reading can make tumor detection more accurate. This leads to better care for patients.
Warning Signs That Warrant Further Investigation Despite Negative CT Results
A negative CT result doesn’t always mean there’s no brain tumor. Patients with ongoing or getting worse neurological symptoms need extra checks. We must watch for signs that show more tests are needed.
Persistent Neurological Symptoms
Those with persistent neurological symptoms like headaches, seizures, or brain fog should get a detailed check-up. Even if CT scans show nothing, these signs might point to a hidden issue.
Healthcare teams should keep a close eye on patients with past brain problems or recent injuries. These situations can lead to false-negative CT results.
Progressive Clinical Deterioration
Progressive clinical deterioration is a big warning sign. If a patient’s health keeps getting worse, despite a negative CT scan, more tests are needed. This is true even if the scan didn’t show anything.
This is key when a patient’s symptoms strongly suggest a brain tumor or serious brain issue. We can’t just rely on one negative CT scan when a patient’s health is declining.
When to Seek a Second Opinion
Knowing when to seek a second opinion is vital. If there’s a gap between what the doctor says and what the scans show, or if the patient’s health keeps getting worse, getting another expert’s view is a good idea.
We urge patients and doctors to act quickly when doubts arise. Early action can greatly improve treatment results.
Multidisciplinary Approach to Brain Tumor Diagnosis
Diagnosing brain tumors requires a team effort. This team includes neurologists, neurosurgeons, radiologists, and oncologists. They work together to find the right treatment.
Integrating Clinical Assessment with Imaging Findings
First, doctors do a detailed check-up. They look at your medical history and do a neurological exam. This helps them find signs of a brain tumor.
Then, they use CT and MRI scans to confirm the diagnosis. These scans give them detailed info about the tumor.
Key benefits of integrating clinical and imaging findings include:
- Enhanced diagnostic accuracy
- Improved treatment planning
- Better patient outcomes
Role of Tumor Boards in Complex Cases
Tumor boards are for tough cases. They bring experts together to plan treatment. This way, they make sure all angles are covered.
These boards are very helpful. They help find the best treatment plans. This improves patient care.
“Tumor boards represent a critical part of cancer care. They help teams work together better.”
Expert Opinion
Evidence-Based Diagnostic Protocols
Using proven diagnostic methods is key. We stick to guidelines based on the latest research. This makes sure diagnoses are accurate and reliable.
We keep our methods up to date. This means patients get the best care for their condition.
Key elements of evidence-based diagnostic protocols include:
- Standardized imaging protocols
- Systematic clinical assessment
- Integration of molecular and genetic testing
By using a team approach and evidence-based methods, we improve brain tumor diagnosis. This leads to better care for patients.
Advanced and Emerging Technologies Improving Brain Tumor Detection
New technologies are making brain tumor detection more accurate. Medical imaging is getting better, leading to more precise diagnostic tools. This helps improve patient care.
Next-Generation CT Systems
Next-generation CT systems are leading this change. They give clearer images, scan faster, and use less radiation. For example, studies have shown they can spot smaller tumors better, helping catch them early.
These systems are great at showing detailed images of hard-to-reach areas. This is key for finding tumors in tricky spots, like the posterior fossa.
AI-Assisted Detection Algorithms
AI-assisted detection algorithms are also a big step forward. They use machine learning to look at images, find patterns, and spot tumors.
AI helps doctors be more accurate and work less hard. AI-assisted detection is better at finding small tumors and low-grade gliomas. These are hard to spot with old methods.
| Technology | Benefits | Impact on Detection |
| Next-Generation CT Systems | Higher resolution, faster scanning, reduced radiation | Improved detection of small tumors |
| AI-Assisted Detection Algorithms | Enhanced accuracy, reduced radiologist workload | Better detection of metastatic lesions and low-grade gliomas |
| Multimodal Imaging Approaches | Comprehensive assessment using multiple imaging modalities | Improved diagnostic accuracy for complex cases |
Multimodal Imaging Approaches
Multimodal imaging uses different scans, like CT, MRI, and PET, together. This gives a full picture of brain tumors. It shows size, location, and how active the tumor is.
Using many scans helps doctors plan better treatments. Multimodal imaging is very useful in hard cases where one scan isn’t enough.
Conclusion: Navigating the Limitations of CT Scans in Brain Tumor Diagnosis
CT scans are key in the first steps of finding brain tumors. Yet, they can miss some types of tumors. The size, location, and density of the tumor can affect how well CT scans work. This might lead to wrong or late diagnoses.
At Liv Hospital, we take a detailed and team-based approach to diagnosing brain tumors. We use CT and MRI scans, along with careful clinical checks and proven diagnostic methods. This ensures we get the diagnosis right and plan the best treatment.
We are committed to top-notch healthcare, as shown in our tumor boards. Here, experts work together to tackle tough cases and create custom treatment plans. By using the newest medical tech and focusing on the patient, we aim for the best results for our patients.
In summary, while CT scans have their limits in diagnosing brain tumors, a thorough approach can greatly help. We are all about giving our patients the best care. We tackle the challenges of brain tumor diagnosis with care and precision.
FAQ
Can a brain tumor be missed on a CT scan?
Yes, a brain tumor can be missed on a CT scan. This happens for many reasons like the tumor’s size, where it is, and how dense it is. Also, CT scans might miss some tumors, like low-grade gliomas or small metastatic lesions.
What are the limitations of CT scans in brain tumor detection?
CT scans have limits in finding brain tumors. They might miss small tumors, those in hard-to-reach spots, or those that look like brain tissue. Stats show CT scans can miss tumors, like low-grade ones or those in the posterior fossa.
How does tumor size affect detection on a CT scan?
The size of a tumor greatly affects if it’s seen on a CT scan. Smaller tumors are harder to spot because they blend in with brain tissue. They might also be in areas that are tough to image.
What is the role of contrast enhancement in CT brain imaging?
Contrast enhancement is key in CT brain imaging. It makes tumors stand out by using contrast agents. But sometimes, non-contrast CT is needed, and there are times when contrast can’t be used.
How does radiation exposure from CT scans impact patients?
Radiation from CT scans is a concern, mainly because of long-term exposure. It’s important to know the radiation dose and weigh the risks and benefits. Steps are taken to lower exposure while keeping accuracy high.
Is CT or MRI more effective for brain tumor detection?
Both CT and MRI are good for finding brain tumors. MRI is more sensitive and specific, but CT is faster. CT might be chosen in emergencies or when MRI isn’t available.
How important is radiologist expertise in tumor detection?
Expertise from radiologists is very important. Their experience and specialization help a lot. A skilled radiologist can spot tumors and tell them apart from other conditions.
When should further investigation be considered despite negative CT results?
More tests are needed if symptoms don’t go away or get worse, even with a negative CT. Getting a second opinion is also a good idea.
What is the benefit of a multidisciplinary approach to brain tumor diagnosis?
A team approach is best for diagnosing brain tumors. It combines clinical checks with imaging and uses tumor boards for tough cases. This method improves accuracy and ensures the right care for patients.
Are there emerging technologies that improve brain tumor detection?
Yes, new tech like next-generation CT systems and AI algorithms are helping. They aim to make diagnosis better and improve patient care.
Can a CT scan detect all types of brain tumors?
No, CT scans can’t find all brain tumors. Some, like low-grade gliomas or small metastatic lesions, are hard to spot because of their nature or location.
What factors affect the visibility of brain tumors on CT scans?
Several things affect if a tumor is seen on a CT scan. Size, location, and density of the tumor matter. Tumors that are small, in hard-to-reach spots, or blend in with tissue are more likely to be missed.
References
- Carll, J., et al. (2025). Guideline of guidelines: PSMA PET in staging newly diagnosed intermediate-risk prostate cancer. BJU International. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40704877/
- Jochumsen, M. R., et al. (2024). PSMA PET/CT for primary staging of prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. European Urology, 85(3), 245“256. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0001299823000557
- Islam, R., et al. (2025). The role of PSMA PET imaging in prostate cancer. Current Oncology Reports, 27(6), 45. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC12126340/