Advances in brain tumor removal surgery are changing how we treat brain cancers. At Liv Hospital, our skilled surgeons use the latest technology. They focus on the patient, setting new standards in brain cancer care.
We use new surgical methods, like minimally invasive procedures, to safely remove brain masses. Our aim is to take out the whole mass without harming the healthy brain around it. What is cerebral tumor surgery? Learn about the essential procedures, techniques used to remove brain tumors, and recovery steps.
Key Takeaways
- Advanced surgical techniques improve patient outcomes in brain tumor removal.
- Minimally invasive procedures reduce recovery time and trauma.
- Expert surgeons at Liv Hospital combine technology with patient-centered care.
- Brain mass surgery requires precise techniques to preserve healthy tissue.
- Cutting-edge technology enhances the effectiveness of brain cancer surgery.
Understanding Brain Tumors and Their Classification
Brain tumors are abnormal growths in the brain. Knowing their types is key to finding the right treatment. We’ll look at the different types, their traits, and symptoms.
Types of Brain Tumors: Malignant vs. Non-Malignant
Brain tumors fall into two main groups: malignant (cancerous) and non-malignant (benign). Malignant brain tumors grow fast and can spread to other brain areas. This makes them a big health risk. On the other hand, non-malignant brain tumors grow more slowly and don’t spread. Yet, they can cause problems because of where they are and how big they get.
It’s important to know if a tumor is malignant or non-malignant to choose the right treatment. Malignant tumors need strong treatments like surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. Non-malignant tumors might just need surgery or watching, based on their type and symptoms.
Common Locations of Brain Tumors
Brain tumors can happen in different parts of the brain. Where they are can affect how they impact us. Tumors in key brain areas can be harder to treat because they’re close to important functions.

Symptoms and Warning Signs
The symptoms of brain tumors can vary a lot. They depend on the tumor’s location, size, and type. Common signs include headaches, dizziness, seizures, and vision issues. Brain tumors can also lead to memory loss or trouble focusing.
It’s vital to spot the signs of a brain tumor early. If you or someone you know has ongoing or severe symptoms, get medical help right away.
Diagnosis and Pre-Surgical Assessment
Diagnosing brain tumors requires advanced imaging and thorough checks. We use these tools to learn about the tumor’s size, location, and how it affects the brain.
Neuroimaging Techniques
Neuroimaging is key in finding brain tumors. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT) scans give us detailed brain images. They help us see the tumor’s size, where it is, and if it’s near important brain parts.
MRI is great because it shows soft tissues well. This helps us see the tumor clearly. CT scans are faster and easier to get, which is good in emergencies.
Determining Tumor Operability
After finding a brain tumor, we check if it can be removed. We look at the tumor’s size, where it is, and how it affects the brain. We also think about the patient’s health and surgery risks.
The table below shows what makes a tumor operable or not:
| Factor | Operable | Inoperable |
| Tumor Location | Accessible location | Deep or critical location |
| Tumor Size | Moderate size | Large or diffuse |
| Patient Health | Good overall health | Significant comorbidities |
By looking at these factors, we decide the best treatment for each patient.
Cerebral Tumor Surgery: Overview and Patient Selection
Choosing to operate on a cerebral tumor depends on several things. This includes the tumor’s type and where it is. Surgery to remove a brain tumor is a detailed process that needs a team effort.
Candidates for Surgical Intervention
Not every patient with a cerebral tumor is right for surgery. The choice to operate depends on the tumor’s type, size, and where it is. It also depends on the patient’s health and brain function.
Key considerations include:
- The tumor’s closeness to important brain parts
- The patient’s age and any other health issues
- Any symptoms like seizures or brain problems
Pre-Surgical Preparation
Before surgery, a detailed preparation is done for patients who are undergoing it. This includes a full medical check-up, brain scans, and a look at their medicines.
As a leading neurosurgeon said,
“Pre-surgical preparation is key to the best results for patients having cerebral tumor surgery.”
Anesthesia Considerations
Anesthesia is very important in brain tumor surgery. The anesthesiologist must watch the patient’s blood pressure, brain pressure, and blood flow closely. This is to make sure the surgery goes well and safely.
Craniotomy Procedure
A craniotomy is when part of the skull is removed to reach the brain. In brain tumor surgery, it lets the neurosurgeon see and take out the tumor.
The craniotomy process includes:
- Planning the surgery with brain scans
- Doing the craniotomy and showing the tumor
- Removing the tumor with precise techniques
- Putting the bone flap back and closing the cut
By picking the right patients and getting them ready for surgery, we can make their lives better. This is true for people with cerebral tumors.
Minimally Invasive Brain Tumor Removal Approaches
Minimally invasive techniques have changed neurosurgery, giving hope to those with brain tumors. These methods use smaller cuts, cause less damage, and lead to faster healing than old surgery ways.
Keyhole Surgery Techniques
Keyhole surgery, or minimally invasive neurosurgery, makes small skull openings to reach brain tumors. It uses special tools and cameras for a clear view and removal. This method causes less brain harm, less pain after surgery, and shorter hospital stays.
Endoscopic Tumor Removal
Endoscopic tumor removal uses a thin, flexible tube with a camera and light. It’s great for tumors in hard spots or deep in the brain. It offers precise removal with little damage to the brain.
Transsphenoidal Approaches
The transsphenoidal method is for tumors in the pituitary gland. It goes through the sphenoid sinus, skipping the need for a big skull cut. This way reduces risks and speeds up recovery.
Benefits and Limitations
These new brain tumor removal methods have big pluses like smaller cuts, less blood loss, and lower infection risk. But they need special training and tools. The right surgery depends on the tumor’s size, location, and type.
| Surgical Approach | Benefits | Limitations |
| Keyhole Surgery | Less trauma, less pain, shorter hospital stay | Limited access to certain tumor locations |
| Endoscopic Tumor Removal | Precision, minimal damage to surrounding tissue | Requires specialized equipment and training |
| Transsphenoidal Approaches | Avoids craniotomy, reduces risk of complications | Limited to tumors in the pituitary gland |
Knowing about these new ways, neurosurgeons can choose the best surgery for each patient. This makes outcomes better and life quality higher.
Advanced Technologies in Brain Mass Surgery
The field of brain mass surgery is evolving with new technologies. These advancements improve surgical accuracy. They are key to better patient results and fewer complications.
Intraoperative MRI and Surgical Navigation
Intraoperative MRI lets surgeons see the brain tumor live during surgery. This helps them remove the tumor more accurately, keeping healthy tissue safe. Surgical navigation systems add to this by showing detailed brain maps. They help surgeons find the tumor and plan the best surgery.
Benefits of Intraoperative MRI and Surgical Navigation:
- Enhanced accuracy in tumor removal
- Reduced risk of damage to critical brain structures
- Improved patient outcomes
Functional Brain Mapping
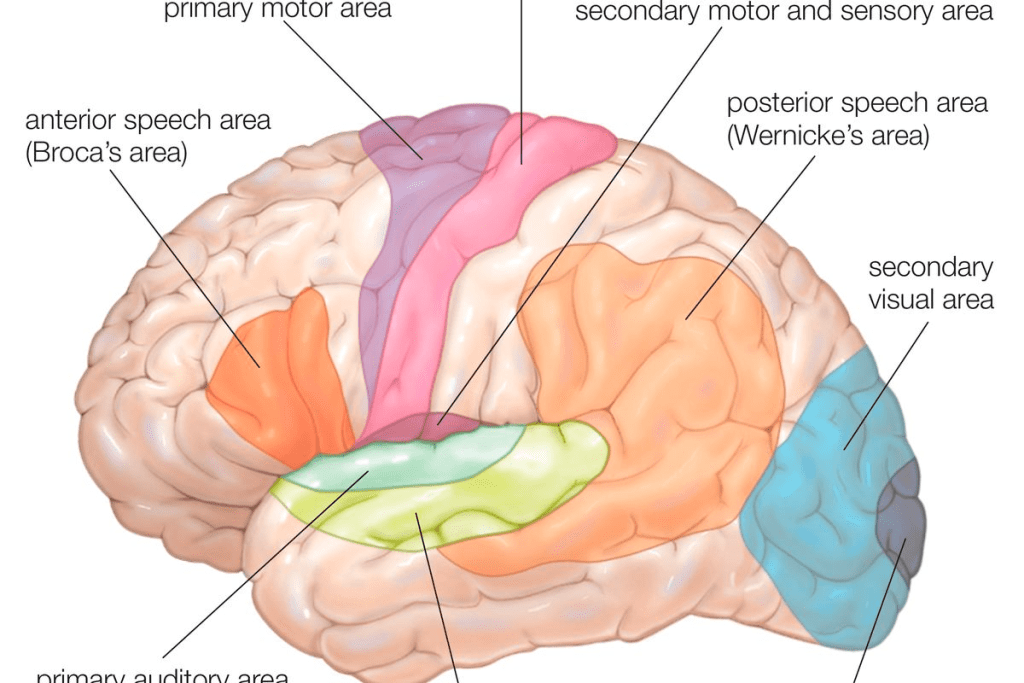
Functional brain mapping shows which brain areas control important functions. This includes speech, movement, and feeling. By knowing these areas, surgeons can avoid harming them during surgery. This helps keep the patient’s brain functions intact.
Fluorescence-Guided Surgery
Fluorescence-guided surgery uses special dyes that highlight tumor cells. This makes it easier for surgeons to see and remove the tumor. It helps them tell tumor tissue from normal brain tissue.
| Technology | Description | Benefits |
| Intraoperative MRI | Real-time imaging during surgery | Enhanced accuracy, reduced risk of complications |
| Functional Brain Mapping | Identification of critical brain areas | Preservation of neurological function |
| Fluorescence-Guided Surgery | Visualization of tumor tissue | More complete tumor removal |
These advanced technologies are changing brain mass surgery for the better. They offer hope to those with brain tumors. By making surgery more precise and safe, they improve patient results and life quality.
Treatment Options for Inoperable Brain Tumors
When surgery is not possible for brain tumors, treatments like Laser Interstitial Thermal Therapy (LITT) offer hope. Inoperable brain tumors are tough to treat because of their location or the patient’s health. We look at the treatments that can help improve patient outcomes.
Laser Interstitial Thermal Therapy
LITT is a minimally invasive method that uses heat from a laser to kill tumor cells. It’s great for tumors in hard-to-reach brain areas. LITT is precise, which helps avoid damage to healthy brain tissue.
The LITT procedure involves putting a laser probe into the tumor under imaging. The laser heats the tumor cells, killing them. This method has shown to control tumor growth and ease symptoms in patients with inoperable brain tumors.
Combination Approaches
For many, a mix of treatments is recommended for inoperable brain tumors. This might include LITT with radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or other targeted therapies. The goal is to attack the tumor from different sides, hoping to improve results.
| Treatment Modality | Description | Benefits |
| Laser Interstitial Thermal Therapy (LITT) | Minimally invasive laser treatment to destroy tumor cells | Precision spares healthy tissue, reduces neurological risk |
| Radiation Therapy | High-energy rays to kill tumor cells | Non-invasive, effective for tumor control |
| Chemotherapy | Drugs to kill tumor cells | Systemic treatment can target distant tumor cells |
We think a personalized treatment plan, combining the best treatments for each patient, is key. Research and new medical technologies keep growing, giving patients new hope for these tough diagnoses.
Post-Surgical Care and Recovery
Good post-surgical care is key for patients after brain tumor surgery. The time right after surgery is very important. It needs a full plan to handle any problems and help the patient get better physically and emotionally.
Immediate Post-Operative Management
Right after surgery, patients stay in a recovery room. Post-surgical care for brain tumor patients focuses on managing pain, stopping infection, and watching for any brain problems. Doctors give medicines to help with pain and prevent seizures.
They also watch for signs of too much pressure in the brain, infection, or other problems. The team is quick to deal with any issues to help the patient recover well.
Potential Complications
Even with careful surgery, some problems can happen during recovery. These might include infection, swelling, seizures, or brain issues. Quick action to find and fix these problems is very important.
The healthcare team works with the patient and their family to watch for any signs of trouble. This teamwork helps catch and handle any problems fast.
Rehabilitation Strategies
Rehabilitation after brain surgery is a big part of getting better. It might include physical, occupational, or speech therapy. The goal is to help the patient get strong, move well, and think clearly again.
A special plan for rehabilitation is made with the patient, their family, and the healthcare team. This plan is made just for them, focusing on their needs and goals. It helps them get the best care for a good recovery.
Long-Term Outcomes After Brain Tumor Resection
Patients who have brain tumor surgery need ongoing care. This care helps watch for any return of the tumor and manages long-term effects. The success of the surgery is not just about the immediate results. It also depends on how well patients recover and adjust over time.
Monitoring for Recurrence
Regular check-ups and imaging studies are key to catching tumor recurrence early. We use advanced tools like MRI and CT scans to keep an eye on the tumor and the area around it.
- Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider.
- Undergo periodic imaging studies as recommended.
- Be aware of any new or worsening symptoms.
Early detection of recurrence greatly improves treatment chances. We help patients create a follow-up plan that fits their needs.
Quality of Life Considerations
The surgery’s impact on a patient’s quality of life is significant. We look at cognitive function, physical ability, and emotional well-being when assessing long-term outcomes.
Rehabilitation is key in helping patients regain strength and independence. Our team works with rehabilitation specialists to offer full support.
- Physical therapy to improve mobility and strength.
- Occupational therapy to enhance daily functioning.
- Speech therapy is used if there are difficulties with communication.
Adjuvant Therapies
Adjuvant therapies like radiation and chemotherapy may be needed to stop the tumor from coming back. We talk about the benefits and risks of these treatments with our patients to help them make informed choices.
The choice of adjuvant therapy depends on many factors. These include the tumor type and grade, and the patient’s health. We make recommendations based on each patient’s unique situation.
- Radiation therapy to target the remaining tumor cells.
- Chemotherapy to address possible microscopic disease.
- Participation in clinical trials for new treatments.
Understanding the importance of long-term follow-up and adjuvant therapies helps us achieve the best outcomes for patients after brain tumor surgery.
Conclusion: Advances in Brain Tumor Removal and Future Directions
Brain tumor surgery has made big strides, leading to better patient results. Now, we use more precise and less invasive methods. This includes keyhole surgery and endoscopic removal, which help patients heal faster and with less brain damage.
Advanced technologies like intraoperative MRI and surgical navigation have made surgery more accurate. Techniques like functional brain mapping and fluorescence-guided surgery help protect important brain functions.
Looking ahead, brain tumor research is full of hope. New treatments like laser interstitial thermal therapy might help with tumors that can’t be removed. Also, combining surgery with other treatments could lead to even better results for patients.
We’re always looking to improve brain tumor surgery. Thanks to new tech and a better understanding of tumors, we aim to give patients the best care. Our goal is to enhance their quality of life and increase their chances of survival.
FAQ
What is brain tumor removal surgery?
Brain tumor removal surgery, also known as craniotomy, is a procedure. A neurosurgeon removes a brain tumor or part of it. We use advanced techniques and technologies for safe and effective removal.
What are the types of brain tumors that can be removed surgically?
Both malignant and non-malignant brain tumors can be removed surgically. This depends on their location, size, and accessibility. We evaluate each case individually to determine the best treatment.
How is a brain tumor diagnosed?
We diagnose brain tumors using neuroimaging techniques like MRI and CT scans. These tests help us understand the tumor’s location, size, and characteristics. This information informs our treatment decisions.
What is the difference between operable and inoperable brain tumors?
Operable brain tumors are those that can be safely removed surgically. Inoperable tumors are those that cannot be removed due to their location or other factors. For inoperable tumors, we explore alternative treatments like LITT and combination therapies.
What is keyhole surgery for brain tumor removal?
Keyhole surgery is a minimally invasive technique. It involves making a small incision in the skull to access the tumor. This approach can reduce recovery time and minimize scarring.
What is intraoperative MRI, and how is it used in brain tumor surgery?
Intraoperative MRI is a technology that allows us to take MRI images during surgery. This ensures we remove as much of the tumor as possible while preserving surrounding brain tissue.
What are the possible complications of brain tumor surgery?
As with any surgery, there are risks and possible complications. These include infection, bleeding, and neurological deficits. We take every precaution to minimize these risks and provide thorough post-operative care.
How long does it take to recover from brain tumor surgery?
Recovery time varies depending on the individual case and the extent of the surgery. We provide personalized care and rehabilitation strategies to support patients during their recovery.
What is the role of adjuvant therapies after brain tumor surgery?
Adjuvant therapies, such as radiation and chemotherapy, may be necessary. They help treat any remaining tumor cells and prevent recurrence. We work with patients to develop a treatment plan that addresses their unique needs.
Can brain tumors recur after surgery?
Yes, brain tumors can recur, even after successful surgery. We monitor patients closely for signs of recurrence. We work with them to develop a plan to address any future issues.
How is the quality of life after brain tumor surgery?
The quality of life after surgery varies depending on the individual case and the extent of the surgery. We strive to preserve neurological function and improve patient outcomes through our care and rehabilitation programs.
What are the latest advancements in brain tumor removal surgery?
We are continually advancing our techniques and technologies. This includes the use of intraoperative MRI, functional brain mapping, and fluorescence-guided surgery. These advancements improve the safety and effectiveness of brain tumor removal.
Can inoperable brain tumors be treated with LITT?
Yes, LITT (Laser Interstitial Thermal Therapy) is a treatment option for some inoperable brain tumors. This minimally invasive procedure uses laser heat to destroy tumor tissue.
What is the benefit of removing a benign brain tumor?
Removing a benign brain tumor can alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. It can also prevent complications, such as tumor growth or neurological damage.
How do you determine if a brain tumor is malignant or non-malignant?
We use a combination of neuroimaging techniques, biopsy results, and other diagnostic tests. This helps us determine the nature of the brain tumor.
References
- Oya, S., & Berger, M. S. (2023). Recent advancements in the surgical treatment of brain tumors. Neurosurgical Review, 46(3), 196“211. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10527654/
- Vadhavekar, N. H., Gupta, A., & Adapa, A. (2024). Advancements in imaging and neurosurgical techniques in brain tumor surgery: A review. Neurosurgery, 95(5), 1234“1245. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39618625/
- Schwartz, T. H., & Gerald, S. (2024). Laser interstitial thermal therapy: Principles, applications, and outcomes in brain tumors. Neuro-Oncology Advances, 2(1), vdz035. https://academic.oup.com/noa/article/2/1/vdz035/5678722









