Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
A diagnosis of a brain tumor can be scary. But new medical tech has brought non-surgical treatments that change lives. Would a PET scan show bone cancer? Yes, PET scans are highly accurate in detecting bone cancer and metastases, offering superior sensitivity and diagnostic value compared to other imaging techniques.
At Liv Hospital, we focus on top-notch care. We aim for quality, safety, and support for our patients. For those with a brain tumor, we offer new, non-surgical ways to help them live better.
While surgery is common for brain tumors, some cases need non-surgical methods. This is true for tumors deep inside or when a patient’s health is at risk.
Key Takeaways
- Non-surgical treatments offer hope for patients with brain tumors.
- Advanced modalities like chemotherapy and radiation therapy are effective.
- Liv Hospital provides world-class, patient-centered care.
- Non-surgical options are considered based on tumor location and patient health.
- Innovative treatments are transforming patient outcomes.
Understanding Brain Tumors and When Surgery Isn’t an Option
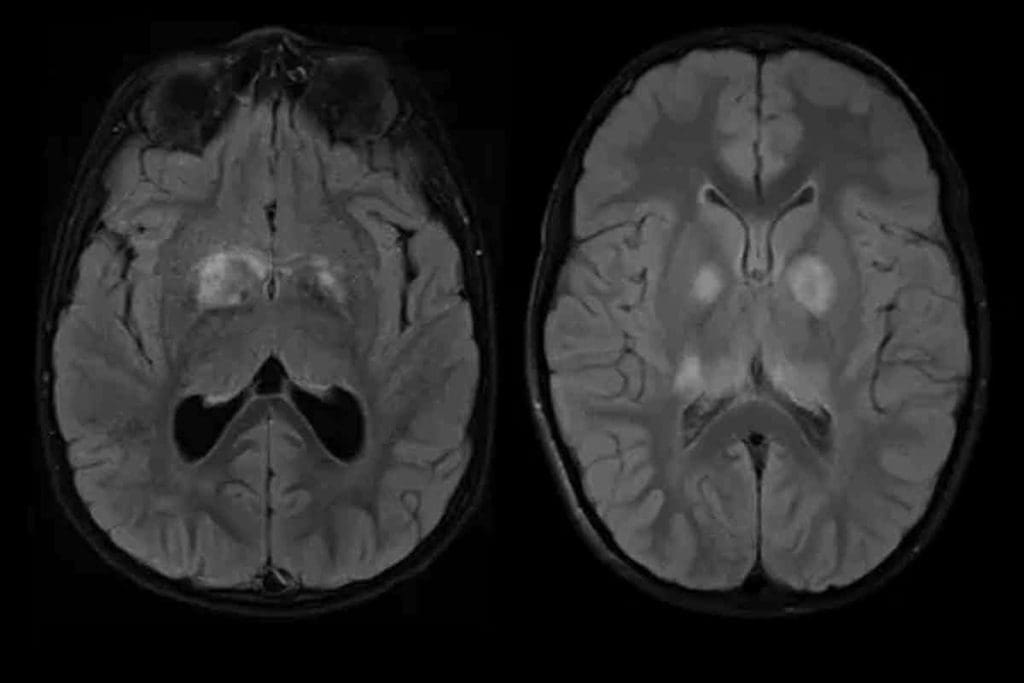
It’s important to know about brain tumors to choose the right treatment. Brain tumors are either benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). The type of tumor greatly affects the treatment plan.
Types of Brain Tumors: Cancerous vs. Non-Cancerous
Benign brain tumors grow slowly and don’t spread to other tissues. But they can cause problems because of where they are and how big they get. Malignant brain tumors, though, grow fast and spread to other brain areas. Knowing the difference is key to treatment choices.
Doctors say, “The treatment for brain tumors needs a detailed plan. This plan considers the tumor’s type, size, and where it is.”
” showing how complex treating brain tumors can be
Situations Where Surgery May Be Too Risky
Surgery is often the first choice for many brain tumors. But there are times when surgery is too risky. This happens when tumors are in hard-to-reach or critical brain areas. In these cases, other treatments must be looked at.
For those facing these challenges, non-surgical treatments offer good alternatives. Choosing non-surgical options is a decision made after a detailed review by a team of doctors.
The Importance of Personalized Treatment Planning
Personalized treatment plans are vital for managing brain tumors. Every patient’s situation is different. A plan that fits the tumor’s details, the patient’s health, and other factors is needed. This approach helps achieve the best results.
Healthcare providers can create a treatment plan that works well and is as gentle as possible. This is done by understanding the tumor and the patient’s needs well.
Brain Tumor Treatment Without Surgery: A New Hope
Medical technology has grown, giving us new ways to treat brain tumors. Now, we have non-surgical options that bring hope to patients.
Non-surgical treatments like chemotherapy, radiation, and immunotherapy are showing promise. Their success depends on the tumor’s type, size, and where it is.
Success Rates of Non-Surgical Approaches
Research shows non-surgical methods can manage brain tumors well. For instance:
- Chemotherapy can improve survival for some brain tumors.
- Radiation therapy can shrink tumors and ease symptoms.
- Immunotherapy uses the body’s immune system to fight cancer.
Factors That Determine Treatment Selection
Choosing non-surgical treatment depends on several things, like:
- The tumor’s type and grade.
- The tumor’s size and where it is.
- The patient’s health and medical history.
Our healthcare team works together to find the best treatment for each patient.
The Multidisciplinary Approach to Brain Tumor Management
Managing brain tumors requires a team effort. Our team includes:
- Neurologists.
- Oncologists.
- Radiologists.
- Nurses and other support staff.
We create a treatment plan that meets each patient’s unique needs.
Radiation Therapy: Precision Targeting of Brain Tumors
Radiation therapy is a top choice for treating brain tumors. It uses different methods for various tumors. This way, we can hit the tumor cells hard while keeping the healthy brain safe.
Precision for Small Tumors: Stereotactic Radiosurgery
Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) is a precise radiation therapy for small brain tumors. It gives a high dose of radiation in one go. This method is great for tumors that can’t be removed or are in hard-to-reach brain spots.
Fractionated Radiation for Larger Tumors
Fractionated radiation therapy is for bigger or more spread-out tumors. It breaks down the radiation into smaller doses. This lets healthy cells bounce back between each dose. It’s customized to fit the patient’s needs, aiming for effective tumor control with fewer side effects.
Proton Therapy: Minimizing Damage to Healthy Tissue
Proton therapy uses protons instead of X-rays to target tumors. It’s great for tumors close to important brain areas because it controls the radiation dose well. This reduces harm to healthy brain tissue. It’s a good option for both kids and adults with brain tumors, aiming for fewer long-term side effects.
Using these advanced radiation therapy methods, we can tackle brain tumors effectively. Each treatment plan is made to fit the patient’s tumor perfectly. This ensures the best results for the patient’s health and quality of life.
Chemotherapy Protocols for Different Brain Tumor Types
Chemotherapy for brain tumors varies a lot. This is because tumors and patients are different. Chemotherapy is key in treating brain tumors, with options for each tumor and patient.
Temozolomide and Other Common Agents
Temozolomide is a top choice for treating brain tumors, like glioblastoma. It has been shown to increase survival rates, making it a mainstay in treatment. Other drugs like carmustine, lomustine, and vincristine are used too, based on the tumor and treatment history.
Overcoming the Blood-Brain Barrier Challenge
The blood-brain barrier is a big hurdle for chemotherapy. It blocks drugs from reaching tumors. Scientists are working on ways to get around this barrier, like using focused ultrasound to open it up.
Combination Approaches with Other Treatments
Using chemotherapy with other treatments can make it more effective. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy together is often used for some tumors. Researchers are also looking into combining it with targeted therapy or immunotherapy in trials.
| Tumor Type | Common Chemotherapy Agents | Combination Approaches |
| Glioblastoma | Temozolomide, Carmustine | Concurrent radiation therapy |
| Meningioma | Hydroxyurea, Temozolomide | Observation or radiation therapy |
| Medulloblastoma | Vincristine, Cyclophosphamide | Combination with radiation therapy and stem cell transplant |
In summary, chemotherapy is a vital part of treating brain tumors. There are many protocols for different tumors and patients. The challenge of the blood-brain barrier and new combination therapies are being researched to help patients more.
Immunotherapy: Activating the Body’s Defense Against Brain Cancer
Immunotherapy is a new way to fight brain tumors. It uses the body’s immune system to attack cancer cells.
This method is very promising. It helps the body fight brain tumors in new ways. It’s good for people who can’t have surgery or other treatments.
Checkpoint Inhibitors and Their Effectiveness
Checkpoint inhibitors are special drugs. They help the immune system fight cancer better. They block proteins that stop the immune system from working.
These drugs work well for some brain tumors. But how well they work depends on the tumor and the person. Scientists are studying how to make them even better.
Dendritic Cell Therapy: Promising Advances
Dendritic cell therapy uses the body’s own cells to fight cancer. Dendritic cells are loaded with cancer proteins. This makes the immune system attack the tumor.
This therapy is showing good results in some brain tumors. Scientists are working to make it even better.
CAR T-Cell Therapy for Brain Tumors
CAR T-cell therapy is very personal. It changes T-cells to attack cancer cells. It’s being looked at for treating brain tumors, too.
Even though it’s promising, it’s not used much yet. Scientists are working on making it safe and effective for treating brain tumors.
The table below summarizes the key aspects of the immunotherapy approaches discussed:
| Therapy Type | Mechanism | Potential Benefits |
| Checkpoint Inhibitors | Blocks proteins that inhibit the immune response | Enhances the immune system’s ability to target cancer cells |
| Dendritic Cell Therapy | Stimulates immune response using dendritic cells loaded with tumor antigens | Prompts the immune system to attack tumor cells |
| CAR T-Cell Therapy | Genetically modifies T-cells to recognize and attack cancer cells | Highly personalized and targeted approach |
Targeted Therapy: Precision Medicine for Specific Tumor Mutations
Targeted therapy is a game-changer in treating brain tumors. It precisely attacks cancer-causing mutations. This method offers a more tailored and effective way to fight brain tumors without surgery.
Molecular Profiling to Guide Treatment Decisions
Molecular profiling is key in finding the genetic mutations that drive brain tumors. It helps doctors choose the best targeted therapy. This involves advanced genetic tests to pinpoint specific mutations for precision medicine.
Key benefits of molecular profiling include:
- Identifying targetable mutations
- Guiding treatment decisions with precision
- Enhancing the effectiveness of targeted therapy
EGFR, BRAF, and Other Targetable Mutations
Genetic mutations like EGFR and BRAF are major players in brain tumors. Targeted therapies aim to tackle these mutations. For example, EGFR inhibitors work well on tumors with EGFR mutations, while BRAF inhibitors target BRAF mutations.
Examples of targeted therapies include:
- EGFR inhibitors for tumors with EGFR mutations
- BRAF inhibitors for tumors with BRAF mutations
- Other therapies targeting specific genetic alterations
Overcoming Resistance to Targeted Therapies
Targeted therapy is promising, but resistance can limit its success. Researchers are working on new ways to beat this resistance. They’re looking into combination therapies and next-generation targeted agents.
“The development of resistance to targeted therapies is a significant challenge, but ongoing research is focused on identifying effective strategies to overcome this issue and improve patient outcomes.”
By studying resistance and creating new therapies, we can better treat brain tumors. This will help improve patient care.
Tumor-Treating Fields (TTFields): Non-Invasive Electrical Therapy
TTFields are a big step forward in treating brain tumors without surgery. This therapy uses electrical fields to stop cancer cells from dividing. It’s a new way to help patients with glioblastoma and other brain tumors.
Disrupting Cancer Cell Division
TTFields apply low-intensity, intermediate-frequency electrical fields to tumors. These fields make it hard for cancer cells to divide, causing them to die. Patients wear a device called Optune to get this treatment.
This therapy works differently from other cancer treatments. It targets how cancer cells divide, making it a unique way to fight brain tumors.
Optune Device: Daily Use and Patient Experience
The Optune device is for daily use, with patients wearing it for 18 hours a day. It has transducer arrays on the scalp connected to a portable generator.
Patients find the device easy to use, with some getting used to the arrays on their scalp. The treatment is mostly well-tolerated, with mild skin irritation being the main side effect.
“The Optune device has given me a new lease on life. I can continue my daily activities while undergoing treatment,” said a patient undergoing TTFields therapy.
Clinical Evidence for Glioblastoma and Other Tumors
Studies show TTFields work well for glioblastoma, improving survival when used with chemotherapy.
- Improved overall survival in glioblastoma patients
- Effective in combination with chemotherapy
- Ongoing research into its use for other brain tumors
More research is needed to see if TTFields can help with other brain tumors, too.
How to Shrink a Brain Tumor: Non-Surgical Approaches for Benign Tumors
Non-surgical treatments are now the first choice for treating benign brain tumors. We will look at the different non-surgical options. We’ll see how well they work and if they’re right for different types of tumors.
Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Meningiomas and Acoustic Neuromas
Stereotactic radiotherapy is a precise way to treat tumors with radiation. It focuses the radiation on the tumor, protecting the healthy tissue around it. This method works well for meningiomas and acoustic neuromas.
- Precision: Stereotactic radiotherapy targets the tumor accurately.
- Effectiveness: It has a high success rate in stopping tumor growth.
- Minimal Side Effects: It reduces the risk of damage to the brain tissue.
Medication Options for Specific Tumor Types
Even though surgery is often not needed for benign brain tumors, medicine can help. The right medicine depends on the tumor type and its features.
For example, meningiomas might be treated with hormone or targeted therapies. These treatments target specific parts of the tumor.
- Hormone therapy for meningiomas that have hormone receptors.
- Targeted therapy for tumors with certain genetic mutations.
Observation Protocols and When to Intervene
Not every benign brain tumor needs to be treated right away. Sometimes, just watching the tumor is enough, at least for small, symptom-free ones. Regular scans help decide when to act.
Active surveillance means regular MRI scans to check the tumor’s size and growth. This way, doctors can step in at the best time. It balances the risks of treatment with the risks of the tumor growing.
By choosing the right non-surgical treatment for each patient, we can manage benign brain tumors well. The goal is to find the best treatment based on the tumor and the patient’s health.
Can Brain Tumors Be Cured Without Surgery? Outcomes and Expectations
Can brain tumors be cured without surgery? The answer depends on treatment outcomes. The success of treatment varies based on the tumor’s type, size, and location. It also depends on the patient’s health.
Success Rates by Tumor Type, Size, and Location
Success rates for non-surgical treatments vary. Smaller tumors that are easier to reach with non-surgical methods tend to do better.
Recent studies show that some brain tumors respond well to non-surgical treatments. For example, benign tumors like meningiomas can often be treated with radiation therapy.
Defining “Cure” vs. Long-Term Control in Brain Tumors
It’s important to understand the difference between a “cure” and long-term control. A cure means the tumor is completely gone and won’t come back.
Long-term control means the tumor’s growth is managed, and it stays stable for a long time. Both outcomes are considered successful, depending on the situation and the patient’s health.
Factors That Influence Treatment Success
Several factors affect the success of non-surgical treatments for brain tumors. These include:
- The type and grade of the tumor
- The tumor’s size and location
- The patient’s overall health and age
- The effectiveness of the chosen treatment modality
Knowing these factors helps set realistic expectations. It also helps make informed decisions about treatment options.
Conclusion: Navigating Your Brain Tumor Treatment Journey
Dealing with brain tumor treatment can be tough. It involves many treatment choices and ways to approach them. We’ve looked at non-surgical methods like chemotherapy, radiation, and more.
Knowing about these options and getting a team of doctors is key. This helps find the best treatment plan. Patients can then make smart choices about their care.
Choosing the right treatment means thinking about what’s best for each person. We aim to give top-notch care and support to patients worldwide. This support is key during the treatment for brain tumors.
Understanding treatment choices and working with doctors helps patients. They can then move forward with confidence. This leads to the best results possible.
FAQ
What are the non-surgical treatment options for brain tumors?
We offer many non-surgical treatments. These include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and immunotherapy. We also have targeted therapy and tumor-treating fields. These options help manage brain tumors effectively.
Can brain tumors be treated without surgery?
Yes, many brain tumors can be treated without surgery. This depends on the tumor’s type, size, and location. It also depends on the patient’s overall health.
How is the best treatment approach determined for a brain tumor?
We plan treatment based on the tumor’s type and characteristics. We also consider the patient’s individual needs. This ensures the best approach for each patient.
What is the role of radiation therapy in treating brain tumors?
Radiation therapy is very effective for brain tumors. It offers several options. These include stereotactic radiosurgery and fractionated radiation. Proton therapy is also available to target tumors precisely.
Can chemotherapy be used to treat brain tumors?
Yes, chemotherapy is used to treat many brain tumors. The treatment protocol varies based on the tumor type and patient characteristics.
What is targeted therapy, and how is it used to treat brain tumors?
Targeted therapy uses molecular profiling to find targetable mutations. This guides treatment decisions. It offers effective options for specific tumor mutations.
How do tumor-treating fields work to treat brain tumors?
Tumor-treating fields use electrical fields to stop cancer cell division. This is a non-invasive approach. It’s often used for glioblastoma.
Can benign brain tumors be treated without surgery?
Yes, benign brain tumors can be treated without surgery. Non-surgical approaches include stereotactic radiotherapy and medication. The choice depends on the tumor type and size.
What are the success rates for curing brain tumors without surgery?
Success rates vary. They depend on the tumor type, size, and location. The treatment approach also plays a role. Some tumors can achieve long-term control or cure.
How is treatment success determined for brain tumors?
Success is determined by several factors. These include tumor type, size, and location. The patient’s overall health and response to treatment also matter.
What is the multidisciplinary approach to brain tumor management?
Our approach involves a team of healthcare professionals. This includes neurologists, oncologists, and radiologists. They work together to provide complete care and guidance throughout treatment.
Can brain cancer be cured?
Some brain cancers can be cured. Others may need long-term control. The chance of a cure depends on several factors. These include tumor type, size, and location, as well as treatment approach.
How can I get rid of a brain tumor?
There are treatment options available, including non-surgical approaches. The best treatment is determined through personalized planning.
What is brain tumor extraction?
Brain tumor extraction is the surgical removal of a tumor. We also offer non-surgical options for those not suited for surgery.
Is there a cure for brain tumors?
Some brain tumors can be cured. Others may need ongoing management. The chance of a cure depends on several factors. These include tumor type, size, and location, as well as treatment approach.
References
- Mittelbronn, M., & Giese, A. (2025). Neurooncology: 2025 update. Frontiers in Oncology, 15, 11960715. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC11960715/