Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
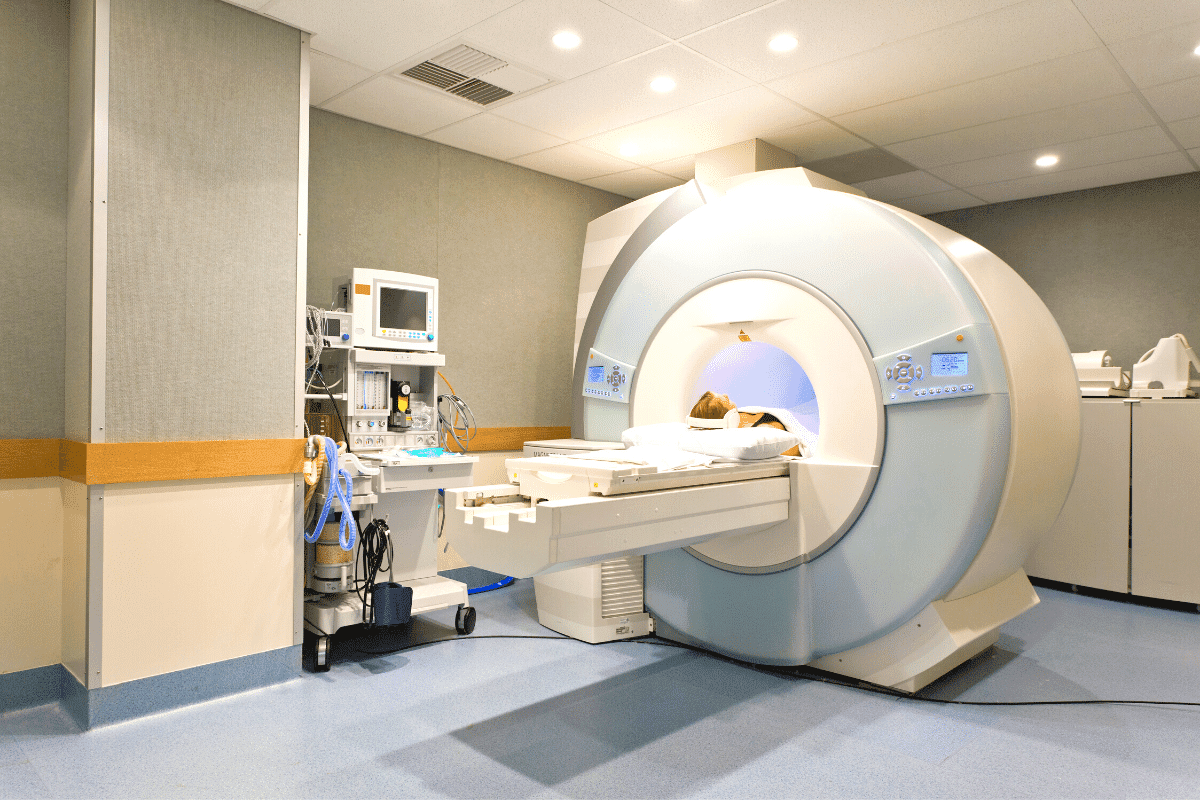
Choosing between MRI and CT scans is key for patient care. At Liv Hospital, we use the latest tech and focus on the patient. This ensures we pick the right tool for each case.
CT scans use X-rays to quickly show images of bones, organs, and blood vessels. They’re great for emergencies and finding things like fractures or bleeding inside. MRIs, on the other hand, use magnets and radio waves to show detailed images of soft tissues, the brain, spinal cord, and joints. They don’t use radiation.
Key Takeaways
- CT scans are faster and often used in emergency situations due to their quick imaging capability.
- MRIs provide more detailed images of soft tissues, making them ideal for diagnosing neurological conditions and soft tissue injuries.
- CT scans involve radiation, whereas MRIs do not, making MRIs safer for certain patient groups.
- The choice between CT scans and MRIs depends on the specific clinical scenario and patient needs.
- Both imaging techniques have their unique strengths and are used based on the diagnostic requirements.
Understanding Medical Imaging Technologies
Diagnostic imaging has grown a lot, helping a lot in healthcare. It gives us detailed views of what’s inside our bodies. This helps doctors diagnose and treat many health issues well.
The Evolution of Diagnostic Imaging
Medical imaging has seen a lot of changes, from X-rays to MRI and CT scans. These new tools have changed how we see inside the body. Now, we can see things much clearer than before.
Key milestones in the evolution of diagnostic imaging include:
- The introduction of X-ray technology, which revolutionized diagnostic medicine by allowing us to visualize internal structures.
- The development of CT scans, which provide cross-sectional images of the body, greatly enhance diagnostic capabilities.
- The advent of MRI technology, which offers detailed images of soft tissues and has become indispensable in diagnosing a range of conditions.
“The development of medical imaging technologies has been key in improving how we diagnose and treat. These tools have changed healthcare, helping doctors make better decisions and manage conditions better.”
The Role of Imaging in Modern Medicine
Medical imaging is very important today. It helps doctors make accurate diagnoses and plan treatments. MRI and CT scans are used a lot because they each have special benefits.
| Imaging Modality | Primary Use | Key Benefits |
| CT Scans | Emergency and trauma situations, bone and structural imaging | Quick and detailed cross-sectional images, excellent for visualizing bones and detecting internal injuries. |
| MRI | Soft tissue evaluation, neurological and spinal conditions | High-resolution images of soft tissues, ideal for diagnosing conditions affecting the brain, spine, and joints. |
Knowing what each imaging tool is good for helps doctors make better choices. This leads to better health for patients.
CT Scan Technology Explained

CT scans let doctors see inside the body in great detail. They use X-rays to make clear images of the body’s inside parts. This makes them perfect for emergencies and finding many health issues.
Operational Principles
CT scans combine X-rays from different angles to show the body’s inside. A rotating gantry holds the X-ray tube and detectors. As it moves around the patient, it gathers data. Then, a computer turns this data into images.
Key components of a CT scanner include:
- The X-ray tube, which produces the X-rays.
- Detectors, which capture the X-rays after they pass through the body.
- A rotating gantry, which houses the X-ray tube and detectors.
- Computer systems, which reconstruct the images from the captured data.
Types of CT Scans
There are many types of CT scans for different needs. Here are a few:
| Type of CT Scan | Description | Clinical Use |
| Non-contrast CT | Uses X-rays without contrast material | Diagnosing acute injuries, kidney stones |
| Contrast-enhanced CT | Uses X-rays with contrast material | Visualizing blood vessels, tumors |
| High-resolution CT | Provides detailed images of small structures | Examining lung tissue, inner ear structures |
A study in the Journal of Radiology found that contrast-enhanced CT scans help find vascular diseases and tumors better.
“The advent of CT technology has revolutionized the field of diagnostic radiology, enabling clinicians to non-invasively visualize the body’s internal structures with high precision.”
– CertifiedRadiologist
The CT Scanning Process
The CT scanning process is fast and simple. Patients lie on a table that slides into the scanner. They must stay very quiet during the scan. The whole process usually takes a few minutes, depending on the scan’s complexity.
Before a CT scan, patients might need to:
- Remove any metal objects or jewelry.
- Wear a hospital gown.
- Get contrast material, if needed.
Knowing how CT scans work and their uses helps patients see their value in healthcare today.
MRI Technology Explained
The MRI machine is a complex device. It uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the body’s inside. This tech is key in medical checks, showing soft tissues without using radiation.
How MRI Machines Work
MRI machines align hydrogen atoms in the body with a strong magnetic field. Then, radio waves disturb these atoms, causing them to send signals. The MRI picks up these signals to make clear images.
We use MRI tech to see inside the body clearly. It’s great for checking the brain, spine, and joints.
Types of MRI
There are many MRI scans, each for different needs. Here are a few:
- Functional MRI (fMRI): Watches brain activity by seeing blood flow changes.
- Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA): Looks at blood vessels and vascular issues.
- Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS): Shows metabolic activity in body areas.
The MRI Scanning Process
The scanning starts with getting ready. Patients remove metal and wear a gown. They then lie on a table that moves into the MRI.
Patients must stay very quiet during the scan. The time needed varies, from 15 to 90 minutes, based on the scan type and area.
We know the process can seem scary. So, we make sure patients know what’s happening and feel at ease.
The Difference Between MRI and CT Scan: Core Distinctions
MRI and CT scans are both key tools in medical imaging. They differ in technology, use, and results. Knowing these differences helps choose the right imaging for different health issues.
Technological Differences
CT scans use X-rays to show body parts inside. MRI machines use magnets and radio waves to make images.
CT Scan Technology works by X-rays passing through tissues at different rates. This makes detailed images of bones, lungs, and more.
MRI Technology aligns hydrogen atoms with a strong magnetic field. Radio waves disturb them, and the signals create detailed images, great for soft tissues.
| Characteristics | CT Scan | MRI |
| Primary Technology | X-rays | Magnets and Radio Waves |
| Best for Imaging | Bones, Lungs, Internal Injuries | Soft Tissues, Neurological Conditions |
| Radiation Exposure | Yes | No |
Image Quality and Detail Comparison
CT scans are quicker and show bones and injuries well. MRI scans are better for soft tissues, like the brain and muscles.
A medical expert says, “MRI shows soft tissues better than CT scans. This is key for diagnosing some brain and muscle problems.”
“The choice between MRI and CT scans should be guided by the specific clinical question and patient needs.”
Radiation Exposure Considerations
CT scans use X-rays, which can slightly increase cancer risk. MRI scans, without X-rays, are safer. This makes MRI better for pregnant women and kids.
It’s important to think about the risks and benefits of each scan. MRI might be safer for repeated tests to avoid X-ray exposure.
When CT Scans Are the Preferred Choice
CT scans are key in emergency situations and for certain injuries or conditions. They offer quick and accurate diagnoses, which is vital in urgent medical cases.
Emergency and Trauma Situations
In emergency departments, CT scans are invaluable for assessing trauma patients. They quickly spot internal injuries, bleeding, and fractures. This helps doctors make fast decisions about patient care. The speed and accuracy of CT scans can be lifesaving.
Bone and Structural Imaging
CT scans are great for imaging bones and detecting structural abnormalities. They show detailed images of bone fractures and degenerative changes. This makes CT scans a key tool for orthopedic and neurosurgical assessments.
Detecting Certain Diseases and Conditions
We also use CT scans to find and track various diseases and conditions. This includes tumors, vascular diseases, and infections. The clear images of internal structures help diagnose these conditions accurately and track their progress or response to treatment.
In summary, CT scans are the top choice when speed, accuracy, and detailed images are needed. By knowing when to use CT scans, healthcare providers can improve patient care and outcomes.
When MRIs Are the Preferred Choice
MRI scans are top picks for checking soft tissues, brain issues, or muscle problems. They give clear images of soft tissues better than other scans. This makes them great for these areas.
Soft Tissue Evaluation
MRI scans are great for looking at soft tissues like organs and blood vessels. They can spot different soft tissues better than CT scans. For example, they help find problems in the liver, kidneys, and other organs in the belly.
Key benefits of MRI for soft tissue evaluation include:
- High-resolution imaging of soft tissues
- Ability to detect subtle changes in tissue composition
- Non-invasive evaluation of organs and blood vessels
Neurological and Spinal Conditions
MRI is the best choice for checking the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. It shows detailed images. This helps doctors spot problems like multiple sclerosis, spinal stenosis, and herniated discs.
The advantages of MRI in neurological and spinal imaging include:
- Detailed visualization of the central nervous system
- Detection of lesions and abnormalities in the brain and spinal cord
- Assessment of nerve root compression and other spinal issues
Joint and Musculoskeletal Imaging
MRI is also key for looking at joint and muscle problems. It can find issues like torn ligaments, meniscal tears, and osteoarthritis. MRI’s clear images help doctors see how bad the damage is.
| Condition | Diagnostic Capability of MRI |
| Torn Ligaments | High-resolution imaging allows for accurate detection |
| Meniscal Tears | Detailed visualization of meniscal structures |
| Osteoarthritis | Assessment of joint degeneration and cartilage loss |
In summary, MRI scans are the go-to for many health issues. They’re best for soft tissues, brain and spinal problems, and muscle or joint issues. MRI’s detailed images help doctors make accurate diagnoses and plan the best treatments.
Safety Considerations and Contraindications
It’s important to know the safety and limits of MRI and CT scans. This knowledge helps make better choices when getting diagnostic tests.
CT Scan Safety Concerns
CT scans use radiation, which can increase cancer risk. The amount of radiation depends on the scan type and body part.
Key safety concerns for CT scans include:
- Radiation exposure, which is a big worry for kids and young adults
- Damage to kidneys in people with existing kidney problems
- Allergic reactions to the contrast dye used
MRI Safety Concerns and Contraindications
MRI scans use a strong magnetic field and radio waves. They are mostly safe but have some risks and things to avoid.
Key safety concerns and contraindications for MRI include:
- Presence of metal implants, like pacemakers or aneurysm clips
- Metal objects in the eye
- Feeling anxious or claustrophobic in tight spaces
Special Considerations for Specific Patient Groups
Some groups need extra care when getting MRI or CT scans.
| Patient Group | CT Scan Considerations | MRI Considerations |
| Pregnant Women | Use of alternative imaging or minimizing radiation dose | Generally considered safe, but careful assessment is needed |
| Children | Minimizing radiation exposure using adjusted protocols | May require sedation or anesthesia for motion control |
| Patients with Kidney Disease | Risk of contrast-induced nephropathy | Use of gadolinium-based contrast agents with caution |
Knowing these safety tips helps doctors make the right choices. This ensures MRI and CT scans are used safely.
Cost, Accessibility, and Practical Considerations
It’s important to know the cost of MRI and CT scans. This knowledge helps patients and doctors make better choices. The cost of these tests can affect how we get medical care.
Comparing Costs of MRI and CT Scans
The price of MRI and CT scans can change a lot. It depends on where you go and the technology used. CT scans are usually cheaper than MRI scans.
Studies show CT scans cost between $300 and $1,000. MRI scans can cost from $1,000 to $3,000 or more. For example, an MRI costs about $2,600 on average, while a CT scan costs around $800.
“The cost difference between MRI and CT scans is significant,” experts say. “Knowing these costs helps us make better health choices.” The price isn’t just for the scan. It also includes costs for contrast agents, radiologist fees, and more.
Insurance Coverage and Availability
Insurance is key in getting MRI and CT scans. Most plans cover both, but much they cover varies. It’s important to check your insurance to know what you’ll pay out of pocket.
Where you can get these scans also matters. CT scans are more common, found in many hospitals and imaging centers. MRI machines are rarer, so you might have to travel further for one.
Patient Experience and Comfort Factors
Getting an MRI or CT scan is different for everyone. CT scans are quick, taking just a few minutes. MRI scans can take 15 to 90 minutes, depending on the scan and body part.
Some people get claustrophobic in MRI machines. Modern MRI machines are designed to be less scary, with open designs and shorter tubes. CT scans are less likely to cause claustrophobia because they are more open and quick.
In summary, choosing between MRI and CT scans involves more than just medical need. Cost, insurance, and how comfortable you feel are also important. Understanding these factors helps us make better choices for our health and comfort.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Imaging Method
Choosing between an MRI and a CT scan depends on several factors. These include clinical indications, patient factors, and practical considerations. We have explored the core distinctions between these imaging modalities.
Highlighting their technological differences, image quality, and radiation exposure considerations. When deciding on the appropriate imaging method, it is essential to consider the specific needs of the patient and the clinical scenario.
For instance, CT scans are often preferred in emergency situations or for bone and structural imaging. MRIs are ideal for soft tissue evaluation and neurological conditions. Understanding the difference between MRI and CT scan technologies enables healthcare providers to make informed decisions.
Ensuring patients receive the most appropriate diagnostic care. By considering factors such as cost, accessibility, and patient comfort, we can optimize the diagnostic process. This ultimately leads to better patient outcomes.
Ultimately, the choice between MRI and CT scans should be guided by a thorough understanding of the strengths and limitations of each modality. As well as the individual needs of the patient. By choosing the right imaging method, we can ensure accurate diagnoses and effective treatment plans.
FAQ
What is the main difference between an MRI and a CT scan?
MRI uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to create images. CT scans use X-rays to make detailed images of the body.
Are CT scans and MRI scans used for the same purposes?
No, they are not. CT scans are better for emergencies and bone imaging. MRI scans are great for soft tissue and neurological issues.
Do CT scans and MRI scans involve radiation?
CT scans use X-rays, a form of radiation. MRI scans don’t use radiation. They use a magnetic field and radio waves.
Which is safer, a CT scan or an MRI?
MRI is safer because it doesn’t use X-rays. But, MRI might not be safe for everyone. It depends on your health and needs.
How do I know whether I should have a CT scan or an MRI?
Your doctor will decide based on your condition and health. They’ll consider what you need to diagnose or treat your condition.
Are there any specific preparations needed for a CT scan versus an MRI?
Yes, preparation varies. For CT scans, you might need to avoid eating or drinking. MRI scans require removing metal objects and sometimes a contrast agent.
How long do CT scans and MRI scans typically take?
CT scans are quick, taking just a few minutes. MRI scans can take longer, sometimes up to an hour.
Can anyone undergo a CT scan or MRI?
Not everyone can. CT scans are not safe for pregnant women or children. MRI scans have restrictions for metal implants and claustrophobia. Always talk to your doctor first.
Are CT scans and MRI scans covered by insurance?
Insurance coverage varies. Many plans cover both scans when they’re medically necessary. But, it depends on your plan and the reason for the scan.
What are the costs associated with CT scans and MRI scans?
Costs vary by location and facility. MRI scans are usually more expensive. Check with your provider and insurance for details.
References:
- Resonance Imaging Versus Computed Tomography in Orthopedic Care: A Systematic Review. Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery, 14(1), 19-32. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9305220East