Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
Understanding the differences between MRI and CT scans is key to your health. At Liv Hospital, we help you choose the right imaging for your needs. MRI shows what CT scan does not by providing more detailed images of soft tissues like the brain, spinal cord, muscles, and joints. This makes MRI better for detecting abnormalities in these areas, while CT is faster and excels at showing bones and organs. The key question, “what does MRI show that CT scan does not,” is answered by MRI’s superior soft tissue contrast and detail.
MRI scans use strong magnets and radio waves to show soft tissues clearly. CT scans use X-rays to image bones, organs, and tissues.
Key Takeaways
- MRI provides greater detail for soft tissues compared to CT scans.
- CT scans are more effective for visualizing bone structures and detecting internal bleeding.
- MRI does not expose patients to ionizing radiation, making it a safer option for repeated scans.
- The choice between MRI and CT scan depends on the specific medical condition being diagnosed.
- MRI is often preferred for evaluating certain types of cancer and soft tissue injuries.
Understanding Medical Imaging Technologies
Medical imaging technologies have greatly improved how we diagnose and treat health issues. We’ve moved from old methods to new, advanced ones. This change has made patient care better and treatment results more effective.
The Evolution of Diagnostic Imaging
Diagnostic imaging has changed a lot over the years. We’ve gone from simple X-rays to complex MRI and CT scans. These new tools give doctors a clear look inside the body, helping them find and treat problems sooner.
As a top expert said,
“The advent of advanced imaging technologies has revolutionized the way we diagnose and manage diseases, giving us unprecedented clarity and detail.”
This shows how big a deal diagnostic imaging is in today’s healthcare.
The Role of Advanced Imaging in Modern Medicine
Advanced imaging is key in modern medicine. It helps doctors make accurate diagnoses and plan treatments. MRI and CT scans give detailed views of the body’s inside, helping doctors spot problems and plan the best treatment.
This precision has made patient care better. It has cut down the need for risky surgeries and improved care quality.
Using advanced imaging in healthcare has also led to better patient management. It gives doctors detailed info on diseases, helping them tailor treatments to each patient. This approach has led to better health results for patients.
The Fundamental Principles of MRI

MRI technology uses nuclear magnetic resonance to show the body’s inside. It’s key in modern medicine, helping with soft tissue issues.
How Magnetic Resonance Imaging Works
MRI machines use strong magnets and radio waves to show body parts. First, a patient gets into the MRI machine, which has a strong magnet. This magnet lines up hydrogen nuclei in the body.
Then, radio waves disturb these nuclei, making signals. These signals help create detailed images.
The magnetic field’s strength matters a lot. Modern MRI machines have fields of 1.5 or 3 Tesla. This lets them show even the smallest body parts clearly.
The Physics Behind MRI Technology
MRI’s physics is based on nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). NMR happens when certain atoms, like hydrogen, are in a strong magnetic field and radio waves. They absorb and send out electromagnetic waves, which are used to make images.
This involves complex physics, like quantum mechanics and electromagnetism. But it results in detailed images. These images help doctors diagnose many health issues.
Types of MRI Machines and Their Capabilities
There are many MRI machines, each with its own uses. The closed MRI machine gives clear images, but it can be hard for those afraid of tight spaces.
Open MRI machines are a better choice for some. They have more room and are easier for patients to relax in. But, they might not show as much detail as closed machines.
There are also functional MRI (fMRI) machines for brain studies and MRA (Magnetic Resonance Angiography) machines for blood vessels. Knowing about these machines helps doctors pick the right one for each patient.
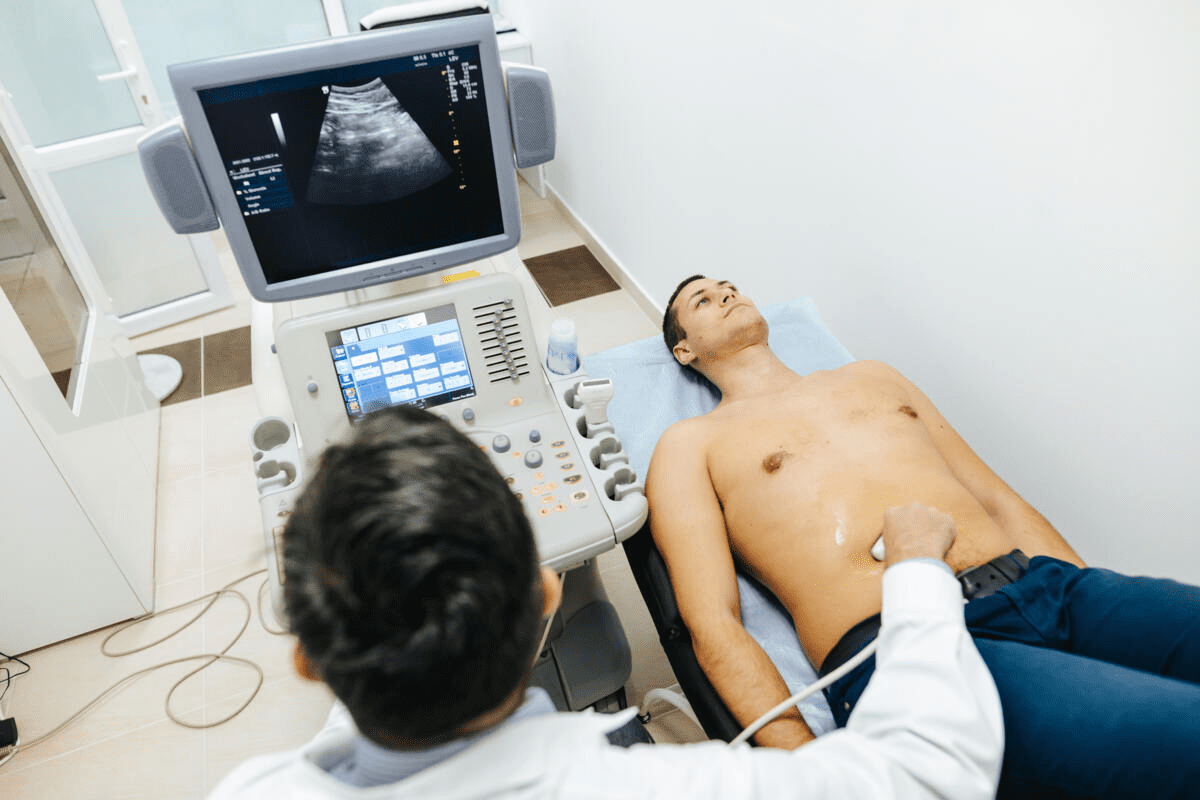
The Mechanics of CT Scanning
CT scanning uses X-ray technology and computer algorithms. It’s fast and effective, giving detailed images of the body’s inside.
How Computed Tomography Functions
CT scanners rotate an X-ray source and detectors around the patient. They capture X-ray measurements from different angles. Then, these measurements are turned into detailed images using advanced algorithms.
Key Components of a CT Scanner:
- X-ray tube
- Detector array
- Gantry
- Computer system
X-ray Technology in CT Scans
X-ray technology is key in CT scanning. The X-ray tube sends X-rays through the patient’s body. The detector array catches these X-rays, showing how much they were blocked.
Advantages of X-ray Technology in CT:
- Fast imaging times
- High-resolution images
- Ability to image dense structures like bone
Evolution of CT Scanning Technology
CT scanning technology has grown a lot over time. Today’s scanners are faster, have better resolution, and use less radiation. New technologies like helical CT and multi-detector CT have made CT scans even better for diagnosis.
| Generation | Characteristics | Advantages |
| First Generation | Single X-ray source and detector | Initial introduction of CT technology |
| Fourth Generation | Multiple detectors, faster scan times | Improved image quality and reduced scan time |
| Modern CT | Helical and multi-detector CT | High-resolution imaging, reduced radiation exposure |
CT scanning technology has come a long way. It’s now a powerful tool for doctors. As it keeps getting better, we can expect even more accurate and quicker diagnoses.
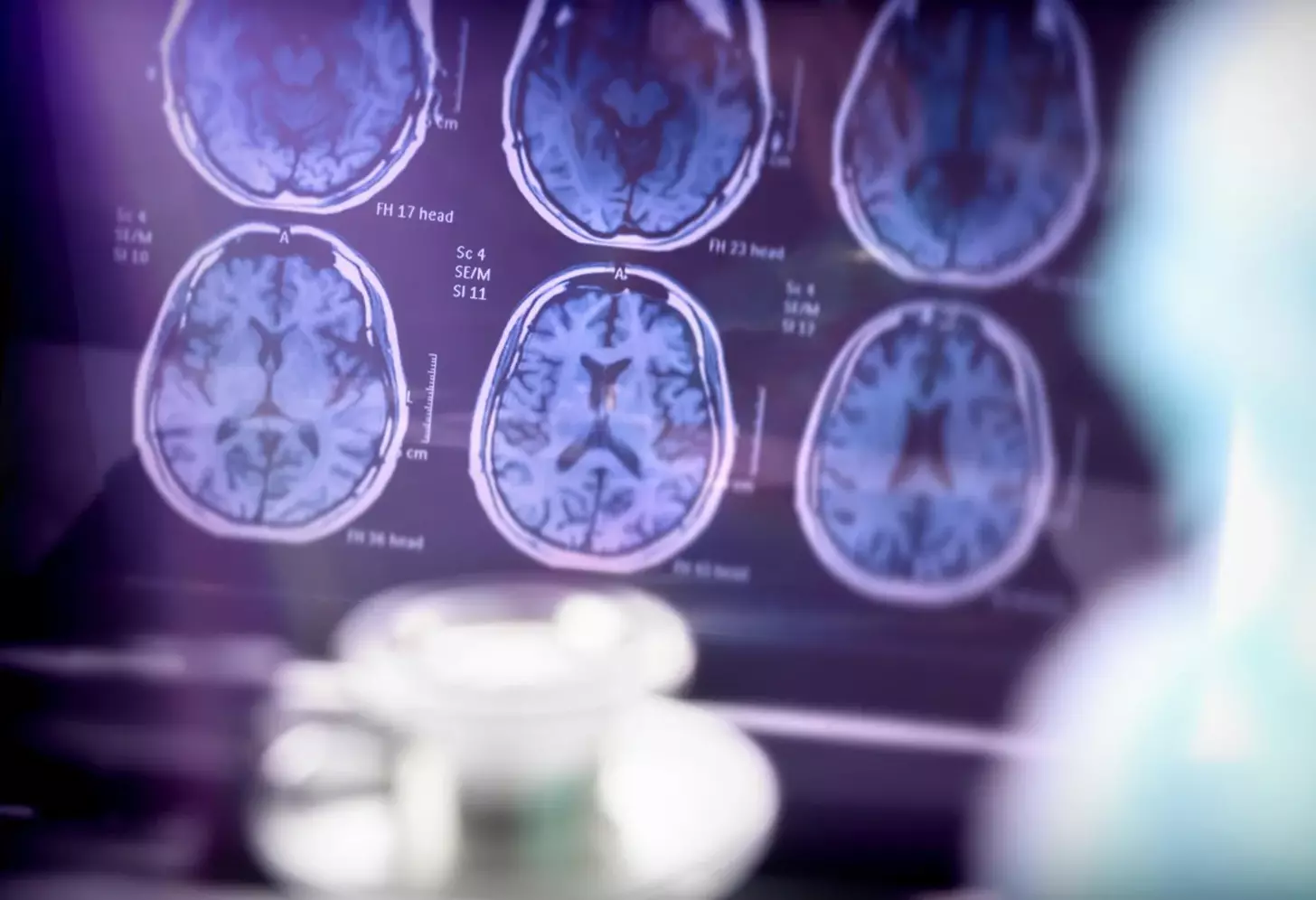
What Does an MRI Show That a CT Scan Does Not?
Understanding the differences between MRI and CT scans is key to accurate diagnoses. Both technologies offer valuable insights into the body’s internal structures. Yet, they have unique strengths and uses.
Superior Soft Tissue Visualization
MRI outshines CT scans in superior soft tissue visualization. It excels at imaging soft tissues like organs, tendons, and ligaments. This makes MRI essential for diagnosing conditions affecting these areas.
It’s vital for spotting tumors, inflammation, and degenerative diseases. Detailed soft tissue imaging is critical here.
Detailed Neural Imaging Capabilities
MRI is also known for its detailed neural imaging capabilities. It gives unmatched views of the brain and spinal cord. This allows for spotting subtle abnormalities that CT scans might miss.
This is why MRI is the top choice for diagnosing neurological conditions. It’s great for detecting multiple sclerosis, stroke, and spinal cord injuries.
Enhanced Detection of Subtle Abnormalities
MRI’s sensitivity to soft tissue contrasts also means it can enhance the detection of subtle abnormalities. This is super helpful in catching diseases early. Small changes in tissue structure can signal the start of a condition.
By showing these small changes, MRI helps in starting treatments early. This leads to more effective care plans.
In summary, MRI has clear advantages over CT scans. It’s better for soft tissue, neural imaging, and spotting small changes. Knowing these differences helps choose the right diagnostic tool for each medical condition.
When CT Scans Outperform MRIs
CT scans are better than MRIs in some areas, like seeing bone structures. MRI is great for soft tissues, but CT scans have their own strengths. They shine in certain situations.
Bone Structure Visualization
CT scans are top-notch for looking at bones. They use X-ray tech to make clear images. This is perfect for checking bone fractures, osteoporosis, and more. CT scans show bone density and structure well, helping doctors make good plans.
Acute Trauma Assessment
For quick trauma checks, CT scans are the go-to. They can fast-track injury checks, spot internal bleeding, and find serious issues. CT scans are fast and accurate, helping doctors act quickly.
Detection of Internal Bleeding
CT scans are also great at finding internal bleeding. This is key in trauma cases. They can spot small bleeds, which is super important. CT scans are key in emergency care for finding bleeding fast.
To wrap it up, while MRI is good for some things, CT scans are better in others. They’re best for bone checks, trauma, and finding internal bleeding.
The Difference Between an MRI and a CT Scan: Technology Comparison
MRI and CT scans are key in medical imaging, but they work in different ways. Knowing how they differ helps us see their strengths and weaknesses in healthcare.
Imaging Technology Distinctions
MRI and CT scans use different physics. MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to show body structures inside. CAT scans use X-rays to make detailed images.
Key differences in imaging technology include:
- MRI: Uses magnetic fields and radio waves, safer for those sensitive to radiation.
- CAT Scan: Uses X-rays, which are ionizing radiation.
Radiation Exposure Considerations
MRI and CT scans differ in radiation exposure. MRI doesn’t use ionizing radiation, safer for pregnant women and kids. CAT scans use X-rays, which carry a small risk of harm.
| Imaging Modality | Radiation Exposure | Typical Use Cases |
| MRI | No ionizing radiation | Soft tissue imaging, neurological conditions |
| CAT Scan | Involves X-ray radiation | Emergency trauma, lung and chest imaging, bone-related conditions |
Image Resolution and Detail Comparison
Both MRI and CT scans give detailed images, but are better in different areas. MRI is great for soft tissues like tendons and organs. CAT scans are better for bones and detecting injuries.
In conclusion, MRI and CT scans have big differences in technology. Knowing these helps doctors choose the right imaging for each case.
Clinical Applications: When Doctors Choose MRI Over CT
In many cases, doctors prefer MRI over CT because it shows soft tissues better. MRI gives detailed images of complex body parts. This makes it a key tool in today’s medicine.
Neurological Conditions
For neurological issues, MRI is often the top choice. It shows the brain and spinal cord in great detail. This helps spot problems like multiple sclerosis, brain tumors, and stroke.
One big plus of MRI is that it can find lesions in the brain and spinal cord. For example, it can spot lesions in the white matter of the brain and spinal cord in patients with multiple sclerosis. This helps doctors plan treatments.
Musculoskeletal Disorders
MRI is also key for diagnosing muscle and bone problems. It shows muscles, tendons, and ligaments clearly. This is great for checking injuries like torn ligaments or tendonitis.
It’s also good for seeing how bad the damage is in conditions like osteoarthritis and osteonecrosis. MRI is perfect for looking at joints, like the knee, to find problems like meniscal tears.
Soft Tissue Pathologies
For soft tissue issues, like tumors and infections, MRI is top-notch. It lets doctors check soft tissue masses closely. This helps tell if a tumor is benign or malignant.
In cases of soft tissue sarcomas, MRI helps plan surgery. It shows the tumor’s size, location, and how it affects nearby areas. This ensures patients get the right treatment.
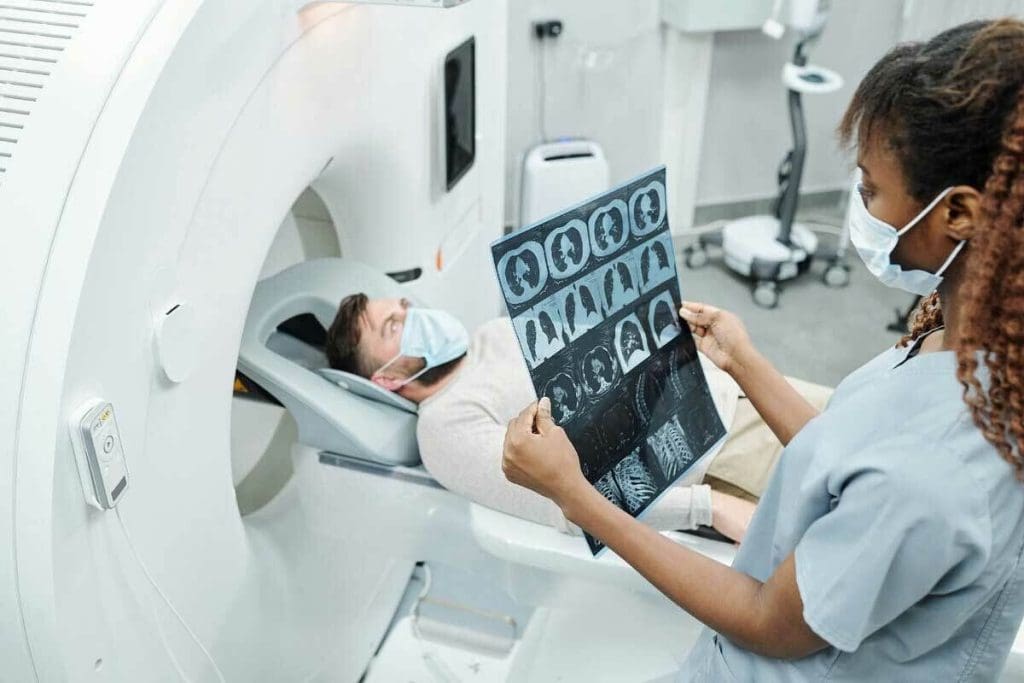
Clinical Applications: When Doctors Choose CT Over MRI
Doctors often pick CT scans over MRI in emergencies because they are quick and accurate. In critical care, every second counts. CT scans can be a lifesaver by providing fast images.
Emergency and Trauma Situations
In emergency rooms, CT scans are the top choice for checking acute injuries and trauma. They quickly show internal injuries like bleeding or organ damage. This helps doctors act fast.
Key benefits of CT scans in emergency situations include:
- Rapid image acquisition
- High sensitivity to acute injuries
- Ability to image patients with life-support equipment
The American College of Radiology says, “CT is the preferred modality for the initial evaluation of most acute traumatic injuries.” This highlights CT scans’ critical role in emergency care.
“The speed and accuracy of CT scans make them invaluable in trauma care, enabling healthcare providers to make quick decisions that can significantly impact patient outcomes.”
Lung and Chest Imaging
CT scans excel in lung and chest imaging. They can spot many conditions, from pneumonia to pulmonary embolism. Their high-resolution images help doctors see lung tissue and airways clearly.
A comparison of CT and MRI for lung imaging is shown in the table below:
| Imaging Modality | Lung Tissue Detail | Detection of Pulmonary Embolism |
| CT Scan | High | Excellent |
| MRI | Limited | Good, but not as sensitive as CT |
Bone-Related Conditions
CT scans are also the go-to for bone-related issues. They offer detailed images of bones. This is perfect for diagnosing fractures, osteoporosis, and other bone problems.
The detailed bone imaging provided by CT scans is key for orthopedic and surgical planning.
Patient Experience and Practical Considerations
Choosing between MRI and CT scans is a big decision. It’s important to think about how each affects patient comfort, safety, and happiness.
Duration and Comfort Factors
How long the scan takes is a key factor. MRI scans can last from 15 to 90 minutes. CT scans, on the other hand, are much quicker, usually done in just a few minutes.
Comfort during the scan is also vital. MRI scans can be tough for those with claustrophobia because you have to stay very quiet in a small space. CT scans are faster, but might make some people feel trapped, too.
Claustrophobia and Anxiety Management
For MRI scans, claustrophobia and anxiety are big worries. Some MRI places have open machines or sedation to help patients relax. CT scans are less likely to cause these feelings because they’re more open.
It’s important for doctors to talk about how to handle anxiety with patients. This might include sedation or choosing a different scan if possible.
Cost and Insurance Considerations
The cost of MRI and CT scans can differ a lot. Prices depend on where you go, where you are, and your insurance. MRI scans are usually pricier because they use more advanced tech and take longer.
| Imaging Modality | Average Cost Range | Insurance Coverage |
| MRI | $1,000 – $3,500 | Varies by insurance provider |
| CT Scan | $300 – $1,500 | Varies by insurance provider |
It’s key for patients to check with their insurance to know what they’ll have to pay for these scans.
Safety Profiles: Is an MRI and CT Scan the Same in Terms of Risk?
It’s important to know how safe MRI and CT scans are. They differ a lot, mainly in how they use radiation and what they can’t do.
Radiation Exposure Comparison
One big difference is radiation. CT scans use X-rays to make images, which means they expose you to radiation. MRI doesn’t use radiation, making it safer for some people, like pregnant women and kids.
But CT scans can raise cancer risk, which is a big worry, mainly for kids. We need to think hard about the benefits and risks of CT scans, like how often they’re used or who they’re for.
Contraindications for Each Imaging Method
Both MRI and CT scans have things they can’t do. MRI can’t be used on people with metal implants or who are claustrophobic. CT scans can’t be used on people with kidney problems or allergies to the dye used.
- MRI contraindications: metal implants, claustrophobia
- CT scan contraindications: kidney disease, contrast agent allergies
Special Considerations for Vulnerable Populations
Some groups need extra care when they get scanned. Pregnant women, kids, and people with certain health issues are at risk. MRI is safer for pregnant women and kids because it doesn’t use radiation.
We should think carefully about when to scan someone. We should pick the best method and try to make it as safe as possible. This means using other methods when we can, reducing radiation, and telling patients about the risks and benefits.
Conclusion: Making Sense of MRI and CT Imaging Differences
It’s important for patients and doctors to know the differences between MRI and CT scans. Both are key tools for diagnosing health issues. Each has its own strengths and weaknesses.
MRI scans are great for seeing soft tissues. They’re best for finding problems in the brain, muscles, and soft tissues. CT scans, on the other hand, are better for looking at bones. They’re often used in emergency situations.
Knowing what each scan can do helps us make better choices. The right choice depends on the health issue and what information is needed. This helps in making the best treatment plans.
As medical imaging gets better, it’s vital to keep up with MRI and CT scans. This ensures patients get the best care possible.
FAQ
What is the main difference between an MRI and a CT scan?
MRI and CT scans differ in how they create images. MRI uses nuclear magnetic resonance to see soft tissues. CT scans use X-rays to show internal structures.
What does an MRI show that a CT scan does not?
MRI is better at showing soft tissues and detailed neural images. It also finds subtle abnormalities better. This makes it great for diagnosing soft tissue and neural conditions.
When are CT scans preferred over MRI?
CT scans are better in emergencies and for lung and chest issues. They’re also good for bone conditions because they can show bones quickly.
Is there a difference in radiation exposure between MRI and CT scans?
Yes, CT scans use X-rays and involve radiation. MRI doesn’t use ionizing radiation, making it safer for some patients.
Can MRI and CT scans be used interchangeably?
No, the choice between MRI and CT scans depends on the situation. Each has its own strengths for different needs.
How do MRI and CT scans differ in terms of patient experience?
MRI and CT scans offer different experiences. Factors like how long it takes, comfort, claustrophobia, and cost affect the choice.
Are there any contraindications for MRI or CT scans?
Yes, some conditions or implants may not be safe for MRI or CT scans. For example, MRI might not be safe for those with certain metal implants. CT scans might not be safe for pregnant women or those with allergies.
How do the image resolution and detail compare between MRI and CT scans?
MRI shows soft tissues well, while CT scans are better for bones and some organs. The right choice depends on what you need to see.
Can MRI detect conditions that CT scans miss?
Yes, MRI can find conditions that CT scans might miss. It’s better soft tissue images and the ability to spot small details are key.
Are there any special considerations for vulnerable populations undergoing MRI or CT scans?
Yes, vulnerable groups like pregnant women, children, or those with certain conditions need special care. This ensures their safety during the scan.
References
- NIH’s National Library of Medicine. (2022). Radiation dose in medical imaging. NIH. Retrieved October 10, 2025, from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35327365/