Last Updated on November 26, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
Knowing the difference between benign and malignant tumors is key for diagnosis and treatment. At Liv Hospital, we focus on patient care and accurate diagnosis. Our goal is to meet international medical standards.
A malignant tumor, like prostate cancer, can spread to other parts of the body. On the other hand, benign tumors are not cancerous and don’t spread. We aim to provide top-notch care for both types of tumors.
Key Takeaways
- Benign tumors are non-cancerous and do not invade surrounding tissues.
- Malignant tumors are cancerous and can metastasize.
- Accurate diagnosis is key for effective treatment.
- Liv Hospital offers patient-centered care with international standards.
- Understanding tumor types is vital for proper treatment.
Understanding Tumors: The Basics
The term ‘tumor’ refers to an abnormal mass of tissue. It can be either benign or malignant. This requires a deeper understanding of their characteristics. Tumors are formed when cells in the body grow and multiply abnormally. This leads to a mass that can be harmless or dangerous.
What Defines a Tumor?
A tumor is defined by its abnormal cell growth. This can result from genetic mutations or environmental influences. Benign tumors are typically slow-growing and do not invade surrounding tissues. On the other hand, malignant tumors are cancerous and can metastasize to other parts of the body.
- Benign tumors are generally not life-threatening and tend to grow slowly.
- Malignant tumors are dangerous as they can invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body.
How Tumors Develop in the Body
Tumors develop due to uncontrolled cell growth. This can be triggered by genetic factors, environmental exposures, or a combination of both. Understanding how tumors develop is key for early detection and effective treatment.
- Genetic mutations can lead to abnormal cell growth.
- Environmental factors, such as exposure to carcinogens, can also contribute to tumor development.
- Lifestyle factors, including diet and smoking, can influence the risk of developing certain types of tumors.
Common Misconceptions About Tumors
There are several misconceptions about tumors. Many believe that all tumors are cancerous. In reality, many tumors are benign and pose little risk to health. It’s essential to understand the differences between benign and malignant tumors to avoid unnecessary anxiety and ensure appropriate medical care.
By understanding the basics of tumor development and characteristics, individuals can better navigate their diagnosis and treatment options. We emphasize the importance of clear medical expertise while maintaining a compassionate and approachable tone to support those affected by tumor diagnoses.
Benign Tumors: Characteristics and Types
Benign tumors are growths that don’t invade nearby tissues or spread to other parts of the body. They are not cancerous and usually don’t threaten a person’s life. But, they can cause health issues by pressing on nearby structures.
The term “tumor” might sound scary, but it’s important to know the difference between benign and malignant growths. Benign tumors are treatable and don’t harm the body much. Knowing about their characteristics helps doctors diagnose and treat them properly.
Definition and Key Features of Benign Tumors
Benign tumors don’t invade nearby tissues and can’t spread. They are usually encapsulated and grow slowly. The main features of benign tumors are:
- Non-invasive growth pattern
- No metastasis
- Typically slow-growing
- Often encapsulated
These traits set benign tumors apart from malignant ones, which are aggressive and can spread.
Common Types of Benign Tumors
There are many types of benign tumors, each with its own characteristics. Some common ones are:
| Type of Benign Tumor | Description | Common Location |
|---|---|---|
| Lipoma | A soft, fatty tumor | Under the skin |
| Fibroma | A tumor composed of fibrous tissue | Skin or internal organs |
| Adenoma | A tumor of glandular origin | Glands such as the thyroid or adrenal |
These tumors can appear in different parts of the body. They may cause symptoms based on their location and size.
Potential Health Impacts of Benign Growths
Even though benign tumors are not cancerous, they can cause health problems. For example, a benign tumor can press on nearby structures, causing discomfort or more serious health issues. A benign tumor in the brain might cause neurological symptoms, while one in the abdomen could lead to digestive problems.
We aim to provide top-notch healthcare with full international patient support. It’s key to understand the characteristics and types of benign tumors for proper diagnosis and treatment. This ensures patients get the best care possible.
Malignant Tumors: Characteristics and Types
Malignant tumors grow aggressively and can spread to other parts of the body. At our institution, we focus on high-quality care and innovative solutions for these patients.
Key Features of Malignant Tumors
Malignant tumors are cancerous and can spread, like prostate cancer. They have several key features:
- Uncontrolled Growth: They grow without stopping and can invade nearby tissues.
- Metastasis: They can spread to other parts of the body through the bloodstream or lymphatic system.
- Aggressive Behavior: These tumors can cause a lot of damage to nearby tissues and organs.
Common Types of Malignant Tumors
There are many types of malignant tumors, each with its own characteristics. Some common ones include:
- Carcinomas: These are the most common type, coming from epithelial cells. Examples are breast, lung, and colon cancers.
- Sarcomas: These tumors start in connective tissues like bones, muscles, and fat.
- Leukemias: This is cancer of the blood cells, marked by an abnormal increase in white blood cells.
- Lymphomas: These cancers affect the lymphatic system, which is part of the immune system.
For more on diagnosing tumors, visit Liv Hospital’s guide on tumor diagnosis.
How Cancer Spreads: Understanding Metastasis
Metastasis is when cancer cells spread from the original site to other parts of the body. This process involves several steps:
- Invasion: Cancer cells invade the surrounding tissue.
- Intravasation: Cancer cells enter the bloodstream or lymphatic vessels.
- Circulation: Cancer cells travel through the bloodstream or lymphatic system.
- Extravasation: Cancer cells exit the bloodstream or lymphatic vessels to form new tumors.
Understanding metastasis is key to developing effective treatments. We are dedicated to providing top-notch care and innovative solutions for patients with malignant tumors.
Benign Tumors and Malignant Tumors Difference: A Comparative Look
It’s key to know the difference between benign and malignant tumors for the right treatment. We offer care for both types, knowing the difference is critical for treatment.
Cellular Structure and Growth Patterns
Benign tumors have clear borders and are wrapped in a layer. Malignant tumors have irregular shapes and spread to other tissues. Benign tumors look like the normal tissue, but malignant ones don’t.
Benign tumors grow slowly and expand. Malignant tumors grow fast and spread. Knowing these differences helps in treating tumors right.
Invasion and Metastasis Capabilities
Malignant tumors can spread to other parts of the body. Benign tumors don’t spread. This ability to spread is a key sign of cancer and affects treatment.
Impact on Surrounding Tissues
Benign tumors push aside other tissues. Malignant tumors invade and harm other tissues. How a tumor affects nearby tissues is important for treatment.
Recurrence Tendencies and Long-term Behavior
Benign tumors might come back if not fully removed. But they’re not usually dangerous. Malignant tumors are more likely to come back and can be deadly if not treated well.
| Characteristics | Benign Tumors | Malignant Tumors |
|---|---|---|
| Cellular Structure | Resembles parent tissue | Exhibits cellular atypia |
| Growth Pattern | Slow and expansive | Rapid and invasive |
| Invasion and Metastasis | No invasion or metastasis | Invasive and metastatic |
| Impact on Surrounding Tissues | Displaces surrounding tissues | Invades and destroys surrounding tissues |
| Recurrence Tendency | May recur if not completely removed | Higher tendency to recur |
Knowing the difference between benign and malignant tumors is key for treatment. By understanding their structure, growth, and behavior, we can better care for patients with tumors.
Diagnosis: Identifying Benign vs. Malignant Tumors
We use many ways to figure out if a tumor is benign or malignant. This helps ensure patients get the right care. Knowing the type of tumor is key to choosing the right treatment.
Initial Screening and Physical Examination
The first step is an initial screening and physical check-up. We check the patient’s overall health and look for signs of a tumor.
- Medical history review
- Physical examination
- Initial laboratory tests
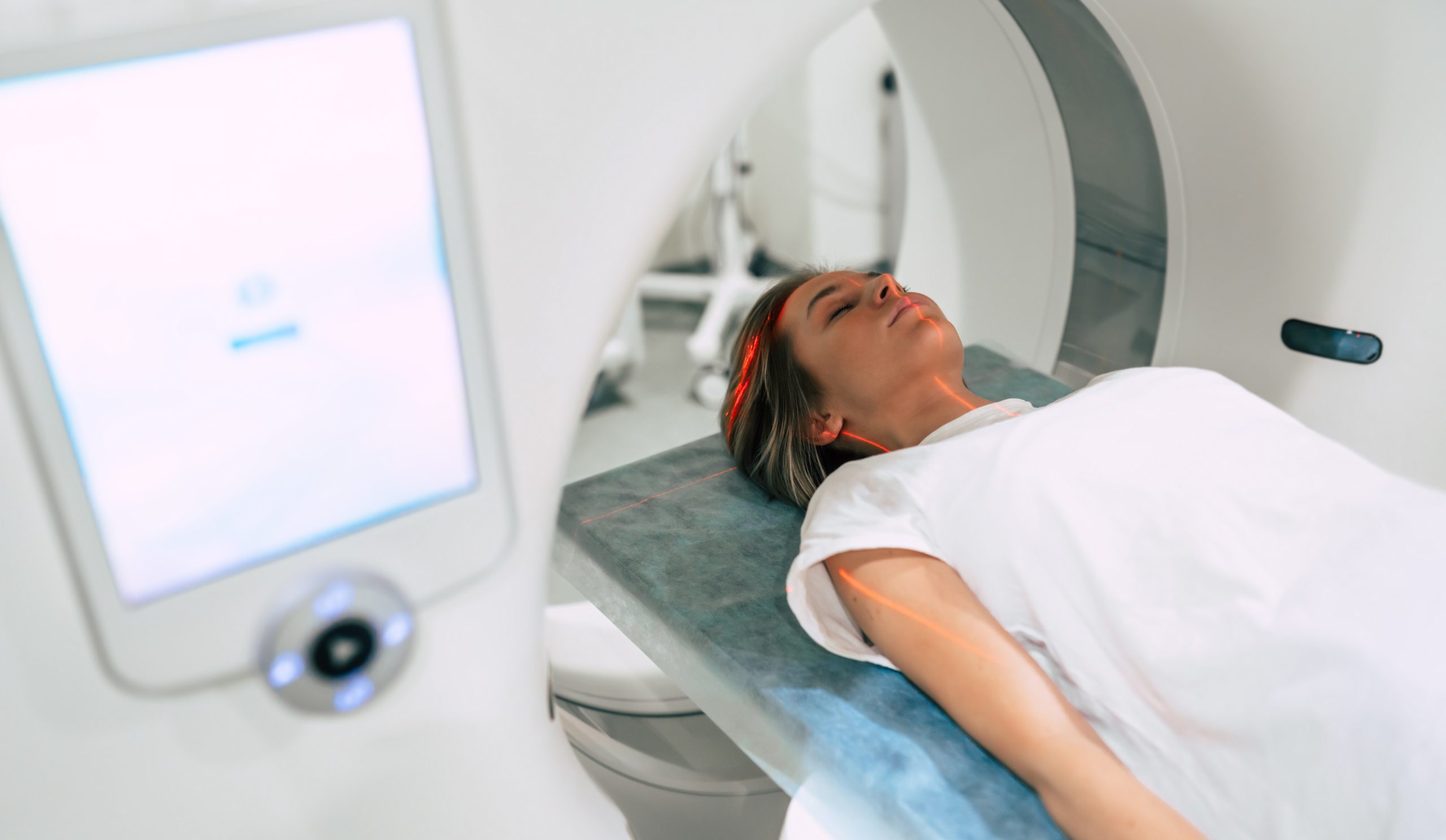
Imaging Techniques for Tumor Detection
Imaging is key in finding tumors and learning about them. Advanced imaging like MRI, CT scans, and PET scans give us detailed info. They show the tumor’s size, where it is, and if it has spread.
Biopsy and Histopathological Analysis
A biopsy takes a tissue sample from the tumor. Histopathological analysis of this tissue is vital. It tells us if the tumor is benign or malignant.
- Biopsy procedure
- Laboratory analysis of tissue samples
- Histopathological examination
Advanced Diagnostic Technologies
We use the latest tech to improve tumor diagnosis. This includes molecular diagnostics and genetic testing. These help us understand the tumor’s behavior and find the best treatment.
Treatment Approaches for Different Tumor Types
Knowing the difference between benign and malignant tumors is key to choosing the right treatment. We offer new ways to treat both types of tumors. Our approach is tailored to each tumor’s unique features.
Treatment Options for Benign Tumors
Benign tumors usually don’t need strong treatments. Watchful waiting or surgical removal might be suggested. This depends on the tumor’s size, where it is, and how it might affect nearby tissues.
Some benign tumors can cause pain or affect how organs work. In these cases, treatment is needed.
- Monitoring: Regular check-ups to track the tumor’s size and any changes.
- Surgery: Removal of the tumor, often preferred if the tumor is causing symptoms or is likely to grow.
- Minimally invasive procedures: Techniques like radiofrequency ablation for certain types of benign tumors.
Treatment Strategies for Malignant Tumors
Malignant tumors, being cancerous, need more aggressive and detailed treatment plans. The main goal is to get rid of the cancer while keeping as much organ function as we can. Treatment strategies may include:
- Surgery: To remove the tumor and some surrounding tissue.
- Chemotherapy: Using drugs to kill cancer cells.
- Radiation therapy: High-energy rays to target and destroy cancer cells.
- Targeted therapy: Drugs that target cancer cells’ specific traits.
- Immunotherapy: Boosting the body’s immune system to fight cancer.
Treatment plans vary based on the tumor type and its characteristics. We focus on a personalized approach, considering each patient’s unique situation.
When Observation May Be Recommended
In some cases, like small, symptom-free benign tumors, watching them might be advised. This means regular checks to see if the tumor changes in size or type.
Emerging Therapeutic Approaches
New treatments are being researched, giving hope for better results. New approaches include:
- Precision medicine: Tailoring treatment to the individual’s genetic profile.
- Advanced immunotherapies: New ways to boost the body’s immune response against cancer.
- Nano-technology: Using nanoparticles to deliver drugs directly to cancer cells.
We are dedicated to keeping up with these new developments. This ensures our patients get the most effective and innovative treatments.
Risk Factors and Prevention Strategies
It’s important to know what causes tumors to grow. Tumors can be either benign or malignant. Knowing the risk factors helps us take steps to prevent them.
Common Risk Factors for Tumor Development
Many things can increase the chance of getting a tumor. Genetic predisposition is a big one. If your family has a history of tumors, you might be at higher risk. Lifestyle choices like tobacco use, diet, and physical activity levels also play a part.
Changing your lifestyle can lower your risk of getting a tumor. Eating a healthy diet full of fruits, veggies, and whole grains is key. Quitting tobacco products and drinking less alcohol is also important. Plus, staying active can help prevent some tumors.
Lifestyle Modifications for Tumor Prevention
Living a healthy lifestyle can help prevent tumors. This means eating right, staying active, and keeping a healthy weight. Stress management through meditation and yoga can also help your overall health.
- Eating a diet rich in fruits and vegetables
- Avoiding tobacco and limiting alcohol consumption
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Maintaining a healthy weight
Screening Recommendations for High-Risk Individuals
If you’re at high risk for tumors, regular check-ups are key. This might include more imaging tests or genetic testing. Your doctor will decide the best schedule for you.
By knowing the risks and taking steps to prevent them, you can lower your chance of getting a tumor. Early detection through screenings can also help improve outcomes if you do get a tumor.
Living with a Tumor Diagnosis: Patient Perspectives
Getting a tumor diagnosis, whether it’s benign or malignant, starts a tough journey for patients. The first shock and uncertainty can be too much. It’s important for patients to get full support. We know each patient’s story is different, and we aim to help with guidance and resources that fit their needs.
Coping with a Benign Tumor Diagnosis
Even though a benign tumor is not cancerous, it can be scary. Patients need reassurance and clear info about their health. Knowing about the tumor and treatment options helps ease worries and helps make smart choices.
Many worry if the tumor will cause symptoms or grow. Talking to a healthcare provider is key to understanding what to expect and any needed steps.
Navigating a Malignant Tumor Diagnosis
A malignant tumor diagnosis comes with its own set of challenges. Understanding the cancer type, stage, and treatment is vital. Emotional support is essential during this time, as patients deal with the news.
Having a support system, like family, friends, or support groups, is important. Counseling and psychological support can also be very helpful.
Support Resources and Patient Communities
Support resources are key for patients dealing with their diagnosis. This includes educational materials, support groups, and online communities. Connecting with others who have gone through similar things offers comfort and advice.
| Support Resource | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Support Groups | Groups where patients can share their experiences | Emotional support and community |
| Educational Materials | Resources providing information on tumor diagnosis and treatment | Informed decision-making |
| Online Communities | Forums and social media groups for patients and families | Accessibility and connection |
We’re dedicated to top-notch healthcare and support for international patients. By giving access to various support resources, we aim to improve the lives of those facing tumor diagnoses.
Conclusion
Knowing the difference between benign and malignant tumors is key for good care. At Liv Hospital, we focus on understanding these differences. This helps us give top-notch care to our patients.
Benign tumors are usually not dangerous, but malignant tumors need quick and strong treatment. It’s vital to know if a tumor is benign or malignant. This helps us choose the right treatment for each patient.
We offer full care for both benign and malignant tumors. We use new solutions and follow strong medical ethics. By knowing the tumor type, we can make treatment plans that fit each patient’s needs. This way, we aim for the best results.
Diagnosing and treating tumors right needs a team effort. Our team works hard to give world-class care. We make sure patients get the support they need, no matter where they’re from.
What is the main difference between benign and malignant tumors?
Benign tumors are not cancerous and don’t spread. Malignant tumors are cancerous and can spread.
How do benign tumors affect the body?
Benign tumors can press on nearby tissues. But they are usually treatable with little harm.
What are the characteristics of malignant tumors?
Malignant tumors are cancerous. They can grow into nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body.
How are benign and malignant tumors diagnosed?
Doctors use screening, physical exams, imaging, biopsy, and lab tests to diagnose tumors.
What are the treatment approaches for benign and malignant tumors?
Benign tumors might not need aggressive treatment. But malignant tumors often need surgery, chemo, and radiation.
Can lifestyle modifications help reduce the risk of developing tumors?
Yes, eating well and avoiding tobacco can lower tumor risk.
What support resources are available for patients with a tumor diagnosis?
Support groups and communities help patients deal with their diagnosis, whether benign or malignant.
What is metastasis, and how does it relate to malignant tumors?
Metastasis is when cancer spreads to other parts of the body. It’s a sign of malignant tumors.
Are there emerging therapeutic approaches for treating malignant tumors?
Yes, new treatments like targeted therapy and immunotherapy offer hope for malignant tumor patients.
How can high-risk individuals detect tumors at an early stage?
Screening is key for early detection in high-risk individuals.