Last Updated on November 26, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
Knowing the difference between benign and malignant tumors is key for good health choices. At Liv Hospital, we stress the need for correct diagnosis and full care.
Benign tumors are not cancerous and usually don’t spread to other tissues. On the other hand, malignant tumors are cancerous and can spread. The gap between these tumors affects treatment choices and results.
We know how scary a tumor diagnosis can be. Our top-notch care aims to help you understand these differences confidently. Knowing the main differences helps patients on their treatment path.
Key Takeaways
- Benign tumors are non-cancerous and typically do not invade surrounding tissues.
- Malignant tumors are cancerous and have the ability to spread.
- Getting a correct diagnosis is vital for the right treatment plan.
- Liv Hospital offers full care and support for tumor patients.
- Understanding the differences between benign and malignant tumors helps patients make better choices.
Understanding Tumor Basics: What You Need to Know
The word ‘tumor’ often makes people scared. But what is a tumor, and how do benign and malignant types differ? We will look into the basics of tumors to clear up any confusion about these abnormal growths.
What Defines a Tumor
A tumor is an abnormal mass of tissue. It happens when cells divide too much or don’t die when they should. Tumors can be either benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Knowing what a tumor is helps us understand cancer and other diseases better.
Benign tumors are usually not dangerous and don’t spread. But malignant tumors are cancerous. They can grow into nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body, a process called metastasis.
Common Misconceptions About Tumors
There are many common misconceptions about tumors. One is thinking all tumors are cancerous. But, as we said, tumors can be either benign or malignant. Another mistake is believing the size of a tumor shows how serious it is. While big tumors might be more of a problem, it’s the type of tumor (benign vs. malignant) that matters more.
It’s key to know the difference between benign and malignant tumors. This knowledge helps patients understand their diagnosis and treatment options better. We will dive deeper into these differences in the next sections, giving you a full view of tumor basics.
What Is the Difference Between Benign Tumors and Malignant Tumors
It’s important to know the difference between benign and malignant tumors. This knowledge helps doctors choose the right treatment and predict how well a patient will do.
Fundamental Distinctions at a Glance
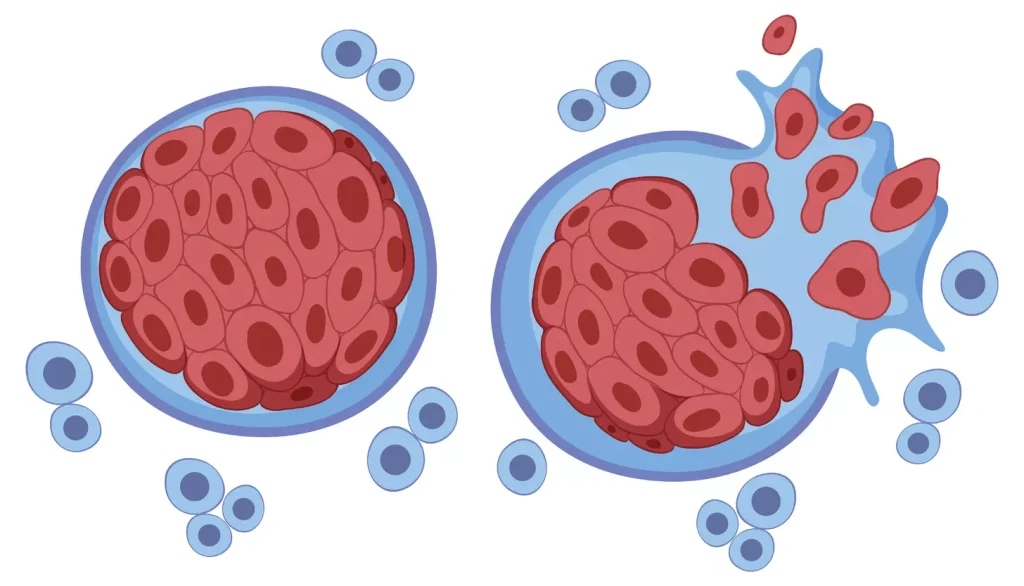
The main differences are in how they grow, spread, and invade tissues. Benign tumors grow slowly, have clear edges, and don’t spread. On the other hand, malignant tumors grow fast, have irregular edges, and can spread to other parts of the body.
Here’s a table to show these differences:
| Characteristics | Benign Tumors | Malignant Tumors |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Pattern | Slow, expansive | Rapid, infiltrative |
| Tissue Invasion | Typically do not invade surrounding tissues | Infiltrate surrounding tissues |
| Metastatic Potentia | No metastatic potentia | Capable of metastasizing |
Why These Differences Matter Clinically
The differences between benign and malignant tumors are key for treatment. Accurate diagnosis is vital to pick the right treatment. Benign tumors might need little to no treatment, while malignant ones require strong treatments like surgery, chemo, and radiation.
It’s vital for doctors to understand these differences to plan effective treatments. Patients also need to know their treatment options and what to expect.
Difference #1: Cellular Composition and Growth Patterns
The main difference between benign and malignant tumors starts at the cell level. These differences help doctors diagnose and treat tumors correctly.
Benign Tumor Cell Characteristics
Benign tumors have cells that look like normal cells. These cells grow slowly and don’t invade other tissues. They are often found in a sac, making them less dangerous.
Key characteristics of benign tumor cells include:
- Well-differentiated cell morphology
- Slow growth rate
- Non-invasive behavior
- Often encapsulated
Malignant Tumor Cell Abnormalities
Malignant tumors have cells that look very different from normal cells. These cells grow fast and invade other tissues. This can damage the normal tissue structure.
| Cellular Feature | Benign Tumor Cells | Malignant Tumor Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Differentiation | Well-differentiated | Poorly differentiated |
| Growth Rate | Slow | Rapid |
| Invasiveness | Non-invasive | Invasive |
Understanding the cell differences between benign and malignant tumors is key. Doctors use these differences to decide how to treat tumors.
Difference #2: Growth Rate and Behavior
Tumors grow at different rates, affecting treatment choices. Knowing these differences helps doctors pick the best treatment and predict how well a patient will do.
Slow vs. Rapid Proliferation
Benign tumors grow slowly, staying small or growing very little over time. Malignant tumors, on the other hand, grow fast, getting bigger quickly. This fast growth is a sign of cancer and makes malignant tumors more aggressive.
Benign tumors have lower cell division rates and don’t spread to nearby tissues. Malignant tumors divide cells more often and spread aggressively. This is why malignant tumors are more dangerous.
Predictable vs. Unpredictable Development
Benign tumors grow in a way that doctors can predict. Malignant tumors, though, grow in unpredictable ways. This makes it hard for doctors to know how they will behave or react to treatment.
This unpredictability is a big worry in cancer treatment. Doctors need to watch patients closely and change treatment plans as needed. This is because malignant tumors can change quickly.
Difference #3: Borders and Tissue Invasion
Tumor borders and tissue invasion are key factors that differentiate benign tumors from their malignant counterparts. The nature of a tumor’s borders and its ability or inability to invade surrounding tissues are critical in determining its benignity or malignancy.
Well-Defined vs. Irregular Margins
Benign tumors typically have well-defined margins, making them distinct from the surrounding tissue. This clear demarcation is a hallmark of benign tumors and aids in their diagnosis. In contrast, malignant tumors often exhibit irregular margins, blending into the surrounding tissue in a less predictable manner. This irregularity can complicate surgical removal and is a sign of the tumor’s aggressive nature.
Encapsulation vs. Infiltration
Another significant difference lies in the concepts of encapsulation and infiltration. Benign tumors are often encapsulated, meaning they are surrounded by a fibrous capsule that separates them from adjacent tissues. This encapsulation facilitates surgical removal and generally indicates a more favorable prognosis. On the other hand, malignant tumors tend to infiltrate surrounding tissues, making their boundaries difficult to define and their removal more challenging. The infiltrative nature of malignant tumors contributes to their local destruction and metastasis.
Understanding these differences is critical for both diagnosis and treatment planning. The characteristics of a tumor’s borders and its invasive nature provide valuable insights into its nature. These insights guide clinical decision-making.
Difference #4: Metastatic Potentia
It’s key to know how tumors spread to understand the difference between benign and malignant growths. Cancer cells spreading to other parts of the body is a sign of malignant tumors.
Benign tumors, though, can’t spread. This is because they have different traits than cancer cells.
Why Benign Tumors Remain Localized
Benign tumors stay in one place because they are not invasive. They can’t break through blood vessels or spread to other tissues.
The cells in benign tumors act like normal cells. They don’t have the changes needed to spread cancer.
“The inability of benign tumors to metastasize is a key factor in their benign nature, as it prevents them from spreading to other parts of the body and causing widespread harm.”
Mechanisms of Malignant Spread
Malignant tumors can spread in different ways. They often go through the lymphatic system or the bloodstream.
Going through the lymphatic system means cancer cells get into nearby lymph nodes. Going through the bloodstream means they travel to other parts of the body.
| Metastasis Route | Description | Common Sites |
|---|---|---|
| Lymphatic Spread | Cancer cells invade nearby lymph nodes | Lymph nodes, regional nodes |
| Hematogenous Spread | Cancer cells enter the bloodstream | Liver, lungs, bones, brain |
Metastasis is a complex process. It involves several steps like invasion and spreading through the bloodstream. Each step needs specific changes in the cells to happen.
Knowing how tumors spread is vital for treating cancer. Doctors can then plan treatments that fit the tumor’s specific needs.
Difference #5: Diagnostic Approaches and Challenges
Accurate tumor diagnosis is key for good treatment. But, it’s not easy. We use many ways to tell if a tumor is benign or malignant. Each method has its own good points and bad points.
Imaging Techniques and Their Limitations
Tools like MRI and CT scans are very important for finding tumors. They show us where the tumor is and how big it is. But, they’re not perfect. Sometimes, they can’t tell if a tumor is benign or malignant just by looking at it.
Limitations of Imaging Techniques:
- It’s hard to tell if a tumor is benign or malignant just by looking at it.
- They can’t always find tiny spread of cancer.
- People can interpret images differently.
A top oncologist said, “Imaging is very helpful, but it can’t replace looking at tissue under a microscope.”
“The diagnosis of cancer is a complex process that involves clinical evaluation, imaging, and histopathology. No single test can provide all the answers.” –
The Critical Role of Biopsy
Biopsy is the most reliable way to diagnose tumors. It involves looking at a tissue sample under a microscope. This helps us know if a tumor is benign or malignant.
The biopsy process is very careful. It involves taking a sample and then examining it. It helps us decide on treatment and gives us information about how likely the tumor is to spread. But, biopsy has its own problems, like mistakes in sampling and needing skilled pathologists.
We know that even with better diagnostic tools, there are always challenges. By using imaging, biopsy, and other tools together, we can get more accurate diagnoses. This helps us give the best care to patients with tumors.
Difference #6: Treatment Strategies and Modalities
It’s important to know the difference between benign and malignant tumors to choose the right treatment. The type of tumor affects the treatment options. These can range from simple management to more complex treatments.
Benign Tumor Management Options
Benign tumors usually need a gentle approach. Monitoring is often used, with regular check-ups and scans to watch the tumor. Sometimes, surgical removal is needed if the tumor is causing problems.
Other options for managing benign tumors include:
- Watchful waiting: Just keeping an eye on it without acting right away.
- Minimally invasive procedures: Like radiofrequency ablation for some benign tumors.
- Hormonal therapy: For tumors that react to hormones.
Malignant Tumor Treatment Approaches
Malignant tumors, being cancerous, need more aggressive treatments. The goal is to get rid of the cancer while keeping as much healthy tissue as possible.
Common treatments for malignant tumors are:
- Surgery: To take out the tumor and affected areas.
- Chemotherapy: Drugs to kill cancer cells.
- Radiation therapy: High-energy rays to target cancer cells.
- Targeted therapy: Focusing on specific molecules in cancer growth.
- Immunotherapy: Boosting the body’s immune fight against cancer.
The treatment for malignant tumors depends on the cancer type, stage, and the patient’s health. A team of doctors works together to create a treatment plan just for the patient.
In summary, the treatment for benign and malignant tumors is very different. Knowing these differences helps doctors give the best care.
Difference #7: Recurrence Risk and Long-term Monitoring
The risk of recurrence is different for benign and malignant tumors. This means we need different follow-up plans. Knowing these differences is key for managing these conditions over time.
Follow-up Protocols for Benign Conditions
Benign tumors usually don’t come back as often as malignant ones. But, the follow-up plans for benign tumors can change based on the tumor’s type, size, and where it is.
- Observation: Many benign tumors are watched closely, with regular check-ups and imaging to see if they change.
- Surgical Removal: Some benign tumors need to be removed surgically. After this, follow-ups are needed to watch for any signs of coming back, but the risk is usually low.
A medical expert says, “The main thing for managing benign tumors is to keep watching them over time to make sure they don’t cause problems.”
“Even for benign conditions, regular follow-ups are key to catch any issues early.”
| Tumor Type | Follow-up Frequency | Duration of Follow-up |
|---|---|---|
| Benign Lipoma | Annual | 5 years |
| Benign Adenoma | Bi-annual | 3-5 years |
Surveillance Strategies for Malignant Disease
Malignant tumors need more careful watching because they have a higher chance of coming back. The follow-up plans are made based on the cancer type, how advanced it is, and the treatments used.
Surveillance Strategies:
- Regular Imaging: CT scans, MRI, and PET scans are used to watch for any signs of coming back.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests and tumor markers help find recurrence early.
- Clinical Examination: Regular check-ups by doctors are important for catching signs of recurrence.
We stress that finding recurrence early is very important for patients with malignant tumors.
Good long-term monitoring needs a team effort. This includes oncologists, radiologists, and primary care doctors to give the best care.
Difference #8: Transformation Potencial
It’s important to know if benign tumors can turn into cancer. Benign tumors are usually not dangerous. But sometimes, they can become cancerous, which is very serious.
Many people wonder if benign tumors can become cancer. The answer depends on the tumor’s type and any conditions that might make it turn cancerous.
Can Benign Tumors Become Malignant?
Studies show that some benign tumors can turn into cancer, but it’s rare. This change is not fully understood. It’s thought to be caused by genetics and the environment.
Experts say that turning a benign tumor into cancer involves many genetic changes. Can a doctor tell if a tumor is cancerous just by looking at it? This shows how hard it is to diagnose tumors.
High-Risk Benign Conditions
Some benign conditions are more likely to turn into cancer. These include:
- Benign tumors with unusual cells
- Tumors in certain places, like the colon or breast
- Conditions that often turn into cancer, like some adenomas
Spotting these high-risk conditions early is key. It helps prevent cancer from developing. Regular check-ups are important for these patients.
Early detection and management of potentially malignant transformations can significantly improve patient outcomes. Knowing about the risks of benign tumors helps doctors give better care.
In summary, while rare, benign tumors turning into cancer is a big concern. More research and careful monitoring are needed to tackle this issue.
When to Seek Medical Attention: Warning Signs and Symptoms
Knowing when to see a doctor is key to treating tumors. It’s important to know the signs of both benign and malignant tumors. This helps in getting timely treatment.
Universal Red Flags for Any Tumor
Some symptoms can mean you have a tumor, whether it’s benign or malignant. These include:
- Unexplained Changes: Unexplained weight loss, changes in appetite, or persistent fatigue.
- Pain: Persistent pain that doesn’t improve with rest or treatment.
- Visible Changes: Noticeable lumps, swelling, or changes in the size or shape of a body part.
- Skin Changes: Changes in skin color, texture, or the appearance of sores that don’t heal.
A medical expert says, “Early detection of tumors significantly improves treatment outcomes.”
“The key to managing tumors effectively lies in recognizing the warning signs early and seeking medical evaluation promptly.”
Symptoms Suggesting Malignancy
Some symptoms can be from benign conditions, but others might mean cancer. These include:
| Symptom | Possible Indication |
|---|---|
| Unexplained Weight Loss | Potential malignancy, specially if loss of appetite is also present |
| Persistent Pain | Could indicate tumor growth or spread |
| Changes in Bowel or Bladder Habits | May suggest tumor presence in or near these organs |
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s vital to see a doctor. Early diagnosis can make a significant difference in treatment outcomes.
We stress the importance of watching your health and getting medical help for unusual or persistent symptoms. Getting checked early can lead to better treatment.
Conclusion: The Critical Importance of Accurate Diagnosis
Getting a correct diagnosis is key to managing tumors well. It helps decide the right treatment and affects how well a patient does. Knowing the difference between cancer and a benign tumor is vital for doctors to plan the best treatment.
At Liv Hospital, we focus a lot on making accurate diagnoses. We use the latest diagnostic methods to ensure our patients get top-notch care. This means they get the right treatment for their specific health issue.
Accurate diagnosis has big benefits. It lets doctors predict how a disease will progress and spot any possible problems early. This helps them create effective treatment plans. As a result, patients get better care and live better lives.
In short, accurate diagnosis is essential in tumor management. By using advanced diagnostic tools and understanding the difference between benign and malignant tumors, we can offer the best care. This leads to better health outcomes for our patients.
What is the main difference between benign and malignant tumors?
Benign tumors grow slowly and don’t spread. They stay in one place. Malignant tumors grow fast, spread, and can go to other parts of the body.
How are benign and malignant tumors diagnosed?
Doctors use scans like ultrasound and CT scans to find tumors. They also do biopsies to check the cells. A biopsy is the best way to tell if a tumor is benign or malignant.
Can benign tumors become malignant?
Yes, some benign tumors can turn into cancer. But this is rare. Doctors watch these tumors closely.
What are the treatment options for benign and malignant tumors?
Benign tumors might need watching or surgery if they bother you. Malignant tumors get treatments like surgery, chemo, and radiation. The treatment depends on the cancer type and stage.
How do growth rates differ between benign and malignant tumors?
Benign tumors grow slowly. Malignant tumors grow fast. Their fast growth is a key difference.
What is metastasis, and how does it relate to benign and malignant tumors?
Metastasis is when cancer cells spread. Benign tumors don’t spread. Malignant tumors can spread, which is a cancer sign.
Why is it important to tell benign from malignant tumors?
Knowing the type of tumor is key for treatment. Malignant tumors need strong treatment to stop spreading. Benign tumors might just need watching or simple surgery.
What are the warning signs that may indicate a tumor is malignant?
Look out for unexplained weight loss, pain, skin changes, unusual bleeding, and trouble swallowing or breathing. These signs mean you should see a doctor right away.
How often should benign tumors be monitored?
How often depends on the tumor type, size, and where it is. Also, your health matters. Benign tumors are checked often to make sure they don’t grow or cause problems.
What is the role of follow-up protocols in managing both benign and malignant tumors?
Follow-up checks are key for watching both types of tumors. They help find any changes or if the tumor comes back. This helps doctors adjust treatment plans for the best results.