Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
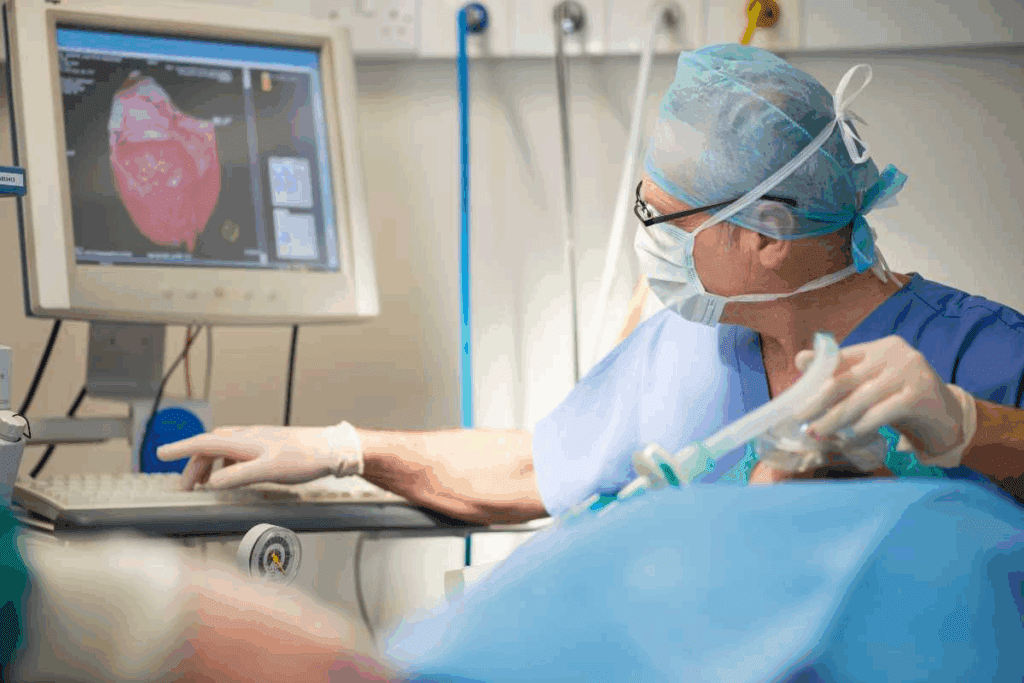
Did you know that heart diseases are a top cause of death globally? Open heart surgery is a key treatment for many cardiac conditions.
Traditionally, heart surgery meant opening the chest to reach the heart. But, new tech has brought minimally invasive cardiac surgery options. These methods cut down on the need for big surgeries.
Now, we’re seeing a big move towards these new ways of treating the heart. Our top doctors are leading this change. They offer treatments that are gentler, reduce recovery time, and leave less scar.
Understanding heart surgery is key for those thinking about surgery for their heart. This complex field has grown a lot. It now treats many heart problems well.
Many heart issues need surgery to work right again. These include:
These issues show why heart surgery is so important. It helps patients live better lives with heart problems.
A cardiac surgical team is a group of experts working together. They include:
“The success of cardiac surgery depends not only on the skill of the surgeons but also on the coordinated effort of the entire surgical team.”
The teamwork of the cardiac surgical team is key. It helps patients do well, whether it’s a CABG or other surgeries.
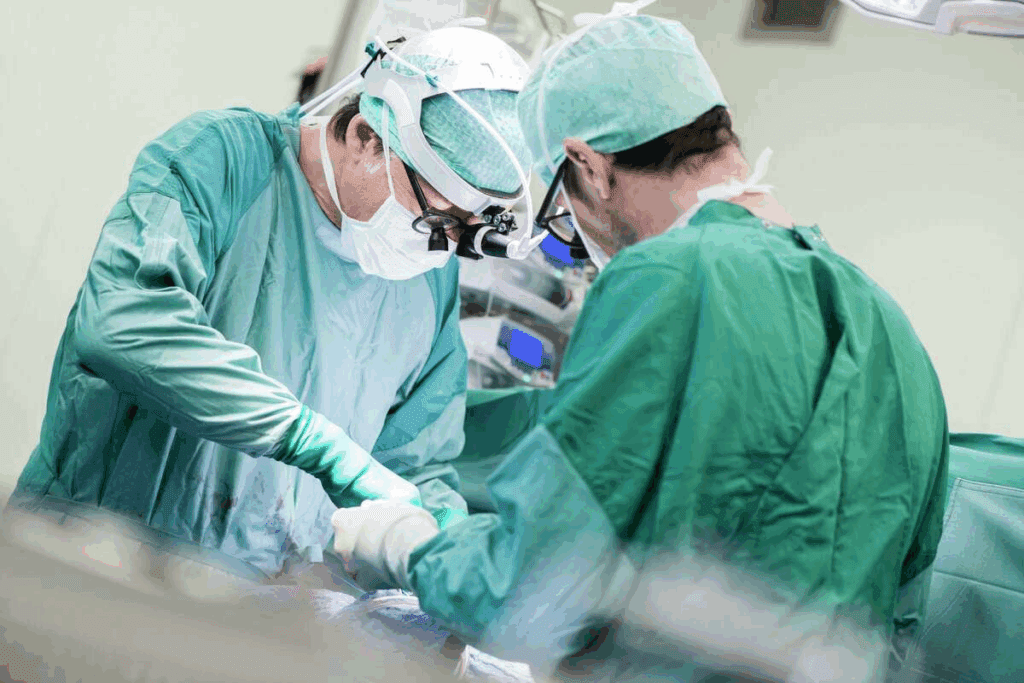
For many years, traditional open heart surgery has been a key part of heart care. It involves opening the chest to reach the heart. Surgeons then fix or replace damaged parts as needed.
The sternotomy approach is a main part of this surgery. It means cutting through the sternum, or breastbone, to get to the heart. The sternum is opened to show the heart, giving surgeons a clear view and direct access.
The sternotomy approach has many benefits:
The heart-lung bypass machine is a key tool in this surgery. It takes over for the heart and lungs, letting surgeons work on a stopped heart.
This machine does several important things:
Using the heart-lung bypass machine helps surgeons do detailed work safely. It makes the surgery more precise and safe.
Cardiac surgery has evolved a lot over time. It has been shaped by ongoing research and innovation. This field has seen big changes, all aimed at making treatments for heart diseases better and safer.
The history of cardiac surgery is filled with important milestones. One big step was the creation of the heart-lung bypass machine. This machine allowed for more complex surgeries. Later, minimally invasive heart surgery came along, making recovery times shorter and scarring less.
| Year | Milestone | Significance |
| 1953 | First successful open-heart surgery using a heart-lung bypass machine | Enabled complex cardiac procedures |
| 1990s | Introduction of minimally invasive cardiac surgery techniques | Reduced recovery times and scarring |
| 2000s | Advancements in robotic-assisted cardiac surgery | Enhanced precision and control |
Several factors have pushed for the development of minimally invasive heart surgery. Patients want procedures that are less invasive and have quicker recovery times. Also, new technology, like better imaging and surgical tools, has helped make these techniques possible.
The journey of cardiac surgical techniques is ongoing. With new research and technology, we can look forward to even better treatments. As cardiac surgery advancements keep coming, we’ll see better results for patients and more types of cardiac surgery available.
Minimally invasive heart surgery is changing how we treat heart conditions. It uses smaller cuts and special tools to cut down on pain and speed up healing. Understanding these new methods is key to improving heart surgery.
Minimally invasive cardiac surgery means using smaller cuts and special tools. This reduces damage to tissues and helps patients recover faster. The main ideas behind these methods are:
These ideas work together to make surgery less invasive and more comfortable for patients.
Using smaller cuts is a big part of minimally invasive heart surgery. It leads to less scarring and less pain after surgery. It also means patients can get back to their normal lives faster.
Special tools are also key. They help surgeons do complex surgeries through small openings.
Some of these tools include:
| Tool | Description | Benefit |
| Endoscopic cameras | Provide high-definition visualization of the surgical site | Enhanced precision and control |
| Robotic instruments | Offer precise manipulation of tissue with minimal invasion | Reduced trauma and improved outcomes |
| Specialized retractors | Allow for optimal exposure of the surgical site through small incisions | Improved access with minimal tissue damage |
By using smaller cuts and advanced tools, we can make heart surgery better. As technology gets better, we’ll see even more benefits for patients.
Minimally invasive heart surgeries have changed cardiac care a lot. They offer patients new ways to avoid traditional open-heart surgery. These new methods cut down on surgical damage, reduce scars, and help patients heal faster. Let’s look at three key types of minimally invasive heart surgeries that have changed how we do cardiac surgery.
MIDCAB lets surgeons do coronary artery bypass grafting without stopping the heart or using a heart-lung machine. They make small cuts between the ribs to reach the heart. The main benefit of MIDCAB is it lowers the risk of problems from using a heart-lung machine. It’s good for patients needing surgery on the front or sides of the heart.
TECAB uses endoscopic methods for a more advanced minimally invasive surgery. It’s done through small openings, with the surgeon watching on a screen. Endoscopic tools and a robotic camera give a clear view, making the surgery more precise. TECAB can be done on a beating heart or with a heart-lung machine, based on the patient’s needs.
Robot-assisted heart surgery is the latest in minimally invasive cardiac surgery. It combines advanced robotic tech with a surgeon’s skill. The robotic system lets the surgeon control tiny instruments inside the chest. It offers high-definition 3D vision and precise tools for complex surgeries through small cuts. Robot-assisted surgery is used for many heart procedures, like fixing the mitral valve or closing holes in the heart.
Each of these minimally invasive heart surgery methods has its own benefits. They meet different patient needs. As technology gets better, we’ll see even more options for heart surgery patients.
Transcatheter heart procedures are changing cardiac care. They offer patients new, less invasive ways to treat heart conditions. This is a big step forward, making treatments for heart valves better.
Cardiology is seeing big changes with these new procedures. They let doctors treat heart issues without opening the chest. This means less time in the hospital and fewer risks for patients.
TAVR is a new way to treat aortic stenosis. It’s when the aortic valve gets too narrow. A new valve is put in through a leg artery, avoiding open-heart surgery.
The good things about TAVR are:
Transcatheter mitral valve repair or replacement is also becoming more common. It helps with mitral regurgitation, where the mitral valve leaks. This is done with a catheter, avoiding a chest incision.
Like TAVR, it uses a catheter for treatment. The exact method depends on the patient’s needs and the device used.
Here’s a comparison of traditional surgery and these new procedures:
| Aspect | Traditional Open-Heart Surgery | Transcatheter Procedures |
| Incision | Large chest incision | Small incision in the leg or arm |
| Recovery Time | Several weeks to months | Significantly reduced, often a few days to weeks |
| Risks | Higher risk of complications | Lower risk, but not without possible complications |
| Hospital Stay | Typically longer | Often shorter, sometimes outpatient |
In conclusion, procedures like TAVR and transcatheter mitral valve repair are changing cardiac care. They offer new, less invasive options. This improves patient outcomes and quality of life.
Percutaneous coronary interventions have changed how we treat coronary artery disease. They offer a less invasive option compared to traditional surgery. These methods help patients recover faster and face fewer risks than open-heart surgery.
Angioplasty and stenting are key in treating coronary artery disease. Angioplasty uses a balloon to open blocked arteries. Stenting places a mesh-like device to keep the artery open.
These steps are vital for improving blood flow to the heart. They help reduce symptoms like angina and enhance patients’ quality of life.
Drug-eluting stents have made stenting even better. These stents release medication to prevent the artery from narrowing again. This greatly improves long-term results for patients.
“The introduction of drug-eluting stents has been a game-changer in the field of interventional cardiology, providing patients with a more durable solution for coronary artery disease.”
New technology has brought advanced techniques to coronary interventions. Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) and optical coherence tomography (OCT) give detailed views of the arteries. This helps place stents more accurately and improves results.
| Technique | Description | Benefits |
| IVUS | Intravascular ultrasound provides detailed images of the coronary arteries. | Enhanced stent placement accuracy, improved outcomes. |
| OCT | Optical coherence tomography offers high-resolution imaging of coronary arteries. | Detailed assessment of stent apposition and artery wall. |
These advanced methods, along with skilled interventional cardiologists, have greatly enhanced treatment for coronary artery disease. They offer patients more effective and less invasive options.
Recovering from open heart surgery takes time and involves several stages. These stages include immediate care after surgery, the first few weeks of healing, and long-term rehabilitation. Knowing what to expect helps patients manage their recovery better and get the best results.
Right after surgery, patients go to the ICU for close watch. Immediate post-operative care focuses on managing pain and checking for any complications. It also ensures the patient’s vital functions are supported.
The ICU team keeps a close eye on the heart function, blood pressure, and other important signs. Patients may have monitors, tubes, and lines for their care.
After leaving the ICU, patients move to a step-down unit or a regular room. The first weeks of recovery are key for healing and getting stronger. They start with simple movements and gradually do more.
Patients and their caregivers get tips on wound care, managing medications, and watching for complications. The open heart surgery recovery time varies, but most leave the hospital in a week or two.
Rehabilitation after heart surgery is a long journey. It includes making lifestyle changes, physical therapy, and ongoing medical care. Patients are told to eat heart-healthy, stay active, and keep up with doctor’s visits.
Cardiac rehab programs help patients recover. They offer a place for exercise, learning, and support. These programs are customized to meet each patient’s needs and can greatly improve recovery outcomes.
Traditional and minimally invasive heart surgeries have different recovery paths. The choice of surgery greatly affects how a patient recovers.
Minimally invasive heart surgery means shorter hospital stays. Patients usually leave the hospital in 3 to 5 days. Open-heart surgery patients stay longer, from 7 to 10 days.
Shorter hospital stays reduce infection risks. It also means patients can get back to their lives sooner.
Pain management differs between the two surgeries. Minimally invasive surgery causes less post-operative pain. This is because of smaller cuts and less damage to tissues. It means patients need less pain medicine, making recovery easier.
Recovery times vary between the two surgeries. Minimally invasive surgery patients get back to normal in 2-4 weeks. Traditional open-heart surgery patients take 6-12 weeks.
This quicker recovery is due to the less invasive nature of the procedure. It results in less tissue damage and trauma.
Minimally invasive heart surgery has changed cardiac care a lot. It brings many benefits to patients. With new medical tech, these benefits are getting clearer, making patients happier and healthier.
One big plus of this surgery is less damage to the body. It uses small cuts, which means less pain and quicker healing. It’s also safer, with fewer risks for patients.
There’s also a cosmetic plus. The small cuts mean less scarring. This is a big deal for people worried about how they’ll look after surgery.
This surgery makes life better for patients. They get to go home sooner and start doing things they love again. It’s a big win for their quality of life.
Let’s look at how it compares to old-school open-heart surgery:
| Aspect | Traditional Open-Heart Surgery | Minimally Invasive Heart Surgery |
| Hospital Stay | Typically 7-10 days | Often 3-5 days or less |
| Recovery Time | 6-12 weeks | 3-6 weeks |
| Pain Level | Higher due to larger incision | Lower due to smaller incisions |
| Scarring | More noticeable scarring | Less noticeable scarring |
The table shows the surgery’s benefits. It means shorter stays, quicker healing, less pain, and less scarring.
The move to less invasive heart surgery brings new risks and challenges. These methods offer benefits like quicker recovery and less pain. Yet, they also come with hurdles for both doctors and patients to face.
Minimally invasive heart surgery needs great skill and precision. Surgeons use small incisions and special tools, which can be tricky to handle. This makes learning and mastering these techniques harder.
Some key challenges include:
A top cardiac surgeon, says, “The technical demands of minimally invasive heart surgery are significant, but the benefits to patients make it a worthwhile challenge.”
“The future of cardiac surgery lies in our ability to balance technological innovation with surgical expertise.”
Even with new techniques, some cases need traditional open heart surgery. This is true for complex procedures, reoperations, and cases with multiple valve repairs or complex coronary artery disease.
| Condition | Preferred Surgical Approach |
| Complex coronary artery disease | Traditional open heart surgery |
| Multiple valve repairs | Traditional open heart surgery |
| Reoperations | Traditional open heart surgery |
It’s key for patients to know that not everyone is a good fit for minimally invasive surgery. A detailed check-up with a cardiac surgeon is needed to decide the best surgery.
We think it’s vital to understand the risks and limits of new heart surgery methods. By looking at the pros and cons, patients and doctors can pick the best treatment together.
Choosing minimally invasive heart surgery depends on many factors. We look at each patient’s unique situation to find the best surgery.
We consider several things when picking patients for minimally invasive heart surgery. These include the heart condition’s type and severity, the patient’s health, and past treatments or surgeries.
Key factors in patient selection include:
| Medical Criteria | Description | Importance in Patient Selection |
| Type of Heart Condition | The specific cardiac issue, such as coronary artery disease or valve dysfunction | High |
| Overall Health Status | The patient’s general health, including the presence of comorbidities | High |
| Previous Surgeries | Any previous cardiac or thoracic surgeries | Medium |
| Age and Physical Condition | The patient’s age and physical fitness level | Medium |
The consultation process is key in deciding if a patient is right for minimally invasive heart surgery. We do a detailed check, talk about their medical history, and explain the risks and benefits.
A thorough consultation includes:
By carefully looking at these factors and having a detailed consultation, we can find the best treatment for each patient. This ensures the best results for those having minimally invasive heart surgery.
Heart surgery is on the verge of a big change, thanks to new technologies. We’re exploring new ways to care for the heart, making treatments better and more precise.
New methods are making heart surgery less invasive. Minimally invasive techniques cut down on recovery time and boost results. These steps are making surgery safer and available to more people.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is also changing heart surgery. AI looks at lots of data to help surgeons make better choices. This could make surgeries safer and more accurate.
Robotics are playing a bigger role in heart surgery. Robots help surgeons do complex tasks with better control. They use special tools that let surgeons work with great detail.
AI and robotics working together could bring even more progress. For example, AI could help robots by analyzing data and predicting outcomes. This could change how we do heart surgeries.
Looking ahead, these technologies will keep improving heart surgery. They offer new hopes and chances for patients all over the world.
Heart surgery has changed a lot, giving patients many choices. From open heart surgery to new, less invasive methods, it’s important to know what’s available. This knowledge helps patients make smart choices about their heart surgery.
People facing heart surgery should understand the good and bad of each option. Thinking about how long it takes to recover, the impact on the body, and how it looks afterward is key. This way, they can choose what’s best for them, considering both their health and personal wishes.
The success of heart surgery depends on teamwork. Patients, doctors, and surgeons working together is essential. With the latest in cardiac surgery, we can find the best treatment for each person. This teamwork helps patients make the right choice for their heart surgery.
Open heart surgery needs a big cut in the chest to reach the heart. Minimally invasive surgery uses small cuts and tools to avoid big damage and help you heal faster.
CABG is a surgery to fix blocked or narrow heart arteries. It uses a graft to improve blood flow. It can be done with big cuts or small ones.
Open heart surgery can last from 3 to 6 hours. It depends on how complex the surgery is. Minimally invasive surgeries might be shorter.
The heart-lung bypass machine takes over the heart and lungs’ jobs. It lets surgeons work on a stopped heart. It’s key for many surgeries, including open heart ones.
Minimally invasive surgery has many benefits. It causes less pain, has shorter hospital stays, and lets you get back to life faster. It also leaves smaller scars.
Minimally invasive surgery has its own risks. It can be harder for surgeons and might not work for all cases. But it’s safer than open heart surgery for many.
TAVR is a small procedure to replace the aortic valve. It’s for people with severe valve problems who can’t have big surgery.
Recovery from open heart surgery varies. Patients usually stay in the hospital for days and recover at home for weeks or months. Minimally invasive surgeries recover faster.
Not all heart problems can be fixed with small surgery. It depends on the problem, your health, and the surgeon’s skills.
Heart surgery is getting better. New small techniques, robotic help, and AI are being explored. These aim to make treatments safer and less invasive.
To see if you’re right for small surgery, talk to a heart specialist. They’ll check your condition and medical history. Then, they’ll talk about your options with you.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!