Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir

At Liv Hospital, we know how important effective bowel cancer treatment is. Bowel cancer, including colon and colorectal cancer, needs a full care plan. Understanding its severity is key to better patient results.
Adjuvant cancer treatment is key in post-surgery care. It lowers the chance of cancer coming back and boosts survival rates in stages II and III. We will look at the top 10 adjuvant chemotherapy drugs changing bowel cancer treatment. Our goal is to offer the best care and put patients first.
Key Takeaways
- Adjuvant chemotherapy is critical for postoperative bowel cancer care.
- Top 10 drugs are highlighted for their effectiveness in treatment.
- Liv Hospital is committed to providing world-class cancer care.
- Improved survival rates and reduced recurrence risk are significant benefits.
- Personalized treatment plans are essential for patient care.
Understanding Adjuvant Chemotherapy for Bowel Cancer
Adjuvant chemotherapy is key in treating bowel cancer after surgery. It aims to get rid of any cancer cells left behind. This treatment lowers the chance of cancer coming back and helps patients do better.
The Role of Post-Surgical Treatment in Eliminating Microscopic Disease
After surgery, bowel cancer patients often get adjuvant chemotherapy. This targets tiny cancer cells that surgery might miss. It’s vital because it kills any cancer cells that could cause the cancer to come back.
The length of adjuvant chemotherapy varies. It can last from 3 to 6 months. This depends on the cancer’s stage and the patient’s health.
Key Benefits of Adjuvant Chemotherapy:
- Reduces the risk of cancer recurrence
- Targets microscopic disease that may remain after surgery
- Improves overall survival rates for bowel cancer patients
Balancing Efficacy and Toxicity in Treatment Planning
We aim to make adjuvant chemotherapy work well without causing too many side effects. We look at the patient’s age, health, and cancer type to pick the best treatment. This way, we get the most benefits with the least harm.
| Factors Considered | Impact on Treatment Planning |
|---|---|
| Patient Age and Health | Influences the choice of chemotherapy drugs and dosage |
| Cancer Stage and Characteristics | Determines the intensity and duration of adjuvant chemotherapy |
| Potential Side Effects | Guides the selection of supportive care measures |
We make a treatment plan that’s just right for each patient. This approach helps ensure they get the best care for their bowel cancer.
5-Fluorouracil (5-FU): The Foundation of Bowel Cancer Treatment
5-Fluorouracil, or 5-FU, has been key in treating bowel cancer for years. It’s a fluoropyrimidine, a vital part of many chemotherapy plans. We’ll look at how it works, how it’s given, and how it’s used with other drugs to boost its effect.
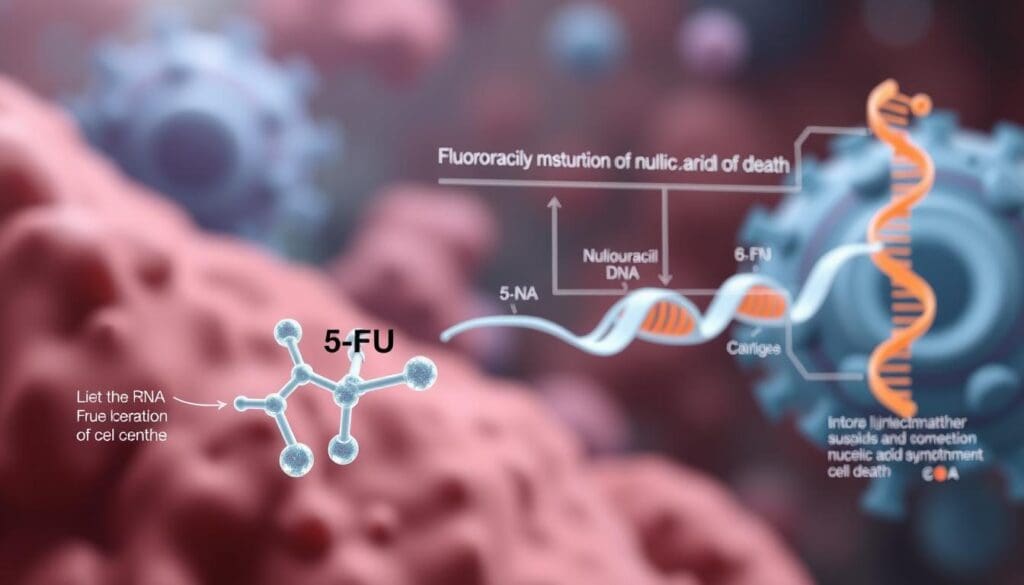
Mechanism of Action and Cell Cycle Interference
5-FU stops cancer cells from growing by messing with DNA making. It turns into 5-fluoro-2′-deoxyuridine monophosphate (FdUMP), which blocks thymidylate synthase. This block stops the making of thymidine, needed for DNA to copy itself. So, 5-FU stops cancer cells from growing fast. Its cell cycle interference is why it’s good against fast-growing tumors.
Administration Methods and Common Side Effects
5-FU can be given in different ways, like through an IV or orally as capecitabine. The choice depends on the treatment plan and the patient. Common side effects include:
- Mucositis
- Diarrhea
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fatigue
- Myelosuppression
These side effects are managed with supportive care and adjusting doses as needed.
Leucovorin Combination for Enhanced Efficacy
5-FU is often given with leucovorin (folinic acid) to make it work better. Leucovorin helps 5-FU’s effects by keeping FdUMP bound to thymidylate synthase. This combo has better response rates and survival for bowel cancer patients. The 5-FU and leucovorin combo is a key part of many chemotherapy plans.
Understanding 5-FU’s role in bowel cancer treatment helps us see its importance. It’s a foundational chemotherapy drug in managing bowel cancer.
Capecitabine (Xeloda): The Oral Alternative to 5-FU
Capecitabine (Xeloda) is a key oral chemotherapy for bowel cancer. It’s a handy alternative to getting shots. We’re here to talk about its benefits and how to manage it.
Conversion to 5-FU Within Tumor Cells
Capecitabine turns into 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) inside cancer cells. This makes the drug work better where it’s needed most. It also means less of the drug goes through the whole body.
The process of turning capecitabine into 5-FU involves several steps. These steps lead to 5-FU, which stops DNA from making new cells. This is how it fights cancer.
Convenience Benefits of Oral Administration
Capecitabine is easy to take by mouth. This makes it simpler for patients to manage their treatment.
This makes life easier for patients. They can keep up with their daily activities without trouble. It also lowers the chance of problems from getting shots, like infections.
Managing Hand-Foot Syndrome and Other Side Effects
Capecitabine has many good points, but it can cause side effects. Hand-foot syndrome (HFS) is a common one. It makes hands and feet red and sore.
| Side Effect | Management Strategy |
|---|---|
| Hand-Foot Syndrome | Moisturize hands and feet, avoid hot water, use gentle soaps |
| Nausea and Vomiting | Take medication with food, use antiemetic drugs as prescribed |
| Diarrhea | Stay hydrated, use antidiarrheal medications as directed |
It’s important to manage side effects well. This helps patients keep a good quality of life. We help patients find ways to lessen these effects and get the best results.
Oxaliplatin (Eloxatin): Platinum-Based Enhancement
Oxaliplatin is a key chemotherapy drug for bowel cancer. It’s used in combination to boost treatment success.
DNA Cross-Linking Mechanism
Oxaliplatin forms platinum-DNA adducts. These disrupt DNA replication and transcription. This DNA cross-linking mechanism kills cancer cells.
Its success in treating bowel cancer comes from killing tumor cells. Oxaliplatin damages DNA, starting a chain of events that kills cancer cells.
Peripheral Neuropathy: Prevention and Management
Oxaliplatin can cause peripheral neuropathy. This is numbness, tingling, and pain in hands and feet. We actively manage this side effect.
Prevention and management strategies include:
- Careful dose management to minimize toxicity
- Monitoring patients for early signs of neuropathy
- Implementing lifestyle changes to reduce symptoms
Cold Sensitivity Considerations During Treatment
Patients on oxaliplatin often feel cold sensitivity. This is discomfort or pain from cold. We guide patients on how to handle this.
To lessen cold sensitivity, patients should:
- Avoid cold drinks and foods
- Wear warm clothing in cold environments
- Use gloves when handling cold objects
Understanding oxaliplatin’s mechanisms and side effects helps us improve treatment. This enhances patient outcomes and quality of life.
Essential Adjuvant Chemotherapy Drugs in Combination Regimens
Combination chemotherapy regimens are a key tool in fighting bowel cancer. They use a mix of drugs to attack cancer cells more effectively. This approach helps lower the chance of cancer coming back and improves how patients do.
FOLFOX: 5-FU, Leucovorin, and Oxaliplatin Protocol
The FOLFOX regimen combines 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU), Leucovorin, and Oxaliplatin. 5-FU stops DNA synthesis in cancer cells. Leucovorin makes 5-FU work better. Oxaliplatin damages DNA in cancer cells, stopping them from growing.
Studies show FOLFOX boosts survival rates in stage III bowel cancer patients. But, managing side effects like Oxaliplatin-induced nerve damage is key.
CAPOX (XELOX): Capecitabine and Oxaliplatin Combination
CAPOX, or XELOX, pairs Capecitabine with Oxaliplatin. Capecitabine is an oral version of 5-FU, making treatment easier at home. Together, they target bowel cancer cells more effectively.
CAPOX is great for those who prefer oral meds over IV ones. But, it’s important to manage side effects like hand-foot syndrome.
FOLFIRI: 5-FU, Leucovorin, and Irinotecan Applications
FOLFIRI combines 5-FU, Leucovorin, and Irinotecan. Irinotecan stops DNA replication in cancer cells by blocking topoisomerase I. It’s used when Oxaliplatin treatments fail.
FOLFIRI is effective but has side effects like diarrhea and low white blood cell counts. Monitoring patients closely and providing supportive care is vital.
We customize these regimens based on patient needs, like tumor stage and health. Choosing between FOLFOX, CAPOX, and FOLFIRI depends on many factors, including past treatments and side effects.
| Regimen | Drugs Used | Key Benefits | Common Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| FOLFOX | 5-FU, Leucovorin, Oxaliplatin | Improved disease-free survival | Peripheral neuropathy |
| CAPOX (XELOX) | Capecitabine, Oxaliplatin | Convenience of oral medication | Hand-foot syndrome |
| FOLFIRI | 5-FU, Leucovorin, Irinotecan | Effective in Oxaliplatin-resistant cases | Diarrhea, neutropenia |
Understanding the different combination regimens helps us tailor treatments to each patient. This approach improves outcomes in bowel cancer care.
Irinotecan (Camptosar) and Trifluridine/Tipiracil (Lonsurf)
Irinotecan and Trifluridine/Tipiracil are key treatments for bowel cancer. They work in different ways. We’ll look at how they function, their side effects, and their place in treatment plans.
Topoisomerase Inhibition Mechanism of Irinotecan
Irinotecan blocks topoisomerase I, an enzyme cancer cells need to grow. This stops DNA replication, helping to fight cancer.
Key aspects of Irinotecan’s mechanism include:
- Inhibition of topoisomerase I enzyme
- Prevention of DNA replication in cancer cells
- Induction of apoptosis in tumor cells
Managing Cholinergic and Delayed Diarrhea
Irinotecan can cause diarrhea, split into early and late types. Early diarrhea is due to the drug’s effect on nerves. Late diarrhea is more severe.
Effective management strategies include:
- Atropine for cholinergic diarrhea
- Loperamide for delayed diarrhea
- Close monitoring of bowel movements
Trifluridine/Tipiracil: Role in Refractory Disease
Trifluridine/Tipiracil is for treating advanced colorectal cancer. It combines trifluridine, a nucleoside analog, with tipiracil to boost its effect.
Benefits of Trifluridine/Tipiracil include:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Anti-tumor activity | Effective against tumors resistant to other treatments |
| Improved survival | Shown to improve overall survival in refractory colorectal cancer |
| Manageable side effects | Common side effects include neutropenia, anemia, and fatigue |
As we move forward in treating bowel cancer, it’s vital to understand drugs like Irinotecan and Trifluridine/Tipiracil. Their unique benefits give patients more hope and options.
Targeted Biologics: Bevacizumab, Cetuximab, and Panitumumab
Targeted biologics like bevacizumab, cetuximab, and panitumumab are key in treating bowel cancer today. They aim at specific molecules that help cancer grow and spread. This makes them more precise than traditional chemotherapy.
These targeted therapies are changing how we treat bowel cancer. By understanding how these biologics work, we can see how they help patients. This knowledge is vital for better treatment outcomes.
Bevacizumab (Avastin): Targeting Tumor Blood Supply
Bevacizumab is a monoclonal antibody that targets VEGF. VEGF helps tumors grow by creating new blood vessels. By stopping VEGF, bevacizumab cuts off the tumor’s blood supply. This slows down tumor growth and spread.
Because of this, bevacizumab is a key part of chemotherapy for bowel cancer.
EGFR Inhibitors: RAS Mutation Testing Requirements
Cetuximab and panitumumab block the EGFR pathway, which can help tumors grow. But, they only work well if the RAS gene is not mutated. Testing for RAS mutations is essential before starting treatment with these drugs.
Integrating Biologics with Traditional Chemotherapy
Using targeted biologics with traditional chemotherapy is now standard for bowel cancer treatment. This approach attacks cancer from multiple angles, which can lead to better results and longer survival. We’re always learning how to mix these treatments for the best effect.
Personalizing Treatment: Factors Influencing Drug Selection
Choosing the right adjuvant chemotherapy drugs is key. Every patient’s battle with bowel cancer is different. So, treatment must fit their specific needs.
Several factors guide us in picking the best chemotherapy. These can be split into tumor characteristics and patient factors.
Tumor Stage and Risk Stratification
The tumor stage is very important. It helps us decide if and how strong the chemotherapy should be. Patients with higher-risk disease may need stronger treatments.
Molecular Subtypes and Biomarker Analysis
The molecular makeup of a tumor is also key. Biomarker analysis helps us find the right drugs. For example, KRAS mutation status can tell us if a patient will benefit from certain therapies.
Patient Factors: Age, Comorbidities, and Performance Status
Age, health conditions, and how well a patient can handle treatment are also important. We look at these to make sure the treatment is right for the patient. Older patients or those with serious health issues may need special treatment plans to avoid side effects and get the best results.
By looking at all these factors, we can tailor care to meet each patient’s needs. This way, we can offer personalized treatment for bowel cancer patients.
Conclusion: Advancing Bowel Cancer Care Through Optimized Adjuvant Therapy
Optimized adjuvant therapy is key in improving bowel cancer care. It helps increase survival rates for patients. Healthcare providers can make treatment plans better by knowing the different adjuvant therapy options.
We talked about how important it is to treat each patient differently. This includes looking at the tumor stage, molecular subtypes, and any health issues the patient might have. Adding targeted biologics to traditional chemotherapy has opened up new possibilities for treating bowel cancer.
As we keep working to improve cancer treatment, we must focus on giving top-notch healthcare. This includes supporting patients from all over the world. By doing this, we can make sure patients get the best care. This will help improve their outcomes and quality of life.
FAQ
What is adjuvant chemotherapy, and how does it help in bowel cancer treatment?
Adjuvant chemotherapy is a treatment given after surgery. It aims to kill any cancer cells left behind. This reduces the chance of cancer coming back. It helps improve survival rates and lower the risk of recurrence in stages II and III colon and colorectal cancers.
How do 5-FU and capecitabine work in bowel cancer treatment?
5-FU stops cancer cells from growing by blocking thymidylate synthase. Capecitabine turns into 5-FU in tumor cells. This makes it a convenient oral option with similar effects.
What are the common side effects of 5-FU, and how can they be managed?
Side effects of 5-FU include nausea, diarrhea, and fatigue. Leucovorin can make it work better and lessen some side effects. Managing these side effects often means adjusting the dose and using supportive care.
What is the role of oxaliplatin in bowel cancer treatment, and what are its side effects?
Oxaliplatin stops cancer cells from copying their DNA. This prevents them from growing. Its side effects include nerve damage and sensitivity to cold. These can be managed with careful dosing and precautions.
How are combination chemotherapy regimens like FOLFOX and CAPOX used in bowel cancer treatment?
Regimens like FOLFOX and CAPOX target cancer cells in different ways. This improves treatment results. The right regimen depends on the patient and their cancer.
What is the significance of RAS mutation testing in bowel cancer treatment?
Testing for RAS mutations is key to decide if EGFR inhibitors like cetuximab and panitumumab are right. Patients with RAS mutations don’t get much benefit from these drugs. So, testing is vital for making treatment plans that work.
How is adjuvant chemotherapy personalized for bowel cancer patients?
Personalizing treatment means looking at many factors. These include the cancer stage, molecular details (like RAS mutation status), and the patient’s health. Biomarkers help guide these decisions.
What are the benefits of integrating targeted biologics with traditional chemotherapy in bowel cancer treatment?
Adding targeted biologics like bevacizumab, cetuximab, and panitumumab to chemotherapy can make treatment better. They target specific parts of cancer cell biology, like blood supply or EGFR signaling.
How do patient factors influence the choice of adjuvant chemotherapy drugs?
When choosing chemotherapy, patient factors like age, health, and how well they can handle treatment are considered. This ensures the treatment is both effective and tolerable for the patient.
What is the role of irinotecan and trifluridine/tipiracil in bowel cancer treatment?
Irinotecan is used in treatments like FOLFIRI for bowel cancer. Trifluridine/tipiracil is for patients who have tried other treatments and failed. Both offer treatment options for those who need them.
References
PubMed Central (NCBI): Predictive Biomarkers for Response to Chemotherapy in Colorectal Cancer
Journal of Global Oncology (AME Groups): Perioperative Chemotherapy for Colorectal Cancer
PubMed Central (NCBI): Postoperative Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Colorectal Cancer
ASCO Publications (Journal of Clinical Oncology): Management of Stage III Colon Cancer in Young Adults
American Cancer Society (Cancer.org): Chemotherapy for Colon or Rectal Cancer