Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
Mastering radiation treatment planning is key to good cancer care. It needs a team effort from many experts. This includes radiation oncologists, medical physicists, and radiation therapists.
At LivHospital, we focus on giving radiation therapy to cancer cells. We also make sure healthy parts get less radiation. Our team works together to make each step of the planning process better for you.
Knowing how radiation treatment planning works helps doctors and nurses do better. It leads to better treatment outcomes and a better life for patients. We’ll show you the important steps and how they make care more precise and personal.
Key Takeaways
- Radiation treatment planning is a critical phase in cancer care.
- A multidisciplinary approach is necessary for effective radiation treatment planning.
- Precision and personalized care are key to the best results.
- LivHospital’s methods make radiotherapy planning fit each patient’s needs.
- Understanding the process helps improve the patient’s quality of life.
The Critical Role of Radiation Treatment Planning in Cancer Care
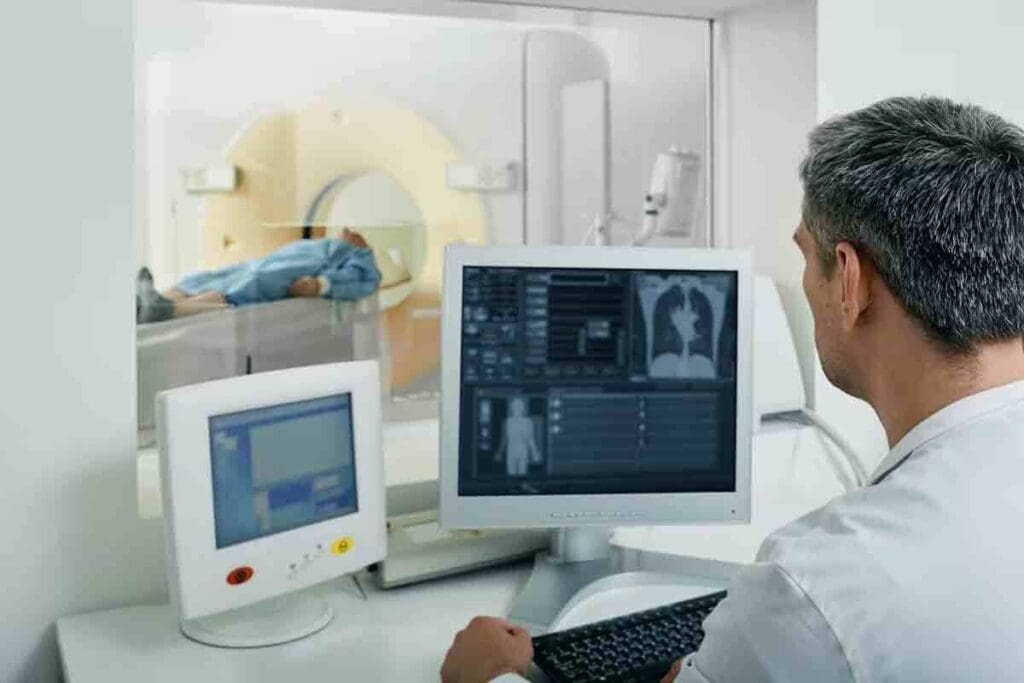
Effective cancer treatment relies on precise radiation planning. This complex process involves teamwork between radiation oncologists, medical physicists, and radiation therapists. We will see how this teamwork leads to successful treatment outcomes.
Definition and Purpose in Modern Oncology
Radiotherapy treatment planning is about making a custom plan for radiation therapy. Its main goal is to give the tumor the right amount of radiation. At the same time, it aims to protect healthy tissues around it.
We use advanced imaging and special software for this. This helps us deliver radiation more accurately.
Balancing Tumor Control and Normal Tissue Protection
Another key part of planning is balancing tumor control with protecting normal tissues. We carefully outline the tumor and healthy areas. Then, we adjust the radiation beams and doses.
This approach boosts treatment success while lowering side effect risks.
Impact on Treatment Outcomes and Patient Quality of Life
The quality of radiation planning affects treatment success and patient quality. Good planning means better tumor control, fewer side effects, and longer survival.
It also helps patients keep a good quality of life during and after treatment. This is because it reduces long-term complications and supports their overall health.
The Multidisciplinary Team Behind Successful RT Planning
Creating a successful radiation therapy treatment plan needs a team of experts. This team includes doctors, nurses, and other healthcare workers. They work together to make sure the treatment is safe and effective for the patient.
New technology in treatment planning software has made radiation therapy better. It supports advanced techniques like 3D conformal and VMAT. The team, including surgeons and oncologists, creates a treatment plan that fits the patient’s needs.
Radiation Oncologists: Clinical Decision Makers
Radiation oncologists decide how much radiation to use and how often. They look at the patient’s health and choose the best treatment. A study on PMC shows they are key in planning radiation therapy.
Medical Physicists: Technical Execution Specialists
Medical physicists handle the technical side of radiation therapy. They make sure the equipment works right and the plan is followed. Their skills are essential for safe treatment.
Radiation Therapists: Implementation Experts
Radiation therapists run the equipment and give the treatment. Their precision is important for the plan’s success.
Dosimetrists: Plan Optimization Professionals
Dosimetrists work on making the treatment plan better. They make sure the tumor gets the right dose and healthy areas are protected. Their work is key to good treatment results.
| Team Member | Role |
| Radiation Oncologist | Clinical decision-making, treatment strategy |
| Medical Physicist | Technical execution, equipment management |
| Radiation Therapist | Treatment delivery, equipment operation |
| Dosimetrist | Plan optimization, dose calculation |
Essential Technologies in Radiation Treatment Planning
Radiation treatment planning uses the latest technologies for precise care. In recent years, big changes have happened in cancer treatment.
Evolution of Treatment Planning Software
Treatment planning software has greatly improved. It now makes more detailed and accurate plans. It uses many images and algorithms to make sure treatments are just right.
This has helped make personalized treatment plans. Each plan is tailored to the patient’s unique needs.
Imaging Modalities: CT, MRI, PET Integration
Using CT, MRI, and PET scans together gives a full view of tumors and tissues. This method makes it easier to define the target volume and protect healthy areas.
Comparing 3D Conformal, IMRT, and VMAT Techniques
There are different radiation therapy methods like 3D conformal, IMRT, and VMAT. Each has its own strengths and is picked for the right reasons. For example, IMRT changes beam intensity, and VMAT delivers doses as it moves, making treatment better and faster.
These advanced technologies and methods improve radiation therapy results. They make treatments more effective and safe. The right choice depends on the patient’s situation and the treatment’s goals.
Step 1: Patient Assessment and Consultation
Understanding each patient’s needs is key in radiation treatment planning. This first step helps us tailor treatments to fit each person’s unique situation.
Initial Evaluation and Treatment Decision-Making
We start by looking at a patient’s medical history and current health. This helps us choose the best treatment. We talk about options with the patient, taking into account their health and cancer stage.
Treatment planning is about figuring out the right doses and treatment length. It’s a detailed process that considers many factors for the best results.
“The art of medicine is long, the craft of life is short, opportunity fleeting, experiment treacherous, judgment difficult.” – Hippocrates
Reviewing Patient History and Previous Treatments
Looking at a patient’s medical history and past treatments is important. It helps us understand their health and plan a treatment that works with their past care.
| Patient History Component | Relevance to Treatment Planning |
| Previous Cancer Treatments | Informs cumulative dose limits and possible interactions |
| Comorbidities | Affects how well they can handle radiation and our treatment plan |
| Medications | May change how radiation works or interacts with treatment |
Setting Treatment Goals and Expectations
Setting clear goals and expectations is vital. We work with patients to understand their needs and concerns. This helps us create a treatment plan that meets their medical needs and supports their well-being.
This way, we can make a treatment plan that’s right for each patient. It helps them during the treatment process.
Step 2: CT-Based Radiation Mapping and Simulation
The second step in mastering radiation treatment planning involves CT-based radiation mapping and simulation. This critical phase enables healthcare professionals to create a detailed map of the tumor and surrounding tissues. It’s essential for effective treatment planning in therapy.
The CT Simulation Process
CT simulation involves taking pictures of the treatment area using a special CT scanner. This process is key to defining target volumes and organs at risk. We use these images to outline the tumor and critical structures, helping the radiation oncologist create an optimal treatment plan.
The CT simulation process happens in a dedicated CT simulator suite. The patient lies on a flat table, and immobilization devices are used to keep them in the same position during scanning and treatments.
Custom Immobilization Devices for Precise Positioning
Custom immobilization devices are vital for precise positioning during radiation treatment. These devices are made for each patient, helping to reduce movement and ensure accurate radiation delivery to the target area.
Using immobilization devices helps lower the risk of radiation exposure to healthy tissues. It also improves the effectiveness of the radiation therapy, often abbreviated as RT.
Reference Marks and Alignment Systems
Reference marks and alignment systems are used for accurate patient positioning during treatment. These marks are made on the patient’s skin or immobilization device. They work with the radiation therapy equipment’s alignment lasers.
By setting up a consistent reference frame, we ensure the patient is positioned accurately and reproducibly for each treatment fraction. This is critical for the success of the treatment planning therapy.
Standardized Terminology and Definitions
Standardized terminology is key in radiation oncology for clear communication among healthcare professionals. We follow established definitions and terminology, like those from international organizations. This ensures consistency in treatment planning and delivery.
Using standardized terminology helps avoid errors. It ensures all treatment team members understand the patient’s treatment plan and goals.
Step 3: Target Volume Definition and Contouring
Defining the target volume is a key step in radiation treatment planning. It needs precision and expertise. We identify the gross tumor volume and expand it to the clinical target volume. We also consider the planning target volume and contour of organs at risk to avoid side effects.
Identifying Gross Tumor Volume (GTV)
The Gross Tumor Volume (GTV) is the visible tumor on imaging studies like CT, MRI, or PET scans. Accurate GTV identification is essential. We use advanced imaging to ensure a complete GTV identification.
Expanding to Clinical Target Volume (CTV)
The Clinical Target Volume (CTV) includes the GTV plus a margin for microscopic disease spread. This expansion is key to treating all tumor areas. The CTV is based on clinical experience and tumor behavior.
Planning Target Volume (PTV) Considerations
The Planning Target Volume (PTV) is an expansion of the CTV for treatment delivery uncertainties. It ensures the CTV gets the prescribed dose. We consider tumor location, patient immobilization, and image guidance when setting the PTV margin.
Contouring Organs at Risk (OARs)
Contouring Organs at Risk (OARs) is vital to reduce radiation to healthy tissues. We carefully outline OARs to optimize the treatment plan. This involves understanding tolerance doses and using dose-volume histogram analysis.
| Target Volume | Description | Considerations |
| GTV | Gross Tumor Volume: Visible extent of the tumor | Accurate imaging and delineation |
| CTV | Clinical Target Volume: GTV plus margin for microscopic disease | Clinical experience and tumor behavior |
| PTV | Planning Target Volume: CTV plus margin for treatment uncertainties | Patient movement, setup variations, image guidance |
By defining and contouring these volumes and OARs carefully, we create a precise radiation treatment plan. This plan effectively treats the tumor while protecting normal tissues. This step is vital in radiation treatment planning, affecting treatment outcomes and patient quality of life.
Step 4: Creating the Individualized Radiation Therapy Treatment Plan
We make treatment plans for each patient to get the best results. This includes using the latest technology and our team’s expertise. We tailor the treatment to fit each patient’s needs.
Dose Prescription and Fractionation Schemes
First, we figure out the dose and how it will be given. This depends on the cancer type, stage, and the patient’s health. The dose prescription is the total radiation for the tumor. The fractionation scheme is how this dose is spread out over time.
“The goal of radiation therapy is to deliver a precise dose of radiation to the tumor while minimizing exposure to surrounding healthy tissues.”
Beam Arrangement and Optimization Strategies
Choosing the right beam arrangement is key. We use advanced software to design the best beam setup. This ensures the tumor gets the right dose while protecting healthy areas. We pick the best beam angles, energies, and intensities for this.
| Beam Arrangement | Description | Benefits |
| 3D Conformal Radiation Therapy | Uses multiple beams shaped to match the tumor | Reduces dose to surrounding tissues |
| Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) | Modulates beam intensity to conform to the tumor shape | Enhances tumor control, reduces side effects |
| Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT) | Delivers radiation in a continuous arc around the patient | Improves treatment efficiency, reduces delivery time |
Plan Evaluation Using Dose-Volume Histograms
Dose-volume histograms (DVHs) help us check the treatment plan’s quality. DVHs show the dose in the tumor and nearby tissues. This lets us see if the plan is working well and make changes if needed.
Plan Iterations and Refinement Process
Creating a treatment plan is a back-and-forth process. We keep checking and improving the plan with DVHs and other tools. This ensures the plan is safe and effective for the patient.
By following this detailed process, we make treatment plans that really help patients. These plans are made just for each patient, aiming for the best results.
Step 5: Quality Assurance and Plan Verification
The success of radiation therapy depends on quality assurance and plan verification. It’s key to make sure the treatment plan is right and works well. This is important for the best results and keeping patients safe.
Physics Checks and Independent Calculations
Physics checks are a detailed review of the treatment plan by medical physicists. They check if it meets all the needed clinical and dosimetric criteria. Independent calculations are done to check the plan’s dose accuracy, adding extra safety.
Patient-Specific QA Measurements
QA measurements for each patient are vital to confirm the treatment plan’s delivery. These include phantom-based QA and other methods. They make sure the dose given is as planned.
Plan Approval Process and Documentation
The plan approval process involves a team reviewing and approving the treatment plan. Documentation of the plan, with all important details and approvals, is key. It keeps a clear record of the treatment.
Timeline Considerations in the Planning Process
Managing time well is essential in radiation treatment planning. It’s important to finish all steps, from simulation to verification, on time. This keeps the treatment effective and safe for patients.
In conclusion, quality assurance and plan verification are critical in radiation treatment planning. By having strict checks and balances, we can ensure our patients get the best care.
Step 6: Treatment Delivery and Monitoring
Getting the right treatment and keeping an eye on it is key to success. We make sure patients get the best treatment by checking their position every day. We adjust the plan if needed.
Daily Setup Verification with Image Guidance
We use image guidance to check if patients are in the right spot every day. This is important to make sure the radiation hits the right area. It helps avoid harming healthy tissues.
By checking the patient’s position daily, we can adjust the treatment as needed. This precision is vital for the best results.
Managing Treatment Adaptations
As treatment goes on, the patient’s body or tumor might change. We watch for these changes and update the treatment plan. This keeps the treatment effective.
Changing the treatment plan needs a team effort. Radiation oncologists, medical physicists, and therapists work together. They make the best decisions for the patient.
Tracking Treatment Response and Side Effects
It’s important to watch how the patient is doing and handle any side effects. We check on the patient regularly. We address any issues that come up.
By keeping an eye on how the patient is doing, we can make smart choices about the treatment. This ensures the patient gets the best care.
Adaptive Planning Considerations
Adaptive planning means updating the treatment plan based on changes. We look at things like tumor shrinkage or weight loss. These changes help us decide if we need to adjust the plan.
Adaptive planning helps keep the treatment effective and focused. It’s important as the patient’s condition changes.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art and Science of Radiation Treatment Planning
Learning how to plan radiation treatments is a big job. It needs a team effort, a dedication to learning, and a focus on making things better. By knowing how to plan treatments, doctors can make sure patients get the best care possible.
Good radiation treatment planning means looking at many things. This includes making sure the tumor is treated correctly and keeping healthy tissues safe. A team of experts works together to make a plan that’s just right for each patient. Keeping up with new technologies and methods helps doctors give their patients the best care.
As radiation oncology grows, it’s key to keep learning and improving how we plan treatments. This way, we can keep making treatments better and improve patients’ lives. It’s all about making a big difference for those fighting cancer.
FAQ
What is radiation treatment planning?
Radiation treatment planning is a detailed process. It defines the target area and sets up beam arrangements. The goal is to create a treatment plan that is precise and effective for cancer patients.
What is the role of a multidisciplinary team in radiation treatment planning?
A team of experts works together in this process. They include radiation oncologists, medical physicists, and others. Their goal is to make a treatment plan that is both safe and effective for each patient.
What technologies are used in radiation treatment planning?
Advanced software and imaging tools like CT and MRI are used. Techniques like 3D conformal and VMAT also play a role. These help in planning complex treatments.
What is the importance of patient assessment and consultation in radiation treatment planning?
Understanding each patient’s needs is key. This allows for a treatment plan that meets their specific needs. It’s a critical step in personalized care.
How is the target volume defined in radiation treatment planning?
The target area is identified and expanded. This includes the gross tumor volume and the clinical target volume. Organs at risk are also considered to minimize side effects.
What is the process of creating an individualized radiation therapy treatment plan?
The process involves several steps. It includes setting the dose and fractionation, arranging beams, and evaluating the plan. The goal is to ensure the plan is effective and well-planned.
Why is quality assurance and plan verification important in radiation treatment planning?
These steps ensure the plan is accurate and delivered correctly. They also make sure everyone involved agrees on the plan.
How is treatment delivery and monitoring managed in radiation treatment planning?
Daily setup verification and image guidance are used. Treatment adaptations and response tracking are also managed. This ensures the plan stays effective throughout the treatment.
What is the significance of mastering radiation treatment planning in cancer care?
Mastering this process is vital for better treatment outcomes. It requires teamwork, ongoing learning, and a focus on quality. This improves patient care and quality of life.
References
- Kim, A., et al. (2023). A Two-Step Treatment Planning Strategy Incorporating Semi-Automated Optimization for Enhanced Quality and Efficiency. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics, 24(2), e13721. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10243331/