Last Updated on November 25, 2025 by
Imaging is key in diagnosing urinary tract issues. We use advanced CT scans for accurate diagnoses. CT urogram and CT scans with or without contrast are two main types. They differ in how they approach and use the urinary tract.
A CT urogram focuses on the urinary system. It uses contrast media to show the kidneys, ureters, and bladder clearly. On the other hand, standard CT scans can be done with or without contrast, based on what’s needed.
Knowing the differences between these scans is vital for the best care and results. We’ll look into their unique uses and how well they work for urinary tract checks.
CT imaging techniques are key in today’s healthcare. They help doctors see inside the body in great detail. We use CT scans to find many health issues, from simple injuries to complex diseases.
A CT scan uses X-rays to make detailed pictures of the body. This tech lets us see inside the body clearly, which is vital for correct diagnosis and treatment. The X-ray tube moves around the body, taking pictures from different angles.
Then, these images are put together to make detailed cross-sections of the body.
Contrast media makes certain parts of the body stand out during a CT scan. It helps doctors see blood vessels, tumors, or other important areas. This makes diagnosing easier.
We use contrast media in many CT scans, like CT urograms. These scans help us see the urinary tract and find problems in it.
How we use contrast media depends on the scan. For example, in a CT urogram with contrast, we give it through an IV. Then, we take pictures at different times to see how the urinary tract works and looks.
The CT urogram is a big step forward in medical imaging, focusing on the urinary system. It uses a special CT scan to look at the kidneys, ureters, and bladder in detail.
A CT urogram is a special CT scan for the urinary tract. It aims to show the urinary system’s details clearly. This helps us spot problems like kidney stones, tumors, and structural issues. Contrast media makes these parts stand out, helping us make accurate diagnoses.
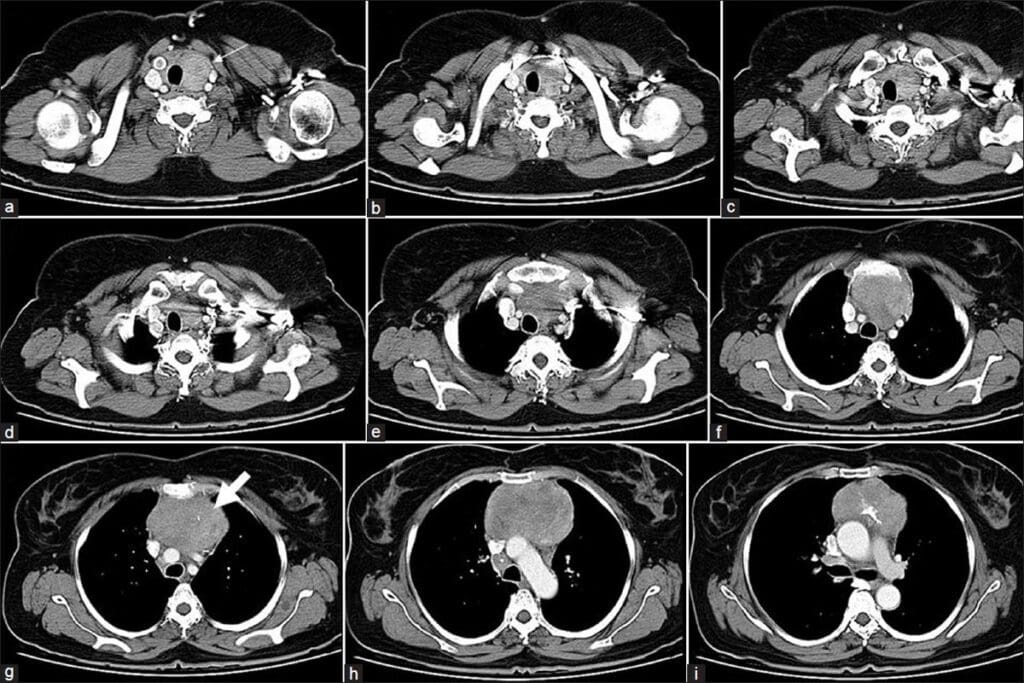
The CT urogram uses contrast media given through an IV. This media lights up the urinary system as it moves through. It shows the kidneys, ureters, and bladder in different stages, giving a full view of their shape and how they work. This is key for finding issues that might not show up in other scans.
A CT urogram has several phases, each showing the urinary tract at different times. The non-contrast phase gives us a starting point. The nephrographic phase focuses on the kidney’s inner parts. The excretory phase shows how the contrast moves through the system, highlighting any blockages or issues.
With the detailed images from a CT urogram, we can better diagnose and treat urinary tract problems. This leads to better care for our patients.
Understanding CT scans with and without contrast is key for accurate diagnoses. We use CT scans to see inside the body. The choice to use contrast media depends on what we need to see.
Non-contrast CT scans are great for finding things like kidney stones or bleeding. They are fast and give us important info without contrast. They’re also good in emergencies when we need to act fast.
Non-contrast CT scans have fewer risks of allergic reactions. They’re also safe for patients with certain health issues that make contrast unsafe.
Contrast-enhanced CT scans use a contrast agent to show certain body parts. This method is best for seeing blood vessels, tumors, and soft tissue issues. The contrast agent makes images clearer for better diagnosis.
We use contrast-enhanced CT scans for detailed views of organs or tissues. This includes checking for vascular diseases, infections, and cancers.
Dual-phase CT protocols scan the patient with and without contrast. This gives us a detailed look at the body’s anatomy and any problems. It’s great for complex cases needing multiple contrast phases.
By mixing non-contrast and contrast-enhanced CT scans, we get a full picture of the patient’s health. This helps us make more accurate diagnoses and treatment plans.
Understanding the difference between CT urogram and standard CT scans is key for diagnosing urinary tract issues. We’ll look at how these two imaging methods differ. This includes their protocols, how contrast is given, their uses, and how much radiation they use.
CT urogram is designed to check the urinary tract. It has several phases, starting with a non-contrast phase and then contrast-enhanced phases. Standard CT scans, on the other hand, can be set up for many different needs. They might use non-contrast or contrast-enhanced protocols.
Key differences in imaging protocols include:
How contrast is given is important for both CT urogram and standard CT scans. For CT urogram, contrast media is used to see the urinary tract’s anatomy and function. The timing is key to get good images of the urinary system.
The contrast administration technique for CT urogram is tailored to:
CT urogram is great for finding issues in the urinary tract, like bladder cancer or kidney stones. Standard CT scans are more versatile. They can check for injuries or cancers in different parts of the body.
Limitations of each modality include:
Both CT urogram and standard CT scans use radiation. The amount depends on the protocol and the scanner technology. We need to weigh the benefits of the scan against the risk of radiation.
Factors influencing radiation exposure include:
CT urogram is a top choice for spotting urinary tract problems. We’ll dive into its effectiveness and uses.
CT urogram is great at finding issues like kidney stones and tumors. It beats other methods in accuracy.
Its clear images help doctors spot small problems early. This leads to better care for patients. It’s also key in finding upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma.
CT urogram is very sensitive and specific. It gives detailed views of the urinary tract in different stages. This boosts its accuracy.
Studies confirm its high sensitivity and specificity. It’s a go-to for doctors to make treatment plans and care for patients better.
New CT urography methods aim to cut down on radiation. Low-tube-voltage and low-iodine-concentration scans reduce radiation by up to 32%.
These changes make patients safer and improve diagnosis. As we learn more, we’ll see better ways to diagnose and treat urinary tract issues.
We’ve talked about how CT urogram and standard CT scans differ, mainly in urinary tract imaging. A CT urogram is a detailed scan that shows the kidneys, ureters, and bladder. It’s key for spotting problems like urothelial carcinoma and other issues.
Standard CT scans, even with contrast, don’t offer the same level of detail as a CT urogram. The right choice depends on what the patient needs. For a full view of the urinary tract, a CT urogram is usually the best option.
For more on CT urography’s technical and clinical uses, check out the National Center for Biotechnology Information. This info highlights the need for the right imaging based on the patient’s health. It ensures accurate diagnosis and effective treatment plans.
A CT urogram is a special CT scan that uses contrast media. It shows detailed images of the urinary tract, like the kidneys, ureters, and bladder. It’s different from a standard CT scan because it focuses on the urinary system.
Contrast media make certain body areas stand out during a CT scan. In a CT urogram, it’s used to highlight the urinary tract. This helps get clear images of the kidneys, ureters, and bladder.
A CT urogram has several phases. These include a non-contrast phase, a phase with contrast, and sometimes a delayed phase. Each phase helps to see the urinary tract and find any problems.
CT urogram gives detailed images of the urinary tract. This helps doctors accurately diagnose and check conditions like kidney stones and tumors.
CT urogram is very good at finding problems in the urinary tract. It’s often compared to ultrasound and MRI because of its high detection rates.
CT urogram is a powerful tool, but it’s not always needed. For some conditions, a standard CT scan might be better. This is because it gives a more general view of the body.
Both CT urogram and standard CT scans use radiation. But, new CT urography methods aim to lower radiation while keeping the images clear.
Contrast media is given through an IV during a CT urogram or contrast-enhanced CT scan. It makes certain areas of the body stand out, helping to get detailed images.
Non-contrast CT scans are good for finding things like kidney stones. Contrast-enhanced CT scans show blood vessels and soft tissues. Using both types of scans together can give a full picture.
Computed tomography urography is another name for CT urogram. It uses CT scanning to look at the urinary tract.
A non-contrast CT scan is often used to find kidney stones. While contrast media can be used, it’s not always needed for this purpose.
A CT cystogram is a CT scan that focuses on the bladder. It’s similar to a CT urogram but looks at the bladder more closely, not the whole urinary tract.
Kalva, S. P., & Meijer, R. (2023). Computed Tomography Urography: State of the Art and Beyond. .https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10204399/
Kawashima, A., Vrtiska, T. J., LeRoy, A. J., Hartman, R. P., & McCollough, C. H. (2004). CT urogram. AJR: American Journal of Roentgenology. Retrieved from https://ajronline.org/doi/full/10.2214/AJR.10.4198
Describes CT urography protocols, diagnostic performance, and comparison to non-contrast imaging.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!