Last Updated on November 26, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
Medical oncologists play a crucial role in cancer treatment, utilizing various therapies to combat the disease. At institutions like Liv Hospital, we emphasize comprehensive, patient-centered care, ensuring the best possible outcomes for our patients.
Defining medical oncology involves understanding the role of these specialists in diagnosing, staging, and managing cancer. Medical oncologists are often the primary healthcare providers for cancer patients, developing personalized treatment plans and collaborating with multidisciplinary teams.
We recognize the importance of clear communication in cancer care, ensuring that patients are informed and supported throughout their treatment journey.
Key Takeaways
- Medical oncologists are central in cancer diagnosis, staging, and management.
- They develop personalized treatment plans for cancer patients.
- Collaboration with multidisciplinary teams is crucial in cancer care.
- Comprehensive, patient-centered care is essential for optimal outcomes.
- Medical oncologists utilize various therapies, including chemotherapy, hormone therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy.
Understanding Medical Oncology: Definition and Scope

Medical oncology is a vital component of cancer care, focusing on the diagnosis and treatment of cancer using various medical therapies. As a subspecialty of internal medicine, medical oncology is dedicated to the diagnosis, treatment, and management of cancer.
The Medical Specialty of Oncology
Oncology, the study of cancer, is a broad medical specialty that encompasses various disciplines, including medical oncology, surgical oncology, and radiation oncology. Medical oncology is concerned with the non-surgical management of cancer, using treatments such as chemotherapy, hormone therapy, and targeted therapy.
We recognize that cancer is a complex and multifaceted disease, requiring a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment. Medical oncologists work closely with other healthcare professionals to develop personalized treatment plans tailored to each patient’s unique needs.
Historical Development of Medical Oncology
The field of medical oncology has evolved significantly over the years, driven by advances in our understanding of cancer biology and the development of new treatments. The emergence of medical oncology as a distinct specialty has been marked by significant milestones, including the introduction of chemotherapy and the development of targeted therapies.
As our understanding of cancer continues to grow, we are witnessing a shift towards more personalized and precision medicine approaches in medical oncology. This evolution is transforming the way we diagnose and treat cancer, offering new hope to patients and their families.
The Role of a Chemo Oncologist in Cancer Care
In the fight against cancer, chemo oncologists are at the forefront, employing cutting-edge therapies to improve patient outcomes. We rely on these medical specialists to diagnose and treat cancer using various therapies, including chemotherapy and hormone therapy. Chemo oncologists, also known as medical oncologists, play a vital role in cancer care, working closely with patients to develop personalized treatment plans.
Primary Responsibilities and Duties
Chemo oncologists have several key responsibilities:
- Diagnosing and staging cancer
- Developing and implementing treatment plans
- Administering chemotherapy and other cancer therapies
- Managing patient care and side effects
- Collaborating with other healthcare professionals to provide comprehensive care
These specialists are crucial in helping patients navigate the complexities of cancer treatment, providing expert care and support throughout the process.
Educational Requirements and Specialization
To become a chemo oncologist, one must undergo extensive education and training. The typical path includes:
- Completing a bachelor’s degree, typically in a science-related field
- Attending medical school to earn an MD or DO degree
- Completing a residency program in internal medicine
- Pursuing additional specialized training in medical oncology through a fellowship program
Chemo oncologists must also obtain certification from the American Board of Internal Medicine (ABIM) in medical oncology. This rigorous training and certification process ensure that chemo oncologists have the necessary expertise to provide high-quality care to cancer patients.
The Diagnostic Process in Medical Oncology
The journey to cancer diagnosis involves a series of careful assessments and tests, all of which are critical in determining the best course of treatment. As medical oncologists, we rely on a comprehensive diagnostic process to understand the nature and extent of the disease.
Initial Assessment and Testing
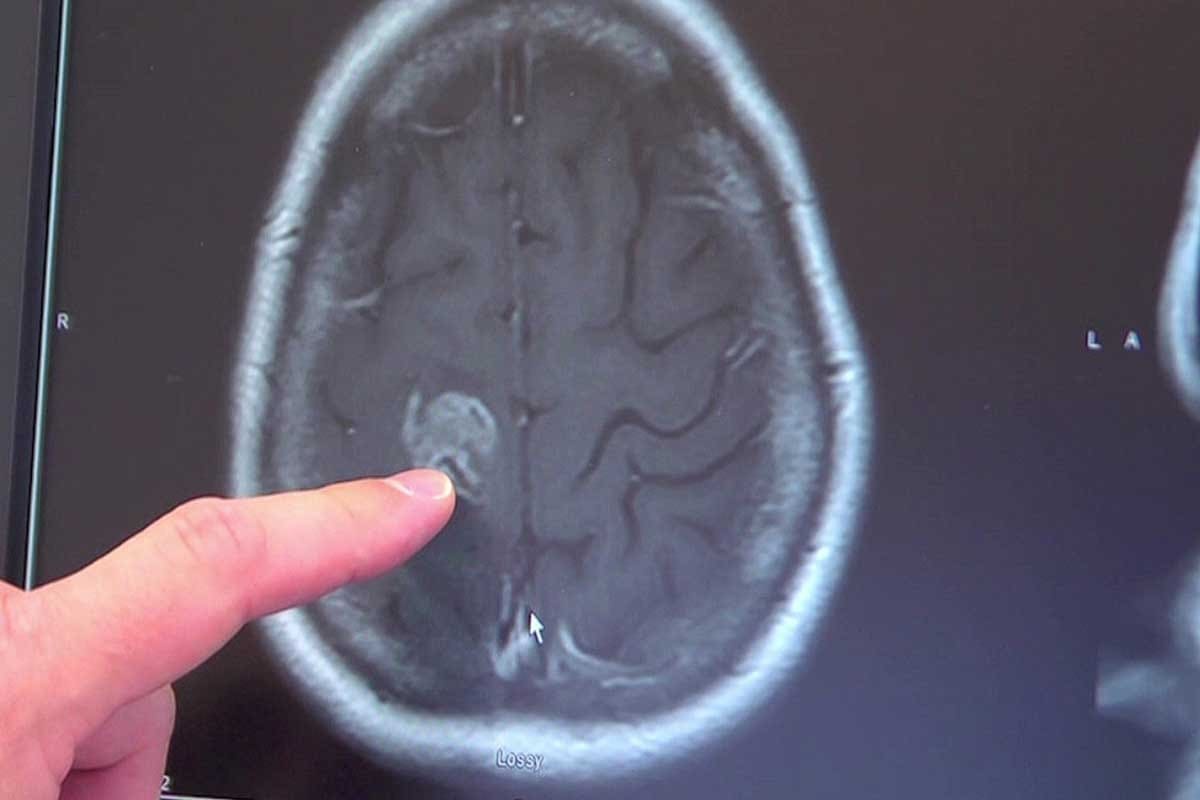
When a patient is referred to us with a suspected cancer diagnosis, we begin with a thorough initial assessment. This includes a detailed medical history, physical examination, and a review of any previous diagnostic tests. We use this information to guide further testing, which may include imaging studies such as CT scans, MRI, or PET scans, as well as laboratory tests like blood work and biopsies.
Imaging studies play a crucial role in diagnosing and staging cancer. For instance, a CT scan can help identify the size and location of tumors, while a PET scan can provide information on the metabolic activity of cancer cells. Laboratory tests, including biopsies, are essential for confirming the diagnosis and understanding the specific characteristics of the cancer.
Cancer Staging and Classification
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, we proceed to stage the cancer. Staging involves determining the extent of the disease, including whether it has spread to other parts of the body. This information is critical for developing an effective treatment plan. We use various staging systems, such as the TNM system, which considers the size of the tumor (T), the involvement of lymph nodes (N), and the presence of metastasis (M).
Accurate staging is vital because it helps us understand the prognosis and choose the most appropriate treatment options. For example, early-stage cancers might be treated with surgery or localized radiation therapy, while more advanced cancers may require systemic treatments like chemotherapy or targeted therapy.
By combining the results of initial assessments, testing, and staging, we can develop a comprehensive understanding of each patient’s cancer. This information allows us to create personalized treatment plans that address the unique needs and circumstances of each individual.
Treatment Modalities Used by Medical Oncologists
As cancer care continues to evolve, medical oncologists are at the forefront, utilizing various treatment modalities to improve patient outcomes. We recognize that each patient’s journey with cancer is unique, requiring a personalized approach to treatment.
Chemotherapy: Principles and Applications
Chemotherapy remains a cornerstone in the treatment of cancer, involving the use of drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing and dividing. We often use chemotherapy in combination with other treatments, such as surgery or radiation therapy, to achieve the best results. The choice of chemotherapy drugs depends on the type of cancer, its stage, and the patient’s overall health.
Key considerations in chemotherapy include:
- The type and stage of cancer
- The patient’s overall health and medical history
- Potential side effects and how to manage them
Hormone Therapy for Cancer Treatment
Hormone therapy is used to treat cancers that are sensitive to hormones, such as certain types of breast and prostate cancer. This treatment works by blocking the body’s natural hormones, which can fuel the growth of cancer cells. We may use hormone therapy alone or in combination with other treatments.
The benefits of hormone therapy include:
- Reducing the risk of cancer recurrence
- Slowing the growth of cancer cells
- Improving quality of life
Targeted Therapy Approaches
Targeted therapy is a type of cancer treatment that targets specific genes or proteins involved in the growth and survival of cancer cells. We use targeted therapies to interfere with the cancer’s ability to grow and spread. These treatments can be more effective and have fewer side effects than traditional chemotherapy.
| Therapy Type | Mechanism of Action | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Chemotherapy | Kills rapidly dividing cells | Doxorubicin, Paclitaxel |
| Hormone Therapy | Blocks hormone production or action | Tamoxifen, Leuprolide |
| Targeted Therapy | Targets specific genes or proteins | Trastuzumab, Erlotinib |
Immunotherapy and Biological Response Modifiers
Immunotherapy is a promising approach that harnesses the power of the immune system to fight cancer. We use immunotherapies to stimulate the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells more effectively. Biological response modifiers are substances that boost the immune system’s response to cancer.
Examples of immunotherapies include:
- Checkpoint inhibitors
- Cancer vaccines
- Adoptive T-cell therapy
By understanding the various treatment modalities available, we can tailor our approach to each patient’s unique needs, improving outcomes and quality of life.
The Medical Oncologist as Care Coordinator
Medical oncologists play a vital role in the comprehensive care of cancer patients, extending beyond treatment to coordinate the overall care journey. As the primary healthcare providers for many cancer patients, medical oncologists are responsible for managing the complex interactions between various healthcare professionals, ensuring that patients receive cohesive and supportive care.
Managing the Cancer Care Team
Effective care coordination is crucial in cancer treatment, involving a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals. Medical oncologists work closely with surgeons, radiation oncologists, nurses, and other specialists to develop and implement personalized treatment plans. They facilitate communication among team members, ensuring that all aspects of a patient’s care are considered and integrated.
Key members of the cancer care team include:
- Surgical oncologists: Responsible for surgical interventions
- Radiation oncologists: Specialize in radiation therapy
- Nurses and nurse practitioners: Provide direct patient care and support
- Pathologists: Diagnose cancer through tissue examination
- Radiologists: Interpret imaging studies
- Supportive care specialists: Address psychosocial and symptom management needs
By managing this team, medical oncologists ensure that all elements of a patient’s care are coordinated effectively.
Long-term Patient Monitoring and Follow-up
Medical oncologists are also responsible for long-term monitoring and follow-up care, crucial for detecting potential recurrence or complications early. This ongoing care involves regular check-ups, imaging studies, and laboratory tests to monitor the patient’s response to treatment and overall health.
| Aspect of Care | Description | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Follow-up Visits | Regular check-ups to monitor patient health and response to treatment | Typically every 3-6 months initially, then annually |
| Imaging Studies | Use of CT scans, MRIs, and PET scans to monitor disease status | As needed based on patient condition and treatment plan |
| Laboratory Tests | Blood tests and other lab work to monitor health and detect potential issues | Regularly, as determined by the treatment plan |
By maintaining close follow-up, medical oncologists can address any issues promptly, improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Through their role as care coordinators, medical oncologists ensure that cancer patients receive comprehensive, supportive care throughout their treatment journey, addressing both medical and psychosocial needs.
Personalized Medicine in Oncology
With the rise of precision oncology, we’re witnessing a significant shift towards personalized cancer care that leverages advanced genetic testing and biomarker identification. This approach is revolutionizing the field of oncology by providing treatments that are tailored to the unique characteristics of each patient’s cancer.
Genetic Testing and Biomarkers
Genetic testing plays a crucial role in personalized medicine by identifying specific genetic mutations within a patient’s cancer cells. These mutations can serve as biomarkers, helping oncologists select the most appropriate targeted therapies. Biomarkers are biological molecules found in blood, other body fluids, or tissues that are a sign of a normal or abnormal process, or of a condition or disease. By analyzing these biomarkers, healthcare providers can predict how a patient is likely to respond to certain treatments.
For instance, genetic testing can reveal if a patient’s tumor has a specific mutation that makes it susceptible to a particular targeted therapy. This information allows for more precise treatment planning, improving outcomes and reducing the risk of unnecessary side effects.
Tailoring Treatment Plans to Individual Patients
Personalized medicine enables us to tailor treatment plans to the individual characteristics of each patient’s cancer. By considering factors such as genetic mutations, biomarker expression, and the patient’s overall health, we can develop targeted treatment strategies that are more likely to be effective.
- Identifying the most effective treatment options based on genetic profiles
- Minimizing trial-and-error approaches to treatment
- Enhancing patient outcomes through targeted therapies
- Reducing healthcare costs by avoiding ineffective treatments
| Benefits of Personalized Medicine | Description |
|---|---|
| Targeted Treatment | Tailors therapy to the individual’s genetic profile |
| Improved Outcomes | Enhances the likelihood of successful treatment |
| Reduced Side Effects | Minimizes exposure to ineffective therapies |
The Future of Precision Oncology
The future of precision oncology holds much promise, with ongoing advancements in genetic testing, biomarker discovery, and targeted therapy development. As our understanding of the genetic underpinnings of cancer continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more sophisticated and effective personalized treatment approaches.
We are moving towards a future where cancer treatment is not just about treating the disease, but about understanding the unique characteristics of each patient’s cancer and tailoring our approach accordingly. This shift towards precision oncology is transforming the landscape of cancer care, offering new hope to patients and their families.
Multidisciplinary Approach to Cancer Treatment
The complexity of cancer requires a multifaceted treatment strategy, highlighting the importance of a multidisciplinary team. Cancer care has become increasingly sophisticated, involving various medical specialties and healthcare professionals working together to provide comprehensive and coordinated care.
Collaboration with Surgical and Radiation Oncologists
Effective cancer treatment often involves a combination of different therapeutic approaches. We work closely with surgical and radiation oncologists to ensure that patients receive the most appropriate and effective treatment plan. Surgical oncologists play a crucial role in the surgical removal of tumors, while radiation oncologists use targeted radiation therapy to eliminate cancer cells.
Benefits of Collaboration:
- Comprehensive treatment planning
- Improved patient outcomes
- Enhanced coordination among healthcare professionals
Working with Supportive Care Specialists
In addition to medical, surgical, and radiation oncologists, supportive care specialists are integral to the multidisciplinary team. These professionals provide essential services such as pain management, nutritional counseling, and psychological support, addressing the holistic needs of cancer patients.
| Supportive Care Service | Description |
|---|---|
| Pain Management | Effective control of pain to improve patient comfort |
| Nutritional Counseling | Personalized dietary advice to support treatment and recovery |
| Psychological Support | Emotional and mental health support for patients and families |
The Tumor Board: Collective Decision Making
A tumor board is a critical component of the multidisciplinary approach, bringing together experts from various fields to discuss patient cases and develop consensus-driven treatment plans. This collective decision-making process ensures that patients receive the most effective and appropriate care based on the latest medical evidence and guidelines.
The tumor board’s collaborative environment fosters a culture of shared knowledge and expertise, ultimately benefiting patient care.
Exemplary Oncology Care: Case Studies and Best Practices
Through its rigorous adherence to the latest medical research and ethical standards, Liv Hospital provides exemplary oncology care that sets a high standard in the field. We recognize the importance of continually updating our treatment protocols to reflect the most current medical knowledge, ensuring our patients receive the best possible care.
Liv Hospital’s Approach to Cancer Treatment
Liv Hospital’s comprehensive approach to cancer treatment is multifaceted, incorporating the latest advancements in medical oncology, including chemotherapy, hormone therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. Our team of specialists works closely together to tailor treatment plans to the individual needs of each patient, ensuring a personalized care approach.
Implementing Up-to-Date Protocols
Staying abreast of the latest developments in oncology is crucial for providing high-quality care. Liv Hospital achieves this through ongoing education and training for our staff, as well as participation in international conferences and workshops. Our commitment to implementing up-to-date protocols is reflected in our treatment outcomes, as evidenced by various studies highlighting the effectiveness of modern oncology practices.
| Treatment Modality | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Chemotherapy | Use of drugs to kill cancer cells | Effective against various cancer types |
| Targeted Therapy | Treatment targeting specific cancer cell characteristics | Reduced harm to healthy cells |
| Immunotherapy | Boosting the body’s immune system to fight cancer | Potential for long-term cancer control |
Ethical Considerations in Oncology Practice
Ethical considerations play a vital role in oncology practice, where decisions often involve complex moral and ethical dilemmas. At Liv Hospital, we are committed to upholding the highest ethical standards, prioritizing patient autonomy, beneficence, non-maleficence, and justice in all our practices. This commitment is reflected in our transparent communication with patients and their families, ensuring they are fully informed and involved in decision-making processes.
By integrating best practices, up-to-date treatment protocols, and a strong ethical framework, Liv Hospital exemplifies exemplary oncology care, providing patients with comprehensive and compassionate treatment.
The Patient Experience with Medical Oncologists
A strong doctor-patient relationship is essential for navigating the complexities of cancer treatment. We recognize that this bond is crucial for effective care, facilitating open communication and trust between patients and their medical oncologists.
Building the Doctor-Patient Relationship
The foundation of a successful doctor-patient relationship lies in effective communication. We strive to create an environment where patients feel comfortable sharing their concerns and questions, allowing us to tailor our care to their individual needs. For new patients, understanding what happens at their first oncology can help alleviate anxiety and foster a sense of preparedness.
By taking the time to listen to our patients and address their unique circumstances, we can build trust and strengthen the doctor-patient bond. This relationship is vital in helping patients navigate the challenges of cancer treatment.
Communication and Shared Decision Making
Shared decision making is a critical component of patient-centered care. We work closely with our patients to understand their preferences, values, and goals, ensuring that treatment plans are aligned with their needs. By collaborating with patients and their families, we can make informed decisions that reflect their unique circumstances.
Effective communication is key to this process, enabling us to clearly explain treatment options, risks, and benefits. We believe that informed patients are better equipped to make decisions about their care, and we are committed to supporting them throughout this process.
Psychosocial Support Throughout Cancer Care
Cancer care extends beyond medical treatment to encompass the emotional and psychological well-being of patients. We recognize the importance of psychosocial support in helping patients cope with the challenges of cancer diagnosis and treatment. Our team is dedicated to providing comprehensive care that addresses the whole patient, not just their disease.
By integrating psychosocial support into our care plans, we can help patients manage stress, anxiety, and other emotional challenges associated with cancer treatment. This holistic approach enables us to provide patient-centered care that improves overall outcomes and enhances quality of life.
Conclusion: The Evolving Role of Medical Oncologists in Modern Healthcare
As we reflect on the role of medical oncologists, it’s clear that their importance in modern healthcare continues to grow. The field of medical oncology is constantly evolving, driven by ongoing research and advancements in treatment modalities that improve patient outcomes.
We have seen how medical oncologists play a critical role in cancer care, from diagnosis to treatment and long-term patient monitoring. Their ability to coordinate care and work collaboratively with other specialists is crucial in providing comprehensive support to patients.
The advancements in cancer care, including personalized medicine and targeted therapies, have significantly enhanced treatment options. As medical oncologists continue to adopt these advancements, their role in modern healthcare becomes increasingly vital.
In this ever-evolving landscape, we recognize the commitment of medical oncologists to delivering high-quality, patient-centered care. Their dedication to staying at the forefront of cancer care advancements ensures that patients receive the best possible treatment outcomes.
As we look to the future, it’s evident that the evolving role of medical oncologists will remain central to improving cancer care and patient outcomes in modern healthcare.
FAQ
What is a medical oncologist?
A medical oncologist is a doctor who specializes in diagnosing and treating cancer using various therapies, including chemotherapy, hormone therapy, and targeted therapy.
What does a medical oncologist do?
Medical oncologists develop personalized treatment plans for cancer patients, manage their care, and coordinate with other healthcare professionals to ensure comprehensive support throughout the treatment journey.
What is the difference between a medical oncologist and a surgical oncologist?
Medical oncologists focus on non-surgical treatments, such as chemotherapy and hormone therapy, while surgical oncologists specialize in surgical procedures to remove tumors and cancerous tissues.
How do medical oncologists diagnose cancer?
Medical oncologists use various diagnostic tests, including imaging studies, biopsies, and laboratory tests, to determine the presence and extent of cancer, and develop a treatment plan accordingly.
What is personalized medicine in oncology?
Personalized medicine in oncology involves tailoring treatment plans to individual patients based on their genetic profiles, biomarkers, and other factors to optimize treatment outcomes.
How do medical oncologists coordinate care?
Medical oncologists manage the cancer care team, communicate with other healthcare professionals, and provide long-term patient monitoring and follow-up to ensure comprehensive and supportive care.
What is the role of a tumor board in cancer care?
A tumor board is a multidisciplinary team that reviews patient cases and develops collective treatment plans, ensuring that patients receive the most effective and comprehensive care.
What are the benefits of a multidisciplinary approach to cancer treatment?
A multidisciplinary approach brings together various healthcare professionals to provide comprehensive care, ensuring that patients receive the most effective treatment plans and supportive care throughout their treatment journey.
How do medical oncologists provide psychosocial support to patients?
Medical oncologists provide emotional and psychological support to patients by building strong doctor-patient relationships, communicating effectively, and addressing their emotional and psychological needs throughout cancer care.
What is the future of precision oncology?
Precision oncology is expected to revolutionize cancer care by tailoring treatment plans to individual patients based on their genetic profiles and biomarkers, leading to more effective and targeted treatments.