Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
Getting a diagnosis of advanced cancer can change your life. It brings uncertainty and tough choices. At Liv Hospital, we focus on caring for you with kindness and understanding.
Advanced cancer means the disease has spread or come back. It’s hard to cure. Knowing about the stages, symptoms, and how metastatic cancer grows is key for good care (Source: Sci Signal. 2025 Jun 24;18(892):eads6550).
We know that stage 4 cancer or late-stage cancer needs a full treatment plan. Our team is known worldwide for top-notch care. We support patients from all over.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the stages and symptoms of advanced cancer is key for good care.
- Metastatic cancer needs a detailed treatment plan.
- Liv Hospital offers caring, respected care for advanced cancer patients.
- Our team supports international patients through their treatment.
- Advanced cancer treatment involves a team effort to fight the disease.
What Defines Advanced Cancer: Key Terminology
To understand advanced cancer, it’s key to know the medical terms. Advanced cancer is in stages III and IV, showing a serious disease progression.
Medical Definition of Advanced Cancer
Advanced cancer is stage III or IV. Stage III has bigger tumors and might have reached nearby lymph nodes. Stage IV has spread to distant organs. We’ll dive deeper into cancer staging later.
Research shows the role of molecular mechanisms in cancer growth. For example, losing STIM2 in colorectal cancer worsens prognosis. Knowing first-line treatments helps manage advanced cancer.
Difference Between Advanced and Early-Stage Cancer
The main difference is how far the cancer has spread. Early-stage cancer stays in one place. Advanced cancer has spread to lymph nodes or distant organs. This affects treatment and outlook.
Common Terminology Patients Should Know
When facing advanced cancer, patients need to know some key terms:
- Metastatic Cancer: Cancer that has spread from the original site to other parts of the body.
- Regional Lymph Node Involvement: Cancer that has spread to nearby lymph nodes.
- Distant Metastasis: Cancer that has spread to organs or tissues far from the original site.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Metastatic Cancer | Cancer that has spread from the original site to other parts of the body. |
| Regional Lymph Node Involvement | Cancer that has spread to nearby lymph nodes. |
| Distant Metastasis | Cancer that has spread to organs or tissues far from the original site. |
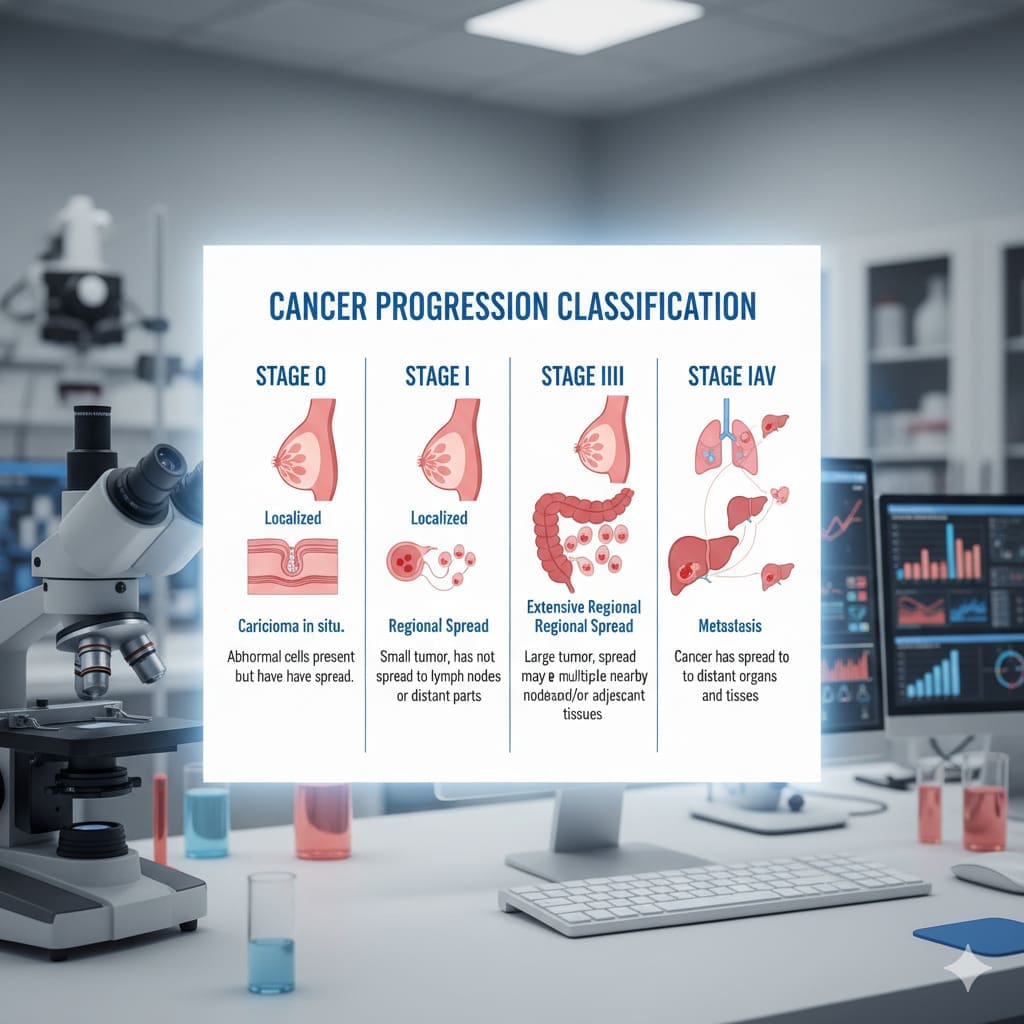
The Staging System: How Cancer Progression is Classified
Accurately staging cancer is key to predicting patient outcomes and choosing treatments. Cancer staging systems categorize cancer progression. This helps healthcare providers make treatment decisions.
We use the staging system to understand cancer’s extent. This is vital for picking the best treatment. The system looks at tumor size, lymph node involvement, and distant metastasis.
Stage III Cancer Characteristics
Stage III cancer means the cancer has grown and may have spread to nearby lymph nodes or tissues. The specifics of Stage III cancer depend on the cancer type.
In some cancers, Stage III means cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes but not to distant parts of the body. We will look at different cancer types later.
| Cancer Type | Stage III Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Breast Cancer | Spread to nearby lymph nodes or tissues |
| Lung Cancer | Spread to lymph nodes or other tissues in the chest |
Stage IV Cancer Characteristics
Stage IV cancer has spread to distant parts of the body, known as metastasis. This stage is considered advanced cancer.
Stage IV cancer needs a detailed treatment plan. This plan often includes various therapies to manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
“The TNM system is widely used to classify the progression of cancer, taking into account the size of the tumor, lymph node involvement, and distant metastasis.”
The TNM Classification System Explained
The TNM classification system is a common method for staging cancer. It looks at three main factors: tumor size and extent (T), lymph node involvement (N), and metastasis to other parts of the body (M).
Understanding the TNM classification is key for healthcare providers. It helps them predict prognosis and develop effective treatment plans.
By using the TNM classification system, we can better understand cancer progression. This helps us make informed treatment decisions.
Types of Advanced Cancer Progression
It’s important for patients and doctors to know about advanced cancer types. These include locally advanced carcinoma, extensive metastatic disease, and recurrent advanced cancer. Each type has its own traits and affects treatment and outlook.
Locally Advanced Carcinoma
Locally advanced carcinoma means the cancer has grown a lot but hasn’t spread far. It’s hard to treat because of its size and how it can invade nearby tissues. Doctors use surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy to try to shrink the tumor and ease symptoms.
For example, colon cancer can become locally advanced if it grows into nearby tissues or lymph nodes. This requires a detailed treatment plan.
Extensive Metastatic Disease
Extensive metastatic disease happens when cancer spreads to many parts of the body. This stage is often harder to treat and has a worse outlook. Treatment usually involves chemotherapy, targeted therapy, or immunotherapy to manage symptoms and slow the disease.
Research shows that extensive metastatic disease is linked to a tougher prognosis. So, catching it early and acting fast is key to managing it well.
Recurrent Advanced Cancer
Recurrent advanced cancer is when cancer comes back after treatment, often more aggressively. It can come back locally, regionally, or distantly. The treatment for recurrent cancer depends on where it comes back, past treatments, and the patient’s health.
Key traits of recurrent advanced cancer include:
- Potential for more aggressive behavior than the original cancer
- Variable treatment options based on previous therapies and patient condition
- The need for a multidisciplinary approach to care, involving various specialists
In summary, knowing about advanced cancer types is vital for effective treatment plans and better patient outcomes. By understanding locally advanced carcinoma, extensive metastatic disease, and recurrent advanced cancer, doctors can provide more tailored and caring care.
The Metastatic Process: Understanding How Cancer Spreads
The metastatic process is a complex series of events. It allows cancer cells to spread from the primary site to distant organs. This involves several key steps, including invasion, intravasation, circulation, extravasation, and colonization.
Common Pathways of Metastasis
Cancer cells can spread through different pathways. These include the bloodstream, the lymphatic system, and bodily cavities. The pathway chosen often depends on the cancer type and location.
For example, carcinomas usually spread through the lymphatic system. Sarcomas, on the other hand, spread through the bloodstream. Knowing these pathways helps predict where cancer will spread and how to treat it.
Why Certain Cancers Metastasize More Easily
Some cancers, like colorectal cancer, are more likely to metastasize. This is due to molecular mechanisms. These mechanisms include genetic mutations that help cancer cells invade and migrate.
Research has identified specific genes and pathways involved in metastasis. For instance, the KRAS gene plays a role in colorectal cancer. Understanding these mechanisms helps in developing targeted therapies to prevent or delay metastasis.
Timeline of Metastatic Development
The timeline for metastatic development varies. It depends on the cancer type, its aggressiveness, and the initial treatment. Some cancers spread quickly, while others may remain dormant for years.
| Cancer Type | Common Sites of Metastasis | Typical Timeline for Metastasis |
|---|---|---|
| Breast Cancer | Bones, Liver, Lungs, Brain | 2-5 years |
| Colorectal Cancer | Liver, Lungs, Peritoneum | 1-3 years |
| Lung Cancer | Brain, Bones, Liver, Adrenal glands | 1-2 years |
Understanding the metastatic process and its timeline is key to managing cancer. Recognizing the pathways and timelines helps healthcare providers create personalized treatment plans.
Recognizing Advanced Cancer Symptoms
It’s important to know the signs of advanced cancer early. This can help get the right treatment sooner. Advanced cancer can cause many symptoms that make life harder.
Systemic Symptoms
Systemic symptoms affect the whole body. Common signs of advanced cancer include:
- Severe Fatigue: Feeling very tired that doesn’t get better with rest.
- Weight Loss: Losing weight without trying, often because of the cancer’s needs.
- Loss of Appetite: Not wanting to eat can lead to malnutrition and weaken the body.
- Persistent Pain: Pain that doesn’t go away with usual treatments.
These symptoms can be very hard to deal with and need careful management.
Organ-Specific Symptoms
Organ-specific symptoms happen when cancer affects certain organs. Some examples are:
- Breathing Difficulties: Cancer in the lungs or pleura can cause shortness of breath.
- Jaundice: Liver problems can turn the skin and eyes yellow.
- Bone Pain: Cancer in bones can cause a lot of pain and increase fracture risk.
- Neurological Symptoms: Brain cancer can lead to headaches, seizures, or changes in thinking.
Knowing these symptoms helps patients and caregivers get the right help.
It’s key for patients and their families to know these signs. This way, they can get the support and care they need. Managing these symptoms well can make life better for those with advanced cancer.
Signs That Cancer Has Metastasized
When cancer spreads, it can cause many symptoms. These depend on where the cancer goes. It’s important for patients and doctors to know these signs to manage the disease well.
Neurological Changes and Headaches
Neurological changes are a sign of metastasis. Cancer in the brain can cause headaches, dizziness, and seizures. “Brain metastases can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life,” says a leading oncologist. “Early detection and treatment are key to managing these symptoms.”
Symptoms like headaches and dizziness happen when cancer reaches the brain. This is because the tumor presses on brain tissue. Patients might also have seizures or feel confused.
Bone-Related Symptoms: Swelling and Fractures
Cancer in bones can cause a lot of pain. Bone metastases can lead to swelling, fractures, and high calcium levels. “Bone metastases are a common complication of advanced cancer,” notes an oncologist. We will look at the bone symptoms of metastatic cancer.
Bone pain is common in patients with bone metastases. This pain can get worse over time. Sometimes, the bone can weaken and break.
Liver Metastasis: Jaundice and Abdominal Swelling
Liver metastases can cause jaundice and swelling in the abdomen. They can also change how the liver works. We will explore the signs and symptoms of liver metastasis.
Jaundice is a sign of liver metastasis. It happens when the liver can’t process bilirubin right. Swelling in the abdomen can also occur due to fluid buildup.
Lung Metastasis: Breathing Difficulties
Lung metastases can cause breathing problems, coughing, and chest pain. Cancer in the lungs can affect airways and lung function. We will discuss the symptoms of lung metastasis and how they affect patients.
Shortness of breath is a common symptom of lung metastasis. Patients may cough or feel chest pain, worse when taking deep breaths. In severe cases, lung metastases can cause respiratory failure.
Diagnostic Approaches for Advanced Cancer
Healthcare experts use many ways to diagnose advanced cancer. Finding out the exact type of cancer is key to choosing the right treatment.
Advanced Imaging Technologies
Imaging technologies are very important in finding and understanding advanced cancer. Computed Tomography (CT) scans, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), and Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans are used. Each one gives different details about the tumor.
CT scans are great for seeing how far cancer has spread. MRI is better for soft tissues, like the brain or spine. PET scans find cancer cells that are active, helping to tell if a tumor is bad or not.
Biopsy Procedures and Genetic Testing
Biopsies are key in diagnosing cancer and learning about its genes. A biopsy takes a small piece of tumor tissue for examination. Fine-needle aspiration biopsy and core needle biopsy are common methods.
Testing the biopsy sample can find specific cancer mutations. This info helps choose the best treatments. For example, finding BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations in breast and ovarian cancers can change treatment plans.
Biomarker Testing for Treatment Selection
Biomarker testing is also very important. Biomarkers are molecules in the body that show cancer or its behavior. For example, PD-L1 expression helps decide if certain immunotherapies will work.
| Biomarker | Cancer Type | Treatment Implication |
|---|---|---|
| PD-L1 | Various cancers | Predicts response to immunotherapy |
| BRCA1/2 | Breast, Ovarian | Influences PARP inhibitor therapy |
| HER2 | Breast | Predicts response to HER2-targeted therapy |
Monitoring Disease Progression
Keeping track of how cancer grows is very important. Imaging and biomarker tests help doctors see how well treatments are working. This helps make changes to treatment plans as needed.
Treatment Options for Advanced Cancer Patients
The treatment for advanced cancer includes many options. These include systemic therapies, palliative care, and clinical trials. As cancer gets worse, the goal changes. It shifts to managing symptoms, slowing the disease, and improving life quality.
Systemic Therapies
Systemic therapies target cancer cells all over the body. They include:
- Chemotherapy: Drugs that kill or slow cancer cells.
- Targeted Therapy: Treats specific molecules that help cancer grow.
- Immunotherapy: Boosts the immune system to fight cancer.
- Hormone Therapy: Lowers hormone levels to slow cancer.
These treatments can be used alone or together, depending on the cancer type and stage.
Palliative Interventions
Palliative care helps with symptoms, pain, and stress of cancer. It includes:
- Pain Management: Controls pain with medications and techniques.
- Symptom Control: Manages symptoms like nausea and fatigue.
- Emotional and Psychological Support: Offers counseling and support to patients and families.
Palliative care improves life quality, even when treatments can’t cure cancer.
Clinical Trials and Emerging Treatments
Clinical trials offer new treatments not yet widely available. They include:
- Immunotherapies: Like tolododekin alfa, showing promise in early trials (Source: NCT06171750).
- Targeted Therapies: Drugs that target specific genetic mutations or pathways.
- Combination Therapies: Using multiple treatments together for better results.
Joining clinical trials can give patients new treatments and help advance cancer care.
Every patient’s fight with advanced cancer is different. Treatment plans are made to fit each person’s needs and wishes. By looking at systemic therapies, palliative care, and clinical trials, patients get care that meets their physical, emotional, and social needs.
Conclusion: Living with Advanced Cancer
It’s key for patients and their families to understand advanced cancer and its signs. Knowing how cancer spreads can help manage it better.
Research shows that knowing about advanced cancer is essential for better patient care. Patients can handle their disease better and make smart choices about their treatment.
Dealing with advanced cancer needs a team effort. It includes managing the disease well and understanding what the future holds. We focus on care that meets patients’ physical, emotional, and social needs.
By giving patients the right info and support, we can improve their life quality. Our aim is to offer top-notch healthcare to international patients looking for advanced treatments.
FAQ
What is advanced cancer?
Advanced cancer is when the disease has spread or come back. It’s hard to cure at this stage. It’s often stage III or IV, where cancer has reached lymph nodes or distant organs.
What are the common symptoms of advanced cancer?
Symptoms include fatigue, weight loss, and pain. Also, neurological changes, bone issues, and breathing problems can occur.
How is advanced cancer diagnosed?
Doctors use imaging, biopsies, genetic tests, and biomarkers to diagnose. These help figure out how far the cancer has spread and what treatments work best.
What are the treatment options for advanced cancer patients?
Options include systemic therapies and palliative care. Systemic treatments aim to slow cancer growth. Palliative care focuses on easing symptoms and improving life quality.
What is the TNM classification system?
The TNM system stages cancer. It looks at the tumor size (T), lymph node involvement (N), and metastasis (M).
How does cancer metastasize?
Cancer cells spread from the main tumor to other parts of the body. This can happen through lymph nodes, blood, or direct invasion.
What are the signs that cancer has metastasized?
Signs include neurological issues, bone problems, liver, and lung metastasis. Symptoms vary based on where and how far the cancer has spread.
Can advanced cancer be treated?
Advanced cancer is tough to cure, but treatments can help. They aim to slow cancer growth, ease symptoms, and improve life quality. Treatment plans are made for each patient based on their cancer type and stage.
What is the role of clinical trials in advanced cancer treatment?
Clinical trials test new treatments. They offer patients access to new therapies that might not be available yet.
How can patients manage advanced cancer symptoms?
Patients can manage symptoms with palliative care, lifestyle changes, and support. This includes pain management, nutrition, and counseling.
What is the importance of monitoring disease progression?
Keeping track of cancer progression is key. It helps adjust treatments, manage symptoms, and improve life quality. Regular check-ups are important for this.
Can patients with advanced cancer receive compassionate care?
Yes, patients can get care that meets their physical, emotional, and social needs. A team of healthcare providers works together to support and manage symptoms.
References
National Cancer Institute (NCI): Advanced Cancer
Canadian Cancer Society: Physical Symptoms of Advanced Cancer
American Cancer Society (Cancer.org): Cancer Staging
Cancer Research UK: Stages of Cancer