Last Updated on November 26, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
Advanced cancer means the disease has spread a lot and grown a lot. It has reached distant organs. At this point, it’s hard to cure, so spotting symptoms early is key.
Signs of late stage cancer symptoms include feeling very tired, losing a lot of weight, and constant pain. These symptoms really affect a person’s life quality. That’s why we need to offer caring and team support.
At Liv Hospital, we know how tough advanced cancer can be. We focus on caring for our patients, building trust and support. Our team works hard to give top-notch healthcare, supporting patients from all over.
Key Takeaways
- Advanced cancer is characterized by extensive growth and metastasis.
- Common symptoms include severe fatigue, unexplained weight loss, and pain.
- Timely recognition of symptoms is key for good care decisions.
- Liv Hospital offers care focused on the patient for advanced cancer.
- Team support is vital for managing late stage cancer symptoms.
What Is Advanced Stage of Cancer: Definition and Scope
The term ‘advanced cancer’ includes several types, like locally advanced carcinoma and advanced metastatic disease. Each type has its own challenges. Advanced cancer means the cancer has spread a lot or come back after treatment.
It’s key for patients and doctors to understand advanced cancer. Knowing the medical terms and differences between early and advanced cancer is important.
Medical Definition of Advanced Cancer
Advanced cancer is when cancer has grown too much to be removed by surgery alone. It has also spread to other parts of the body. This includes two main types: locally advanced carcinoma and advanced metastatic disease.
Locally advanced carcinoma is when cancer has grown a lot but hasn’t spread to other parts of the body. On the other hand, advanced metastatic disease is when cancer has spread to other parts of the body. This usually needs treatments like chemotherapy.
Distinguishing Between Advanced and Early-Stage Cancer
Knowing the difference between advanced and early-stage cancer is key for treatment. Early-stage cancer is usually treatable with surgery or radiation.
Advanced cancer needs a different approach. It often involves chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and care to manage symptoms. A leading oncologist says, “Advanced cancer care is about managing the disease and improving quality of life.”
“The goal of advanced cancer care is not just to extend life, but to live it to the fullest, with dignity and as much comfort as possible.”
Understanding advanced cancer is the first step in dealing with it. By knowing the differences, patients and doctors can create better care plans.
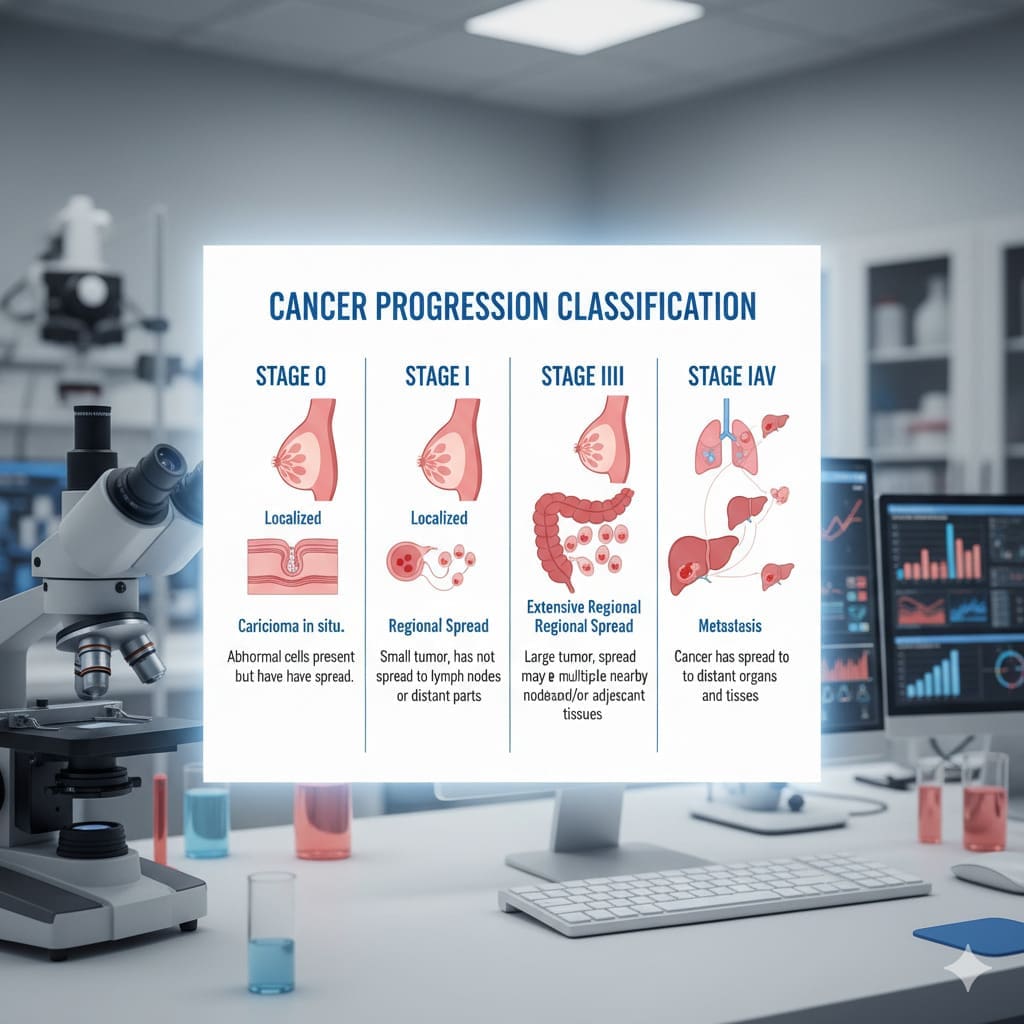
Understanding Cancer Staging Systems
It’s key for patients to understand cancer staging systems. This helps them know their diagnosis and treatment options. Cancer staging shows how far cancer has spread in the body.
The TNM classification is the most common system used. It looks at three main factors:
- T – Size of the tumor and nearby tissue invasion
- N – Nearby lymph nodes involvement
- M – Spread to other body parts
TNM Classification System
The TNM system gives a detailed way to classify cancer. For example, a cancer might be T2N1M0. This means the tumor is moderate in size, a few lymph nodes are involved, and there’s no spread to distant parts.
Stage III vs. Stage IV Cancer
Cancer stages range from I to IV, with Stage IV being the most advanced. Stage III cancer means the cancer is bigger and might have spread to nearby lymph nodes or tissues. But it hasn’t reached distant parts of the body.
Stage IV cancer is when cancer has spread to distant organs or tissues. This is also called metastatic cancer.
For lung cancer, Stage IV cancer life expectancy depends on health, treatment response, and cancer specifics.
Knowing the difference between these stages is vital. It helps patients understand their prognosis and treatment goals. While Stage III might aim for a cure, Stage IV focuses on improving quality of life through palliative care.
Key Characteristics of Advanced Cancer
“Advanced cancer” includes cases like locally advanced carcinoma and metastatic disease. Each has its own treatment and prognosis. Advanced cancer grows a lot and spreads to distant organs, affecting patient care and outcomes.
Locally Advanced Carcinoma
Locally advanced carcinoma means cancer has grown a lot in the original site. It might also spread to nearby tissues and structures. This stage is risky and needs strong treatments.
- Extensive Local Growth: Cancer that has grown significantly within the original site.
- Invasion of Nearby Structures: Cancer that has invaded nearby tissues and organs, complicating surgical options.
- Potential Impact on Surrounding Organs: The cancer’s growth can affect the function of surrounding organs, leading to various symptoms and complications.
Knowing about locally advanced carcinoma helps in making good treatment plans. These plans might include surgery, radiation, and other treatments.
Advanced Metastatic Disease
Advanced metastatic disease means cancer has spread to distant organs like the bones, liver, or lungs. This stage is hard to manage and often focuses on comfort care. Key points include:
- Distant Metastasis: Cancer cells have traveled through the bloodstream or lymphatic system to establish new tumors in distant organs.
- Multiple Sites of Disease: Advanced metastatic cancer often involves multiple sites of metastasis, complicating treatment decisions.
- Prognostic Implications: The presence of distant metastases generally indicates a poorer prognosis, though outcomes can vary based on cancer type, metastasis sites, and patient health.
For more on advanced metastatic disease, check out studies in Molecular Cancer.
Advanced cancer care needs a team effort. It includes the latest treatments and support to improve life quality. Understanding advanced cancer helps doctors tailor care for each patient.
Common Pathways of Cancer Progression
Cancer progression is a complex process. It involves cancer cells spreading to different parts of the body. Knowing how this happens is key to finding better treatments and improving patient care.
How Cancer Spreads Throughout the Body
Cancer spreads through two main ways: the bloodstream and the lymphatic system. It starts when cancer cells invade nearby tissues and then enter these systems.
Spread through the bloodstream: Cancer cells can get into blood vessels and travel to distant organs. There, they may form new tumors. This is called hematogenous spread.
Spread through the lymphatic system: Cancer cells can also get into lymphatic vessels. They then travel to lymph nodes. From there, they can spread to other parts of the body.
Common Sites of Metastasis
Some cancers tend to spread to specific organs. For example, breast cancer often goes to the bones, lungs, and liver.
| Primary Cancer | Common Sites of Metastasis |
|---|---|
| Breast Cancer | Bones, Lungs, Liver |
| Lung Cancer | Brain, Bones, Liver, Adrenal glands |
| Colorectal Cancer | Liver, Lungs, Peritoneum |
“The pattern of metastasis is influenced by various factors, including the type of primary cancer, its location, and the patient’s overall health.” –
Knowing these pathways and common metastasis sites is vital. It helps predict the metastatic cancer prognosis and plan targeted treatments.
Key Symptoms of Advanced Stage Cancer
It’s important to know the symptoms of advanced stage cancer to help care for patients. As cancer gets worse, patients may feel many symptoms that make life harder.
General Systemic Symptoms
Advanced cancer often shows through symptoms that affect the whole body. These symptoms include:
- Severe Fatigue: Feeling very tired that doesn’t get better with rest.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Losing a lot of weight without changing diet or exercise.
- Changes in Appetite: Not wanting to eat or having trouble eating.
These symptoms can make it hard for patients to do everyday things. It’s key to manage these symptoms to keep patients’ quality of life good.
Organ-Specific Symptoms
Some symptoms are specific to the organs affected by cancer. For example:
- Lung Cancer: Symptoms include a long-lasting cough, trouble breathing, or chest pain.
- Liver Cancer: Symptoms are jaundice, belly pain, or swelling.
- Bone Metastasis: Symptoms are bone pain, fractures, or too much calcium in the blood.
Knowing the specific symptoms for each organ can help in giving better care and support.
Red Flag Symptoms Strongly Associated with Stage IV Cancer
Some symptoms are very linked to Stage IV cancer and need quick attention. These include:
- Neck Lump: A lump in the neck can mean cancer has spread to lymph nodes.
- Chest Pain: Ongoing chest pain can show cancer has spread to the lungs or chest.
- Back Pain: Severe back pain can mean cancer has spread to the spine.
Spotting these red flag symptoms early can help manage the disease better. It can also improve the patient’s quality of life.
Cancer Recurrence and Progression Timeline
The time it takes for cancer to come back varies a lot. It depends on the type of cancer and the person. Knowing this helps doctors manage what patients can expect and plan for follow-up care.
Can Cancer Develop in 3 Years After Diagnosis?
Cancer can come back or get worse in 3 years after being diagnosed. This depends on the cancer type, its stage, and how well the first treatment worked. For example, cancers like pancreatic or lung cancer might come back quickly. But cancers like breast or prostate cancer might take longer.
Early detection and treatment are key to stopping or slowing cancer’s return. Regular check-ups and monitoring are important to catch any signs of cancer coming back early.
Factors Affecting Cancer Progression Rate
Several things can affect how fast cancer gets worse, including:
- Cancer Type and Stage: More aggressive cancers and those found later tend to get worse faster.
- Genetic Mutations: Some genetic changes can make cancer grow faster.
- Initial Treatment Response: How well the first treatment works can greatly affect how fast cancer gets worse.
- Patient’s Overall Health: Other health issues and the patient’s overall health can also play a role.
Knowing these factors helps doctors create a treatment plan that fits each patient’s needs. This can lead to better results in advanced cancer care.
Dealing with cancer recurrence or progression is tough for patients and their families. Our goal is to offer full support and care. We focus on both the medical and emotional needs of those living with cancer.
Treatment Approaches for Advanced Cancer
When cancer reaches its advanced stages, the main goal of treatment is to ease symptoms. This shift focuses on improving the patient’s quality of life. We understand that each patient’s journey is unique. So, we tailor our treatment approach to meet their specific needs.
Goals of Treatment in Advanced Cancer
The main goals of treating advanced cancer are:
- Managing symptoms to reduce discomfort
- Improving or maintaining quality of life
- Extending life expectancy if possible
- Supporting patients and their families emotionally and psychologically
We create a care plan that covers physical, emotional, and social needs.
Palliative vs. Curative Approaches
In advanced cancer, the difference between palliative and curative treatments is clear. Palliative care aims to ease symptoms and improve quality of life for patients and their families. Curative treatments aim to remove the cancer. For many, palliative care is the main focus, but some may get curative treatments in trials or with new therapies.
We stress the importance of starting palliative care early. It has been shown to improve outcomes and patient satisfaction.
Emerging Therapies for Advanced Cancer
The field of cancer treatment is always changing, with new therapies emerging. Some of these include:
- Immunotherapy, which uses the body’s immune system to fight cancer
- Targeted therapy, which targets specific cancer cells while protecting healthy cells
- Precision medicine, tailored to the patient’s genetic profile
These new treatments offer hope for better outcomes and quality of life for advanced cancer patients. We keep up with these advancements to ensure our patients have access to the latest options.
We combine proven treatments with new therapies and compassionate care. Our goal is to make a significant difference in the lives of patients with advanced cancer.
Living with Advanced Cancer: Quality of Life Considerations
For those with advanced cancer, keeping a good quality of life is key. It’s not just about the physical side of the disease. It also means tackling the emotional and mental hurdles that come with it.
Managing Symptoms and Side Effects
It’s vital to manage symptoms and side effects well. This helps patients with advanced cancer live better. Symptoms like pain, fatigue, and nausea can really affect daily life.
We use many ways to tackle these symptoms. This includes medicines, changes in lifestyle, and other therapies. For example, managing pain might involve medicines, nerve blocks, and relaxation methods.
| Symptom | Management Strategies |
|---|---|
| Pain | Analgesics, nerve blocks, relaxation techniques |
| Fatigue | Exercise, energy conservation, nutritional support |
| Nausea | Antiemetics, dietary changes, acupuncture |
Emotional and Psychological Support
Emotional and psychological support is just as important. We know the disease’s impact can be huge. It affects not just the patient but their families too.
We offer counseling, support groups, and other resources. This helps patients deal with their diagnosis and treatment. We also encourage talking openly about feelings and hopes. This creates a caring space where patients feel heard and supported.
“The psychological support we provide is tailored to the individual needs of our patients, acknowledging the unique journey each person undertakes.”
We aim to improve the quality of life for our patients by addressing both physical and emotional needs. This all-encompassing approach ensures patients get the care and support they need. It helps them face the challenges of advanced cancer.
Conclusion
It’s key for patients and their families to grasp the advanced stage of cancer. This stage means the cancer has spread far from where it started. It needs a care plan that covers both physical and emotional needs.
We’ve looked at what advanced cancer is, its symptoms, and how it’s treated. We’ve also talked about the different stages of cancer. Advanced cancer is complex and needs a care plan that focuses on quality of life.
As we keep improving in cancer research, patients need a team of healthcare experts. Knowing about advanced cancer helps patients make better choices about their care. This way, they get the best support on their journey.
FAQ
What is advanced stage cancer?
Advanced stage cancer means the cancer has spread far or grown a lot. It’s hard to treat and causes symptoms like tiredness, weight loss, and pain.
What are the key characteristics of advanced cancer?
Advanced cancer grows near other parts and spreads far. It affects treatment and how long you might live.
How is cancer staged, and what is the TNM classification system?
Cancer is staged using the TNM system. It looks at the tumor size, nearby lymph nodes, and if it has spread. This helps decide the best treatment.
What is the difference between Stage III and Stage IV cancer?
Stage III means the cancer is growing near other areas. Stage IV means it has spread to distant places. Treatment and outlook are different for each.
Can cancer recur or progress within 3 years after diagnosis?
Yes, cancer can come back or grow within 3 years. This depends on the type and how it was treated.
What are the common symptoms of advanced stage cancer?
Symptoms include tiredness, weight loss, and pain. They also depend on the affected organs. Look out for neck lumps, chest pain, and back pain.
What are the treatment approaches for advanced cancer?
Treatment for advanced cancer focuses on comfort and quality of life. New treatments like immunotherapy offer hope.
How can patients with advanced cancer manage their symptoms and side effects?
Patients can manage symptoms with care. This includes pain relief, nutrition, and emotional support. It improves their life quality.
What is the importance of quality of life for patients with advanced cancer?
Quality of life is key for those with advanced cancer. It affects their physical and mental health. Good care is essential.
What is metastatic cancer prognosis?
Metastatic cancer prognosis varies. It depends on the cancer type, how far it has spread, and individual factors. It’s generally harder to treat than localized cancer.
What are the final stages of cancer symptoms?
Symptoms in the final stages include pain, tiredness, breathing issues, and mental changes. Managing these is important for comfort and dignity.
What is end-stage cancer treatment?
End-stage cancer treatment aims to ease symptoms and improve life quality. Treatment plans are tailored to each patient’s needs.
References
National Cancer Institute (NCI): Advanced Cancer
Canadian Cancer Society: Physical Symptoms of Advanced Cancer
Cancer Research UK: Managing Symptoms in the Last Few Weeks and Days
PubMed Central (NCBI): Palliative Care in Advanced Cancer: Clinical Applications