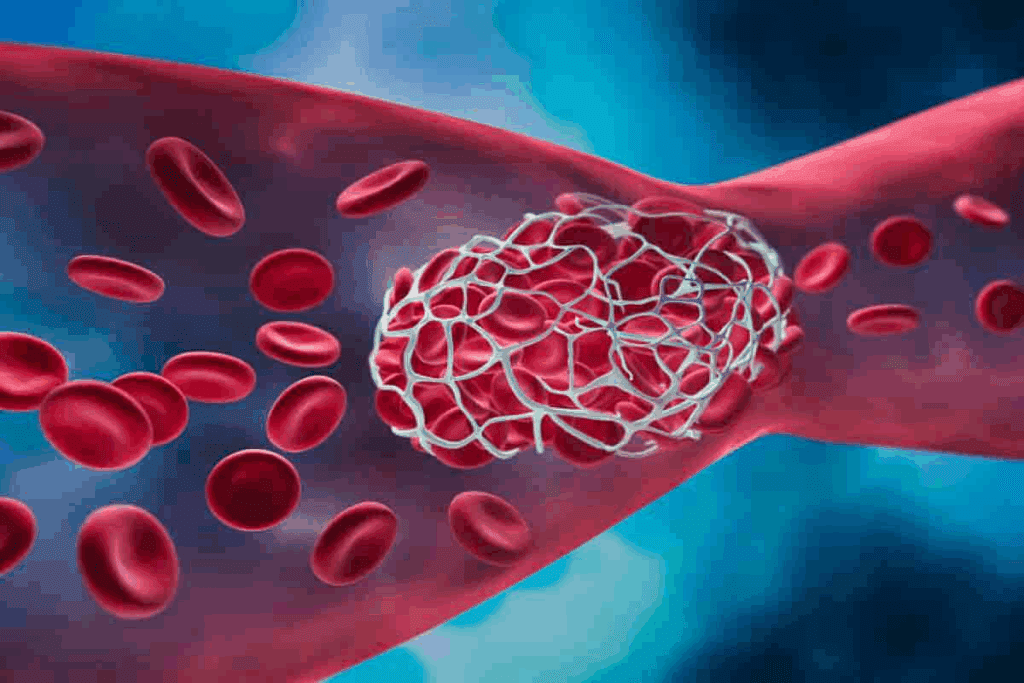
Understanding medical terms related to blood clotting is essential for patients, caregivers, and healthcare professionals alike. At LivHospital, we recognize how important clear communication is in medicine—it supports accurate diagnosis, effective treatment, and better outcomes.
If you’ve ever wondered what is another term for blood clotting, the medical term is coagulation. This process helps stop excessive bleeding after an injury by forming clots that seal wounds and protect the body from blood loss.
By learning another term for blood clotting and related medical vocabulary, patients can better understand their health information and engage more confidently in medical discussions. In this guide, we provide clear definitions and synonyms for key blood clotting terms to help people worldwide gain better medical understanding and care.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding blood clotting medical terms is key for clear talk in medicine.
- Coagulation is the medical term for blood clotting.
- Knowing these terms helps improve patient care and treatment results.
- Clear definitions of medical terms help international healthcare seekers.
- Accurate terms are essential for correct diagnosis and treatment.
The Vital Process of Blood Clotting
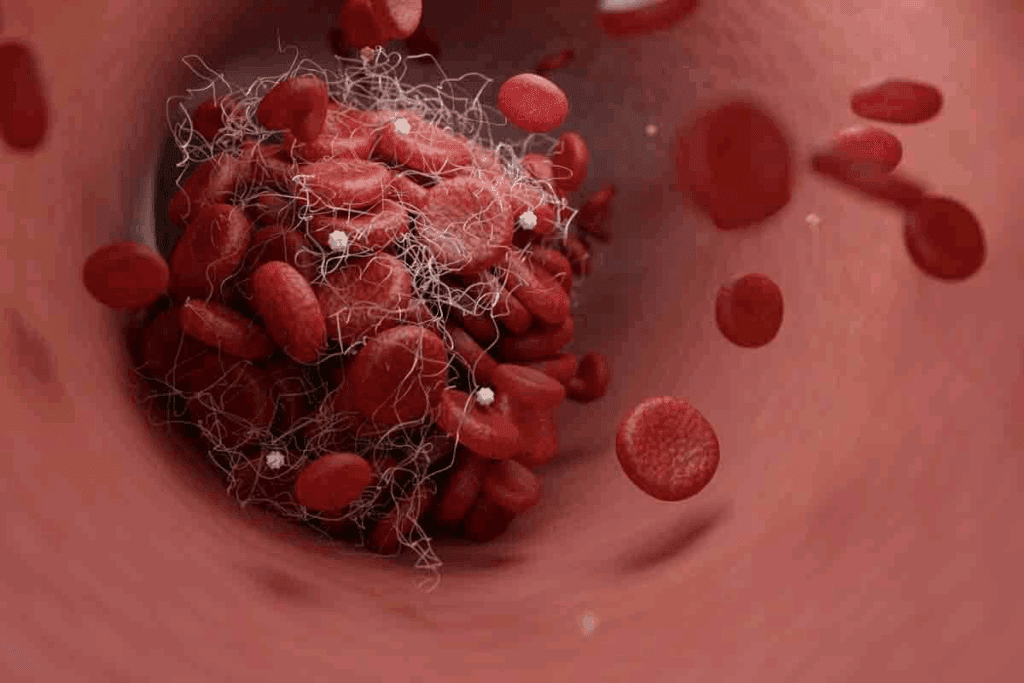
When a blood vessel gets damaged, the body quickly starts to clot blood to stop too much bleeding. This complex process involves many steps and components. It ends with a blood clot that seals the injured vessel.
How Blood Clotting Prevents Excessive Bleeding
Blood clotting, or coagulation, is key to stopping big blood loss when a vessel is hurt. It starts with platelets sticking to the injury site. Then, a fibrin clot forms, acting as a plug to seal the vessel and stop bleeding.
People with clotting disorders, like hemophilia, face severe bleeding issues. This shows how vital blood clotting is.
The Clotting Cascade: A Step-by-Step Process
The clotting cascade is a series of chemical reactions that make a blood clot. It involves clotting factors, proteins in blood plasma. These factors are activated in a specific order, leading to thrombin and fibrin formation.
- The process starts with factor VII activation, triggering a chain of reactions.
- Clotting factors work together to make prothrombinase, converting prothrombin to thrombin.
- Thrombin then turns fibrinogen into fibrin, forming the clot.
This step-by-step process makes sure blood clotting happens fast and right when needed. It also helps avoid unwanted clotting.
Coagulation: Another Term for Blood Clotting
In medical terms, coagulation means the same as blood clotting. It’s key to stop too much bleeding when a blood vessel gets hurt. This process uses many factors and cells to make a clot that seals the damage.
Clinical Definition and Medical Usage
Coagulation is when blood turns from liquid to gel to form a clot. It’s vital for keeping the right balance between bleeding and clotting. Doctors use it to understand and treat bleeding and clotting problems.
The term coagulation is often used with blood clotting. But it really talks about the steps to make a clot. Coagulation factors, a set of proteins, are key in this process. They work together to make a fibrin clot.
Difference Between Coagulation and Hemostasis
Coagulation and hemostasis are related but not the same. Hemostasis is about stopping bleeding, including vascular spasm and clot formation. Coagulation is a part of hemostasis, focusing on making a fibrin clot. Hemostasis stops too much blood loss, while coagulation makes the clot that does it.
Coagulation Factors and Their Roles
Coagulation factors are proteins in blood that help with clotting. There are 13 of them, each with a special role in clotting. They work one after another to make a fibrin clot. Knowing about these factors helps doctors diagnose and treat clotting problems.
The factors are named with Roman numerals (I to XIII). Factor I is fibrinogen, which turns into fibrin to make the clot. Important factors include Factor II (prothrombin), Factor VIII, and Factor IX. Not having enough of these can lead to bleeding disorders like hemophilia.
Thrombus: The Medical Term for a Formed Blood Clot
A thrombus is a clot that sticks to the inside of a blood vessel. It can block blood flow. This can cause serious health problems, depending on where and how big the clot is.
We will look at what a thrombus is, where it forms, and the difference between arterial and venous thrombi. Knowing this helps doctors diagnose and treat conditions better.
Characteristics and Structure of a Thrombus
A thrombus is made of blood cells, platelets, and fibrin, a protein that holds the clot together. The firmness of a thrombus can vary. Some are hard and stable, while others are soft and can break easily.
Many things affect a thrombus’s characteristics. These include blood flow, any health conditions, and the person’s overall health.
Common Locations for Thrombus Formation
Thrombi can form in any blood vessel, but some places are more common. These include:
- Deep veins, mainly in the legs (deep vein thrombosis)
- Arteries that supply the heart (coronary thrombosis)
- Arteries that supply the brain
- Veins in the pelvis or lungs
These areas are more likely to have thrombi because of blood flow, vessel damage, or health conditions.
Arterial vs. Venous Thrombi
Thrombi are classified by where they form: in arteries or veins. Arterial thrombi are in arteries and linked to atherosclerosis. They can cause heart attacks or strokes.
Venous thrombi are in veins and often seen in DVT. They can travel to the lungs and cause a pulmonary embolism.
It’s important to know the difference between arterial and venous thrombi for the right treatment.
Embolus: When Blood Clots Become Mobile
An embolus happens when a blood clot breaks free and moves through the blood. This is a serious health issue. It’s a big worry for doctors.
The Process of Becoming an Embolus
First, a blood clot forms in a blood vessel. Then, if it breaks off, it can travel. This can block blood flow in important organs.
Types of Emboli
There are different kinds of emboli. They are named based on what they are made of and where they block blood flow. The main types are:
- Thromboembolism: This is the most common type, caused by a blood clot.
- Air embolism: This happens when air bubbles get into the blood.
- Fat embolism: This is caused by fat globules in the blood, often after a bone fracture.
Potential Consequences of Embolic Events
Embolic events can lead to serious problems. The risks depend on where the clot goes. Here are some common risks:
| Location of Embolus | Potential Consequence |
| Lungs | Pulmonary embolism, potentially life-threatening |
| Brain | Stroke, leading to neurological deficits or death |
| Heart | Myocardial infarction (heart attack) |
It’s important to know about the dangers of emboli. Spotting the signs early can help a lot. This can make a big difference in how well a patient does.
Thrombogenesis and Thrombopoiesis: The Origin of Blood Clots
It’s important to know how blood clots form to prevent and treat them. This process is called thrombogenesis or thrombopoiesis. It’s complex and involves many factors.
Defining the Formation Process
Thrombogenesis is when a blood clot forms in the blood vessels. It starts when the body tries to stop bleeding after an injury. The clot is made of platelets, fibrin, and other cells.
The making of a blood clot is a controlled process. It’s vital for stopping too much blood loss. But, it can be harmful if it gets out of control.
Virchow’s Triad: Three Factors in Clot Formation
Virchow’s triad explains the three main reasons for clot formation. These are changes in blood flow, too much clotting, and damage to the blood vessel lining. Knowing these factors helps us understand the risk of clotting.
- Blood Flow Changes: Changes in blood flow, like stasis or turbulence, can lead to clotting.
- Hypercoagulability: This is when the body clots too much, which can be genetic or caused by other factors.
- Endothelial Injury: Damage to the blood vessel lining starts the clotting process by exposing collagen and tissue factor.
Risk Factors That Trigger Thrombogenesis
Many things can trigger or increase the risk of clotting. These include genetic factors, lifestyle choices, and certain health conditions.
| Risk Factor | Description | Examples |
| Genetic Factors | Inherited conditions that affect blood clotting | Factor V Leiden, Antithrombin deficiency |
| Lifestyle Factors | Choices or circumstances that increase clotting risk | Prolonged immobilization, smoking |
| Medical Conditions | Diseases or states that predispose to clotting | Cancer, pregnancy |
Knowing about these risk factors and how clots form is key to preventing and managing blood clotting disorders. By identifying those at risk and taking preventive steps, we can lower the chance of blood clots.
Venous Thromboembolism (VTE): Collective Term for Venous Clots
Venous thromboembolism is a serious condition where blood clots form in veins. It can lead to life-threatening problems. This term covers two major conditions: deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE).
Causes and Symptoms of Deep Vein Thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis happens when a blood clot forms in deep veins, usually in the legs. The main reasons for DVT are Virchow’s Triad: blood stasis, hypercoagulability, and injury to the vein lining. Symptoms include swelling, pain, and discoloration of the affected limb.
It’s important to know the risk factors for DVT. These include being immobile for a long time, surgery, cancer, and genetic conditions. Knowing these helps in preventing and treating DVT early.
Pulmonary Embolism: A Life-Threatening Complication
A pulmonary embolism happens when a clot travels to the lungs and blocks blood flow. This is a serious condition that needs immediate medical help. Symptoms include shortness of breath, chest pain, and coughing up blood.
PE is a medical emergency. Quick diagnosis and treatment are key to saving lives.
Prevention and Treatment Approaches for VTE
To prevent VTE, we use anticoagulant medications, mechanical methods like compression stockings, and keeping patients mobile. Treatment involves anticoagulation therapy to stop more clots and, in severe cases, thrombolysis to dissolve clots.
Below is a table summarizing prevention and treatment for VTE:
| Approach | Description | Application |
| Anticoagulant Medications | Prevent new clot formation and reduce risk of PE | Prophylactic and therapeutic |
| Mechanical Prophylaxis | Compression stockings to improve blood flow | Prevention in high-risk patients |
| Mobilization | Early movement to reduce blood stasis | Post-operative and immobile patients |
| Thrombolysis | Dissolve existing clots | Severe cases of PE or DVT |
Understanding VTE, its causes, symptoms, and treatments is key to managing and preventing it. By knowing the risks and using the right strategies, we can lower VTE incidence and its serious complications.
Hemostasis and Fibrinolysis: Balancing Clot Formation and Dissolution
The balance between hemostasis and fibrinolysis is key to keeping our blood vessels healthy. Hemostasis stops bleeding after an injury. Fibrinolysis dissolves clots that have formed.
This balance is important to avoid too much bleeding or unwanted clots. When we get hurt, the body quickly forms a clot to stop the bleeding. This is done through hemostasis, which involves platelets and fibrin clots.
Fibrin and Fibrinogen: Building Blocks of Clots
Fibrin and its precursor, fibrinogen, are vital for clotting. Fibrinogen is a protein made by the liver and found in our blood. When we bleed, thrombin turns fibrinogen into fibrin, forming a clot.
This clot is essential for stopping the bleeding and starting the healing process.
Platelets and Thrombocytes: Cellular Components
Platelets, also known as thrombocytes, are small cells that help stop bleeding. When we get hurt, platelets stick to the damaged area and attract more. This forms a platelet plug, which is then strengthened by the fibrin clot.
The Fibrinolytic System: Breaking Down Clots
The fibrinolytic system breaks down clots. This is done by the enzyme plasmin, which breaks down fibrin into smaller pieces. This system is important for removing clots and keeping our blood vessels open.
In summary, the balance between hemostasis and fibrinolysis is critical for our vascular health. Knowing about fibrin, fibrinogen, platelets, and the fibrinolytic system helps us understand blood clotting.
Anticoagulation Terminology: Understanding Treatment Vocabulary
It’s key for patients at risk of blood clots to grasp anticoagulation therapy. This therapy uses medicines to stop blood clots from forming or growing.
We’ll look into the various medicines used in this therapy. These include anticoagulants, thrombolytics, and antiplatelets. Each has a special role in managing blood clots.
Anticoagulants: Preventing Clot Formation
Anticoagulants stop new blood clots from forming and prevent existing ones from growing. They’re called “blood thinners,” but they don’t actually thin the blood. Common ones are:
- Warfarin
- Rivaroxaban
- Apixaban
- Dabigatran
These medicines mess with the body’s clotting process. This makes it harder for clots to form. Regular monitoring is needed to get the dosage right.
Thrombolytics: Dissolving Existing Clots
Thrombolytics dissolve clots that have already formed. They’re used in emergencies, like heart attacks or strokes, to quickly open up blood flow.
Thrombolytic therapy uses drugs to break down clots. Examples include:
- Alteplase
- Tenecteplase
These medicines are strong and used when the clot risk is high.
Antiplatelets: Inhibiting Platelet Aggregation
Antiplatelets stop platelets in the blood from sticking together to form clots. They’re used to prevent artery clots.
Common antiplatelet medicines are:
- Aspirin
- Clopidogrel
- Prasugrel
It’s vital to understand the differences between these medicines for effective treatment. Knowing how anticoagulants, thrombolytics, and antiplatelets work helps both patients and healthcare providers make better treatment choices.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Blood Clotting Terminology
Knowing blood clotting terms is key for good communication in healthcare. We’ve looked at important words like coagulation, thrombus, embolus, and thrombogenesis. These terms help us understand blood clotting better.
When you know these words, you can handle your medical care better. Patients can understand their health issues, treatments, and risks. This knowledge helps them make smart choices about their health.
It’s very important to know about blood clotting terms. It helps in clear talks, lowers stress, and leads to better health. As medical science grows, knowing these terms will keep being important for both patients and doctors.
FAQ
What is the medical term for blood clotting?
The term for blood clotting is coagulation. It’s when blood turns from liquid to a gel-like or solid state.
What is a thrombus?
A thrombus is a blood clot in a blood vessel. They often form where blood flow is slow or uneven.
What is the difference between a thrombus and an embolus?
A thrombus stays in the blood vessel where it formed. An embolus breaks loose and travels in the blood. Knowing this helps us treat conditions better.
What is thrombogenesis?
Thrombogenesis is the formation of blood clots. It involves factors like blood flow changes, clotting tendency, and injury to the blood vessel lining.
What is venous thromboembolism (VTE)?
VTE includes deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE). It’s a serious condition that needs quick medical care.
What is the role of anticoagulation therapy in managing blood clots?
Anticoagulation therapy uses medicines to prevent or treat blood clots. We use different drugs to manage blood clotting and prevent problems.
What is the difference between coagulation and hemostasis?
Coagulation is the process of blood clotting. Hemostasis is keeping blood vessels intact and preventing too much bleeding. Both are key for blood vessel health.
What is fibrinolysis?
Fibrinolysis is breaking down blood clots. It’s vital for keeping blood vessels healthy and preventing clotting problems.
What are the risk factors for thrombogenesis?
Risk factors for thrombogenesis include genetics, immobility, trauma, and certain health conditions. Knowing these helps us prevent and manage blood clotting issues.
What is the medical term for a blood clot that breaks loose and travels through the bloodstream?
An embolus is a blood clot that breaks loose and travels in the blood. It can cause serious issues like pulmonary embolism and stroke.
Reference
Gives a comprehensive explanation of blood clots, including causes, symptoms, and the risks associated with thrombosis and embolism.



































