Last Updated on November 17, 2025 by Ugurkan Demir
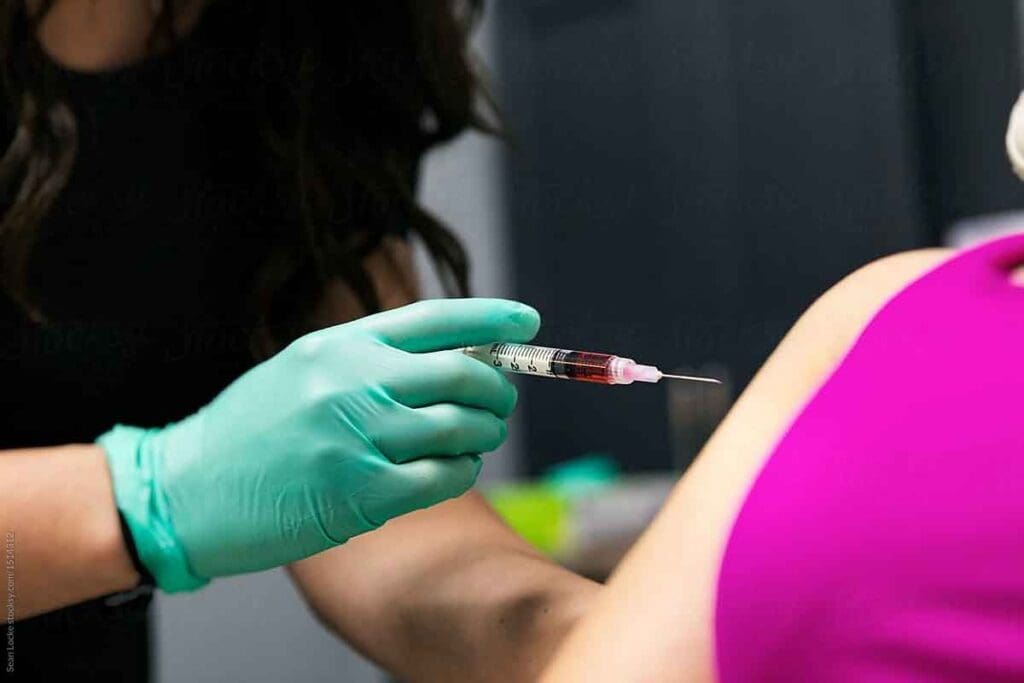
Vitamin B12 is key to our health, helping with red blood cell production, DNA formation, and nerve function. Not getting enough Vitamin B12 can cause serious problems like fatigue, brain fog, and nerve issues. At Liv Hospital, we make sure to provide the correct Vitamin B12 Injection Dose for Adults to address these problems effectively.
Choosing the right Vitamin B12 dosage is very important for treatment. The usual dose is 1000 micrograms (mcg). It’s given either by injection into a muscle or under the skin. The schedule starts with daily shots for a week, then weekly for a month, and then monthly to keep it up.
Vitamin B12 is key to many body functions that keep adults healthy. We’ll look at what Vitamin B12 does, signs of a lack, and when shots are needed.
Vitamin B12 helps with energy production, nerve function, and making red blood cells. It’s also important for DNA, fatty acids, and amino acid metabolism. Without enough Vitamin B12, you might feel tired, have nerve problems, or anemia.
Signs of Vitamin B12 shortage include fatigue, weakness, pale skin, and shortness of breath. You might also feel numbness or tingling in the hands and feet, have trouble walking, or notice changes in thinking. Spotting these signs early is key to getting help.
The normal dose of B12 injection is important for treatment. Shots are suggested for those with a Vitamin B12 deficiency, like those with absorption issues or who can’t get enough from food. The B12 dose injection is a quick way to boost Vitamin B12 levels, helping those who can’t absorb it well from food. Knowing the right vitamin B12 intramuscular dose is vital for good treatment.
The standard dose for vitamin B12 injections in adults is key for both doctors and patients. It’s vital for fixing deficiencies and keeping vitamin B12 levels right.
The usual dose for vitamin B12 shots is 1000 mcg, or 1 mL. This 1000 mcg dose is the go-to for shots in the muscle or under the skin. It’s chosen because it effectively fixes vitamin B12 deficiency in most adults.
The 1000 mcg dose is chosen for its quick fix of vitamin B12. Vitamin B12 is key to making red blood cells and keeping the nervous system healthy. A high dose ensures the body gets what it needs, even in severe cases.
It’s important to note that injection doses are much higher than oral supplements. Oral supplements have 2.4 to 2.6 mcg of vitamin B12. But injections give a much bigger dose.
Oral supplements face challenges in the digestive system, where absorption can be low, mainly in those with certain gut issues. Injections, on the other hand, skip the digestive system for a more direct and effective delivery of vitamin B12.
Vitamin B12 injections can be given in different ways. This meets the needs of various patients and clinical situations. The choice of how to give the injection depends on the patient’s health, the desired effect, and the doctor’s opinion.
Intramuscular injections are a common way to give Vitamin B12. This method injects the vitamin into a muscle, usually in the deltoid or gluteal area. IM injections allow for slow absorption into the blood, providing a longer-lasting effect.
Key considerations for IM injections include:
Subcutaneous injections put Vitamin B12 into the fatty tissue just under the skin. This method is often used for patients who need injections often or have less muscle mass.
Benefits of subcutaneous administration include:
Intravenous Vitamin B12 is usually used for severe deficiency cases or when quick correction is needed. IV administration gives the vitamin directly into the blood, which is critical in some situations.
A study on the National Institutes of Health website says IV Vitamin B12 administration can be effective for quick correction. But, it needs close medical watch because of the risk of bad reactions.
| Administration Route | Typical Use Cases | Key Benefits |
| Intramuscular (IM) | Standard treatment for Vitamin B12 deficiency | Slower absorption, sustained release |
| Subcutaneous | Patients requiring frequent injections or with limited muscle mass | Easier self-administration, reduced muscle irritation |
| Intravenous (IV) | Severe deficiency, rapid correction needed | Immediate delivery into the bloodstream |
The frequency of vitamin B12 injections depends on how severe the deficiency is and how well the patient responds. We explain the usual protocol for B12 injection frequency. This includes everything from daily injections at first to monthly doses later on.
At the start, patients often get daily vitamin B12 injections for a week. This is to quickly fix the deficiency. The Neo-B12 injection datasheet says this helps to quickly fill up B12 stores.
Daily injections at the beginning are key for:
After the first week, injections are given weekly for a month. This phase keeps building up B12 stores and helps with recovery.
Weekly injections in this phase are important for:
After the first two phases, maintenance therapy starts with monthly injections. This long-term plan keeps B12 levels right and stops deficiency from coming back.
Monthly injections in the maintenance phase are key for:
| Phase | Injection Frequency | Duration |
| Initial | Daily | 1 week |
| Secondary | Weekly | 1 month |
| Maintenance | Monthly | Ongoing |
By sticking to this plan, doctors can make B12 injection schedules that fit each patient’s needs. This ensures the best treatment and health results.
Adults needing Vitamin B12 shots must follow certain guidelines. We’ll cover how to give Vitamin B12 shots, including how to measure the dose, where to inject, and how to do it yourself.
The usual dose for Vitamin B12 shots is 1 mL, which is 1000 mcg. This amount is enough for most adults and helps fix any deficiency without overdoing it.
Remember, this dose is based on medical advice. It might change based on how well you respond to treatment and your specific needs.
Choosing the right spot for Vitamin B12 shots is important. You can use the deltoid or gluteal muscles. Switching up where you inject helps avoid soreness and ensures the shot works well.
Changing where you inject helps keep the treatment comfortable and effective.
If you’re giving yourself Vitamin B12 shots, following these steps is key:
Getting these steps right under a doctor’s watch helps you do it safely and right.
Intravenous Vitamin B12 is key for severe deficiency cases. When an acute Vitamin B12 deficiency is present, quick action is needed. This is to avoid serious health issues.
Administering Vitamin B12 via IV needs careful thought and medical watch. The usual dose is between 1 mg and 2.5 mg per dose. This is done under a doctor’s care.
We suggest the following IV dosing plan:
| Condition | Dose | Frequency |
| Severe Deficiency | 1 mg | Daily for 1 week |
| Moderate Deficiency | 1 mg | Weekly for 4 weeks |
| Maintenance | 1 mg | Monthly |
The speed of IV administration is important to avoid bad effects. Vitamin B12 injections should be given slowly. This is usually not more than 1 mL per minute.
Important things to consider for the rate of administration include:
For severe Vitamin B12 deficiency with neurological symptoms or severe anemia, emergency steps are needed. This includes quick IV Vitamin B12, watching the patient closely, and being ready for any problems.
Emergency steps include:
By sticking to these guidelines and protocols, healthcare workers can manage Vitamin B12 deficiency well. This helps prevent serious problems.
Cyanocobalamin and hydroxocobalamin are the two main types of Vitamin B12 used in injections. Each has its own special features.
Cyanocobalamin is a man-made Vitamin B12. It’s known for being stable and effective in treating B12 deficiency.
Key Properties:
Hydroxocobalamin is another Vitamin B12. It’s popular because it lasts longer. This makes it great for those needing less frequent shots.
Benefits:
The choice between cyanocobalamin and hydroxocobalamin depends on individual patient needs. Some people might prefer one over the other.
| Characteristics | Cyanocobalamin | Hydroxocobalamin |
| Duration of Action | Shorter | Longer |
| Frequency of Injections | More frequent | Less frequent |
| Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher |
Understanding the differences between cyanocobalamin and hydroxocobalamin helps healthcare providers. They can tailor Vitamin B12 injection therapy to meet each patient’s needs.
Tiaminal and other Vitamin B12 injection formulas give doctors many choices for treating B12 deficiency. It’s important to know the differences to treat patients well.
There are many Vitamin B12 injection brands available. Each has its own mix of ingredients. Some well-known brands include:
These brands vary in what they contain, how much, and when to use them. For example, hydroxocobalamin lasts longer, so it’s given less often.
When changing Vitamin B12 products, knowing the dosage is key. The usual dose is 1000 mcg (1 mL). But different products have different amounts. For example:
| Product | Concentration | Equivalent Dose |
| Tiaminal | 1000 mcg/mL | 1 mL |
| Hydroxocobalamin | 1000 mcg/mL | 1 mL |
| Cyanocobalamin | 1000 mcg/mL | 1 mL |
Doctors need to know these equivalencies to keep care consistent when switching products.
Insurance for Vitamin B12 injections can change a lot. It depends on the product and the patient’s insurance. Important factors include:
Doctors should understand these to help patients deal with insurance issues. This ensures they get the treatment they need.
In cases of severe Vitamin B12 deficiency, special dosing is key for treatment. This deficiency can cause serious health issues like fatigue, neurological problems, and blood problems. We will look at how to manage these cases, focusing on intensive treatment and addressing neurological issues.
For severe B12 deficiency, a high-dose treatment is often needed. This involves giving large doses of B12 injections, possibly every day or week, for a certain time. The aim is to quickly fill up Vitamin B12 stores and ease symptoms.
Example Protocol: A first step might be daily injections of 1000 mcg of Vitamin B12 for a week. Then, weekly injections for a month follow. This aggressive method helps fix the deficiency fast and improve health.
Severe B12 deficiency can cause serious neurological problems. These include nerve damage, brain function decline, and even dementia. Treating these issues requires a careful B12 dosing plan. Higher doses and more frequent shots may be needed for recovery.
Clinical Evidence: Research shows high-dose B12 therapy can greatly improve neurological function in severe cases. The choice between cyanocobalamin and hydroxocobalamin might also depend on the neurological symptoms.
It’s vital to watch how patients react to B12 injections, mainly in severe cases. Doctors should check symptoms, blood work, and neurological status often. This helps adjust treatment for better results.
Adjustment Criteria: Decisions on treatment changes depend on the initial deficiency level, neurological symptoms, and how well the patient responds. Blood tests, like serum B12 levels and complete blood counts, are key to making these decisions.
To get the most from B12 injections, knowing how to measure and adjust dosages is key. Getting the dosage right is important for health benefits. Adjustments are often needed based on how a patient responds and lab results.
It’s important to understand the units for B12 injections. Dosages are usually in micrograms (mcg), milliliters (mL), or milligrams (mg). Remember, 1 mL is about 1000 mcg.
Conversion Guidelines:
A common dosage is a 1 mL injection with 1000 mcg of Vitamin B12. Knowing these conversions helps in adjusting dosages for individual needs.
Several factors might need a change in B12 injection dosage. These include how severe the deficiency is, how well the patient responds, and their health conditions.
| Factor | Potential Adjustment |
| Severe Deficiency | Higher initial doses or more frequent injections |
| Poor Response to Treatment | Increased dosage or alternative administration route |
| Underlying Health Conditions | Adjusted dosage based on specific condition and patient response |
Regular lab tests are key to checking if B12 injections are working. They look at serum B12 levels, complete blood count (CBC), and neurological function markers.
Monitoring Schedule:
By watching these lab results and making dosage changes as needed, doctors can tailor B12 therapy for each patient.
Understanding the right dose of Vitamin B12 is key to effective therapy. We’ve looked at how Vitamin B12 is important for adults and the standard doses. We’ve also talked about how it’s given, like through injections or shots.
Every person is different, so treatment needs to be tailored. The usual dose is 1000 mcg, but it might change based on how severe the deficiency is. It’s also important to check how well the treatment is working with regular tests.
Healthcare providers can create a treatment plan that fits each person’s needs. This not only fixes the deficiency but also makes life better for those affected. Knowing about the different types of B12 and how to give them is important for this.
Adults usually get 1000 mcg (1 mL) of Vitamin B12. This dose is often enough to treat most deficiencies.
You start with daily shots for a week. Then, you get one a week for a month. After that, you need one every month.
You can get Vitamin B12 shots in three ways: intramuscularly (IM), subcutaneously, or intravenously (IV). Each method has its own benefits and is suited for different needs.
Cyanocobalamin is a man-made Vitamin B12. Hydroxocobalamin is natural and lasts longer. It’s better for some patients.
Yes, if you’re trained and guided, you can give yourself shots. Just make sure to follow the right dose and choose the right spot.
The standard dose is 1 mL, which is 1000 mcg of Vitamin B12. Always check the product’s instructions and talk to a healthcare provider.
You’ll find brands with cyanocobalamin or hydroxocobalamin. The brand and type depend on your prescription and needs.
Doctors use lab tests to check your Vitamin B12 levels. They also look at your symptoms and how you respond to treatment.
Insurance coverage varies. Always check with your provider to see if they cover specific Vitamin B12 shots and what you’ll pay.
Getting Vitamin B12 through an IV needs a doctor’s watch. There are special dosing rules and emergency plans for serious cases.
Your dose might change based on lab tests, how you’re feeling, and other factors. Always talk to your doctor to adjust your dose.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!