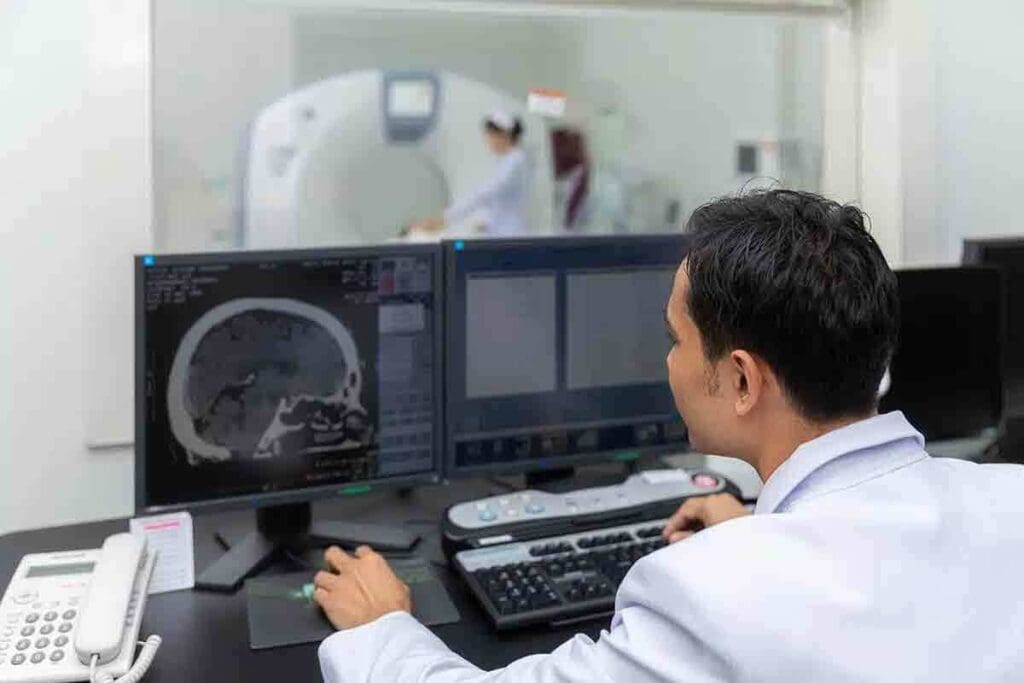
At Liv Hospital, we use top-notch imaging to help diagnose and treat patients. An FDG PET CT scan is a cutting-edge tool. It mixes Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and Computed Tomography (CT). This gives a detailed look at the body’s metabolic and anatomical parts.
The FDG PET CT scan uses a special tracer called fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG). It helps find cancer cells and check if treatments are working. Cancer cells take up more glucose, which shows up on the scan. This way, we can spot and diagnose problems more accurately.
Key Takeaways
- FDG PET CT scans combine PET and CT technologies for detailed diagnostics.
- The scans use a radioactive tracer called fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) to spot cancer cells.
- FDG PET CT scans help plan treatments and check if they’re working.
- Cancer cells take up more glucose, which shows up on PET scans.
- Liv Hospital uses advanced FDG PET imaging for precise diagnoses and treatment plans.
The Fundamentals of Medical Imaging and Diagnostic Scans
Medical imaging has changed a lot, thanks to new technologies. Now, doctors can see the body in great detail. This is a big step from the early days of X-rays. Today, tools like PET and CT scans are key in healthcare.
Evolution of Medical Imaging Technologies
Medical imaging has grown a lot over time. At first, we only had X-rays, which showed just two dimensions. Then, CT scans came along, giving us a three-dimensional view. This was a big leap forward.
Later, PET scans let us see how the body works, not just what it looks like. When PET and CT scans were combined into one, called PET/CT, it was a huge step. This mix helps doctors see both how the body looks and how it works. For example, FDG PET/CT scans are key in finding and tracking tumors.
The Need for Metabolic and Anatomical Information
Doctors need to know both how the body works and what it looks like. PET scans use FDG (Fluorodeoxyglucose) to see how tissues function. This is very important in finding cancer, as cancer cells use glucose differently.
CT scans show the body’s structure. Together, PET and CT scans give a full picture. This helps doctors stage cancer, check how treatments are working, and find cancer that has come back.
| Diagnostic Modality | Primary Information Type | Clinical Application |
| PET Scan | Metabolic | Cancer detection, metabolic activity assessment |
| CT Scan | Anatomical | Structural assessment, tumor localization |
| PET/CT Scan | Both Metabolic and Anatomical | Cancer staging, treatment monitoring, disease recurrence detection |
By using PET and CT scans together, doctors can make better choices. This leads to better care for patients. FDG PET/CT scans are a big step forward in fighting cancer and other diseases.
What Is an FDG PET CT Scan: Technology and Integration
PET and CT scans together give a full view of how the body works and its structure. This mix is key to making accurate diagnoses. It helps doctors find and understand abnormal activity with great detail.
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Components
The PET part of an FDG PET CT scan uses a special tracer, Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG). It shows where the body is most active. The PET scanner picks up the signals from this tracer, making images that show the body’s activity.
PET scans check how active tissues are. This is very helpful in finding cancer. Cancer cells use more glucose than normal cells, so they show up on PET scans.
Computed Tomography (CT) Elements
The CT part gives detailed pictures of the body’s structure. It does this by measuring how X-rays are blocked as they go through the body. These measurements are turned into images that show the body’s layout.
CT scans are vital for understanding the body’s structure. This helps doctors make sense of the metabolic info from PET scans. Together, PET and CT scans can pinpoint where and how active certain areas are.
How PET and CT Technologies Work Together
PET and CT scans together make a powerful tool for diagnosis. The PET scan shows where the body is most active. The CT scan gives the body’s layout, helping to understand where and how active certain areas are.
In cancer diagnosis, this combo is very helpful. It helps find the main tumor, see how active it is, and spot any spread. This info is key for figuring out the cancer’s stage and planning treatment.
| Technology | Function | Benefit |
| PET | Detects metabolic activity | Identifies areas of high glucose uptake, useful in cancer diagnosis |
| CT | Provides anatomical detail | Offers a structural context for metabolic information |
| PET/CT | Combines metabolic and anatomical information | Enhances diagnostic accuracy and treatment planning |
FDG Meaning in Medical Terms: Decoding the Abbreviation
Knowing what FDG means in medical terms is key to understanding its use in imaging. FDG is short for fluorodeoxyglucose, a substance used in PET scans. It helps show how the body’s cells work. We’ll look into what FDG is, its chemical makeup, and why it’s a top choice for PET scans.
What Does FDG Stand For: Fluorodeoxyglucose Explained
FDG is short for fluorodeoxyglucose. It’s a glucose molecule with fluorine-18, a radioactive tag. This lets FDG be used in PET scans, showing how tissues work.
The Biochemistry of FDG as a Glucose Analog
FDG works like glucose because cells take it up the same way. But, unlike glucose, FDG isn’t fully broken down by cells. This lets PET scans spot it, showing where cells are really active. This is why FDG is great for finding cancer, as it shows where cells are using a lot of glucose.
For more on FDG’s chemistry, check out NCBI’s book on PET/CT imaging.
Why FDG Is the Preferred Radiotracer in PET Imaging
FDG is the top choice for PET scans because it shows where cells are using a lot of glucose. Cancer cells use more glucose than normal cells. So, FDG PET scans are great for finding and tracking cancer. This makes FDG a key tool in fighting cancer, helping doctors diagnose, stage, and monitor treatment.
The FDG PET CT Procedure: Patient Experience and Protocol
Understanding the FDG PET CT procedure is key to a smooth experience. We walk you through each step, from preparation to after the scan. This ensures your comfort and clarity.
Preparation Requirements and Guidelines
To get accurate results from the FDG PET CT scan, specific preparation is needed. Fasting for a certain period before the scan is usually required. This helps get clear images. We also tell patients to avoid hard exercise before the scan to prevent muscle glucose uptake.
“Proper preparation is key to a successful FDG PET CT scan,” say medical experts. Our team gives you detailed instructions. This includes dietary restrictions and any other specific needs.
What Happens During the Scan
During the FDG PET CT scan, you’ll lie on a table that slides into the scanner. The process is painless and takes about 30 minutes to an hour. Our team makes sure you’re comfortable the whole time.
Post-Scan Procedures and Safety Considerations
After the scan, you can usually go back to your normal activities unless told not to by your doctor. Drinking plenty of water helps flush out the radiotracer. We also suggest watching for any unusual reactions, though they are rare.
Your safety and comfort are our top priorities during the FDG PET CT procedure. If you have concerns or questions, our team is here to help.
Understanding FDG Uptake Patterns in Normal and Diseased Tissues
Knowing how FDG is taken up by tissues is key to accurate diagnosis. FDG uptake patterns help tell normal from diseased tissues. This is very important in cancer diagnosis and treatment.
FDG, or Fluorodeoxyglucose, is a glucose-like substance that cells take up. Cancer cells, with their high metabolic rate, take up more FDG than normal cells. This difference is why FDG PET CT scans are used in oncology.
How Cancer Cells Metabolize FDG Differently
Cancer cells use FDG differently from normal cells because they have a high glycolysis rate. This is known as the Warburg effect. It leads to more FDG uptake in cancer cells.
- Cancer cells have more glucose transporters on their surface, making it easier for FDG to enter.
- The high metabolic rate of cancer cells means more FDG gets trapped inside the cells.
- This results in more FDG in cancerous tissues than in normal tissues.
Normal Physiological FDG Distribution
FDG uptake is often linked to cancer, but there are normal patterns to recognize. This helps avoid misinterpretation.
Normal FDG uptake is seen in various organs and tissues. For example:
- The brain uses a lot of glucose for energy.
- The heart uses glucose as its main energy source.
- The liver and kidneys, which deal with FDG metabolism and excretion.
Interpreting Standardized Uptake Values (SUVs)
Standardized Uptake Values (SUVs) measure FDG uptake in tissues. SUVs help compare uptake between scans and patients.
When looking at SUVs, consider:
- The SUVmax, the highest SUV value in a region of interest.
- The patient’s medical history and current condition.
- Other imaging findings and clinical parameters for accurate diagnosis.
Understanding FDG uptake patterns and SUVs helps healthcare professionals make accurate diagnoses. This leads to effective treatment plans.
Clinical Applications of FDG PET CT in Oncology
FDG PET CT has changed oncology by giving vital information for cancer diagnosis and treatment planning. We use this tech to better care for our patients and improve their outcomes.
Cancer Detection, Staging, and Restaging
FDG PET CT is key in finding cancer, figuring out how far it has spread (staging), and checking if it has moved (restaging). Knowing the exact stage is key for picking the right treatment. We use FDG PET CT to spot the main tumor, find where cancer has spread, and see how much disease is present.
- Detecting primary tumors and metastases
- Accurate staging for treatment planning
- Restaging to check for disease return or growth
Treatment Response Monitoring
Watching how well treatment works is very important in oncology. FDG PET CT lets us see how active tumors are metabolically, showing if treatment is working early on. This helps us make changes to treatment plans quickly, helping patients do better.
- Quick check of treatment success
- Finding non-responders for other treatments
- Confirming complete response for next steps
Recurrence Surveillance
Keeping an eye out for cancer coming back is a big part of caring for patients long-term. FDG PET CT helps find recurrence early, when it’s easier to treat. Regular checks with FDG PET CT can boost survival and quality of life.
By using FDG PET CT, we offer full care to cancer patients, from first diagnosis to treatment and follow-up. This all-in-one approach helps us manage cancer better and improve patient results.
Beyond Cancer: FDG PET CT in Inflammatory and Infectious Diseases
FDG PET CT is not just for cancer anymore. It’s also great for looking at inflammatory and infectious diseases. It shows both how the body is working and where problems are.
Differentiating Polymyalgia Rheumatica and Rheumatoid Arthritis
FDG PET CT helps tell PMR and RA apart. It looks at how much FDG is taken up in joints and around them. PMR shows uptake in the shoulders, hips, and bursae, while RA shows uptake in the hands and feet.
This helps doctors make better diagnoses and treatment plans. Knowing the difference is key because PMR and RA need different treatments.
Fever of Unknown Origin and Infection Localization
When you have a fever and don’t know why, FDG PET CT can find the cause. It spots areas with more FDG, helping find infections or inflammation. This is great when other tests can’t find the problem.
Using FDG PET CT helps doctors decide on the right treatment. It can find problems that other tests miss, thanks to its whole-body scans.
Vascular Inflammation Assessment
FDG PET CT is also good for checking inflammation in blood vessels. This is important for heart health. It shows how much inflammation there is and who might be at risk.
Knowing about vascular inflammation helps doctors decide on treatments. This shows how useful FDG PET CT is for many health issues, not just cancer.
Cardiac and Neurological Applications of FDG-PET Imaging
FDG-PET imaging is not just for cancer. It also helps check heart health and diagnose brain diseases. It gives important metabolic info for managing heart and brain issues.
Myocardial Viability Assessment
In heart care, FDG-PET checks if the heart muscle is alive. This is key to choosing the right treatment for heart disease or heart attacks. It spots the heart muscle that can get better with new blood flow.
Viability assessment with FDG-PET looks at how much FDG the heart muscle takes up. High uptake means the tissue is alive. Low uptake might mean scar tissue. Doctors use this info to pick the best treatment.
Neurodegenerative Disorders Diagnosis
In brain health, FDG-PET helps find and manage diseases like Alzheimer’s, frontotemporal dementia, and Parkinson’s. It shows how brain cells use glucose, helping spot different diseases and track how they progress.
For Alzheimer’s, FDG-PET shows low glucose use in certain brain areas. This helps doctors diagnose Alzheimer’s and tell it apart from other dementias.
Epilepsy Focus Localization
FDG-PET is also great for epilepsy, helping find where seizures start. It spots abnormal glucose use, guiding surgery to better control seizures.
FDG-PET is very helpful when MRI doesn’t give clear answers. It adds vital info for surgery planning.
In short, FDG-PET imaging is vital beyond cancer. It helps in heart and brain health, improving diagnosis and treatment for serious conditions.
Conclusion: Advances and Future Directions in FDG PET CT
FDG PET CT scans have changed how we diagnose diseases. They have made diagnosing more accurate and have helped in many fields like cancer, heart issues, and brain diseases.
The future looks bright for FDG PET CT. New radiotracers and better scanner technology are on the horizon. These advancements will make FDG PET CT even more useful in hospitals.
We are dedicated to top-notch healthcare and helping patients worldwide. By keeping up with FDG PET CT’s progress, we aim to make treatments better and outcomes better for everyone.
FAQ
What is an FDG PET CT scan?
An FDG PET CT scan is a test that combines two technologies. It uses Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and Computed Tomography (CT). This combination gives detailed information about the body’s metabolic and anatomical structures.
What does FDG stand for in medical imaging?
FDG stands for Fluorodeoxyglucose. It’s a glucose analog used in PET imaging. It highlights areas of high metabolic activity.
How does FDG PET CT work?
The FDG PET CT scan combines PET’s functional info with CT’s anatomical details. This gives a complete view of the body’s structures.
What is the role of FDG in PET imaging?
FDG is used in PET imaging because it’s taken up by cells with high metabolic rates. This includes cancer cells, helping detect and monitor diseases.
How should I prepare for an FDG PET CT scan?
To prepare, follow dietary restrictions and avoid strenuous activity. Your healthcare provider will give specific guidelines for accurate results.
What happens during an FDG PET CT scan?
You’ll be injected with FDG and then undergo PET and CT scans. These are done on a combined PET/CT scanner.
How is FDG uptake interpreted in PET imaging?
FDG uptake is measured using Standardized Uptake Values (SUVs). SUVs quantify the FDG taken up by tissues. This helps identify abnormal metabolic activity.
What are the clinical applications of FDG PET CT in oncology?
In oncology, FDG PET CT is used for cancer detection, staging, and monitoring treatment response. It’s also used for surveillance for recurrence, providing vital info for treatment decisions.
Can FDG PET CT be used for conditions other than cancer?
Yes, it’s used for diagnosing and managing inflammatory and infectious diseases. It also assesses myocardial viability and diagnoses neurodegenerative disorders.
What are the benefits of using FDG PET CT?
FDG PET CT provides both metabolic and anatomical information. This enhances diagnostic accuracy and guides treatment decisions.
Are there any safety considerations after an FDG PET CT scan?
After the scan, you may be advised to avoid close contact with pregnant women and young children. This is due to the small amount of radiation involved.
What is the future of FDG PET CT technology?
The future of FDG PET CT includes new radiotracers and improved scanner technology. These advancements are expected to enhance its utility in clinical practice.
References
- Medical Imaging Consultants Australia (MIC). (2025, March 27). FDG PET CT Imaging. https://www.mic.ca/for-patients/procedure-information/pet-ct-scan/fdg/
- Hofman, M. S., et al. (2016). How We Read Oncologic FDG PET/CT. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 57(11), 1761-1766. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5067887/