Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
Radiation therapy, also known as radiotherapy, is a key part of cancer care. It’s used in about 60% of all cancer cases. We use radiation therapy for cancer to harm cancer cells. This helps shrink tumors or get rid of them.
At Liv Hospital, radiation therapy is a main part of cancer treatment. It gives patients a way to heal and look forward to a better future. We use high-energy ionizing radiation to treat cancer and reduce its symptoms, and we guide our patients through every step of how radiation is done to ensure safe and effective care.
Cancer treatment radiation can cure cancer, stop it from coming back, or slow it down. As a top cancer treatment center, we aim to provide the best care. We support patients from all over with our international patient support and guidance.
Key Takeaways
- Radiation therapy is used in approximately 60% of all cancer cases.
- It targets and damages cancer cells to shrink tumors or eliminate malignancies.
- Cancer treatment radiation can cure cancer, prevent its return, or slow its growth.
- Radiation therapy is a key part of modern cancer care.
- Liv Hospital offers personalized radiation therapy for cancer treatment.
Understanding Radiation Therapy Basics
Cancer treatment often includes radiation therapy. It targets cancer cells with great precision. This method damages the DNA of cancer cells, stopping them from dividing and growing.
Definition and Purpose of Radiation Treatment
Radiation therapy is a cancer treatment that uses high-energy radiation. It targets and damages the DNA of cancer cells. The main goal is to kill cancer cells or slow their growth, helping patients recover or manage symptoms.
How Radiation Works Against Cancer Cells
Radiation therapy delivers ionizing radiation to cancer cells, damaging their DNA. When DNA is too damaged, cancer cells can’t divide or die. This helps control tumor growth and relieve symptoms.
| Mechanism | Effect on Cancer Cells |
| DNA Damage | Cancer cells stop dividing |
| Cell Death | Tumor shrinkage |
| Growth Inhibition | Symptom alleviation |
The Role of Radiation in Modern Cancer Treatment
Radiation therapy is key in modern cancer treatment. It offers both curative and palliative benefits. It can be used alone or with surgery and chemotherapy to improve treatment results. We keep improving radiation therapy to be more precise and reduce side effects.
Understanding radiation therapy basics helps patients see its importance in their treatment. We aim to provide full care that meets both physical and emotional needs.
Types of Radiation Therapy for Cancer
There are many types of radiation therapy for cancer. Knowing about them is key for effective treatment. The right choice depends on the cancer type, its location, and the patient’s health.
External Beam Radiation Therapy
External beam radiation therapy uses a machine outside the body to send beams at cancer cells. It’s great for tumors that are easy to reach and have clear boundaries. The National Cancer Institute says it’s a top choice for treatment.
Precision is key in this therapy. It lets doctors give high doses of radiation to the tumor. This helps protect healthy tissues nearby.
Internal Radiation Therapy (Brachytherapy)
Internal radiation therapy, or brachytherapy, puts a radioactive source inside or near the tumor. It’s good for cancers that are hard to get to with external beam radiation.
Brachytherapy can be temporary or permanent, based on the cancer and treatment plan. It delivers a high dose of radiation right to the tumor. This reduces damage to nearby tissues.
Intravenous Radiation and Systemic Approaches
Intravenous radiation gives radioactive materials through a vein. It targets cancer cells all over the body. This method is used for cancers that have spread or might spread.
Intravenous radiation is less common than other methods. But it’s a valuable option for some cancers. It offers a targeted way to fight systemic disease.
“Radiation therapy is a critical part of cancer treatment,” says cancer guidelines. It offers many approaches tailored to each patient’s needs.
How Radiation is Done: The Treatment Process
The journey of radiation therapy starts with a first meeting. Then, a series of steps follow to make sure the treatment is precise. This ensures the radiation works well without harming healthy tissues.
Initial Consultation and Assessment
The first step is the initial consultation. Our team checks if radiation therapy is right for the patient. They look at the patient’s medical history and current health. We also talk about the patient’s overall health, cancer stage, and any past treatments.
Treatment Planning and Simulation
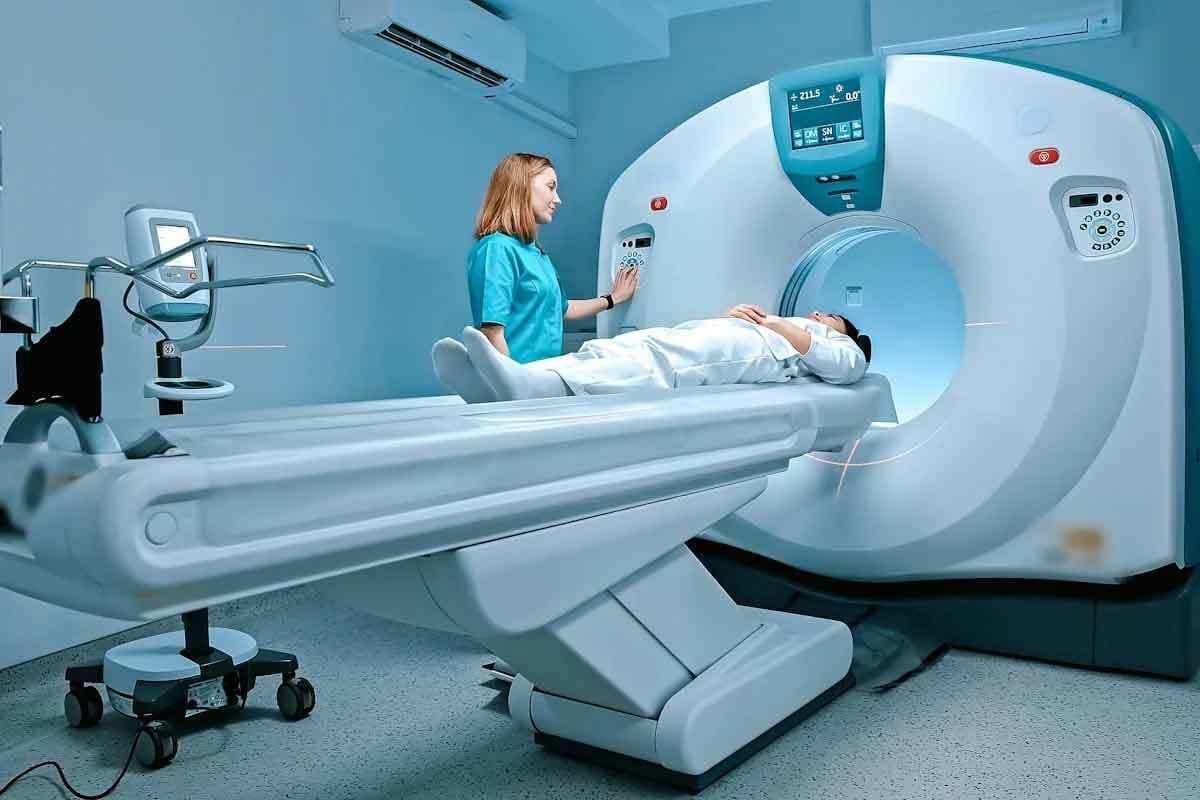
Next, we move to treatment planning and simulation. This important step uses advanced imaging like CT scans to plan the treatment. We use special equipment to position the patient for each session. This makes sure the treatment is accurate and consistent.
- CT scans create a detailed map of the tumor and tissues around it.
- The radiation oncologist marks the tumor and important areas to avoid.
- A treatment plan is made, outlining the radiation dose and angles.
The Delivery Process
After the plan is set, the treatment starts. Patients usually get treated on an outpatient basis, with sessions daily, Monday to Friday, for weeks. During each session, the patient is placed on a table. The radiation therapist uses a linear accelerator to deliver the radiation to the tumor.
Our team watches the patient’s progress closely. We adjust the treatment plan as needed for the best results. With advanced technology and care, we aim to improve our patients’ lives through effective radiation therapy.
Targeted Radiation Therapy: Precision Techniques
Targeted radiation therapy is a big step forward in fighting cancer. It offers both precision and effectiveness. This method lets doctors give radiation that fits the tumor’s exact shape and size. This way, it protects the healthy tissues around it.
3D Conformal Radiation Therapy
Three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy (3D-CRT) uses advanced imaging to create a 3D image of the tumor. It shapes the radiation beams to match the tumor’s shape. This ensures the tumor gets the right dose while keeping healthy tissues safe. The main benefit of 3D-CRT is it cuts down on side effects by reducing radiation to important areas.
Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT)
Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) is a step up from 3D-CRT. It shapes and changes the intensity of the radiation beams. This makes it even more precise in targeting the tumor. IMRT is great for tumors near important structures or with complex shapes.
Image-Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT)
Image-Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT) uses imaging like CT scans or X-rays during treatment. It checks the tumor’s position before or during treatment. This lets doctors make adjustments in real-time, improving the accuracy of the radiation. This is key for tumors that move with breathing or other body functions.
Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Radiotherapy
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) and stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) are very precise. They give high doses of radiation to small, well-defined tumors in a few fractions. SRS is for brain tumors, and SBRT is for tumors elsewhere in the body. These methods need accurate patient setup and image guidance for precise delivery.
These advanced radiation therapy techniques are big steps forward in cancer treatment. They offer better results and fewer side effects. By combining these precise methods with other treatments, doctors can create detailed plans for each patient.
- Precision Techniques: Techniques like IMRT, IGRT, and SRS/SBRT enhance the accuracy of radiation therapy.
- Reduced Side Effects: By minimizing exposure to healthy tissues, these techniques reduce the risk of side effects.
- Improved Outcomes: Targeted radiation therapy can lead to better treatment outcomes by ensuring that tumors receive adequate doses of radiation.
Preparing for Radiation Therapy in Cancer
Getting ready for radiation therapy is a big step. It includes medical checks, lifestyle changes, and getting ready emotionally. We’ll guide you through these steps to help you feel more ready and confident.
Medical Evaluations and Tests
Before starting, you’ll have many medical tests. These help check your health and understand your cancer. You might have:
- Blood tests to check your health and find any problems
- Imaging tests like CT scans, MRI, or PET scans to find the tumor
- Biopsy results to learn about your cancer
These tests help your doctors create a treatment plan just for you.
| Test Type | Purpose | What to Expect |
| Blood Tests | Check your overall health | Having your blood drawn for analysis |
| Imaging Tests | Find the tumor’s exact location | Going through CT, MRI, or PET scans |
| Biopsy | Learn about your cancer’s biology | Having a tissue sample analyzed |
Lifestyle Adjustments Before Treatment
Changing your lifestyle before treatment can help. It can make side effects less and improve how well you do. Here are some tips:
- Eat a healthy diet full of nutrients
- Drink lots of water to stay hydrated
- Avoid smoking and drink less alcohol
- Exercise regularly, as your doctor suggests
Mental and Emotional Preparation
Radiation therapy can be tough on your mind and heart. Getting ready mentally and emotionally is key. Here’s how:
- Get support from family, friends, or groups
- Try relaxation techniques like meditation or deep breathing
- Learn about your treatment and what to expect
By doing these things, you can handle the emotional side of radiation therapy better.
Research shows that getting ready for radiation therapy can really help. It can make tumors smaller and even cure some cancers, depending on the type.
Managing Side Effects of Cancer Treatment Radiation
Radiation therapy for cancer can cause side effects. It’s important to have strategies to manage them. We know it’s tough, but with the right approach, patients can handle it better.
Common Short-Term Side Effects
Short-term side effects of radiation therapy depend on the treated area. Common issues include:
- Fatigue: Feeling tired or exhausted, which can be managed with rest and gentle exercise.
- Skin reactions: Redness, irritation, or dryness of the skin, which can be soothed with specific creams and lotions.
- Nausea and vomiting: These can be managed with anti-nausea medication, mainly when the abdomen is treated.
Managing Fatigue: Patients should eat well, drink plenty of water, and do light exercises to fight fatigue.
Long-Term Side Effects and Management Strategies
Radiation therapy can sometimes harm healthy tissues, causing long-term side effects. These can include:
- Fibrosis: Scarring of tissues, which can lead to stiffness and limited mobility.
- Secondary cancers: In rare cases, radiation can cause new cancers, a risk that is carefully weighed against the benefits of treatment.
Management Strategies: For long-term side effects, we use different strategies. For fibrosis, physical therapy helps. For secondary cancers, regular check-ups are key for early detection.
| Side Effect | Management Strategy |
| Fatigue | Rest, gentle exercise, balanced diet |
| Skin reactions | Specific creams and lotions |
| Nausea and vomiting | Anti-nausea medication |
| Fibrosis | Physical therapy |
| Secondary cancers | Regular follow-up appointments |
Understanding and managing radiation therapy side effects can improve patients’ quality of life. It’s a team effort between patients, caregivers, and healthcare providers to tackle these challenges together.
Combining Radiation Therapy with Other Cancer Treatments
We often mix radiation therapy with other treatments to help cancer patients more. This way, we can make treatment plans that fit each patient’s needs. It makes radiation therapy work better.
Radiation and Surgery: Timing and Benefits
Using radiation therapy and surgery together is common in cancer treatment. Neoadjuvant radiation therapy is given before surgery to make tumors smaller. Adjuvant radiation therapy is used after surgery to kill any cancer cells left behind.
The timing of radiation therapy depends on the cancer type, stage, and the patient’s health. For example, in breast cancer, radiation is often given after a lumpectomy. This helps get rid of any tiny cancer cells.
Radiation and Chemotherapy: Synergistic Effects
Combining radiation therapy with chemotherapy is also common. Chemotherapy makes cancer cells more sensitive to radiation. This makes them easier to damage.
This method is used for many cancers, like head and neck, lung, and cervical cancers. It can lead to better control of cancer and higher survival rates.
Radiation and Immunotherapy: Emerging Approaches
Using radiation therapy with immunotherapy is a new area of research. Immunotherapy boosts the body’s immune system to fight cancer. Radiation therapy helps by releasing tumor antigens for the immune system to target.
Early studies show promising results. Some patients see effects where radiation therapy not only treats the tumor but also affects distant tumors. This could change how we treat some cancers.
Does Radiation Cure Cancer? Effectiveness and Outcomes
Radiation therapy’s success in treating cancer is complex. It depends on many factors. We’ll look at how radiotherapy affects cancer treatment outcomes. This includes shrinking tumors and improving survival rates.
How Radiotherapy Shrinks Tumors
Radiotherapy damages cancer cells’ DNA, stopping them from growing. This leads to cancer cell death, shrinking tumors. Effective tumor shrinkage improves symptoms and quality of life for patients.
We use advanced radiation techniques like Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) and Image-Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT). These methods target tumors precisely while protecting healthy tissues.
Success Rates for Different Cancer Types
Radiation therapy’s success varies by cancer type and stage. For example, it’s very effective for some head and neck cancers and early-stage breast cancer. Here are some success rates:
- Early-stage breast cancer: High cure rates with radiation therapy following surgery.
- Prostate cancer: Radiation therapy is a common and effective treatment, with high long-term survival rates.
- Lung cancer: Radiation therapy can be used alone or in combination with other treatments, showing varying degrees of success depending on the stage.
Curative vs. Palliative Radiation Approaches
Radiation therapy can have curative or palliative goals. Curative radiation aims to eliminate cancer entirely. Palliative radiation aims to ease symptoms and improve quality of life when a cure is not possible.
Understanding radiation therapy’s goals is key for managing patient expectations and making informed decisions.
Factors Affecting Treatment Response
Several factors influence how well a patient responds to radiation therapy. These include:
- The type and stage of cancer.
- The overall health of the patient.
- The specific radiation technique used.
- The dose and fractionation schedule of radiation.
By carefully considering these factors, we can tailor radiation therapy to maximize its effectiveness for each individual patient.
Post-Treatment Care and Recovery
After radiation therapy, post-treatment care is key. Patients need to watch for side effects and make lifestyle changes. This helps them recover well.
Follow-Up Appointments and Monitoring
Follow-up visits are very important. They help doctors see if the treatment worked. They also check for cancer coming back and manage side effects.
At these visits, patients might have tests like imaging and blood work. This helps doctors check their health and cancer status. It’s a chance to talk about any problems or symptoms.
Managing Ongoing Side Effects
Radiation therapy can harm healthy tissues, causing side effects. Managing these is a big part of recovery. We help patients find ways to lessen these effects, like medicine or lifestyle changes.
Side effects can include tiredness, skin changes, and digestive issues. Knowing about these and having a plan can help patients recover better.
Lifestyle Recommendations After Radiation Therapy
Living a healthy lifestyle is important after radiation therapy. Eating well, staying hydrated, and exercising regularly are good. We also advise against smoking and drinking too much alcohol.
Stress-reducing activities like meditation or yoga can also help. These changes can improve patients’ well-being and quality of life after treatment.
Conclusion: Advances in Radiation Therapy for Cancer Treatment
Radiation therapy has seen big improvements, making treatments more precise and effective for cancer patients. New technologies and techniques are making cancer treatment better. This therapy targets and destroys cancer cells, leading to better results.
Research shows that radiotherapy can shrink tumours, helping patients feel better and live better lives. The future of radiation therapy is bright, with ongoing research aiming to make treatments even better.
By using the latest in radiation therapy, we can offer more effective treatments for cancer patients. Our aim is to provide top-notch healthcare with full support and guidance. We’re dedicated to leading in radiation therapy innovation.
FAQ
What is radiation therapy and how is it used in cancer treatment?
Radiation therapy uses high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells. It’s used in about 60% of cancer cases. This treatment can be used alone or with other treatments.
How does radiation therapy work against cancer cells?
It damages the DNA of cancer cells, causing them to die. This helps shrink tumors and improve survival chances.
What are the different types of radiation therapy?
There are several types, including external beam and internal radiation therapy. The choice depends on the tumor’s location and type.
What is the treatment process for radiation therapy?
The process starts with a consultation and treatment planning. This ensures the radiation targets the tumor without harming healthy tissues.
How can I prepare for radiation therapy?
You’ll need medical evaluations and lifestyle changes. Mental preparation is also key to reduce side effects.
What are the possible side effects of radiation therapy?
Side effects include fatigue and skin reactions. Your healthcare team will help manage these.
Can radiation therapy be combined with other cancer treatments?
Yes, it can be used with surgery, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy. The benefits depend on the cancer type and treatment goals.
Does radiation therapy cure cancer?
It can cure some cancers, but not all. Success rates vary based on the cancer type and stage.
What is targeted radiation therapy?
It uses precise techniques to target tumors. This minimizes damage to healthy tissues.
What kind of follow-up care is needed after radiation therapy?
Follow-up appointments are essential. They help manage side effects and detect any recurrence.
How does radiation therapy shrink tumors?
It damages cancer cells’ DNA, leading to cell death. This causes tumors to shrink.
What is the role of radiation therapy in modern cancer treatment?
It’s a key treatment, used to cure or relieve symptoms. Advances in technology improve its effectiveness.
What is the difference between curative and palliative radiation approaches?
Curative radiation aims to eliminate cancer. Palliative radiation focuses on symptom relief and improving quality of life.
References
“Radiation Therapy for Cancer.” (n.d.). In NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK343621/