Last Updated on November 4, 2025 by mcelik
Tyrese Haliburton’s recent Achilles tendon rupture during the NBA Finals highlights the importance of the test for torn Achilles tendon. AHow Long Do Stem Cell Injections Last? torn Achilles often causes a sudden “pop” and sharp pain near the heel, followed by swelling and difficulty pushing off the foot when walking. The Thompson test is commonly used, where the calf muscle is squeezed while lying prone; if the foot doesn’t move downward, the tendon is likely ruptured. Early diagnosis is critical to avoid long recovery times and complications. Imaging like MRI may confirm the extent of the injury if needed.
It’s vital to quickly diagnose such injuries, mainly for athletes and those who do a lot of physical activities. Catching it early can greatly affect treatment success and how soon you can get back to normal.
Knowing the Achilles tendon’s anatomy is key for doctors and those interested in its injuries. It’s a complex part that helps us walk, run, and jump. It connects the calf muscles to the heel bone.
The Achilles tendon is a strong band of tissue. It lets us push our foot down, thanks to the calf muscles and the heel bone. It’s built to handle a lot of stress but can get injured, often during intense activities.
It’s not just about moving the foot; it also helps us feel where our foot is. Knowing this helps us understand how injuries happen and how to stop or treat them.
Even though it’s strong, the Achilles tendon has weak spots. The most common injury is in the mid-substance of the tendon, about 2-6 cm above where it meets the heel. This area gets hurt easily because it doesn’t get much blood.
Another common injury spot is where the tendon meets the heel. This area gets a lot of stress, leading to insertional tendinopathy. Knowing these weak spots helps prevent and diagnose injuries.
Achilles tendon ruptures can happen for many reasons. This includes sports injuries and medical conditions. Knowing why they happen helps in preventing and treating them.
Sports injuries are a big reason for Achilles tendon ruptures. This is true for sports that need quick movements, like running and jumping. Basketball, soccer, and tennis are often to blame. A sudden muscle contraction can cause the tendon to rupture.
Examples of sports-related injuries include:
As we get older, our Achilles tendons get less flexible and more likely to get hurt. This makes older athletes more at risk for ruptures.
The role of age in Achilles tendon health is multifaceted:
| Age Group | Tendon Characteristics | Rupture Risk |
| 20-30 | High elasticity, strong | Low |
| 40-50 | Moderate elasticity, some degeneration | Moderate |
| 60+ | Low elasticity, significant degeneration | High |
Some medical conditions can make you more likely to get an Achilles tendon rupture. These include diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and infections. These conditions can harm the tendon directly or indirectly.
Medical conditions that can affect Achilles tendon health:
Knowing these risk factors helps in preventing and catching Achilles tendon ruptures early.
Knowing the signs of an Achilles tendon rupture is key to getting the right treatment. When the tendon tears, it shows in different ways. It’s important to spot these symptoms early.
When an Achilles tendon ruptures, the pain is sudden and severe. It feels like a kick or hit in the back of the leg. You might also hear a snapping or popping sound.
Some people feel their ankle is unstable or weak. This makes it hard to stand on tiptoes or push off with the hurt leg.

Not all symptoms show up right away. Swelling and bruising around the ankle can take hours or days to appear. The swelling can spread up the leg.
Walking or standing on toes becomes hard because of the pain and weakness. This is a sign of the rupture.
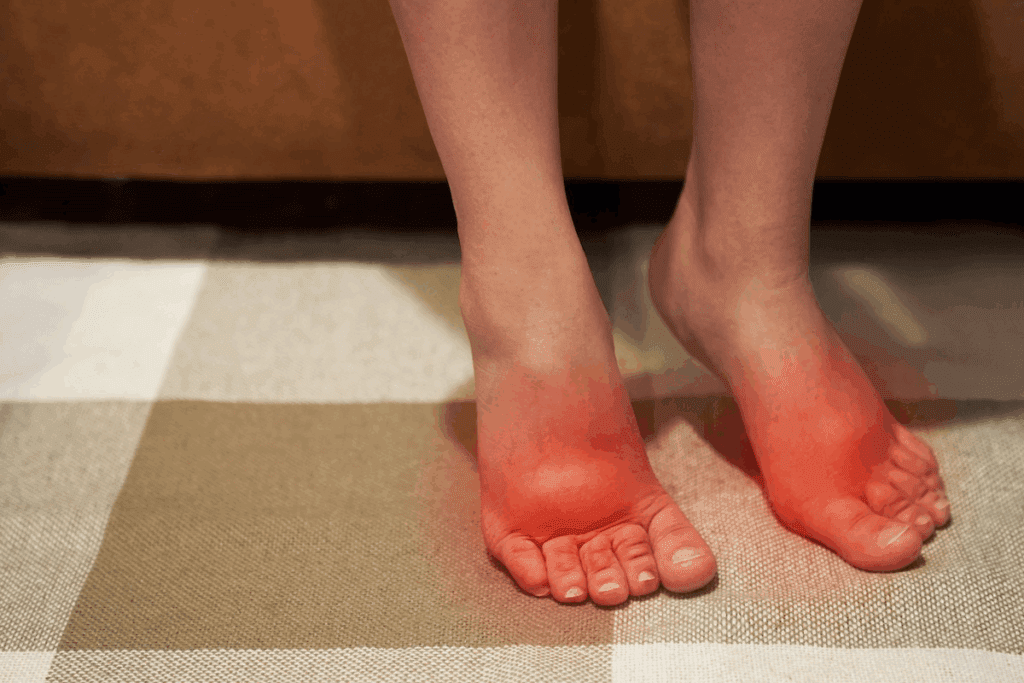

Swelling is a big symptom of Achilles tendon ruptures. It happens around the ankle and can go down to the foot or up the leg. In some cases, the swelling is so bad you can’t wear shoes or put pressure on it.
Watching the swelling and other symptoms is important. They help doctors figure out what’s wrong.
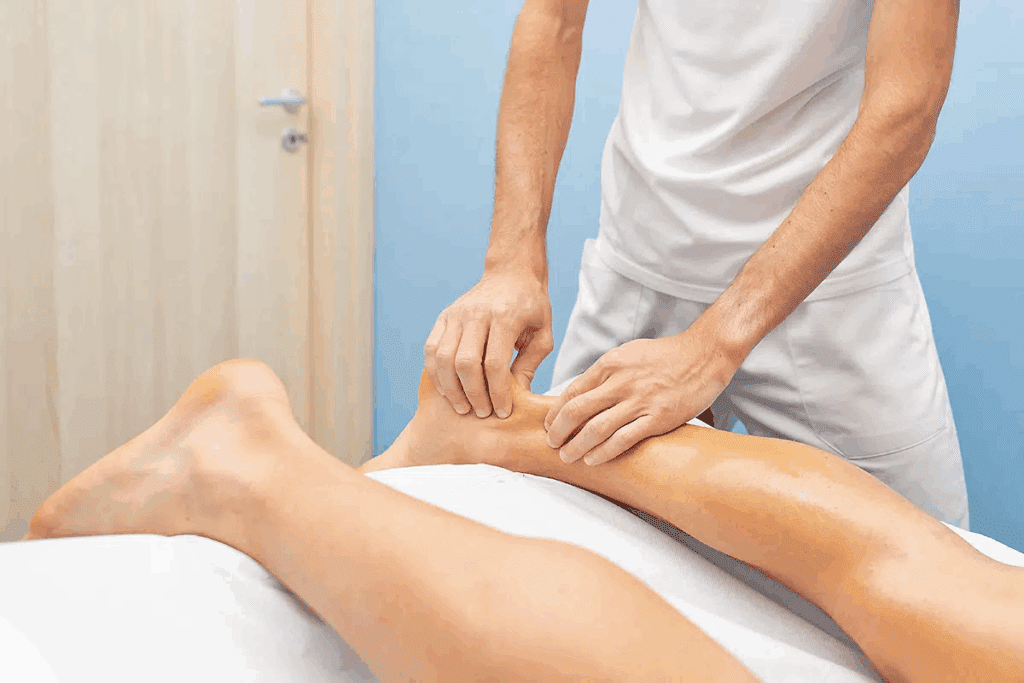
Diagnosing an Achilles tendon rupture often involves a simple yet effective clinical test known as the Thompson squeeze test. This test is a key tool that healthcare professionals use to check the Achilles tendon’s health.
To do the Thompson squeeze test, the patient lies on their stomach with their feet hanging off the table. The doctor then squeezes the calf muscle to see if the foot flexes. Proper technique is essential for getting accurate results.
A positive Thompson test means no foot flexion when the calf is squeezed, showing a likely Achilles tendon rupture. If the foot does flex, the test is negative, meaning the tendon is probably okay.
| Test Result | Indication |
| Positive | Absence of plantar flexion; likely Achilles tendon rupture |
| Negative | Presence of plantar flexion; Achilles tendon likely intact |
Though the Thompson squeeze test is useful, it has its limits. False negatives can happen if the test is done wrong or if there’s a partial rupture. So, doctors need to use their judgment and might do more tests to confirm the diagnosis.
In summary, the Thompson squeeze test is a simple yet effective way to check for Achilles tendon ruptures. Knowing how to do and understand the test, and its limits, is key for healthcare professionals.
While a doctor’s diagnosis is key, you can do a quick check at home. This can help figure out if you might have a torn Achilles tendon.
To check for a torn Achilles, look for any visible signs. Check for swelling or bruising around the tendon area. You can also do a simple calf squeeze test:
Don’t try to test yourself in some cases. If you’re feeling severe pain or if you’ve had a big injury, get help right away. Don’t try to check yourself.
Write down your symptoms before you see a doctor. Keep a record of:
This info can help doctors make a better diagnosis.
The foot movement test is a key tool for spotting Achilles tendon problems. It checks how well the foot moves and its strength, focusing on plantar flexion and dorsiflexion.
Plantar flexion is when you point your foot down. It’s important because the Achilles tendon helps with this action. If the injured foot can’t point down as well as the healthy one, it might have an Achilles injury.
Dorsiflexion is when you lift your foot up towards your shin. The Achilles tendon is mainly involved in pointing the foot down. But, checking how well you can lift your foot up can also show if there’s a problem with the Achilles tendon. If you can’t lift your foot up as much, it could be due to pain or stiffness.
It’s important to compare how the injured and healthy sides move. This helps spot any differences and understand how bad the injury is. It also helps track how well you’re getting better and if the treatment is working.
| Movement | Injured Side | Uninjured Side |
| Plantar Flexion | Reduced Strength | Normal Strength |
| Dorsiflexion | Limited Range | Full Range |
By looking at how the foot moves, doctors can learn a lot about Achilles tendon injuries. They check plantar flexion and look for dorsiflexion limitations. Comparing movement between the two sides helps them figure out what’s wrong and how to fix it.
Diagnosing Achilles tendon injuries needs a detailed check, including looking at weakness. The Achilles tendon is key for walking and running. It’s important to check its strength to spot injuries or weaknesses.
Weakness in the Achilles tendon can come from overuse, degeneration, or injuries. Strength testing and functional movement assessments are main ways to check the tendon’s health.
Strength testing checks the muscle-tendon unit’s power. For the Achilles tendon, this includes:
These tests show how weak the tendon is and help plan rehabilitation.
Functional movement assessments look at how the Achilles tendon works in daily activities and sports. This includes:
| Assessment | Description | Indicators of Weakness |
| Single-leg heel raise | Standing on one leg, the individual raises their heel | Inability to perform the raise or significant asymmetry |
| Walking or running gait analysis | Observation of gait patterns during walking or running | Altered gait patterns, such as limping or reduced push-off |
| Jumping or hopping tests | Assessing the ability to jump or hop | Reduced height or distance, or inability to perform |
By mixing strength testing with functional movement assessments, doctors get a full picture of the Achilles tendon’s health.
Checking weakness in the Achilles tendon is complex. It involves both strength tests and functional assessments. These methods help people understand their tendon’s health and take the right steps for recovery or prevention.
To confirm the severity of an Achilles tendon injury, healthcare professionals often turn to diagnostic imaging. This method is key in evaluating the extent of damage to the Achilles tendon. It helps guide treatment decisions.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a top choice for seeing Achilles tendon injuries. An MRI gives detailed images of the tendon’s structure. It can spot tears, ruptures, or other damage.
During an MRI for an Achilles tear, patients lie on a table that slides into a large machine. The procedure is usually painless but might cause claustrophobia in some.
Key benefits of MRI for Achilles tendon injuries include:
Ultrasound is also valuable for checking Achilles tendon injuries. It uses sound waves to create images of the tendon’s structure. Ultrasound is great for seeing how the tendon moves in real-time.
Advantages of ultrasound include:
While MRI and ultrasound are main tools, X-rays and other imaging might be used too. X-rays can spot bony issues or calcifications in the tendon. Other options, like CT scans, might be used in complex cases.
Medical experts say, “Diagnostic imaging is key for accurately diagnosing and managing Achilles tendon injuries.” Using these methods well can greatly improve treatment outcomes and patient recovery.
It’s important to know the difference between Achilles tendonitis and tendon rupture. Both can cause pain and discomfort. But, they need different treatments and have different recovery times.
Tendonitis and tendon rupture are two different injuries. Tendonitis is when the tendon gets inflamed and irritated. This usually happens from too much use or strain.
A tendon rupture is a more serious injury. It happens when the tendon tears, either partially or completely.
Even though they’re different, tendonitis and tendon rupture can share similar symptoms. Both can cause pain and swelling in the Achilles tendon area. But, the way and how long you feel these symptoms can tell you a lot.
Tendon rupture usually causes sharp, severe pain right away. It also makes it hard to move right away. Tendonitis, on the other hand, might start slowly.
When checking for these conditions, doctors might find tenderness and swelling. But, they need to do more tests to tell them apart. A detailed history and specific tests, like the Thompson squeeze test, are key.
Sometimes, just looking and feeling might not be enough. Doctors might need to do more tests, like ultrasound or MRI. These tests can show detailed pictures of the tendon. They help doctors see if there’s damage and how bad it is.
By using both clinical checks and imaging tests, doctors can accurately diagnose and treat Achilles tendon injuries. This is true for both tendonitis and ruptures.
It’s key to know if an Achilles tendon injury is partial or complete to treat it right. The severity of the tear affects the treatment and how long it takes to heal.
An Achilles tendon rupture can be partial or complete. A partial tear is less severe, while a complete tear is a full tear. Knowing the extent of the injury helps in choosing the right treatment.
Partial ruptures might have milder symptoms and might not need surgery. But, they need careful management to avoid further damage.
There are grading systems for Achilles tendon injuries. One system grades injuries by their severity:
| Grade | Description | Symptoms |
| 1 | Mild injury | Mild pain, minimal swelling |
| 2 | Moderate injury | Moderate pain, noticeable swelling |
| 3 | Severe injury (complete rupture) | Severe pain, significant swelling, difficulty walking |
Understanding the severity of an Achilles tendon tear helps doctors create a treatment plan tailored to the patient’s needs.
Choosing to get medical help right away after an Achilles tendon injury can make a big difference. It’s important to know how serious the injury is and when you need to see a doctor fast.
Some symptoms mean you need to go to the doctor right away. These include:
If you notice any of these signs, you should get medical help quickly.
Waiting too long to get medical help for an Achilles tendon rupture can cause more problems. These include:
| Complication | Description |
| Increased Risk of Re-rupture | Not getting treatment right away can make the tendon weaker and more likely to break again. |
| Prolonged Recovery Time | Not getting help quickly can make recovery take longer. This can affect your daily life and sports performance. |
| Chronic Pain and Weakness | Not treating an Achilles tendon rupture can lead to ongoing pain and weakness in the leg. |
Doctors stress that getting treatment quickly is important. It helps avoid these problems and ensures a good recovery.
“The timing of treatment for an Achilles tendon rupture is critical. Early intervention can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the risk of long-term damage.”
Knowing when to go to the doctor is key for anyone with an Achilles tendon injury. Spotting the warning signs and knowing the risks of waiting too long helps you recover faster and better.
Getting a correct diagnosis for an Achilles tendon tear is vital. A doctor will carefully check you to make sure. This is done when you show signs of a tendon injury.
A doctor will do several tests to check the tendon. They might use the Thompson squeeze test or check how strong your ankle is. These tests help find any problems with the tendon.
Key components of the clinical examination include:
Doctors use what they find in the exam and imaging to make a diagnosis. Ultrasound or MRI can show the tendon’s structure. This helps confirm if there’s a tear.
| Diagnostic Tool | Advantages | Limitations |
| Clinical Examination | Non-invasive, quick, and cost-effective | May not detect partial tears or subtle injuries |
| Ultrasound | Dynamic imaging, relatively low cost | Operator-dependent, may not visualize deep structures as clearly as MRI |
| MRI | High-resolution imaging of soft tissues, detects partial tears | Higher cost, not as readily available as ultrasound |
Some people might want a second opinion if they’re unsure or not happy with the first plan. A second opinion can offer new insights or treatment options.
Deciding on a second opinion depends on how comfortable you are with the diagnosis and treatment. Talking openly with your doctor is important. It helps make sure you get the best care for you.
Knowing the treatment options for a torn Achilles is key for patients. They need to decide between non-surgical and surgical methods. This choice depends on the rupture’s severity, the patient’s health, and their activity level.
Non-surgical treatments aim to let the tendon heal naturally. This includes wearing a cast or boot and then physical therapy. It’s often chosen for less severe ruptures or for those not suited for surgery.
Non-surgical methods avoid surgery’s risks and might have shorter recovery times. Yet, there’s a higher chance of the tendon rupturing again. It’s important for patients to be closely watched by doctors to heal properly.
Younger, more active patients or those with complete ruptures often need surgery. The surgery reconnects the torn tendon, using open or minimally invasive methods. Surgery can lead to a stronger repair and lower re-rupture risk, but it also has surgery-related risks like infection.
Choosing surgery should be a thoughtful decision after talking to an orthopedic specialist. After surgery, a rehabilitation program is key. It includes a period of rest followed by physical therapy.
The healing process for Achilles tendon ruptures has several stages. First, the tendon needs time to heal, often with immobilization. Later, the focus shifts to strengthening and improving movement, leading to full activity.
A well-planned rehabilitation program is vital for recovery, whether non-surgical or surgical. Patients should work with healthcare professionals to create a rehabilitation plan that fits their needs and goals.
Diagnosing and treating Achilles tendon ruptures needs a full approach. This includes initial tests and a recovery plan. Knowing the tendon’s anatomy and its symptoms is key for quick medical help.
A proper diagnosis uses physical tests and imaging. The Thompson Squeeze Test and foot checks are part of it. MRI or ultrasound also play a role.
Treatment varies based on the rupture’s severity. Options range from non-surgical to surgical methods. A good recovery plan is vital for avoiding future injuries.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments of Achilles tendon ruptures is the first step. It helps individuals start their recovery and get back to their activities.
The Thompson squeeze test is a way to check for Achilles tendon ruptures. It involves squeezing the calf muscles. This is to see if the foot can move down, which is hard to do if the tendon is torn.
At home, you can try the Thompson squeeze test. Or, check if your foot can move up and down. But, it’s best to see a doctor for a sure diagnosis.
Signs of a torn Achilles tendon include sudden pain and swelling. You might also feel weak in your ankle. Walking or standing on tiptoes can be hard.
Doctors use a few ways to diagnose a rupture. They look at your medical history and do a physical exam. They might also use MRI or ultrasound to see the injury.
Achilles tendonitis is when the tendon gets inflamed. It can hurt and stiffen. A rupture, on the other hand, is when the tendon tears. This usually causes sudden pain and swelling, and you might not be able to move your ankle well.
If you have severe pain, swelling, or trouble walking, get help right away. Also, seek medical help if you’ve had a big injury or trauma to your ankle.
There are a few ways to treat a rupture. You might get your ankle immobilized and then start rehab. Or, you might need surgery to fix the tendon. The best treatment depends on how bad the injury is and other things.
Recovery time varies. It can take months to a year or more to get back to normal. It depends on how bad the injury was and the treatment you got.
No, it’s not a good idea to keep exercising with a torn tendon. It can make the injury worse and cause more problems.
Imaging tests like MRI or ultrasound help doctors see the injury. They use this info to decide on treatment and check if it’s working.
Doctors look at a few things to figure out how bad the tear is. They do a physical exam, use imaging tests, and check how well you can move. This helps them decide on the best treatment.
Healing and rehab have different steps. First, your ankle is immobilized. Then, you start doing exercises to get stronger and more flexible. After that, you can start doing activities again and get back to sports.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!