Last Updated on November 17, 2025 by Ugurkan Demir

Are you feeling leg discomfort without a clear reason? It’s important to know the signs of deep vein thrombosis. This knowledge can help you get the right treatment quickly.
At Liv Hospital, we focus on keeping our patients safe and healthy. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) happens when a clot forms in a deep vein. This usually occurs in the lower leg, thigh, or pelvis. It can lead to knee pain.
It’s key to spot the signs of DVT early. This can prevent serious problems. If you notice unusual symptoms in your leg, you should see a doctor right away.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a condition where a blood clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the legs. It can happen to anyone. But, certain things like lifestyle, health conditions, or genetics can make you more likely to get it.
DVT happens when a blood clot forms in the deep veins, often in the legs. This clot can block blood flow, causing swelling, pain, and other issues.
The symptoms of DVT can vary. They often include leg pain, swelling, redness, and warmth. Sometimes, there are no symptoms at all. That’s why knowing the risk factors is so important.
Blood clots from DVT usually form in the lower leg or thigh. The calf veins and the popliteal vein behind the knee are at high risk. Clots can also form in the femoral vein in the thigh.
These areas are key because clots here can travel to the lungs. This can cause a pulmonary embolism, a serious and potentially deadly condition.
Blood clots form when the body’s clotting mechanism gets out of balance. This can be due to immobility, injury to a vein, or genetic predispositions. When a vein is injured, the body tries to stop bleeding by forming a clot. But in DVT, this process happens for no reason, leading to a clot.
Knowing how blood clots form is key to understanding the risks. By recognizing the signs and symptoms, people can get help early. This can help prevent serious complications.

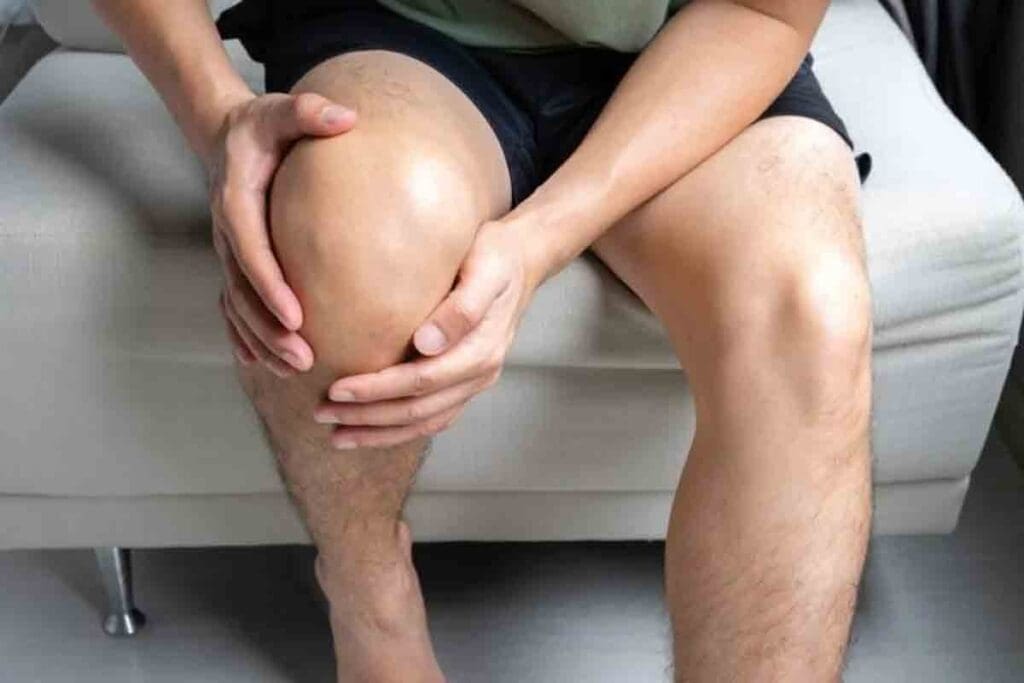
Knee pain from a blood clot is different from other knee pain. This pain often comes from Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT). It can look like other common knee problems.
DVT pain starts as a dull ache or sharp cramp. It usually happens in the calf, thigh, or behind the knee. This pain can stay for a long time and get worse if not treated.
The pain from a blood clot can feel different in intensity. It might also come with swelling or redness. Knowing these signs helps tell DVT pain apart from other knee pain.
Knee pain from a blood clot is often mistaken for sprains, strains, or meniscal tears. This mistake happens because DVT symptoms can look like common knee injuries.
Doctors need to think about DVT when they see knee pain. This is true, even more so for people at risk for blood clots.
Blood clots make knee pain by blocking blood flow and causing inflammation. This can lead to pain and swelling, often felt behind the knee or in the calf.
Knowing why knee pain happens is key to treating it right. For DVT, quick medical help is needed to avoid serious problems.
Persistent pain behind the knee or in the calf might mean you have a blood clot in your leg. This pain is often linked to Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT). DVT is when a blood clot forms in the deep veins, usually in the legs.
The pain from DVT can feel different. Some people get a dull ache that lasts, while others feel sharp, cramping sensations. The pain’s feel can change from person to person. It’s important to notice any pain that doesn’t go away.
The way pain gets worse can tell us a lot. For DVT, the pain might start off mild but get worse over time. It could be there all the time or only when you’re standing or walking. Knowing how the pain changes can help figure out if it’s from a blood clot.
Pain from DVT can be in different places. It’s common in the calf or behind the knee, but it can also be in the thigh or along the vein. The pain might move or spread. Knowing these changes is key to spotting DVT symptoms.
DVT often shows up as swelling in one leg. This swelling happens because the blood flow is blocked by a clot. Fluid builds up in the affected limb.
Checking both legs for differences can help spot DVT. Swelling in one leg is a big warning sign. Stand or sit with both legs out and compare their sizes.
Asymmetry between the two legs can be a red flag for DVT. If one leg looks much bigger than the other, it’s time to get checked out.
DVT swelling often comes with pain or discomfort. The swelling is usually in just one leg and can be mild or severe. The skin might look tight or shiny because of the swelling.
“The swelling associated with DVT can cause significant discomfort and is often a sign that something is amiss.”
A swollen foot can also hint at DVT. When a clot blocks deeper veins, it can swell the foot. This swelling might hurt or feel heavy in the foot.
Watching for these signs and getting medical help if they don’t go away is key. Catching DVT early can make treatment much more effective.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) often shows as an unusual warmth in the affected area. This symptom is easy to miss but is very important. It can mean there’s a blood clot present.
Blood clots can make the area warm because of inflammation. The body sends more blood to fight the clot, causing warmth or heat.
The inflammation from a blood clot also means more activity in the area. This can make the area feel warmer. This warmth is not just a surface feeling. It can show there’s a serious problem.
To see if there’s unusual warmth, compare the temperature of the affected leg with the other. You can do this by lightly touching both legs with the back of your hand.
If you notice a big difference in temperature, it might mean there’s a blood clot. Be gentle when checking to avoid discomfort or moving the clot.
Warmth in the leg can mean DVT, but it’s not the only reason. Infection, injury, or other inflammation can also cause it.
Dr.
John Smith, a vascular surgeon, says, “It’s important to look at all symptoms, like swelling, pain, and redness, to really know if it’s DVT.”
If you feel unusual warmth, see a doctor for a full check-up.
Skin changes and surface signs are key signs of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT). These symptoms are important for diagnosis and should not be ignored.
Redness or discoloration of the affected leg is a common sign of DVT. The skin may look reddish or bluish, more so than the other leg. This happens because of inflammation and blood clotting.
The area with DVT may feel tender to the touch. This is because of inflammation from the clot, making the skin sensitive. It’s important to check gently, as rough handling could dislodge the clot.
Visible surface veins are another sign of DVT. The clot blocks normal blood flow, making veins near the skin’s surface more visible. This is more noticeable in people with less body fat.
Spotting these skin changes and surface signs is key for early DVT detection and treatment. If you or someone you know has these symptoms, getting medical help quickly is essential.
Functional and systemic signs are key indicators of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT). They should not be ignored. These symptoms can greatly affect a person’s life quality. If not treated, they can lead to severe problems.
Many people with DVT feel leg fatigue or heaviness. This feeling can last all day, getting worse after standing or walking. It’s important to tell this apart from general tiredness, as it affects only the leg.
The heaviness comes from blocked blood flow due to the clot. As the clot grows, it blocks normal blood flow. This leads to fluid and waste buildup in the leg, causing the feeling of heaviness or fatigue.
Pain that worsens when standing or walking is a key DVT symptom. This pain comes from increased pressure on leg veins when moving. It makes the discomfort from the clot worse.
| Activity | Effect on Pain |
| Standing | Increased pain due to venous pressure |
| Walking | Pain worsens due to muscle contraction and venous pressure |
| Resting | Pain may decrease as pressure on veins reduces |
Unexplained leg weakness can be a DVT symptom. It comes from reduced blood flow and possible nerve issues from the clot. This weakness might be slight and not always painful, so it’s important to watch for it.
Some people may have all these symptoms at once. This can really affect their ability to move and overall health. If these symptoms keep happening or get worse, it’s important to see a doctor.
Spotting these signs early can help get a diagnosis and treatment quickly. This can prevent serious issues like pulmonary embolism.
Knowing the risk factors for DVT is key to preventing it. Deep Vein Thrombosis can happen due to genetics, environment, and lifestyle.
Several factors can increase your risk of DVT. These include:
Preventing DVT requires lifestyle changes and medical steps. Some effective ways include:
It’s important to watch for DVT after surgery, more so for major surgeries. Doctors will look for signs and symptoms and might use ultrasound to find blood clots.
Understanding risk factors and taking steps to prevent them can greatly reduce DVT risk. By knowing the common risk factors and using preventive strategies, you can lower your chance of getting this serious condition.
It’s important to quickly find and treat deep vein thrombosis. This helps prevent serious problems like pulmonary embolism. Doctors use a mix of checking the patient’s history, doing physical exams, and running tests to find blood clots in the leg.
Medical imaging is key in spotting DVT. Ultrasound is top because it’s safe and very good at finding clots in deep veins.
Other methods like venography, CT scans, and MRI might be used too. But they’re not the first choice for finding DVT.
| Diagnostic Method | Description | Usage |
| Ultrasound | Non-invasive imaging using sound waves | Primary method for DVT diagnosis |
| Venography | Invasive imaging using contrast dye | Used when ultrasound is inconclusive |
| CT Scan | Cross-sectional imaging using X-rays | Used to detect DVT and other conditions |
Blood tests help find DVT by checking for certain substances. The D-dimer test is the most common. It looks for pieces left over when a clot breaks down.
For more on DVT diagnosis and treatment, check out Mayo Clinic’s DVT page.
When you’re being checked for DVT, expect a detailed look at your medical history and a physical exam. Doctors will look for signs like swelling, redness, and warmth in your leg.
If DVT is thought to be present, you’ll probably get an ultrasound or another imaging test. This will confirm if there’s a blood clot.
Knowing when to get medical help can save lives. Blood clots in the leg are serious and need quick treatment.
Some symptoms mean you need to go to the hospital fast. These include severe swelling, pain, or trouble breathing. If you see these emergency warning signs, get help right away.
A pulmonary embolism (PE) happens when a blood clot goes to the lungs. Signs of PE include:
These symptoms are urgent and need immediate care. A pulmonary embolism is very dangerous.
| Symptom | Description |
| Shortness of Breath | Difficulty breathing or feeling winded even when sitting |
| Chest Pain | Pain or discomfort in the chest that gets worse with deep breaths |
| Coughing up Blood | Coughing or spitting up blood or bloody mucus |
Blood clots in the legs, or deep vein thrombosis (DVT), are very serious. They can turn into pulmonary embolism if they break loose. The danger of blood clots is huge; they need quick medical care.
Knowing the risks and spotting symptoms early can help a lot. If you’re at risk or have symptoms, don’t wait to get medical help.
It’s important to know the signs of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) to get help fast. This summary talks about the main signs of blood clots in the leg. These include ongoing pain, swelling, warmth, skin changes, and trouble moving.
DVT is a serious issue that needs quick medical care to avoid serious problems. Knowing the risks and symptoms helps people get help if they have unusual leg pain or discomfort.
In short, knowing about DVT symptoms and taking steps to prevent them can lower the risk of blood clots. If you think you have a blood clot, see a doctor right away for the right diagnosis and treatment.
A blood clot in the leg can cause swelling and redness. The area may feel warm and the skin might look pale or blue-tinged.
Blood clots in the legs can be serious. They can break loose and travel to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism.
Symptoms of a blood clot in the calf include pain and swelling. The area may feel warm and look red or discolored. Pain can get worse when standing or walking.
Yes, some people can feel a DVT as a persistent pain or discomfort in the affected leg. Others may not notice any symptoms.
After surgery, signs of DVT include swelling and pain. The area may feel warm and look red or discolored. Patients should be closely monitored for these symptoms.
Medical imaging, like ultrasound, and blood tests are used to detect a blood clot in the leg.
Symptoms of deep vein thrombosis in the calf include pain and swelling. The area may feel warm and look red or discolored. Pain can get worse when standing or walking.
In some cases, a blood clot in the leg may be visible as a swollen or discolored area. But often, the clot is not visible, and diagnosis requires medical imaging.
The pain location for deep vein thrombosis can vary. It often occurs in the calf or behind the knee and may radiate to other areas of the leg.
Spotting a blood clot in the leg involves recognizing symptoms like swelling, pain, warmth, and redness or discoloration. If these symptoms occur, seek medical attention.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!