Last Updated on November 4, 2025 by mcelik
Did you know that shoulder tendonitis affects millions of people worldwide? It causes pain and discomfort that can really impact daily life. Repetitive motion and poor posture are big contributors to this condition.
It’s important to know what causes shoulder tendonitis to prevent and treat it well. Many things, like age, job, and lifestyle, can lead to it.
Shoulder tendonitis is a complex issue. It involves the anatomy of the shoulder and how tendonitis works. The shoulder is a joint that allows for many movements. This makes it more likely to get injured, including tendonitis.
The shoulder joint is called the glenohumeral joint. It’s a ball-and-socket joint made of the humerus, scapula, and clavicle. The rotator cuff, a group of muscles and tendons, surrounds the joint. It helps keep the shoulder stable and allows for movement.
The rotator cuff has four muscles: the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis. Tendons link these muscles to the humerus. This lets us move our arm in different ways. The subacromial space, between the acromion and the humeral head, is a common spot for tendonitis. This happens from too much movement or pressure.
| Structure | Function |
| Rotator Cuff | Provides stability and facilitates movement |
| Tendons | Connect muscles to bones, enabling movement |
| Subacromial Space | Area prone to tendonitis due to compression or repetitive motions |
Tendonitis happens when tendons get inflamed or irritated. This usually comes from too much movement, overuse, or direct injury. The process starts with micro-tears in the tendon. This leads to inflammation, pain, and swelling.
The pathophysiology of tendonitis goes through three stages:
Knowing these stages helps in finding the right treatment and prevention for shoulder tendonitis.
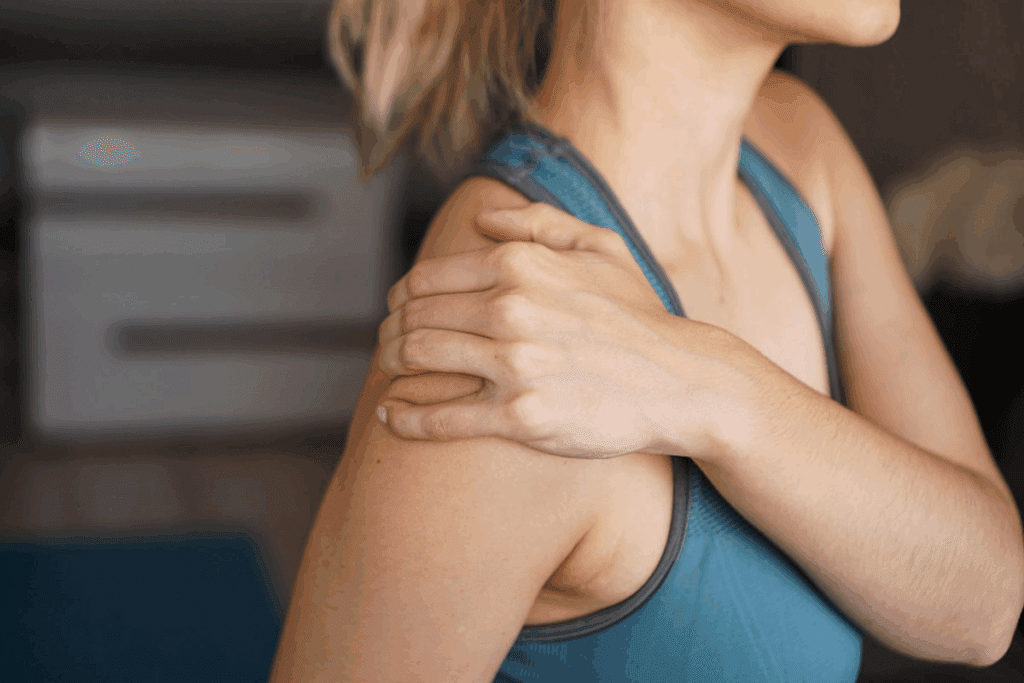

Knowing what causes shoulder tendonitis is key to preventing and managing it. This condition can come from sudden injuries, repeated actions, or aging.
Shoulder tendonitis can happen from sudden or long-term causes. Sudden injuries, like falls, can cause immediate pain and swelling. Long-term wear and tear, from doing the same thing over and over, can also lead to it.
Acute Causes: Sudden injuries, such as falls or direct trauma, can cause immediate damage to the tendons, leading to acute tendonitis.
Chronic Causes: Doing the same thing over and over, poor posture, and aging can cause chronic tendonitis. This is marked by slow pain and stiffness.
There are many risk factors for shoulder tendonitis. Knowing these helps spot who’s at risk and how to prevent it.
| Risk Factor Category | Description | Examples |
| Repetitive Motions | Repeated strain on the tendons | Overhead throwing, lifting, or repetitive arm movements |
| Age-Related Degeneration | Natural wear and tear over time | Aging, reduced tendon elasticity |
| Poor Posture | Abnormal shoulder alignment | Forward head posture, rounded shoulders |
By knowing the causes and risk factors of shoulder tendonitis, we can prevent it and manage its symptoms better.
Doing the same thing over and over without a break can hurt your shoulder tendons. This is common in people who do the same task a lot, like at work or in sports.
Microtrauma means small injuries to the tendons that happen many times. When tendons get too much strain and don’t get to rest, these injuries add up. This leads to inflammation and pain, which is tendonitis.
Factors contributing to microtrauma accumulation include:
Some activities are more likely to cause shoulder tendonitis because they involve a lot of the same motion. These include:
| Activity | Description | Risk Factor |
| Overhead Sports | Sports that involve throwing or overhead movements, such as baseball or tennis. | High repetitive strain on shoulder tendons. |
| Assembly Line Work | Jobs that require repetitive lifting or reaching. | Continuous strain on shoulder and arm. |
| Swimming | Particularly strokes that involve overhead movements. | Repetitive strain on shoulder tendons. |
It’s important to know about the dangers of doing the same thing too much. By spotting risky activities and finding ways to lessen the harm, you can lower your chance of getting tendonitis.
Shoulder tendonitis is common among athletes, mainly those in overhead sports and weightlifting. These athletes face repetitive strain and overuse. This can lead to tendonitis.
Overhead sports like tennis, swimming, and baseball often cause shoulder tendonitis. The repetitive overhead motions can irritate the tendons. This results in pain and less performance.
Weightlifting and resistance training can also lead to shoulder tendonitis. This is true if proper form is not followed. Lifting heavy weights can strain the tendons, causing micro-tears and inflammation.
Athletes can lower their risk of shoulder tendonitis with prevention strategies. They should warm up well before training, use correct technique, and slowly increase workout intensity.
Workplaces can lead to shoulder tendonitis, mainly in jobs that are risky. Jobs that involve a lot of repetition, heavy lifting, and bad ergonomics are more likely to cause this problem.
Some jobs are more likely to cause shoulder tendonitis. These include:
Repetitive motion and overuse are big problems in these jobs. They can cause small injuries that lead to tendonitis.
Improving ergonomics at work is key to avoiding shoulder tendonitis. This means:
OSHA says, “Ergonomic solutions can lower the risk of musculoskeletal disorders, like tendonitis. They do this by making the workplace fit the worker’s needs.”
“Ergonomics is about designing the job to fit the worker, not forcing the worker to fit the job.”
By focusing on ergonomics and knowing the risks of certain jobs, employers can help prevent shoulder tendonitis in their workers.
Aging plays a big role in shoulder tendonitis. As we get older, our tendons start to break down. This makes it easier for tendonitis to develop.
As we age, our tendons lose their stretchiness. They become more likely to get hurt. This makes it harder for them to heal and can cause pain and inflammation.
The aging process changes tendons at a cellular and molecular level. For example, they make less collagen, a key tendon part. They also can’t handle stress as well, raising the risk of tendonitis.
To manage age-related risks, we need to make lifestyle changes. Regular exercise, staying at a healthy weight, and being physically fit can help. These steps can lower the chance of getting shoulder tendonitis.
It’s also key to use the right techniques when exercising and not overdo it. Strengthening the muscles around the shoulder helps support the tendons. This can prevent injuries.
| Age Group | Risk Factors | Preventive Measures |
| 40-55 years | Increased tendon stiffness, reduced collagen production | Regular stretching, strengthening exercises |
| 56 years and above | Further decline in tendon elasticity, increased risk of chronic conditions | Low-impact exercises, maintaining a healthy weight, proper nutrition |
Understanding how age affects shoulder tendonitis helps us take action. By being proactive, we can keep our tendons healthy as we age.
Good posture is key to avoiding shoulder tendonitis. This condition is common in many people. Bad posture puts uneven stress on the shoulder, leading to tendon inflammation and pain.
Several postural issues can cause shoulder tendonitis. These include:
These problems come from many sources. They include muscle imbalances, sedentary lifestyles, and poor workspace ergonomics.
Fixing poor posture needs stretching, strengthening, and being aware. Some good ways to do this are:
The table below shows some common ways to fix postural problems linked to shoulder tendonitis:
| Postural Problem | Corrective Technique | Benefit |
| Forward Head Posture | Chin Tucks | Improves head alignment |
| Rounded Shoulders | Shoulder Blade Squeeze | Strengthens upper back muscles |
| Kyphosis | Chest Stretch | Enhances flexibility in the chest |
By fixing common postural problems and using corrective techniques, people can lower their risk of shoulder tendonitis.
Understanding muscle imbalances is key to preventing and treating shoulder tendonitis. Muscle imbalances happen when muscles on one side are stronger or tighter than the other. This can cause abnormal movement and put pressure on the tendons.
Many things can cause muscle imbalances in the shoulder. Poor posture, repetitive actions, or past injuries are common culprits. For example, if the deltoids are stronger than the rotator cuff, it can lead to bad shoulder mechanics and tendonitis.
To spot muscle imbalances, you need to check the strength and flexibility of your shoulder muscles. Look out for:
A physical therapist or trainer can give a detailed check-up. They can tell you which muscles are out of balance and suggest exercises to fix it.
Strengthening the shoulder muscles is a great way to prevent tendonitis. Good exercises include:
| Exercise | Target Muscle | Repetitions |
| External rotations | Infraspinatus, Teres minor | 3 sets of 12 |
| Internal rotations | Subscapularis | 3 sets of 12 |
| Scapular squeezes | Trapezius, Rhomboids | 3 sets of 15 |
A sports medicine specialist, says, “Strengthening the rotator cuff and scapular stabilizers is key. It keeps the shoulder healthy and prevents tendonitis.”
By focusing on exercises that target muscle imbalances, you can lower your risk of tendonitis. Regular workouts and proper training are key to preventing this condition.
It’s important to know how shoulder impingement and tendonitis are connected. Shoulder impingement happens when the rotator cuff tendons get compressed or irritated. This leads to pain and makes it hard to move the shoulder.
Shoulder impingement and tendonitis are closely linked. The constant pressure on the tendons can cause inflammation and irritation. This leads to tendonitis. Shoulder impingement/rotator cuff tendinitis is common, mainly in people who do a lot of overhead activities.
The rotator cuff tendons are at risk of impingement because of their location. When these tendons face repetitive stress, it can cause inflammation and tendonitis.
It’s key to spot the signs of shoulder impingement early. Common symptoms include:
These symptoms can be managed with physical therapy, lifestyle changes, and sometimes surgery.
| Symptom | Description | Common Causes |
| Pain when lifting | Pain experienced when lifting the arm overhead | Repetitive overhead activities |
| Night pain | Pain that worsens at night, specially when lying on the affected shoulder | Impingement of tendons |
| Weakness | Weakness in the shoulder or arm | Tendonitis or tendon damage |
By understanding the link between shoulder impingement and tendonitis, we can take steps to prevent and manage these issues. This improves our shoulder health.
Shoulder tendonitis can be a long-term effect of not rehabilitating injuries well. An injury can start a chain of events leading to tendonitis if not managed right.
Past shoulder injuries can raise the risk of tendonitis. Injuries can damage tendons, making them prone to inflammation and wear. Also, the healing process can create scar tissue that’s not as strong or flexible as the original tissue.
Key factors that contribute to the increased risk include:
Rehabilitation is key to avoiding long-term injury effects, like tendonitis. A good rehab program can help restore function, lower re-injury risk, and aid in healthy tendon healing.
Effective rehabilitation strategies include:
| Strategy | Description | Benefits |
| Physical Therapy | Exercises tailored to improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion | Enhances recovery, reduces scar tissue |
| Gradual Return to Activity | Progressive reintroduction to normal activities and sports | Prevents re-injury, builds confidence |
| Strengthening Exercises | Targeted exercises to strengthen the muscles around the shoulder | Improves stability, reduces risk of tendonitis |
Understanding the effects of past injuries and the importance of rehab can help manage the risk of shoulder tendonitis.
Shoulder tendonitis often starts with underlying health issues. These problems can affect the body’s muscles and tendons. This makes it more likely for tendonitis to occur.
Autoimmune disorders happen when the body attacks its own tissues. Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and lupus can cause tendon inflammation. This includes the tendons in the shoulder, raising the risk of tendonitis.
People with autoimmune disorders should watch out for shoulder tendonitis. They should work with their doctors to manage their condition well.
Metabolic issues, like diabetes and obesity, can increase tendonitis risk. These conditions make it harder for the body to heal and repair tendons. This makes them more prone to injury.
Managing metabolic conditions can lower the risk of shoulder tendonitis. This can be done through lifestyle changes and medical treatment.
It’s important to understand how inflammatory conditions and systemic factors lead to shoulder tendonitis. By tackling these health issues, people can lower their tendonitis risk. This helps keep their musculoskeletal system healthy.
Many people don’t realize that their daily actions can cause shoulder tendonitis. Simple movements can lead to pain in the shoulder.
Actions like lifting, carrying, or reaching can harm your shoulders if done wrong. For example, lifting heavy things with your arm out can stress your tendons.
Activities that might hurt your shoulders include:
Changing how you move daily is key to avoiding shoulder tendonitis. Pay attention to how you do tasks and adjust to ease shoulder strain.
Here are some ways to improve:
| Activity | Improper Technique | Proper Technique |
| Lifting Objects | Lifting with arm extended | Lifting with arm close to the body |
| Carrying Bags | Carrying on one shoulder | Distributing weight evenly across both shoulders |
| Reaching | Stretching or straining to reach | Using a step stool or ladder to avoid overstretching |
By knowing and fixing bad techniques in daily life, you can lower your risk of shoulder tendonitis.
Environmental and lifestyle factors are big players in shoulder tendonitis. They can make the condition worse. It’s key to know how they affect us.
Our surroundings, like temperature and climate, affect our tendons. Cold climates make tendons stiffer and more injury-prone. Hot and humid conditions cause more inflammation and pain. A study on the National Center for Biotechnology Information website shows how big of a role environment plays in tendon health.
“The link between environment and tendon health is complex,” experts say. It involves many changes in our body.
Lifestyle choices like sleep quality, stress levels, and recovery practices are key to tendon health. Bad sleep hampers tendon repair. High stress raises muscle tension and injury risk. Good rest and stress management, like meditation or yoga, can help.
By tackling these factors, we can lower our risk of shoulder tendonitis. We can also better manage it.
Knowing what causes shoulder tendonitis is key to preventing and managing it. Recognizing risks from repetitive motion, sports, work hazards, and aging helps. This knowledge lets people take steps to lower their risk of getting it.
Strategies like good posture, strengthening exercises, and correcting how we move help a lot. Also, paying attention to work ergonomics and living a healthy lifestyle are important for shoulder health.
If you already have shoulder tendonitis, there are treatments like physical therapy and medicine. A good plan for managing it includes these treatments, lifestyle changes, and prevention steps. This helps ease symptoms and stops them from coming back.
By being proactive and informed about preventing shoulder tendonitis, you can keep your shoulder healthy. This helps you enjoy life to the fullest.
Shoulder tendonitis is when the tendons in the shoulder get inflamed or irritated. This usually happens from doing the same thing over and over, using the shoulder too much, or getting hurt.
Shoulder tendonitis can be caused by many things. These include doing the same motion a lot, getting hurt from overuse, standing or sitting wrong, getting older, playing sports, lifting weights, working jobs that hurt your shoulder, and getting hurt before.
Doing the same motion a lot can hurt the tendons. This is because it causes tiny injuries that add up. It’s worse when you’re doing things that make you lift your arms up or lift heavy things.
Yes, sports that make you lift your arms up a lot can hurt your shoulders. This includes tennis, swimming, and baseball. Lifting weights can also hurt your shoulders because it strains them too much.
Bad posture can hurt your shoulders. It makes the muscles work wrong and puts too much strain on the tendons. This can lead to tendonitis if you keep sitting or standing wrong.
Muscle imbalances can make your shoulder move wrong. This puts more stress on the tendons and can cause tendonitis. It’s important to find and fix these imbalances.
Yes, if you got hurt before and didn’t heal right, it can hurt your shoulder more. It changes how you move and puts more stress on the tendons.
Conditions that make your body inflamed can hurt your tendons. This is because the inflammation can affect the tendons and make them more likely to get hurt.
Things like the weather and how you live can affect your tendons. This includes how well you sleep, how stressed you are, and how you recover. These things can help or hurt your tendons.
To prevent tendonitis, keep your posture right, exercise your shoulders, avoid doing the same thing too much, and use the right technique in sports and daily activities.
Shoulder impingement syndrome makes your shoulder hurt when you lift your arm or reach up. It feels like your shoulder is being pinched or irritated, which can be a sign of tendonitis.
To manage getting older, stay healthy by exercising right for your age and ability. Also, take care of any health problems to lower your risk of tendonitis.
Rehab is key after a shoulder injury. It helps you move right again, gets your muscles strong, and stops long-term damage that could lead to tendonitis.
Yes, doing things the wrong way can hurt your shoulders. It causes strain and overuse injuries, which can lead to tendonitis.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!